Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work
Uploaded by
ChienOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work
Uploaded by
ChienCopyright:
Available Formats
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work?
- Air Purifier Guide Page 1
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work?
air purifier
The latest air purifier Advanced design quality assurance
en.tivy.com.cn/
What is the Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value?
The Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value, also known simply as MERV, measures the performance of air purifiers, specifically large purifiers intended to clean an entire house or building.
Large, whole-house purifiers are not evaluated in the same manner used to measure the effectiveness of small, portable air cleaners, which are sometimes given Clean Air Delivery Ratings
(CADR) instead.
Whole house and building air purifiers usually receive MERV ratings of between 1 and 16, though the upper limit is sometimes extended to 20. Common residential air purification systems
tend to fall within a narrower range. Higher numbers translate to more effective air filtration. According to the online encyclopedia Wikipedia, "The scale is designed to represent the worst case
performance of a filter when dealing with particles in the range of 0.3 to 10 micrometers."
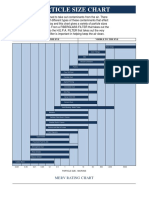
MERV Rating Chart
ASHRAE Standard 52.2 ASHRAE Standard 52.1 Application Guidelines
Particle Size Removal Efficiency
MERV Dust-Spot Efficiency Particle Size and Typical
Typical Applications Typical Air Filter Type
Rating 0.3 to 1 0.3 to 1 0.3 to 1 Percent Contaminant
in 0.1 - 0.2 µm particle
20 ≥ 99.999 -
size < 0.3 µm
Virus (un attached) Electronics manufacturing
19 ≥ 99.999 in 0.3 µm particle size - Carbon Dust Pharmaceutical manufacturing HEPA/ULPA Filters
Sea Salt Carcinogenic materials
18 ≥ 99.99 in 0.3 µm particle size -
All combustion smoke
17 ≥ 99.97 in 0.3 µm particle size -
16 > 95 > 95 > 95 - 0.3-1 µm
All bacteria
15 85-95 > 90 > 90 > 95
Droplet nuclei (sneeze) Bag Filters - Non supported (flexible) microfine fiberglass or synthetic media, 12 to 36 inches
Superior commercial buildings
14 75-85 > 90 > 90 90-95 Cooking oil deep.
Hospital inpatient care
Most smoke
General surgery
Insecticide dust Box filters - Rigid style cartridge, 6 to 12 inches deep.
13 < 75 > 90 > 90 80-90 Most face powder
Most paint pigments
12 - > 80 > 90 70-75 1-3 µm
Legionella
11 - 65-80 > 85 60-65
Humidifier dust Superior residential Pleated filters - Extended surface with cotton or polyester media or both, 1 to 6 inches thick.
10 - 50-65 > 85 50-55 Lead dust Better commercial buildings
Milled Flour Hospital laboratories Box Filters - Rigid style cartridge, 6 to 12 inches deep.
Auto emission particles
9 - < 50 > 85 40-45
Nebulizer drops
8 - - > 70 30-35 3-10 µm
Mold
7 - - 50-70 25-30
Spores Pleated filters - Extended surface with cotton or polyester media or both, 1 to 6 inches thick
6 - - 35-50 < 20 Dust mite body parts and droppings Better residential
Cat and dog dander Commercial buildings Cartridge filters - Viscous cube or pocket filters
Hair spray Industrial workspaces
Fabric protector Throwaway - Synthetic media panel filters
5 - - 20-35 < 20
Dusting aids
Pudding mix
> 10 µm
Pollen
Dust mites Throwaway - Fiberglass or synthetic media panel, 1 inch thick
Cockroach body parts and droppings Minimum filtration
4 - - < 20 < 20 Spanish moss Residential window air Washable - Aluminum mesh, foam rubber panel
Sanding dust conditioners
Spray paint dust Electrostatic - Self-charging (passive) woven polycarbonate panel
Textile fibers
Carpet fibers
(Table Data Source - United States Environmental Protection Agency)
Who Uses MERV Ratings?
The MERV rating system was initially created by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (or ASHRAE for short) in 1987. However, this evaluation
system was based on older methods that date back to 1968, when ASHRAE issued "Standard 52," the first formal testing standard for filters. According to an article by engineer Donald Newell,
the purpose of the Standard has not changed since its early days, and is designed to determine the following attributes of air filters:
Particle removal capability
Resistance to airflow
Expected operating life
MERV ratings measure only the first quality, however. The MERV rating of an air cleaner is determined according to updated standards set by the ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2-1999.
How is an Air Cleaner's MERV Rating Determined?
Air cleaners are given MERV ratings based on the results of a series of tests. Simply put, the process works as follows:
1. Test particles are introduced into the air of the testing area. These particles fall into one of twelve categories, based on size. The smallest category contains particles ranging from .3 to .4
micrometers (also known as "microns"). The largest includes particles from 7 to 10 micrometers.
2. The air is then passed through the filter being tested. The density of particles in the air is measured before and after the air passes through the filter to determine how effective the filter is
at removing pollutants in each size category.
After this is done, the process is repeated five more times, so that there are ultimately six measurements for each of the twelve categories. The MERV number is assigned based on the worst
result. Hence the "minimum" in "Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value."
What Does an Air Cleaner's MERV Rating Mean for You?
A helpful chart detailing what MERV ratings mean can be found at http://www.mechreps.com/PDF/Merv_Rating_Chart.pdf. Of particular interest is the column detailing what types of
pollutants are filtered out at each level.
http://www.airpurifierguide.org/faq/merv-ratings 9/28/2012 5:05:10 PM
What Are MERV Ratings and How Do They Work? - Air Purifier Guide Page 2
A helpful chart detailing what MERV ratings mean can be found at http://www.mechreps.com/PDF/Merv_Rating_Chart.pdf. Of particular interest is the column detailing what types of
pollutants are filtered out at each level.
Precise technical details will be less important to the average customer than an answer to the question, "What MERV ratings are acceptable for my home?" The United States Environmental
Protection Agency provides some information on this matter. "Medium efficiency filters with a MERV of 5 to 13," it states, "are reasonably efficient at removing small to large airborne
particles. Filters with a MERV between 7 and 13 are likely to be nearly as effective as true HEPA filters at controlling most airborne indoor particles." Furthermore, the EPA adds that "medium
efficiency air filters are generally less expensive than HEPA filters, and allow quieter HVAC fan operation and higher airflow rates than HEPA filters since they have less airflow resistance."
HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are the top-of-the-line air filters. Most homes are not capable of having whole-house HEPA filtration systems installed without extensive
modification. Therefore, the EPA's recommendation of filters with a MERV rating from 7 to 13 is something that potential customers should keep in mind.
The National Air Filtration Association gives a roughly similar answer. The highest range it recommends for residential systems is 9-12; higher numbers are said to be suited for hospitals or
commercial buildings rather than homes.
Limitations of the MERV Rating System
An air cleaner's MERV rating is based on its ability to filter out undesirable particles from the air. Not all indoor air pollution is particle-based, however. Gasses contribute significantly to
pollution as well. The ability of an air purifier to remove particles is not predicative of its ability to remove gasses, so the MERV rating is not helpful in this regard.
Newell's article cautions that air filters given the ASHRAE test "are likely to perform worse than predicted because of various installation conditions." This is known as the "installation effect."
Therefore, it is important to remember that MERV ratings are assigned based on a purifier's performance in carefully controlled testing conditions, and not the "real world."
And finally, as stated above, MERV ratings are only relevant to large air cleaners intended to affect whole buildings. Common small portable air cleaners do not have MERV ratings.
Conclusion
The MERV rating system is a helpful way to describe the capabilities of different large air cleaners. It is determined through rigorous testing and is gives the worst-case performance of the filter,
so the MERV number is not inflated. No one should forget to consider MERV ratings when shopping for such cleaners. There are, however, other factors to consider as well, so it would be a
mistake to think that buying the right air filtration system is a simple matter of picking the unit with the highest MERV.
Sources referred to in this article:
Mechanical Reps., Inc. "MERV Rating Chart." http://www.mechreps.com/PDF/Merv_Rating_Chart.pdf
National Air Filtration Association. "Understanding MERV: NAFA User’s Guide for ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 52.2-2007." http://www.nafahq.org/LibaryFiles/Articles/Article006.htm
Newell, Donald A. "Interpreting Filter Performance." http://www.emcorservicesnynj.com/news/FilterPerformanceByDN.pdf
United States Environmental Protection Agency. "Guide to Air Cleaners in the Home." http://www.epa.gov/iaq/pubs/airclean.html
Wikipedia. "Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value." http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minimum_Efficiency_Reporting_Value
Wilkinson, Ron. MC2 "Market & Competitive Convergence -- Air Filters: New Facilities, New Standard." http://www.foustco.com/_fileCabinet/ProductInstructions/HVACFilters/merv_
explanation.pdf
http://www.airpurifierguide.org/faq/merv-ratings 9/28/2012 5:05:10 PM
You might also like
- Atmosphere Mini PDFDocument36 pagesAtmosphere Mini PDFReshmi Sreelal70% (10)
- Aim High 5Document14 pagesAim High 5ramy abaza75% (16)
- MERV Visual Ratings SheetDocument1 pageMERV Visual Ratings SheetNoel GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Merv Filter?: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA)Document2 pagesWhat Is A Merv Filter?: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA)Sharifur RehmanNo ratings yet
- MervDocument1 pageMervAbdullah.N FAAliNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating ChartDocument1 pageMerv Rating ChartsabotaaageNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating ChartDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chartleoncio garciaNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating ChartDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chartfrancisco_mateoNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFAdonia ManikNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFmherold2No ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFJorge SandovalNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFShahrukh AnsariNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFLapecillaNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating ChartDocument1 pageMerv Rating Charttugrul tanNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFFernandoCalixtoNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFRinette MarcanoNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFprabhanshu241991No ratings yet
- Merv Rating Chart PDFDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chart PDFPépé TechopathamNo ratings yet
- Merv PDFDocument1 pageMerv PDFmanojNo ratings yet
- What Does MERV MeanDocument1 pageWhat Does MERV MeanDarren DangaNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating ChartDocument1 pageMerv Rating Chartgenas7265No ratings yet
- Air Handler Air Filter Sell SheetDocument1 pageAir Handler Air Filter Sell SheetmaznahNo ratings yet
- Catalog - Low ResDocument30 pagesCatalog - Low ResrjasmiNo ratings yet
- ParticleSize PDFDocument2 pagesParticleSize PDFOktavianus Paul MulalindaNo ratings yet
- Particle SizeDocument2 pagesParticle SizeSoe Thu AungNo ratings yet
- What Does MERV Rating MeanDocument1 pageWhat Does MERV Rating MeanMiguel Guzman TortoleroNo ratings yet
- 1 Can HEPA Filter Capture The Coronavirus PDFDocument3 pages1 Can HEPA Filter Capture The Coronavirus PDFmazen mmNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Brochure HVAC PDFDocument16 pagesSpectrum Brochure HVAC PDFDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Flyer Hencolin EngDocument16 pagesFlyer Hencolin Eng漢克林No ratings yet
- Comparison EU Standards Vs ASHRAE 52Document6 pagesComparison EU Standards Vs ASHRAE 52moejamal800% (1)
- Merv Ratings ChartDocument1 pageMerv Ratings ChartAydar GalimovNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Mini PDFDocument35 pagesAtmosphere Mini PDFSai agaranNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere MiniDocument37 pagesAtmosphere MiniTummy say SlimmyNo ratings yet
- 3SI - MOP Proposal Face Mask-Min PDFDocument22 pages3SI - MOP Proposal Face Mask-Min PDFverawati100% (1)
- Begg Cousland Envirotec - Mist Elimination Equipment - 2018Document12 pagesBegg Cousland Envirotec - Mist Elimination Equipment - 2018Dũng LêNo ratings yet
- Typical Contamination LevelsDocument8 pagesTypical Contamination LevelsVasant bhoknalNo ratings yet
- Rydair Fy2016 160527095114Document26 pagesRydair Fy2016 160527095114hanyassawyNo ratings yet
- En 14683-2005Document1 pageEn 14683-2005vipinbioNo ratings yet
- TheNow Cataelogo ActualizadoDocument20 pagesTheNow Cataelogo ActualizadoronnysiguasNo ratings yet
- Sasolwax SP30 TDSDocument2 pagesSasolwax SP30 TDSLaboratorio Inkctech0% (1)
- 2 - Filtration of Oil PRINT Version Aug 2017Document23 pages2 - Filtration of Oil PRINT Version Aug 2017MarkNo ratings yet
- Understanding ASTM Levels For FacemasksDocument2 pagesUnderstanding ASTM Levels For Facemasksbob bobNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Filtration Solutions Brochure - ENDocument8 pagesLubricant Filtration Solutions Brochure - ENJohn CuestaNo ratings yet
- Particle SizeDocument2 pagesParticle SizeAce Glen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Filtration BasicsDocument55 pagesFiltration BasicsLorena Dominguez100% (2)
- An Overview of Mask Ratings Classified by Leading Standards PDFDocument1 pageAn Overview of Mask Ratings Classified by Leading Standards PDFzaenalNo ratings yet
- INTERNO - Streamer Duct Chamber (2022-08)Document16 pagesINTERNO - Streamer Duct Chamber (2022-08)Antonio MeloNo ratings yet
- Healthway For Schools: Professional Dfs Air Filtration SystemsDocument2 pagesHealthway For Schools: Professional Dfs Air Filtration SystemsLuis LCNo ratings yet
- Evo Filters 174004403 - ENDocument4 pagesEvo Filters 174004403 - ENandre_silva_camposNo ratings yet
- Metasys CompresorDocument8 pagesMetasys CompresorPlatigue ClangNo ratings yet
- Ultrapoly PE: The Prefilter For The Removal of Solid Contaminants in GasesDocument2 pagesUltrapoly PE: The Prefilter For The Removal of Solid Contaminants in GasesHendri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Merv Rating ChartDocument1 pageMerv Rating ChartShahrukh AnsariNo ratings yet
- Clean Oil Guide: Grain of Salt Tobacco SmokeDocument36 pagesClean Oil Guide: Grain of Salt Tobacco Smokedawson creminNo ratings yet
- MERV Filter Efficiency GuideDocument1 pageMERV Filter Efficiency GuideIslam Abdou AbbasNo ratings yet
- HVAC 终版4Document32 pagesHVAC 终版4budi santosoNo ratings yet
- YASEE Nebulizer FlyerDocument8 pagesYASEE Nebulizer FlyerpoliverosNo ratings yet
- Reporting Value Which Was Developed by The American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioner EngineersDocument1 pageReporting Value Which Was Developed by The American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioner EngineersSri HarshaNo ratings yet
- SafePads - Technical Data SheetDocument6 pagesSafePads - Technical Data SheetShivam PatelNo ratings yet
- An Illustrated Atlas of Tooth Carving and Wax‐Up Techniques -- Shivappa, Anil Bangalore -- 2020 oct 16 -- Wiley -- 10_1002_9781119573609 -- 4cb28bfe73ad7f81152f94a202ee8227 -- Anna’s ArchiveDocument240 pagesAn Illustrated Atlas of Tooth Carving and Wax‐Up Techniques -- Shivappa, Anil Bangalore -- 2020 oct 16 -- Wiley -- 10_1002_9781119573609 -- 4cb28bfe73ad7f81152f94a202ee8227 -- Anna’s ArchiveGlassyNo ratings yet
- TSB 2000010 Technical Overview of The STERILIZABLEBAGDocument4 pagesTSB 2000010 Technical Overview of The STERILIZABLEBAGdatinjacabNo ratings yet
- Polyglot BeginningsDocument30 pagesPolyglot BeginningsJefferson Netto100% (4)
- Ias 16 HW1Document3 pagesIas 16 HW1Raashida RiyasNo ratings yet
- Roy Arden: Against The Day, Vancouver Art Gallery and Douglas & Mcintyre, 2007Document2 pagesRoy Arden: Against The Day, Vancouver Art Gallery and Douglas & Mcintyre, 2007kuntokinteNo ratings yet
- Diaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1Document2 pagesDiaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1John Rafael Obera DiazNo ratings yet
- Film ArtsDocument29 pagesFilm ArtsRoselyn Estrada MunioNo ratings yet
- CIP CollinsDocument2 pagesCIP CollinsValerie F. LeonardNo ratings yet
- LBO ModelingDocument66 pagesLBO Modelingalexander ThielNo ratings yet
- Y Aquasilvi CultureDocument14 pagesY Aquasilvi CultureCeejey EscabarteNo ratings yet
- Rathmore Parish NewsletterDocument2 pagesRathmore Parish Newsletterapi-199024311No ratings yet
- Gr. Ourhoud - Tender No - Dde 19 - 12 33590 - Supply of Bearing - BeltsDocument2 pagesGr. Ourhoud - Tender No - Dde 19 - 12 33590 - Supply of Bearing - BeltsOussama AmaraNo ratings yet
- Aggravating CircumstanceDocument4 pagesAggravating CircumstanceMindalyn Muring AripNo ratings yet
- POD 2.0 User Manual - EnglishDocument97 pagesPOD 2.0 User Manual - Englishpjf626No ratings yet
- Educational Implications of Classical ConditioningDocument2 pagesEducational Implications of Classical Conditioningmekit bekeleNo ratings yet
- Le1 Aio LT6 S AkDocument1 pageLe1 Aio LT6 S AkbesamundoNo ratings yet
- Excellent e With My Knowledge Effort While Making A Positive Contribution To Promoting The Individual Opportunity and Professional GrowthDocument3 pagesExcellent e With My Knowledge Effort While Making A Positive Contribution To Promoting The Individual Opportunity and Professional GrowthInter MaccessNo ratings yet
- 26 Rules To Becoming A Successful SpeakerDocument46 pages26 Rules To Becoming A Successful SpeakerSpeakerMatch100% (23)
- FURTHER MATHEMATICS Scheme of WorkDocument7 pagesFURTHER MATHEMATICS Scheme of WorkAdeneye Emmanuel ImoleAyo100% (1)
- Jazz Improvisation Lesson Plan 2 17 17Document2 pagesJazz Improvisation Lesson Plan 2 17 17api-310967404No ratings yet
- A Film Review General Luna and Macario SDocument5 pagesA Film Review General Luna and Macario SjasminjajarefeNo ratings yet
- NMax Application DataDocument4 pagesNMax Application DataKenneth T. Guillermo0% (1)
- 1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EDocument3 pages1-To-8 4K HDMI Distribution Amplifier: HD-DA8-4K-EthomvalensiNo ratings yet
- TheAncientWisdom AnnieBesantDocument153 pagesTheAncientWisdom AnnieBesantJose Fernandez Romero100% (2)
- Gross Income PDFDocument18 pagesGross Income PDFRon RamosNo ratings yet
- HNNE Term Proforma Front Sheet 2008 With InstructionsDocument4 pagesHNNE Term Proforma Front Sheet 2008 With InstructionsMaribel MuevecelaNo ratings yet
- I Feel PrettyDocument1 pageI Feel PrettyRachele DaniNo ratings yet
- 35.1 Manalili vs. Court of Appeals (G.R. No. 113447 October 9, 1997 (280 SCRA 400) ) - Case DigestDocument2 pages35.1 Manalili vs. Court of Appeals (G.R. No. 113447 October 9, 1997 (280 SCRA 400) ) - Case DigestAmir Nazri KaibingNo ratings yet
- Ito 2015Document8 pagesIto 2015laurabarbosamedNo ratings yet