Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan
Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Eman AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Eman AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
Date__________ Class__________
Subject___________ Duration_______
Topic______________ Term: __________
Unit 15
Learning Objectives: After studying this chapter, the students will be able to
i. State Coulomb's law and explain that force between two point charges is reduced in a medium
other than tree space using Coulomb's law.
ii. Derive the expression - 1/4πE q/r2 tor the magnitude of the electric field at a distance 'r from a
point charge q.
iii. Describe the concept of an electric field as an example of a field of force.
iv. Define electric field strength force per unit positive charge.
v. Solve problems and analyze information using E = F/q.
vi. Solve problems involving the use of the expression E=1/4π E q/r2,
vii. Calculate the magnitude and direction of r he electric field at a point due two charges with the
same or opposite signs.
viii. Sketch the electric field lines tor two point charges of equal magnitude with same or opposite
signs
ix. Describe the concept of electric dipole.
x. Define and explain electric flux.
xi. Describe electric flux through a surface enclosing a charge.
xii. State and explain Gauss's law.
xiii. Describe and draw the electric field due to an infinite size conducting plate of positive or
negative charge
xiv. Sketch the electric field produced by a hollow spherical charged conductor.
xv. Sketch the electric field between and near the edges of two infinite sizes oppositely charged
parallel plates.
xvi. Define electric potential at a point in terms of the work done in bringing unit positive charge or
potential.
xvii. Solve problems by using the expression 4
xviii. Describe that the electric field at a point is given by the negative of potential gradient at that
point.
Teacher ‘s Signature Principal Signature’s
Lesson Plan
Date__________ Class__________
Subject___________ Duration_______
Topic______________ Term: __________
Unit 15
Learning Objectives: After studying this chapter, the students will be able to
i. Describe the concept of steady current.
ii. State Ohm's law.
iii. Define resistivity and explain its dependence upon temperature.
iv. Define conductance and conductivity of conductor.
v. State the characteristics of a thermistor and its use to measure low temperatures.
vi. Distinguish between e.m.f and P.d using the energy considerations.
vii. Explain the internal resistance of source and its consequences for external circuits.
viii. Describe some sources of e.m.f.
ix. Describe some sources of e.m.t.
x. Describe the conditions for maximum power transfer.
xi. Describe thermocouple and its function.
xii. Explain variation of thermoelectric e.m.f th temperature.
xiii. Apply Kirchhoff s first law as conservation on of charge to solve problem.
xiv. Apply Kirchhoff s second law as conservation of energy to solve problem.
xv. Describe the working of rheostat in the potential divider circuit.
xvi. Describe what a Wheatstone bridge is and how it is used to find unknown resistance.
xvii. Describe the function of potentiometer to measure and compare potentials without drawing
any current the circuit.
xviii. Current electricity is the study charges in motion. Simple electrical circuits can be solved by
applying Ohm's law. For other circuits, Kirchhoff rules are applied.
Teacher ‘s Signature Principal Signature’s
Lesson Plan
Date__________ Class__________
Subject___________ Duration_______
Topic______________ Term: __________
Unit 15
Learning Objectives: After studying this chapter, the students will be able to
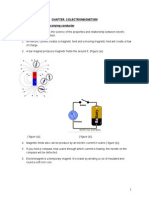
i. Explain the magnetic fields an example of a field of force produced cither by current-carrying
ii. conductors or by permanent magnets
iii. Describe magnetic effect of current.
iv. Describe and sketch field lines pattern due to a long straight wire.
v. Explain that a force might act on a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
vi. Investigate the factors affecting the force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
vii. Solve problems involving the use of F- BIL sinҨ.
viii. Define magnetic flux density and its units.
ix. Describe the concept of magnetic flux (Ҩ) as scalar product of magnetic field (B) and area (A)
using the
x. relation, B.A = BLA
xi. State Ampere's law.
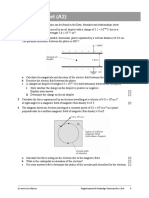
xii. Apply Ampere's law to find magnetic flux density.
xiii. Describe quantitatively the path followed by a charged particle shot into a magnetic field in a
direction perpendicular to the field.
xiv. Explain that a force my act on a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field.
xv. Describe the method to measure the e/m of an electron by applying magnetic field and electric
field on a beam of electrons. s principle to
xvi. Predict the turning effect on a current carrying coil in a magnetic field and the construction and
working of a galvanometer.
xvii. Explain how a given galvanometer can bè converted into a voltmeter or ammeter of a 5pein g
xviii. Describe the use of galvanometer / millimeter (analogue and digital
Teacher ‘s Signature Principal Signature’s
Lesson Plan
Date__________ Class__________
Subject___________ Duration_______
Topic______________ Term: __________
Unit 15
After studying this chapter, the students will be able to
i. Describe the terms time period, frequency, instantaneous peak value and root mean square
value of an
ii. alternating current and voltage. an
iii. Represent a sinusoidally alternating current or voltage by an equation of the form x=x, sin wt
iv. Describe the phase of A.C and how phase lags and leads in A.C Circuits.
v. Identify inductors as important components of A.C circuits termed as chokes (devices which
present a
vi. high resistance to alternating current).
vii. Explain the flow of A.C through resistors, capacitors and inductors. Apply the knowledge to
calculate
viii. the reactance's of capacitors and inductors.
ix. Apply the knowledge to calculate the reactance of capacitors and inductors.
x. Describe impedance as vector summation of resistances and reactance
xi. Construct phasor diagrams and carry out calculations on circuits including resistive and reactive
xii. components in series.
xiii. Solve the problems using the formula of A.C Power.
xiv. Explain resonance in an A.C circuit and carry out calculations using the resonant frequency
formula
xv. Describe that maximum power is transferred when the impedances source and lad match to
each other.
xvi. Describe the qualitative treatment of Maxwell' s equations and production of electromagnetic
waves
xvii. Become familiar with electromagnetic spectrum (ranging from radio waves toy-rays).
Teacher ‘s Signature Principal Signature’s
You might also like
- Electromagnetic Fields and Waves - Magdy F. Iskander - Text PDFDocument741 pagesElectromagnetic Fields and Waves - Magdy F. Iskander - Text PDFandrik supaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringFrom EverandIntroduction to Electromagnetic EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 12th SLO Model Paper IIIDocument2 pages12th SLO Model Paper IIIajaz ahmadNo ratings yet
- RNFetchBlobTmp O54w64jyignr8bl2pihfdDocument11 pagesRNFetchBlobTmp O54w64jyignr8bl2pihfdyashvardhan.manghani23No ratings yet
- Derivation of All ChapterDocument6 pagesDerivation of All Chapterplutouec86% (14)
- Other Educational PortalsDocument8 pagesOther Educational PortalsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Valliammai Engineering CollegeDocument11 pagesValliammai Engineering CollegeRagunathan NarayananNo ratings yet
- X Physics 2011: Online University - Your Resource To Education!Document7 pagesX Physics 2011: Online University - Your Resource To Education!abhi9333No ratings yet
- PHS1019 - Physics For Computer Studies Syllabus Outline-2023Document9 pagesPHS1019 - Physics For Computer Studies Syllabus Outline-2023lavey kellyNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Phy Imp QuestionsDocument5 pagesClass 12 Phy Imp Questionsrajeshsharma4121No ratings yet
- Theo Question emDocument2 pagesTheo Question emhamirNo ratings yet
- 14 Computer Aided Design Electrical ApparatusDocument87 pages14 Computer Aided Design Electrical ApparatusKARTHIKEYANNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SohailDocument7 pagesLesson Plan SohailMuhammad FayazNo ratings yet
- PH 110 Course Outline 2019-2020 Academic YearDocument4 pagesPH 110 Course Outline 2019-2020 Academic Yearmusamugabazi68No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentRuprabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Поурочный план 11 класс Free and Forced Electromagnetic wavesDocument7 pagesПоурочный план 11 класс Free and Forced Electromagnetic wavesСымбат ХусайноваNo ratings yet
- Important Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsDocument3 pagesImportant Derivations Type Questions in PhysicsJaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- PHS1019 - Module OutlineDocument9 pagesPHS1019 - Module OutlineJaiiNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Xi 079 PDFDocument3 pagesImportant Questions Xi 079 PDFJessica PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 7Document7 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 7HemantNo ratings yet
- Cbse Paper Leak PDFDocument7 pagesCbse Paper Leak PDFRohan AroraNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 Indore Class Xii Physics Assignment For Summer Vacation 2019-20 ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya No.2 Indore Class Xii Physics Assignment For Summer Vacation 2019-20 ElectrostaticsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel CombinationDocument24 pagesSeries and Parallel Combinationalzidi0% (1)
- XI Physics 2023-24Document4 pagesXI Physics 2023-24frcqatilNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFDocument8 pages12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDFAshish ChaharNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Physics On The Go 1.3 MechanicsDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Physics On The Go 1.3 MechanicsSamin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - Physics: Other Educational PortalsDocument7 pagesSample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - Physics: Other Educational PortalsSourabh SirradhanaNo ratings yet
- FEE (3rd) May2022Document1 pageFEE (3rd) May2022hs099318No ratings yet
- Physics Essential Unit 7 (E07)Document5 pagesPhysics Essential Unit 7 (E07)Jaxon FlameNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Special PlanDocument2 pagesClass 12 Special Plankharanshubanker165No ratings yet
- MLL Autumn BreakDocument1 pageMLL Autumn Breakmahadevipatil.patil04No ratings yet
- Sen. Gil Puyat National High School: Email AddDocument3 pagesSen. Gil Puyat National High School: Email AddRaymond BugagaoNo ratings yet
- Guess Paper Class - Xii Subject - PhysicsDocument5 pagesGuess Paper Class - Xii Subject - PhysicsTanmay KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Physics Xii Summer HHW 2024Document2 pagesPhysics Xii Summer HHW 2024mmozahid50No ratings yet
- Physics XII 12-10-2017Document49 pagesPhysics XII 12-10-2017Neelkant DubeyNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS XII Paper (2024)Document2 pagesPHYSICS XII Paper (2024)HammadurRehman 2006No ratings yet
- Phy 107 Course SpecificationDocument14 pagesPhy 107 Course SpecificationEric John EnriquezNo ratings yet
- ImpDocument10 pagesImpSakthi DharshiniNo ratings yet
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNo ratings yet
- BP&QP 1Document6 pagesBP&QP 1Akash AchuNo ratings yet
- BOOKLET ElectricityDocument26 pagesBOOKLET Electricitysureshthevan0% (1)
- 12th PHY ImpDocument6 pages12th PHY ImpmuzaffarusNo ratings yet
- Class XII Summer AssignmentDocument17 pagesClass XII Summer AssignmentArumugam AnandNo ratings yet
- NSAA Specification 2021 PhysDocument14 pagesNSAA Specification 2021 Phys/Mad As A Hatter /No ratings yet
- 12 Science HHWDocument26 pages12 Science HHWOmkar VikalNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work 2010Document22 pagesScheme of Work 2010Sivabalan BionicNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 W 5-6Document12 pagesGeneral Physics 2 W 5-6NOEMI AMADORNo ratings yet
- EC2253 - ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Question BankDocument8 pagesEC2253 - ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS Question Bankkalyan thallapaneniNo ratings yet
- EE6302 Electromagnetic TheoryDocument11 pagesEE6302 Electromagnetic TheoryAnonymous TJRX7CNo ratings yet
- 12thQuestionBank (KSU)Document9 pages12thQuestionBank (KSU)sohailmushtaq1001No ratings yet
- New Book ContinuationDocument7 pagesNew Book ContinuationEisle Keith Rivera TapiaNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi College of Engineering and Technologies Department of Eee Ee T35 Electromagnetic Theory Unit I: Electrostatic Field 2 MarksDocument5 pagesRajiv Gandhi College of Engineering and Technologies Department of Eee Ee T35 Electromagnetic Theory Unit I: Electrostatic Field 2 MarksgondesianandNo ratings yet
- Forms of Quadratic FunctionDocument2 pagesForms of Quadratic FunctionTheKnow04No ratings yet
- Phy Part I AssignmentDocument16 pagesPhy Part I Assignmentketan waghNo ratings yet
- Physics Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhysics Important QuestionsLaxman KumawatNo ratings yet
- EMF Question BankDocument11 pagesEMF Question BankMADHINI BALAMURALI ECENo ratings yet
- Module 5 CapacitanceDocument1 pageModule 5 CapacitancePhysics TwelveNo ratings yet
- XII PhysicsDocument55 pagesXII PhysicsCharu BhanotNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1Document28 pagesPhysics Paper 1AbhishekGuptaSarmaNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Emrs Physics SyllabusDocument4 pagesEmrs Physics SyllabusNscience freakNo ratings yet
- Effects of Magnetically Treated Water On Germination and Growth of Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum: Under Poor Soil Fertility and Deficit IrrigationDocument9 pagesEffects of Magnetically Treated Water On Germination and Growth of Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum: Under Poor Soil Fertility and Deficit IrrigationSundeeNo ratings yet
- Magnetism 2024Document4 pagesMagnetism 2024Immanuel BobbyNo ratings yet
- M - Tech Model QuestionsDocument124 pagesM - Tech Model QuestionsKeisher DmeNo ratings yet
- Phsys Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesPhsys Important QuestionsRamya. RNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ElectromagnetismDocument29 pagesChapter 3 ElectromagnetismAnonymous oW9OeJvEvNo ratings yet
- CH 3 EMI AC PDFDocument68 pagesCH 3 EMI AC PDFUtkarsh Mishra0% (1)
- Appreciation To NDT 3.1Document162 pagesAppreciation To NDT 3.1walesh_vx5No ratings yet
- Sardar Patel Institute of Technology: Applied Physics - I Handbook Semester - I ACADEMIC YEAR 2013-2014Document13 pagesSardar Patel Institute of Technology: Applied Physics - I Handbook Semester - I ACADEMIC YEAR 2013-2014Shoaib ShaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Moving Charges and MagnetismDocument8 pagesChapter-4 - Moving Charges and MagnetismAdarsh Silkoti100% (1)
- Du Physics 2018Document6 pagesDu Physics 2018Soumyashree paridaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 26Document3 pagesWorksheet 26Subarna Lamsal100% (1)
- Introduction (Coordinate Systems) : Lesson PlanDocument1 pageIntroduction (Coordinate Systems) : Lesson PlanLatif KhanNo ratings yet
- EMF Report For 230kV in Myanmar-20200816Document21 pagesEMF Report For 230kV in Myanmar-20200816sjcgraceNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL PRINCIPLES of BRAIN PHYSICS IIDocument38 pagesPHYSICAL PRINCIPLES of BRAIN PHYSICS IINicolae MaziluNo ratings yet
- Udgam School For Children: SUBJECT: Science Worksheet CH-13Document10 pagesUdgam School For Children: SUBJECT: Science Worksheet CH-13YASHVI MODINo ratings yet
- Magnet: Discovery and Development PhysicsDocument18 pagesMagnet: Discovery and Development Physicsca_luisgNo ratings yet
- Science 5 - Q3 - W9Document7 pagesScience 5 - Q3 - W9Mathleen DescalzoNo ratings yet
- Q3-Science 5-Week 7Document19 pagesQ3-Science 5-Week 7BUENA ROSARIONo ratings yet
- Kerala SSLC Physics CH 1-7 Easy Note (Eng Med)Document32 pagesKerala SSLC Physics CH 1-7 Easy Note (Eng Med)Asish Thampi100% (3)
- Physics For Jee Main and Advanced Magnetism and Emi 1St Edition Shashi Bhushan Tiwari All ChapterDocument67 pagesPhysics For Jee Main and Advanced Magnetism and Emi 1St Edition Shashi Bhushan Tiwari All Chapterjoyce.bongiorno295100% (9)
- Physics VCE Unit 3 Notes 2018Document62 pagesPhysics VCE Unit 3 Notes 2018fullname isNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12th Board Question Bank PDFDocument743 pagesPhysics Class 12th Board Question Bank PDFVineet sharma100% (1)
- Faraday Rotation + Verdet Constant PosterDocument1 pageFaraday Rotation + Verdet Constant PosterAndrew PalmerNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic WavesDocument65 pagesAlternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic WavesMaulitaNo ratings yet
- E.M. WavesDocument11 pagesE.M. WavesSatish Sharma100% (1)
- Filtración Hidráulica ParkerDocument8 pagesFiltración Hidráulica ParkeriosalcidoNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Unit 8 PDFDocument60 pagesPart 3 Unit 8 PDFSaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Magnetic Fields: Electricity and MagnetismDocument11 pagesChapter 16 Magnetic Fields: Electricity and MagnetismeltytanNo ratings yet