Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thursday 05 To Perform Brinell Hardness Test and Determine Hardness Number of Given Specimen
Thursday 05 To Perform Brinell Hardness Test and Determine Hardness Number of Given Specimen
Uploaded by
Fatima ImamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thursday 05 To Perform Brinell Hardness Test and Determine Hardness Number of Given Specimen
Thursday 05 To Perform Brinell Hardness Test and Determine Hardness Number of Given Specimen
Uploaded by
Fatima ImamCopyright:
Available Formats
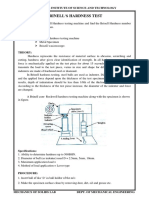
Experiment # 05
To perform Brinell hardness test and determine hardness number of
given specimen
1. Apparatus
Brinell hardness tester, microscope, ball indenter, Vernier caliper, scale.
Theoretical Background
2. Hardness
Hardness as we have defined previously is the mechanical property of the material that
determines the ability of the material to resist deformation or penetration through it. The
material like ceramics, concrete are hard material.
2.1. Advantage of the hard materials
The big advantage of the hard material comes under compressive load because hard
materials possess very good strength under compressive load. Hard materials are not
suitable for the purposes where tensile load is applied because of their low tensile
strength.
Due to their property to bear more load under compression hard materials are used in
construction purposes where compressive load is applied, for instance, concrete is
used most widely used in construction purposes due to its good capability to
withstand under compressive loading.
3. Hardness number
Hardness number is a parameter that is used for measuring of hardness of the specimen.
Greater the penetration of indentation in the material greater will be the hardness number
and the more will be the hardness of the material.
4. Methods to measure the hardness number of a material
Following are two most widely used methods for hardness number.
1. Rockwell hardness
2. Brinell hardness
We have already discussed Rockwell hardness in this section we will only describe
Brinell hardness.
5. Factors affecting the hardness testing
Following are the factors that affect the hardness testing of the equipment.
1. The surface where the test is being performed should be clean and there should be not
any dirt, oil etc. present.
2. The indenter must face the specimen perpendicularly i.e. the indenter is supposed
indent the surface through its vertical movement. If inclination occur, it will provide
wrong results.
3. The indenter scale should be completely visible for taking readings and readings
should be completely visible.
6. Brinell hardness
Brinell hardness number is ratio of the load applied to the surface area of the indentation.
In Brinell hardness, an indentation of known diameter is pressed hydraulically into the
specimen and extent of its penetration gives us the Brinell hardness number.
Unit of Brinell number is kgf/mm2.
The Brinell hardness numbers of some common materials are given in the table
Type of Material B.H.N
Mild steel 120 HB
Pure aluminium 15 HB
Copper 35 HB
Lead 5 HB
Stainless steel 200 HB
Table 1
7. Procedure
8. Observations and calculations
Least count of microscope scale = 0.05 mm
Diameter of indenter = 10 mm
No. of Load Indentation Indentation depth P
B.H .N=
obs. applied diameter D−√ D 2−d 2 πDt
P d t=
2
(kg) (mm) (mm)
1
2
3
9. Discussion
10.Comments
11.References
[1] mtil.illinois.edu/eq-brin.htm
[2] https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/Brinell%20hardness
You might also like
- ENGR 244 Lab1Document10 pagesENGR 244 Lab1SamuelNo ratings yet
- Thursday 01 To Perform The Tensile Test On Given Specimen by Using Hounsfield Tensometer and Determine The Mechanical Properties of The MaterialDocument39 pagesThursday 01 To Perform The Tensile Test On Given Specimen by Using Hounsfield Tensometer and Determine The Mechanical Properties of The MaterialFatima Imam100% (3)
- Strength Exp 2 Brinell Hardness TestDocument13 pagesStrength Exp 2 Brinell Hardness Testhayder alaliNo ratings yet
- BrinellDocument3 pagesBrinellkoushipriyathamNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness ReportDocument3 pagesBrinell Hardness Reportjaibalayya100% (1)
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument4 pagesBrinell Hardness TestBaibhav MohantyNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness Test (New)Document8 pagesBrinell Hardness Test (New)innocentsoul100% (2)
- BHT & VHTDocument8 pagesBHT & VHTMoHammadNashatSabbahNo ratings yet
- Brunel Hardness TestDocument8 pagesBrunel Hardness TestSalam AlbaradieNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test-LOAYDocument7 pagesHardness Test-LOAYBin IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For HardnesstestDocument12 pagesLaboratory Manual For Hardnesstest15 Saad HassanNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument21 pagesBrinell Hardness TestenginearswebNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument2 pagesHardness TestGurdeep KohliNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Hardness Test: March 2019Document12 pagesLaboratory Manual For Hardness Test: March 2019Ehh ManNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument7 pagesBrinell Hardness TestabdulazizNo ratings yet
- 2 Sem Recap: Chapter 7: Limits, Fits and Engineering TolerancesDocument30 pages2 Sem Recap: Chapter 7: Limits, Fits and Engineering Toleranceslaxmikanta sahuNo ratings yet
- Ae2130 Practicum Report Hardness TestDocument22 pagesAe2130 Practicum Report Hardness TestSilviaNo ratings yet
- Materials Engg Hardness TestDocument8 pagesMaterials Engg Hardness TestSourav KayalNo ratings yet
- The Hardness of Solids: Home Search Collections Journals About Contact Us My IopscienceDocument36 pagesThe Hardness of Solids: Home Search Collections Journals About Contact Us My IopscienceKalinga BalNo ratings yet
- c1 Mechanical PropertiesDocument46 pagesc1 Mechanical PropertiesHusnal TaufiqNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument23 pagesUnit IIvizhideepaNo ratings yet
- MEM 412 - EXPERIMENT 4 - Brinall Hardness TestDocument4 pagesMEM 412 - EXPERIMENT 4 - Brinall Hardness TestboatcomNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test: Hardness Is A Measure of The Resistance To Localized Plastic Deformation Induced by EitherDocument6 pagesHardness Test: Hardness Is A Measure of The Resistance To Localized Plastic Deformation Induced by EitherApril FlowerNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument3 pagesBrinell Hardness TestJanakiramNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids LabDocument2 pagesMechanics of Solids LabAltimate SonaNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness Test: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Document7 pagesBrinell Hardness Test: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Amisha SharonNo ratings yet
- Bri NellDocument3 pagesBri NellAshutosh Khatua 0929No ratings yet
- TOM Unit 2 PDFDocument23 pagesTOM Unit 2 PDFNikhil NagarajanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Dureza Brinell y RockwellDocument7 pages1 - Dureza Brinell y RockwellJorge AtienciaNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument10 pagesBrinell Hardness Testmohammad. 21No ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics Lab Report: Hardness TestDocument6 pagesSolid Mechanics Lab Report: Hardness TestNo NameNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument8 pagesHardness Testعماد المعماريNo ratings yet
- TESTDocument7 pagesTESTeldhopaul19894886No ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument5 pagesBrinell Hardness TestMYasirNo ratings yet
- مواد هندسية, اختبار الصلادةDocument10 pagesمواد هندسية, اختبار الصلادةprince amerNo ratings yet
- Zinc Coated NutsDocument18 pagesZinc Coated NutsFaiz Uddin SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument13 pagesHardness TestMohammad FrehatNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Brinell Hardness Test IntroductionDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1 Brinell Hardness Test IntroductionAhmad Abd100% (1)
- University of Jordan: Experiment No. (2) : Hardness TestDocument6 pagesUniversity of Jordan: Experiment No. (2) : Hardness Testjohn rozz bbNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument9 pagesHardness Testshmosaali133No ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness TestDocument8 pagesBrinell Hardness TestabdulazizNo ratings yet
- Som Exp 8Document5 pagesSom Exp 8Sania BatoolNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestsDocument6 pagesHardness TestsMed GhzNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestingDocument3 pagesHardness TestingtuanNo ratings yet
- Document (1) - 1Document28 pagesDocument (1) - 1Saad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Bms HB 3000-b Brinell-HardheidstesterDocument20 pagesBms HB 3000-b Brinell-HardheidstesterKumara SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EMMDocument40 pagesLab Manual EMMArooshNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestingDocument7 pagesHardness Testingromesaali23No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Lab (Me-205L) : Experiment # 10Document21 pagesMechanics of Materials Lab (Me-205L) : Experiment # 10Mushaf KhalidNo ratings yet
- A.C.T. College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument16 pagesA.C.T. College of Engineering & TechnologyJegan ParamasivamNo ratings yet
- Title:: 1.0 AbstractDocument9 pagesTitle:: 1.0 AbstractKalai ArasuNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 3 Hardness TestDocument7 pagesEXPERIMENT 3 Hardness TestHairi HangNo ratings yet
- Advanced SOM. LAB. Manual-2Document15 pagesAdvanced SOM. LAB. Manual-2Sudip LouhaNo ratings yet
- Buehler MicroHardness Testing MethodsDocument7 pagesBuehler MicroHardness Testing Methodspipedown456No ratings yet
- HardnessDocument11 pagesHardnessglorialidwin.b dace mechNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Hardness Test)Document14 pagesAssignment 1 (Hardness Test)Azri LunduNo ratings yet
- 3 MS & M PR Manual 2020 - 2021Document56 pages3 MS & M PR Manual 2020 - 2021Anil ChauvanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Lab Manual: Mechanical Engineering Second Year Section B, B - 2Document27 pagesStrength of Material Lab Manual: Mechanical Engineering Second Year Section B, B - 2Satvik YelluriNo ratings yet
- Hardness ReportDocument11 pagesHardness Reportcheyaya100% (8)
- 穆賢 K1006117 HardnessTestDocument18 pages穆賢 K1006117 HardnessTestMuhammad AbizardNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature and Wind Speed On Efficiency of PV ModuleDocument16 pagesEffect of Temperature and Wind Speed On Efficiency of PV ModuleFatima ImamNo ratings yet
- Straight Line Law - Towards Saturation Saturated Curve at Wetted Surface TemperatureDocument18 pagesStraight Line Law - Towards Saturation Saturated Curve at Wetted Surface TemperatureFatima ImamNo ratings yet
- Thursday 03 To Determine Diametrical Deflection of A Circular Bar Subjected To Diametrical LoadingDocument7 pagesThursday 03 To Determine Diametrical Deflection of A Circular Bar Subjected To Diametrical LoadingFatima ImamNo ratings yet
- Week 13Document45 pagesWeek 13Fatima ImamNo ratings yet
- Thursday 02 Investigation of Load - Deflection Characteristics of A Helical Spring Under TensionDocument10 pagesThursday 02 Investigation of Load - Deflection Characteristics of A Helical Spring Under TensionFatima ImamNo ratings yet
- Thursday 04 To Perform The Rockwell Hardness Test and Determine The Hardness of The Given SpecimenDocument6 pagesThursday 04 To Perform The Rockwell Hardness Test and Determine The Hardness of The Given SpecimenFatima ImamNo ratings yet
- Fracture Analysis of Wind Turbine Main Shaft PDFDocument11 pagesFracture Analysis of Wind Turbine Main Shaft PDFKaio Dos Santos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 - Shearing Stresses in Beams and Thin-Walled MembersDocument15 pagesChap 6 - Shearing Stresses in Beams and Thin-Walled MembersroselleNo ratings yet
- Spanner ReportDocument24 pagesSpanner ReportBiswajit DashNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Liquid CrystalsDocument38 pagesIntroduction of Liquid CrystalsJohn Vladimir A. BulagsayNo ratings yet
- 21TR1 E1a2-20200401Document6 pages21TR1 E1a2-20200401toddflyNo ratings yet
- Weld and Base Metal Discontinuities: Module 9 - 1Document13 pagesWeld and Base Metal Discontinuities: Module 9 - 1Alejandro RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Beam Column JointDocument6 pagesBeam Column JointAnonymous KyLhn6No ratings yet
- A Tribological Approach To Tire Wear: Research Paper ProposalDocument3 pagesA Tribological Approach To Tire Wear: Research Paper ProposalSyed Danish FayazNo ratings yet
- Polymers PDFDocument39 pagesPolymers PDFAngelo Luis RosNo ratings yet
- M2-CV-RC-D-005 (Anchor Bolt Details)Document19 pagesM2-CV-RC-D-005 (Anchor Bolt Details)neerajNo ratings yet
- 04 Strain 03 Volumetric Strain PDFDocument3 pages04 Strain 03 Volumetric Strain PDFHappy Kumar JainNo ratings yet
- Crystallisation - Faculty LectureDocument24 pagesCrystallisation - Faculty Lecturesoumitra hazraNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design Recommendations For High-Strength ConcreteDocument261 pagesSeismic Design Recommendations For High-Strength ConcreteDaniele Di LucaNo ratings yet
- CH 2. Strain Energy FunctionsDocument11 pagesCH 2. Strain Energy FunctionsMaurice Lopez RavelNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Physical Metallurgy - Materials Science and Engineering - MIT OpenCourseWareDocument3 pagesLecture Notes - Physical Metallurgy - Materials Science and Engineering - MIT OpenCourseWareSharek HasanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Zirconia Reinforced Lithium Silicate Glass-CeramicDocument7 pagesMechanical Properties of Zirconia Reinforced Lithium Silicate Glass-CeramicVictoria Moreno MNo ratings yet
- Tee (T) Section Properties - Calculator - CALC RESOURCEDocument9 pagesTee (T) Section Properties - Calculator - CALC RESOURCEsreekanth6959646No ratings yet
- Machine Ddesign ReviewDocument51 pagesMachine Ddesign ReviewMico Cañete100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document57 pagesChapter 9Pavan PonnadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12: Equilibrium and ElasticityDocument11 pagesChapter-12: Equilibrium and ElasticityJustin FieldsNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modelling of Infilled Frame Structures - A General ReviewDocument18 pagesAnalytical Modelling of Infilled Frame Structures - A General ReviewSuman TiwariNo ratings yet
- Me MCQDocument4 pagesMe MCQsangam100% (1)
- Materials Research Bulletin: Xiaolian Chao, Zhongming Wang, Ye Tian, Yanzhao Zhou, Zupei YangDocument10 pagesMaterials Research Bulletin: Xiaolian Chao, Zhongming Wang, Ye Tian, Yanzhao Zhou, Zupei YangSamah SamahNo ratings yet
- Course and Instructor Information: Chemical Engineering Department School Year 2017 - 2018Document11 pagesCourse and Instructor Information: Chemical Engineering Department School Year 2017 - 2018Robert DelfinNo ratings yet
- Answer All The Questions (5 X 2 10)Document13 pagesAnswer All The Questions (5 X 2 10)Robinson PrabuNo ratings yet
- 17-4 PHDocument4 pages17-4 PHfahimshah1301No ratings yet
- Polyglycolic Acid (PGA) Resin: Superior Barrier PerformanceDocument2 pagesPolyglycolic Acid (PGA) Resin: Superior Barrier PerformanceiyerpadmaNo ratings yet
- Plastics: by Dr. V Phanindra Bogu Dept. of Mech. EnggDocument18 pagesPlastics: by Dr. V Phanindra Bogu Dept. of Mech. EnggV Phanindra BoguNo ratings yet
- Assign 3 SolutionsDocument5 pagesAssign 3 SolutionsAnshu Kumar Gupta100% (3)