Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsGear Pump
Gear Pump
Uploaded by
BorysCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Rta48 - Operation ManualDocument13 pagesRta48 - Operation ManualBorysNo ratings yet
- Rta48 - Sea Trail TestsDocument16 pagesRta48 - Sea Trail TestsBorysNo ratings yet
- 1d Dvs Sulzer Rta48t Codebook 812Document812 pages1d Dvs Sulzer Rta48t Codebook 812BorysNo ratings yet
- Air ComDocument54 pagesAir ComBorysNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Hydraulic Driven Deck MachineryDocument180 pagesInstruction Manual For Hydraulic Driven Deck MachineryBorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac:) Usttifiw-26Document60 pagesAtoyac:) Usttifiw-26BorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac: Flistnllhf-20Document85 pagesAtoyac: Flistnllhf-20BorysNo ratings yet
- FlowmeterDocument22 pagesFlowmeterBorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac: (Listnolhf-23Document70 pagesAtoyac: (Listnolhf-23BorysNo ratings yet
- Arr. of Pilot Ladder: Tsunelshi Shipbuilding Co .. LTDDocument33 pagesArr. of Pilot Ladder: Tsunelshi Shipbuilding Co .. LTDBorysNo ratings yet
- HF-7 Rudder CarrierDocument22 pagesHF-7 Rudder CarrierBorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac: Listnol HF - 1Document124 pagesAtoyac: Listnol HF - 1BorysNo ratings yet
- HF-19 Anchor Chain CableDocument3 pagesHF-19 Anchor Chain CableBorysNo ratings yet
- Ea-4 Test Record of Generator Control SystemDocument54 pagesEa-4 Test Record of Generator Control SystemBorysNo ratings yet
- HG-4 Docking PlanDocument3 pagesHG-4 Docking PlanBorysNo ratings yet
- Ed-15 Electric Propeller Shaft Revolutions and Electric Revolution Counter (Incl Inst and Test Report)Document58 pagesEd-15 Electric Propeller Shaft Revolutions and Electric Revolution Counter (Incl Inst and Test Report)BorysNo ratings yet
- Ed-10 Magnetic CompassDocument7 pagesEd-10 Magnetic CompassBorysNo ratings yet
- Ec-5 MotorDocument38 pagesEc-5 MotorBorysNo ratings yet
- Tsa/Ssr Type: Instruction Book For Roots BlowerDocument19 pagesTsa/Ssr Type: Instruction Book For Roots BlowerBorysNo ratings yet
- Ec-10 Emergency Switchboard (Incl Test Report)Document72 pagesEc-10 Emergency Switchboard (Incl Test Report)Borys100% (1)
- Docking PlanDocument1 pageDocking PlanBorysNo ratings yet
- List No: Nishishiba Electric Co., LTDDocument17 pagesList No: Nishishiba Electric Co., LTDBorys100% (1)
- MD-7-0005 Emergency Diesel GeneratorDocument152 pagesMD-7-0005 Emergency Diesel GeneratorBorysNo ratings yet
- Ed-2 Electro Magnetic Log (Incl Inst and Test)Document75 pagesEd-2 Electro Magnetic Log (Incl Inst and Test)Borys100% (1)
- Ed-1 Digital Auto PilotDocument256 pagesEd-1 Digital Auto PilotBorys100% (3)
- MD-1 Main Diesel Generator EngineDocument49 pagesMD-1 Main Diesel Generator EngineBorys100% (1)
- Sulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingDocument1 pageSulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingBorysNo ratings yet
- Sulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingDocument1 pageSulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingBorysNo ratings yet
- Mb-4 Operation and DataDocument348 pagesMb-4 Operation and DataBorysNo ratings yet
- Incinerator PDFDocument52 pagesIncinerator PDFBorysNo ratings yet
Gear Pump
Gear Pump
Uploaded by
Borys0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesOriginal Title
gear pump
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesGear Pump
Gear Pump
Uploaded by
BorysCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 11
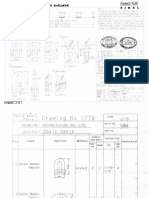
WESTERN TIDE
$1065 ae |
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FOR
MOTOR-DRIVEN GEAR PUMPS
March, 1986 x
S HEISHIN PUMP WORKS CO, LTD
10.
ML
12,
Contents
Purpose
Scope of Application
Outline of Construction
‘Transport
Prevention of Vibration
Installation
Piping pee ee eee ‘i ccete teen eee
Connection .
8-1. Alignment
8-2. Checking of Alignment
Operation ceeee ee
9-1. Preparation before Operation
9-2. Operation
9-3. Stopping
Maintenance ce teee eee
10-1. Cautions during Operation
10-2, Cautions during Standstill
Inspection
11-1. Periodical Inspection
11-2. Overhaul
11-3. Checkup .
11-4. Assembly
‘Troubles and Remedies
Aaa OAH AKA BD
Instruction Manual for Motor-driven Gear Pumps
Purpose
This manual has been prepared for the standard motor-driven gear pumps used on
commercial vessels for the convenience of persons concerned with handling pumps who
belong to shipbuilders and shipowners.
Note: ‘This manual covers items common to pumps in general. So for such details as the per-
rissible limit of clearances of rotating parts, list of patticulars, outline drawings, sectional
assembly drawings, test results; list of spate parts and tools, etc. refer to the respective
data separately prepared by manufacturers.
Scope of Application
‘This manual is applicable to A.C. motor driven ordinary pumps such as lubricating
oil, fuel oil and fuel valve cooling oil pumps (hereinafter called pumps).
Note: For special pumps such as cargo oil pumps, bilge pumps, main or auxiliary machinery driven
pumps which are different from ordinary pumps in service or construction, tefer to their
respective instruction manuals.
Outline of Construction
‘This pump has in its casing one set of gear and shaft supported with bearings and liquid
is contained between the teeth. With the rotation of the gear, liquid is continuously dis-
charged around the casing inside. (See the reference figure)
The bearings located inside the seal section are self-lubricated with the liquid. The
lubrication liquid is supplied to oil passage through oil openings provided on the discharge
side and fs returned to the suction side after lubrication of the bearings.
‘The safety valve protects the pump or the motor by opening the port and by-passing
the liquid to the suction side when the discharge pressure rises abnormally higher than the
set pressure.
Reference: The procedure for controlling the set pressure is that after the adjust screw of the
safety valve is fully tightened with discharge/suction valves fully open, these valves,
are gradually closed to set the discharge pressure at the set pressure and the suction
pressure at ~380mmHg. Thon the adjust sorew is slowly untightened and locked at a
point where the discharge pressure or the suction pressure fluctuates very slowly.
When control is over, pump operation is started with dischargo/suotion valves open.
Transport
In transport it is necessary to proceed as follows.
a. When lifting, pay attention to safety in respect to the weight of the units lifted
and the method of using wires.
b. Be careful to avoid damage to accessories such as piping, valves, cocks, etc.
Prevention of Vibration
In order to minimise the vibration of pump and piping, pay sufficient attention to the
reinforcement of pump foundation and piping supports.
-1-
6. Installation
In installation, pay attention as follows:
b.
4.
Piping
Pump foundation must be as rigid and strong as practical.
Considering operation and overhaul, give as ample space as possible.
Installation face must be flat.
Location of installation must be determined in consideration of pump suction
head.
Sufficiont attention must be given to piping since it has a great effect on pump
performance.
a. Suction pipe must be as short as possible, and bends must be as few as possible
to minimize friction loss.
b. Suction pipe must be free from air pocket or air invasion.
c. Valves on the suction side must be guarded against air invasion through the
gland.
4. Filter must be provided on the suction side for pump protection.
Flanges connecting to the suction and discharge nozzles should be placed
correctly in order to avoid disturbance of pump alignment when flange bolts are
‘unduly tightened.
f. Precautions must be taken so that expansion and contraction due to temperature
and weight of piping and valves may not abnormally affect the pump. And at the
same time, precautions must be taken to avoid misalignment of the flange caused
by pipe vibration.
g. _ Interior of the piping must be as clean as possible.
8, Connection
8-1
8-2
a.
Alignment
(On completing installation, the alignment must be checked and care must be
taken so that no misalignment will occur after connectirig with piping. Since align-
‘ment is duly carried out in the factory, unreasonable readjustment should be avoided.
Even though misalignment occurs, readjustment must be made carefully by loosening
both of the bolts on the suction and discharge flanges and the foundation. After the
alignment is made, a knock pin shall be inserted.
Horizontal pump
It is desirable that adjustment be made by inserting a liner between common
bedplate and foundation, but if necessary, shims can be placed between common
bedplate and motor base.
Vertical pump
‘Adjustment is made by placing shims between motor and motor base.
Checking of alignment
Untighten the bolts of the shaft coupling between pump and motor and check
-2-
the alignment at four points, 90° apart, on the coupling periphery.
For comparing the distance between the faces, fix a dial indicator on the shaft
coupling of the motor side as shown in Fig. 1 (a) and give the motor coupling one
complete rotation by hand. Then half of the variation in readings is taken as the
value of measurement, which must comply with the value in Table 1,
PAL
Fig. 1
(oy
Table 1. Table 2.
No. of motor frame | Coupling periphery No. of motor frame | Coupling end face
= (ram) = (mm)
/ML8OL (ML5~1601) 0.08 and tess ‘M182M (MLS~182M) amor
and less and less
1M200M (215-2008) = ‘M160 (0MLS-~160M)
ms 0.08 and i ees 0.18 and less
a.
e.
£.
For measuring the clearance between coupling faces, insert a thickness gauge at
four points of equal interval as shown in Fig. 1 (b). Then the value of measure-
ment, which must comply with the value in Table 2.
Ensure the rotating direction of the motor.
Tighten the coupling bolts.
Rotate the pump by hand to see whether it rotates smoothly.
Note: A thickness gauge should be adopted for alignment only at the times of repair, intermediate
{inspection and periodical inspection, It is preferable to use a dial indfeator for checkup
after initial instalation or piping arrangement.
9. Operation
Operation after installation or reassembly must be carried out in the following
order:
9-1.
a
b.
e
Preparation before operation
Fully open the valves of both suction and discharge sides.
Open the air vent valve (or cock) on the casing top to fill the casing with liquid.
If the pump is located above the suction level, pull the plug out of the casing top
and fill the casing with oil while rotating the pump by hand in order to fully
spread oil over the teeth and the bearings. Keep the air vent plug (or cock) on the
discharge side open.
4.
9-2
9-3,
b.
See that the cock (or plug) of the pressure gauge and compound gauge is open.
Rotate the pump by hand to see whether it turns smoothly.
Operation
Start the motor, but at first repeat “ON’ and “OFF” operations once or twice
and enter into operation on confirming that there is no abnormal condition with
respect to rotating direction, noise, vibration, starting current, etc.
Tighten the air vent plug (or cock) after speed has risen, and air is discharged
from the air vent and liquid is pumped up in some time. If liquid is not pumped
up in about 30 seconds after start-up, stop the motor and check the cause.
Avoid dry operation absolutely as the sliding contact surfaces of the bearings,
the teeth and the mechanical seal are of self-lubrication construction.
Pay a careful attention in the winter season because there may be a fear of
excessive torque of motor and abnormal noise and vibration of pump caused
by oil viscosity increase. Some treatment such as heating is preferable.
Stopping
Stop the motor.
After stopping the pump, close the suction valve and then close the discharge
valve.
10. Maintenance
In order to maintain an efficient operation over a long period, the utmost care must
be taken.
10-1. Cautions during Operation
a
b.
‘Try to operate the pump within the range of the design condition.
Check the vibration, noise, pressure gauge and ammeter. If abnormal condition
is surveyed stop the pump immediately. Particularly, for the pump provided with
mechanical seal, protect against vibration in view of the service life of the
mechanical seal,
Pay attention to bearing temperature rise. If the bearing housing can be felt by
hand safely, there is no fear, otherwise, measure the temperature with a ther-
mometer. Keep the permissible bearing temperature at “ambient temperature plus
40°C” or “liquid temperature plus 20°C”. If low viscosity oil outside the range
of design condition, be careful as the bearings and the gear may be seized.
Keep a small amount of continuous leak from the gland. ‘Too hard tightening of
the packing will cause premature wear of the shaft and the sleeve, overheating
and overload. Especially pay a careful attention to a case where oil of high
temperature or low viscosity is used.
When a mechanical seal is used, oil leak is generally very small. If oil leaks in
rips, check the seal.
Never thiottle the valve on the suction anid discharge sides. Adjust the flow by
means of the by-pass valve on the discharge side.
~4-
Never operate with the valve closed on the discharge si
rise of the liquid in the casing will cause seizure,
See whether the stand by pump is reversing due to the leakage from its non-
return valve.
In the case of a pump with automatic starting and stopping device, check the
pressure at the start and stop of pump as well as the interval of operation, and
if the interval is too short, check the system.
In the case of automatic operation under central control system, take care of
the indication of gauge on the control panel board.
Keep the strainer clean to avoid clogging.
otherwise q temperature
10-2. Cautions during Standstill
Keep closed the discharge and suction valves. But such valves must be kept open
in a case where the pump is of auto start type with a foot valve or a check valve,
where the pump is under positive suction head or where oil is accumulated in the
pump casing in some way or other.
When the pump is shut down over a long period, the pump must be rotated by
hand or motor periodically (once a week or so)
11. Inspection
11-1. Periodical Inspection
Excepting the case of abnormal conditions, it is desirable to carry out inspec-
tion periodically in the following way, but since it varies according to the method.
of mounting, place of installation, liquid Handled, ete, it is preferable that the
operator should make a final plan of inspection in accordance with conditions.
Item
Period
‘Every 12 | Every 4
months or | years or
£8,000 hrs | 20,000 hrs
‘Action to be taken 7
Every 3
months
Ball bearing
‘Check up inner and outer races as well as
balls for exfoliation, and if its trace is found, °
renew it,
Line beating
‘Check up sliding surfaces for conditions of
contact and flaw. Measure inside diameter
and take necessary steps according to
‘manufacturer's recommendation.
Gland packing| Check up condition of fitting and amount of
leakage. Renew it if leakage is too much.
seal
| iiechanical
‘Chock up condition of mating faces. a
Renew it,
Shaft sleeve
‘Check up contact points and flaw in portions
facing packing and bearing. Measure outside
diameter and take necessary steps according
‘to manufacturer's recommendation,
Shaft
‘Check up conditions of contact, flaw in
sliding faces. Measure the outside diameter o
Of journal and treat it according to manu-
facturer’s recommendation,
ring
‘Check up surface flaw and condition of a
deterioration. Renew it if deformed.
Renew i t
=Ge
‘Throttle the discharge valve to raise discharge
Safety Valve | pressure and confirm operation of the safety 0
valve. =
Check up tooth surfaces and condition of its
setting to the shaft. Measure the outside A
diameter and width and treat it according to
‘manufacturer's recommendation.
‘Check up condition of wear and renew them
if abnormal points are found.
Gear
Shaft couph
ing bolts and
rubber rings es a
Foundation | See to it that the foundation bolts are 5
bolts tightened enough.
Note: The hours quoted refer to the operating hours.
11-2, Overhaul
When overhauling the pump, attention must be paid as follows:
a. Understand the construction well by referring to the assembly drawing and make
no mistake in the order of overhaul.
b. When separating fit and flange faces, use jack bolts and wooden hammers, and
never apply force with chisels or drivers.
¢. When removing the rotating element, take care to avoid flaw on sliding faces and
machined surfaces. It is preferable not to overhaul the mechanical seal unless
there is anything abnormal.
d. When removing rotating parts from the shaft, draw off each one carefully after
removing the locking device.
Handle the longsized-parts such as shaft carefully so that it may not bend.
f, Handle the parts carefully, by arranging them on sheets of paper or cloth in
good order.
g. At overhauling, put suitable match marks as many as p
when reassembling.
ible to avoid mistakes
11-3. Checkup
Measure each sliding part and take necessary steps according to manufacturer's
recommendation.
11-4. Assembly
Carry out assembly, by reversing the order of disassembly and paying attention
as follows:
a. Remove dust and stain from each part by washing it thoroughly with kerosene.
Repair it if flaw is found.
b. Fit the locking device perfectly in each rotating part if necessary.
When fitting the parts with match marks such as fittings and gear, be sure to
follow them.
& Before assembling the sliding contact faces of the bearings, tooth faces and
‘mechanical seal, apply enough clean lube oil to them.
e, When fitting the bearings and side cover, take into account the position of oil
channel for bearing lube oil and return oil and the direction of pump discharge
and suction.
-6-
Insert each packing in good order softly one by one from the bottom, staggering
each joint by 90° or 180° to a fixed position and support it lightly with the
packing gland.
g Carefully fit the mechanical seal and then confirm its movement by hand.
h. Tighten the bolts with an equal force.
i, Check up the alignment as mentioned in Section 8.
i. Rotate the pump by hand to see that it turns smoothly.
12, Troubles and Remedies
Should troubles occur, their causes must be traced and necessary remedies must be
carried out. The following, for instance, can be conceivable as troubles.
‘Troubles Causes Remedies
+ Motor is in trouble. + Repair motor a
+ Pump seizes. + Repair pump.
. + No power source. + Check up electric system,
Pump does not start. * "Wiring is broken, or relay, ete. | + Repair
are in trouble
+ Foreign matters exist in the * Overhaul the pump and remove
pump. them,
c * Pump is not well filled with oil.| > Fill again,
+ Air is not vented enough. + Open air plug (or cock)
+ Valves are not open
+ Valves will not open
Pump starts, but does not | + Pump is sucking air.
Open valves.
Repair valves.
Check up suction system and gland
discharge liquid. packing.
+ Suction pipe or strainer is + Clean suction pipe or strainer.
clogged.
* Motor rotating ditection is + Change wiring,
wrong.
+ Pump is sucking air * Check up suction system, and gland
packing,
+ Pump speed are too low. * Correct electric source.
+ Safety valve is open. + Adjust its setting
+ Suction pipe or strainer is + Clean it.
Pump starts, but specified | clogged.
capacity or discharge + Liquid viscosity is too low. * Check design specification.
pressure are not reached | » Gear shaft is worn, + Renew it.
+ Suction pressure is too high. + Check viscosity.
+ Suction Pressure shall be within
-380mmHg.
+ Confirm full opening of suction valve]
+ Instruments are wrong. + Replace them with new ones.
~ Air pockets exist in suction line| + Correct piping
Pump starts and discharges | + Pump is sucking air. * Check up suction system,
liquid but soon ceases to | + Pump is sucking air through Check up sealing pipe.
discharge liquid stuffing box. ‘Adjust mechanical seal.
Adjust packing.
* Abnormal metal contact exists | + Check clearance,
the rotating parts.
+ Connection is wrong + Check up alignment
ump warts, but motor | * P2OHIG i 00 tiahtened. * onwn gind tetris ew
sets overloaded. = Pump shaft is bent. + Renew shaft.
* Motor isin trouble. + Repair it
= Liquid viscosity is too high. * Conform it to design condition.
+ Foreign matters exist in tho | Remove them.
pump.
+ Discharge pressure is too high. | Conform it to design condition.
+ Bearings are wrong + Renew them,
Lubricant is in shortage ~ Check oll supply to bearings and
return ol system.
+ Connection is wrong. + Check up alignment.
+ Bearings ate wrong + Renew them
Pump starts, but bear. | + Shaft is bent + Renew it
ings get overheated + Thrust has increased + Check whether excessive woar exists
: con beating side ot whether pump i
in abnormal suction pressure
condition.
+ Bearing assembly is wrong. _| + Readjst bearings.
> Connecting i wrong. ~ Check up alignment
+ Shaft is bent. + Renew shaft
, + Installation is wrong * Correct installation con
+ Foundation is weak. + Reinforce foundation
+ Other vibration is transmitted, | + Reinforce piping
Tee Sans, bat bia | + cautation exist. * Conform suction pressure and
takes place. viscosity to design condition.
+ Bearings are worn + Renew them.
+ Safety valve is chattering + Repair i
+ Foreign matters exist in the | Ovethaul the pump to remove them
pump
+ Tooth contact is wrong + Renew the gear
In case troubles cannot be remedied in spite of the above counter-measures, the causes
may be in the design conditions of the pump, so it is preferable to consult the shipyard or
manufacturer.
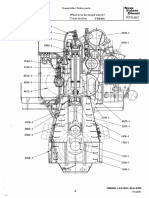
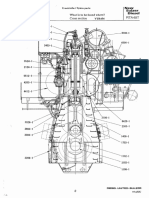
Vertical motor-driven gear pump
ao
(Reference Fig.)
|
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Rta48 - Operation ManualDocument13 pagesRta48 - Operation ManualBorysNo ratings yet
- Rta48 - Sea Trail TestsDocument16 pagesRta48 - Sea Trail TestsBorysNo ratings yet
- 1d Dvs Sulzer Rta48t Codebook 812Document812 pages1d Dvs Sulzer Rta48t Codebook 812BorysNo ratings yet
- Air ComDocument54 pagesAir ComBorysNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Hydraulic Driven Deck MachineryDocument180 pagesInstruction Manual For Hydraulic Driven Deck MachineryBorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac:) Usttifiw-26Document60 pagesAtoyac:) Usttifiw-26BorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac: Flistnllhf-20Document85 pagesAtoyac: Flistnllhf-20BorysNo ratings yet
- FlowmeterDocument22 pagesFlowmeterBorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac: (Listnolhf-23Document70 pagesAtoyac: (Listnolhf-23BorysNo ratings yet
- Arr. of Pilot Ladder: Tsunelshi Shipbuilding Co .. LTDDocument33 pagesArr. of Pilot Ladder: Tsunelshi Shipbuilding Co .. LTDBorysNo ratings yet
- HF-7 Rudder CarrierDocument22 pagesHF-7 Rudder CarrierBorysNo ratings yet
- Atoyac: Listnol HF - 1Document124 pagesAtoyac: Listnol HF - 1BorysNo ratings yet
- HF-19 Anchor Chain CableDocument3 pagesHF-19 Anchor Chain CableBorysNo ratings yet
- Ea-4 Test Record of Generator Control SystemDocument54 pagesEa-4 Test Record of Generator Control SystemBorysNo ratings yet
- HG-4 Docking PlanDocument3 pagesHG-4 Docking PlanBorysNo ratings yet
- Ed-15 Electric Propeller Shaft Revolutions and Electric Revolution Counter (Incl Inst and Test Report)Document58 pagesEd-15 Electric Propeller Shaft Revolutions and Electric Revolution Counter (Incl Inst and Test Report)BorysNo ratings yet
- Ed-10 Magnetic CompassDocument7 pagesEd-10 Magnetic CompassBorysNo ratings yet
- Ec-5 MotorDocument38 pagesEc-5 MotorBorysNo ratings yet
- Tsa/Ssr Type: Instruction Book For Roots BlowerDocument19 pagesTsa/Ssr Type: Instruction Book For Roots BlowerBorysNo ratings yet
- Ec-10 Emergency Switchboard (Incl Test Report)Document72 pagesEc-10 Emergency Switchboard (Incl Test Report)Borys100% (1)
- Docking PlanDocument1 pageDocking PlanBorysNo ratings yet
- List No: Nishishiba Electric Co., LTDDocument17 pagesList No: Nishishiba Electric Co., LTDBorys100% (1)
- MD-7-0005 Emergency Diesel GeneratorDocument152 pagesMD-7-0005 Emergency Diesel GeneratorBorysNo ratings yet
- Ed-2 Electro Magnetic Log (Incl Inst and Test)Document75 pagesEd-2 Electro Magnetic Log (Incl Inst and Test)Borys100% (1)
- Ed-1 Digital Auto PilotDocument256 pagesEd-1 Digital Auto PilotBorys100% (3)
- MD-1 Main Diesel Generator EngineDocument49 pagesMD-1 Main Diesel Generator EngineBorys100% (1)
- Sulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingDocument1 pageSulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingBorysNo ratings yet
- Sulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingDocument1 pageSulzer 6RTA 48T General DrawingBorysNo ratings yet
- Mb-4 Operation and DataDocument348 pagesMb-4 Operation and DataBorysNo ratings yet
- Incinerator PDFDocument52 pagesIncinerator PDFBorysNo ratings yet