Professional Documents
Culture Documents
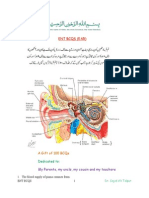
ENT 50 McQs
ENT 50 McQs
Uploaded by
Uzair KhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ENT 50 McQs
ENT 50 McQs
Uploaded by
Uzair KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Caloric test has
a) Slow component only
b) fast component only
c) Slow + Fast components
d) fast components occasionally
Ans: c
2.Carhart’s notch is characteristically seeh at
a)1000hz
b)2000hz
c)4000hz
d)6000hz
Ans: b
3.Gradenigo’s syndrome does not consist of
a) abducent nerve palsy
b) Retro orbital pain
c) aural discharge
d) Palatal palsy
Ans: d
4.In Acoustic neuroma the following is not seen
a) Auditory defect
b) Sensory aphasia
c) Motor aphasia
d) Changes in audiometry
Ans: c
5.Myringotomy is done on the …quadrant of the tympanic membrane
a) Postero inferior
b) Postero superior
c) antero inferior
d) antero superior
Ans: a
6.In unsafe CSOM with cholesteatoma and sensorineural deafness treatment choice
a) simple mastoidectomy
b) modified radical mastoidectomy
c)radical mastoidectomy
d) tympanoplasty
Ans: c
7.Organ of corti is situated in
a) scala media
b) ScalaTympanum
c) Scala Vestibule
d) Saccule
Ans:a
8.Endolymphatic hydrops is associated with
a) Otosclerosis
b) CSOM
c) wax impacted ear
d) presbycusis
Ans: d
9.Positive Rinnetest is seen in
a) Otosclerosis
b) csom
c) wax impacted ear
d) Presbycusis
Ans: d
10.Pulsatile otorrhea seen in
a) Glomus tumour
b) CSF otorrhea
c) ASOM
d) fistula
Ans: c
11.Commonest cause of deafness in childhood is
a) ASOM
b) CSOM
c) deaf-mutism
d) foreign body
Ans: b
12.Otosclerosis is associated with all except
a) conductive deafness
b) common in males
c) Mostly affects stapes
d) Run in families
Ans: b
13.Common cause of facial palsy is
a) Bell’s palsy
b) Mastoid surgery
c) Guillian Barre syndrome
d) Injury to facial nerve
Ans: a
14.The land mark on the lateral surface of temporal bone which acts as a guide to surgeryto the
antrum is the
a) trauman’s triangle
b) temporal line
c) suprameatal spine of Henle
d) notch of Rivinus
e) None of the above
Ans: c
15.Destruction of right labyrinth causes nystagmus to
a) right side
b) Left side
c) rotatory nystagmus
D) No nystagmus
Ans: b
16.The secretomotor nerve fibres of sphenopalatine ganglion supply the
a) Lacrimal gland
b) Parotid gland
c) submandibular gland
d) sublingual gland
Ans: a
17.In conductive deafness Weber test is lateralized to:
a) deaf ear
b) normal ear
c) Both ears
d) Any of the above
Ans: a
18.Hyposthesia of the posterior aspect of the external auditory canal may be an early sign of
a) Trigeminal neuralgia
b) costens syndrome
c) Lateral sinus thrombosis
d) Multiple sclerosis
e) acoustic neuroma
Ans: e
19.Pulsatile tinnitus in ear is due to
a) Malignant otitis media
b) osteoma
c) mastoid reservoir
d) glomus jugulare tumour
Ans: d
20.Impairment of hearing due to noise starts at
a)1000Hz
b)2000Hz
c)3000Hz
d)4000 Hz
Ans: d
21.Management of otogenic cerebral abscess is
a) radical mastoidectomy
b) of abscess fodrainage llowed by mastoidectomy
c) conservative treatment with antibiotics
d) drainage of abscess only
Ans: b
22.Absolute bone conduction test (ABC) is shortened in
a) conductive deafness
b) perceptive deafness
c) both a&b
d) none of the above
Ans: b
23.All of the following are the features of cholesteatoma except
a) filled with keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
b) Deafness
c) erodes bone
d) lymphatic permeation
Ans: d
24.In majority of the cases with otosclerosis the tympanic membrane is
a) normal
b) flamingo pink
C) blue
d) yellow
Ans: a
25.The syndrome of sensorineural hearing loss together with hereditary nephritis is
a) alports syndrome
b) fabry’s syndrome
C) Nail patella syndrome
d) Edward syndrome
Ans: a
26.Ototoxic drugs are all except
a) Kanamycin
b) streptomycin
c) gentamicin
d) ampicillin
Ans: d
27.A patient hears better in Noise the diagnosis is
a) Hyperacusis
b) Hypoacusis
c) presbycusis
d) paracusis
Ans: d
28.Dryness of eyes is caused by injury to facial nerve at
a) chorda tympani
b) cerebellopontine angle
c) tympanic canal
d) geniculate ganglion
Ans: a
29.The aost mobile part at the tympanic membrane
a) central
b) peripheral
c) both
d) none of the above
Ans: a
30.The commonest site of otogenic brain abscess occurring due to CSOM is
a) frontal lobe
b) parietal lobe
c) temporo petrosal lobe
d) occipital lobe
Ans: c
31.In blast injury most common organ affected
a) eardrum
b) stomach
c) lungs
d) all of the above
Ans: a
32. Condition where a pulsatile tumour is found in external auditory meatus which bleeds to touch
a) cholesteatoma
b) polyp
c) glomus tumour
d) malignancy middle ear
Ans: c
33. Organ of cortt is arranged along the inner edge of
a) Reissners membrane
b) Basilar membrane
c) stria vascularis
d) none of the above
Ans: b
34.Cochlear implant used in
a) sensory neural deafness
b) conductive deafness
c) Mixed
d) None
Ans: a
35.Tone decay test is done to find out
a) Otosclerosis
b) Cochlear lesions
c) Retrocochlear lesions
d) Menier’s disease
Ans: c
36.Which of the following statement regarding eustachian tube dysfunction is wrong?
a) Un Distorted light image on the anterior quadrant of tympanic membrane
b) No movement of the tympanic membrane on Seagul’s method
c) Malleus is easily visible
d) Lusterless tympanic membrane
Ans: a
37.Bell’s palsy not responding to steroid what will be the further line of management?
a) Increase the dose of steroid
b) Vasodilators and ACTH
c) surgical decompression
d) electrical nerve stimulation
Ans: c
38. The facial nerve
a) Is motor to the tensor tympani muscle
b) In the internal auditory canal lies inferior to the cochlear nerve
c) Is the nerve in the internal auditory meatus to the most frequently affected by a neuroma
d) Medial wall of the middle ear
Ans: d
39.Otosclerosis occurs in the
a) Lateral wall of the middle ear
b) Roof of the middle ear
c) Floor of the middle ear
d) Medial wall of the ear
Ans: d
40.Acute suppurative otitis media is treated using
a) erythromycin
b) penicillin
c) streptomycin
d) chloramphenicol
Ans: b
41.Before attempting tympanoplasty operation the surgeon must look for
a) Disruption of ossicular chain
b) no infection in the sinuses
c) the ear has been dry
d) cochlear reserve
Ans: d
42.A patient of CSOM with cholesteatoma present with acute onset of vertigo treatment is
a) Immediate exploration
b) antibiotics steroids
c) Labyrinthine sedatives
d) Labyrinthine sedatives only
Ans: a
43. Monoaural diplacusis is present in a lesion of
a) acoustic nerve
b) pontine glioma
c) cochlea
d) efferent auditory neurons
Ans: c
44.Blue drum is seen in
a) tympanosclerosis
b) secretory otitis media
c) otosclerosis
d) myringitis bullosa
Ans: b
45.Nerve supply of tympanic membrane is
a) auriculo temporal
b) auricular branch of vagus
c) lesser occipital
d) greater occipital
Ans: a
46.Appreciation of sound occurs in
a) organ of corti
b) Basilar membranae m
c) cochlear nuclei
d) transverse temporal gyrus
Ans: c
47.Meniers disease is associated with
a) cochlear deafness
b) conductive deafness
c) retrocochlear deafness
d) mixed
Ans: d
48.Acoustic neuroma commonly affects the cranial nerve
a) 5th
b) 6th ‘
c) 7tb
d) 8th
Ans: d
49.Common cause of eustachian tube disease is due to
a) adenoids
b) sinusitis
c) otitis media
d) pharyngitis
Ans: a
50. A 3year old child presents with fever and earache on examination there is congested tympanic
membranae with slight bulge . the treatment of choice is
a) myringotomy with penicillin
b) myringotomy with grommet
c) only antibiotics
d) wait and watch
Ans: a
You might also like
- EAR MCQdoneDocument71 pagesEAR MCQdoneAbdur Raheem QureshiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology TestDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology TestPao Parel100% (1)
- Ent Bcqs 2Document22 pagesEnt Bcqs 2Ghazi Uddin Ahmed100% (1)
- امتحان ENT دفعة ٣١Document14 pagesامتحان ENT دفعة ٣١محمد عبد القاهر السروري100% (1)
- ENT End-of-Posting Questions (30 Sep'05)Document6 pagesENT End-of-Posting Questions (30 Sep'05)John M. HemsworthNo ratings yet
- MCQ 4 ENTDocument6 pagesMCQ 4 ENTapi-2618676650% (2)
- Otolaryngology Mcqs & SBAs 2nd EditionDocument6 pagesOtolaryngology Mcqs & SBAs 2nd EditionJohn M. Hemsworth100% (1)
- (Ugo Fisch, Thomas Linder) Temporal Bone Dissectio PDFDocument66 pages(Ugo Fisch, Thomas Linder) Temporal Bone Dissectio PDFTiara Audina Darmawan100% (1)
- I Am Sharing '100-mcq-complete-ENT' With YouDocument31 pagesI Am Sharing '100-mcq-complete-ENT' With Youhassan qureshi100% (1)
- Ent Bcqs 3Document18 pagesEnt Bcqs 3Ghazi Uddin Ahmed0% (1)
- ENT Best Answer Select The One Best Answer:-: Omdurman Islamic University Medical Students AssociationDocument22 pagesENT Best Answer Select The One Best Answer:-: Omdurman Islamic University Medical Students AssociationAbd AlsalihiNo ratings yet
- A. It Consists of Squamous EpitheliumDocument7 pagesA. It Consists of Squamous EpitheliumUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Questions ENT 2021Document28 pagesQuestions ENT 2021Ranjan Prasad100% (1)
- ENTDocument2 pagesENTNikita Nanwani0% (1)
- MCQ in Orl CourseDocument46 pagesMCQ in Orl CoursesulnaikNo ratings yet
- ENT MCQsDocument14 pagesENT MCQsAlmushawth Emmo100% (6)
- Wa0000Document16 pagesWa0000hassan qureshi100% (1)
- ENT MCQ (Not Answered)Document75 pagesENT MCQ (Not Answered)mohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- ENT MCQs (Girls 1428-29)Document7 pagesENT MCQs (Girls 1428-29)Sheikha100% (9)
- 426 C1, ENT MCQsDocument10 pages426 C1, ENT MCQsSheikhaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bank: Mcqs by TopicDocument136 pagesMCQ Bank: Mcqs by TopicHadzrie Hamdan100% (1)
- ENT MCQs Eiad NahlaDocument11 pagesENT MCQs Eiad Nahlaadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- ENT Practice MCQs With Key 4th Year MBBSDocument7 pagesENT Practice MCQs With Key 4th Year MBBSPatrick BatemanNo ratings yet
- MCQ ENT. DR NemerDocument7 pagesMCQ ENT. DR Nemeradham bani younesNo ratings yet
- ENT McqsDocument15 pagesENT McqsVitorLópezNo ratings yet
- Second and Third Year Ent McqsDocument6 pagesSecond and Third Year Ent Mcqsadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- A. Paresthesia of The CheckDocument26 pagesA. Paresthesia of The Checkadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- 1-The Eustachian Tube Is Opened by Contraction ofDocument10 pages1-The Eustachian Tube Is Opened by Contraction ofNofouz MaswadaNo ratings yet
- ENT Paper 3Document13 pagesENT Paper 3John M. HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Ent Mcqs 3Document8 pagesEnt Mcqs 3Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- MCQs EntDocument10 pagesMCQs EntMarrium Habib100% (3)
- MCQ ENT 2Document3 pagesMCQ ENT 2api-26186766100% (1)
- EennttDocument13 pagesEennttSuresh Kumar BansalNo ratings yet
- Ent 25 ExamDocument8 pagesEnt 25 ExamAbd Alsalihi100% (1)
- ENT MCQforstudents AnswersDocument30 pagesENT MCQforstudents AnswersOlaNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQDocument2 pagesEnt MCQtariq_siddiqui_11100% (1)
- OtologiDocument13 pagesOtologimr_curiousityNo ratings yet
- Ent-Mcq-C2 426Document7 pagesEnt-Mcq-C2 426Sheikha100% (5)
- 3 RfajDocument81 pages3 RfajSheikhaNo ratings yet
- ENT MCQsDocument13 pagesENT MCQsSheikha100% (2)
- MCQ It Blok 19 2006Document15 pagesMCQ It Blok 19 2006Anonymous XuDFuevOxNo ratings yet
- MCQ EntDocument5 pagesMCQ EntShashi LimbachiyaNo ratings yet
- Otology Ent McqsDocument134 pagesOtology Ent McqsAbouzr Mohammed ElsaidNo ratings yet
- (ENT-OPT-FRS) End-Posting Examination Questions (G5) - 20180208 - 175513Document23 pages(ENT-OPT-FRS) End-Posting Examination Questions (G5) - 20180208 - 175513Steph StephanieNo ratings yet
- 1st Term ENTDocument9 pages1st Term ENThassan qureshi0% (1)
- AllDocument54 pagesAlladham bani younesNo ratings yet
- ENT MCQS (Ear, Pharynx, Tonsils, Deep Neck Infections, Oral Cavity)Document88 pagesENT MCQS (Ear, Pharynx, Tonsils, Deep Neck Infections, Oral Cavity)sidsudp75% (4)
- Ent Mcqs 4Document7 pagesEnt Mcqs 4Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- E.N.T-Otorhinolaryngology Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Then Select The Single Best Answer Part I: Otology/EarDocument3 pagesE.N.T-Otorhinolaryngology Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Then Select The Single Best Answer Part I: Otology/EarJohn M. Hemsworth100% (1)
- Aiims Adr Plexus EntDocument32 pagesAiims Adr Plexus Entkishorechandra75% (4)
- MCQ Final 2014Document19 pagesMCQ Final 2014JohnSon100% (1)
- Ent MCQSDocument18 pagesEnt MCQSJustine Nyangaresi100% (2)
- MCQ Ent 2023-24-1Document37 pagesMCQ Ent 2023-24-1Mani MozhiNo ratings yet
- Ent Exam-1Document19 pagesEnt Exam-1anuchittakattuNo ratings yet
- ENT BCQsDocument19 pagesENT BCQsSajid AliNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQDocument6 pagesEnt MCQapi-26186766100% (8)
- 5th Year Exam Tests Without ImagesDocument31 pages5th Year Exam Tests Without ImagesCristinaNo ratings yet
- OtorhinolaryngologyDocument10 pagesOtorhinolaryngologyRayyanNo ratings yet
- MCQ KhaldounDocument9 pagesMCQ Khaldounadham bani younesNo ratings yet
- Lymph Notes E.N.T MQsDocument65 pagesLymph Notes E.N.T MQsAli QuwarahNo ratings yet
- General MICROBIOLOGYDocument56 pagesGeneral MICROBIOLOGYUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Class: - DR MehnazDocument42 pagesGood Morning Class: - DR MehnazUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial DrugsDocument19 pagesAntimicrobial DrugsUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GrowthDocument20 pagesBacterial GrowthUzair Khan100% (1)
- A. It Consists of Squamous EpitheliumDocument7 pagesA. It Consists of Squamous EpitheliumUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Laryngocele: Images in Clinical MedicineDocument1 pageLaryngocele: Images in Clinical MedicineUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Ent Mcqs 4Document7 pagesEnt Mcqs 4Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Ent Mcqs 3Document8 pagesEnt Mcqs 3Uzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Stimuli & Response (English) : 1.1 Human Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesChapter 1: Stimuli & Response (English) : 1.1 Human Nervous Systemdayana zulkefliNo ratings yet
- Mastoiditis NCP Sensory PerceptionDocument15 pagesMastoiditis NCP Sensory Perception081907475889100% (1)
- Recommended Procedure: TympanometryDocument25 pagesRecommended Procedure: TympanometryNinikNo ratings yet
- Grade - 1 Health ActivitiesDocument82 pagesGrade - 1 Health Activitiesaimee.library.mathematicsNo ratings yet
- English For Medicine Part One ChaptersDocument200 pagesEnglish For Medicine Part One ChaptersГулина ЭгембердиеваNo ratings yet
- Assessment Method Used Normal Findings: Head Head Is Free FromDocument6 pagesAssessment Method Used Normal Findings: Head Head Is Free FromGil PerezNo ratings yet
- 5 SensesDocument5 pages5 SensesRandm SouvenirNo ratings yet
- Light and SoundDocument1 pageLight and SoundlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Final Behav Neuroscience PSYC3600 Spring 2021 - Student'sDocument23 pagesFinal Behav Neuroscience PSYC3600 Spring 2021 - Student'sSandip AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Does Auriculotherapy Have Therapeutic E EctivenessDocument10 pagesDoes Auriculotherapy Have Therapeutic E EctivenessprdpjbNo ratings yet
- Lymph Notes E.N.T MQsDocument65 pagesLymph Notes E.N.T MQsAli QuwarahNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Migration TMDocument4 pagesEpithelial Migration TMHafidzoh NajwatiNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade 4 English Q1 W5Document25 pages2 Grade 4 English Q1 W5markanthony08No ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument4 pagesSpecial SensesGrayson JamesNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument297 pagesIlovepdf MergedHarshith Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 MRNA Pfizer - BioNTech Vaccine Analysis PrintDocument66 pagesCOVID-19 MRNA Pfizer - BioNTech Vaccine Analysis PrintMaldita.esNo ratings yet
- Abpg1103 - Take Home ExaminationDocument8 pagesAbpg1103 - Take Home ExaminationNurul Syahirah Mohamad AliNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument44 pagesFundamentals of Nursingtheglobalnursing100% (2)
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our Senses Subjective QuestionsDocument14 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our Senses Subjective QuestionskenyzNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Mod 3 JournalDocument12 pagesAP Psych Mod 3 Journal5662649No ratings yet
- Med Trans ReviewerDocument1 pageMed Trans ReviewerDenise CerdaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of EarDocument29 pagesEmbryology of Earaishagani04No ratings yet
- Sound and Hearing - Oscar Van DillenDocument5 pagesSound and Hearing - Oscar Van DillenMusicalite MusicaliteNo ratings yet
- Espirio User Manual EN GLISH - Rev.7 (12.05.2020)Document41 pagesEspirio User Manual EN GLISH - Rev.7 (12.05.2020)arielNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions For Students Otorhinolaryngology 5 Year MedicalDocument4 pagesExam Questions For Students Otorhinolaryngology 5 Year Medicallulondon1100% (1)
- Learning Material Topic 7 Eyes and Ears AssessmentDocument4 pagesLearning Material Topic 7 Eyes and Ears AssessmentDevi NurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests For ENTDocument32 pagesDiagnostic Tests For ENTNalafNo ratings yet
- Behind-The-Ear Hearing Aids CP / CPX: Instructions For UseDocument52 pagesBehind-The-Ear Hearing Aids CP / CPX: Instructions For UseArif AliNo ratings yet