Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute Urinary Retention
Uploaded by
Robert Daniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views4 pagesAcute urinary retention is the sudden inability to urinate from the bladder. It is a painful emergency condition that requires immediate treatment, often involving inserting a catheter into the urethra or bladder to drain the urine. Acute urinary retention can be caused by obstructions like an enlarged prostate, infections, neurological issues, medications, spinal problems, or injuries and has higher rates in men over 70 years old. Symptoms include an inability to urinate and pain in the lower abdomen from a full bladder. Emergency treatments involve draining the bladder through catheterization or surgery.
Original Description:
Original Title
Acute urinary retention
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcute urinary retention is the sudden inability to urinate from the bladder. It is a painful emergency condition that requires immediate treatment, often involving inserting a catheter into the urethra or bladder to drain the urine. Acute urinary retention can be caused by obstructions like an enlarged prostate, infections, neurological issues, medications, spinal problems, or injuries and has higher rates in men over 70 years old. Symptoms include an inability to urinate and pain in the lower abdomen from a full bladder. Emergency treatments involve draining the bladder through catheterization or surgery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views4 pagesAcute Urinary Retention
Acute Urinary Retention
Uploaded by
Robert DanielAcute urinary retention is the sudden inability to urinate from the bladder. It is a painful emergency condition that requires immediate treatment, often involving inserting a catheter into the urethra or bladder to drain the urine. Acute urinary retention can be caused by obstructions like an enlarged prostate, infections, neurological issues, medications, spinal problems, or injuries and has higher rates in men over 70 years old. Symptoms include an inability to urinate and pain in the lower abdomen from a full bladder. Emergency treatments involve draining the bladder through catheterization or surgery.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Acute urinary retention
Acute urinary retention is the suddenly installed inability to remove
urine from the bladder. It is a painful condition and requires the
application of emergency treatment, which often involves urethro-
bladder catheterization or cystostomy (suprapubic catheterization).
Acute urinary retention is a condition found in many medical
emergencies, with a higher frequency in men compared to women,
more common in men over the age of 70 years. Acute urinary
retention has also been recognized as a consequence of premature
urethral catheter removal in retropubic radical prostatectomies.
Causes of urinary retention
The causes of urinary retention are numerous and, depending on the
mechanism by which this retention occurs, can be obstructive,
infectious - inflammatory, neurological, drug or other causes.
• Obstructive causes
In men - benign prostatic hyperplasia, urethral meatus stenosis,
phimosis, paraphimosis, prostate cancer;
In women - cystocele, rectocele, uterine prolapse, uterine fibroids,
gynecological malignancies, ovarian cyst;
In both sexes - bladder stones, gastrointestinal or retroperitoneal
malignancies, impact with feces, bladder cancer, ureteral strictures,
the presence of foreign bodies.
• Infections and inflammation
In men - prostate, prostate abscesses, balanitis;
In women - acute vulvovaginitis, vaginal pemphigus, lichen planus
vaginal
In both sexes - biliary disease, genital herpes, varicella-zoster virus
infection, cystitis, peri-ureteral abscesses;
• Medicinal causes
- Anticholinergics - antipsychotics, antidepressants, respiratory
anticholinergics;
- Opioids and anesthetics;
- Alpha-adrenergic agonists;
- Benzodiazepines;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Calcium channel blockers;
- Antihistamines;
- Alcohol.
Neurological causes
- Autonomic or peripheral nerves: neuropathies, polio, pernicious
anemia, tabes, spinal injuries, diabetes, Guillain-Barre syndrome;
- Brain disorders encountered in: multiple sclerosis, cardiovascular
disease, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, hydrocephalus;
- Diseases of the spine: disorders of the intervertebral disc, multiple
sclerosis, spina bifida, transverse myelitis, tumors, ponytail
syndrome, hematoma or intramedullary abscess, trauma to the spine,
spinal stenosis.
• Other causes
In men - penile trauma, fractures, injuries
In women - postpartum complications, dysfunction of the urethral
sphincter.
In the occurrence of acute urinary retention incriminated causes may
be: ureteral or bladder stones that have migrated and cause
obstruction along the path of urine removal from the bladder
(urethra), urinary tract infections, nervous system damage, alcohol
consumption, various allergies, consumption of various drugs
(ipratropium bromide, albuterol, epinephrine), prolonged exposure
to low temperatures, spinal disorders, complications from
anesthesia.
Symptoms encountered in acute urinary retention
In acute urinary retention the patient is unable to remove urine from
the bladder, has discomfort and hypogastric pain (lower abdomen),
presents with a bladder relaxed and firm consistency on palpation -
an aspect called globe bladder hard.
The constant accumulation of urine in the bladder determines its
relaxation, reaching, in certain situations, enormous dimensions.
This relaxation causes constant suprapubic pain, which will not
subside until the urine is removed.
Interventions in acute urinary retention
• stimulating the urine evacuation by applying warm compresses on
the pubic region, opening the valve stimulates the elimination of
urine evacuation;
• bladder evacuation survey (bladder catheterization) - not to be
traumatic and will not suddenly evacuate the contents of the bladder
- danger of bleeding. probe will be fixed = probe "to remain"; and
the patient will be transported to the hospital if the operation was
performed at home, with the thought of the urinary catheter. It also
differentiates between urinary retention and anuria.
• if the survey cannot be performed, an evacuation puncture of the
bladder will be performed - the evacuation will be done slowly, and
after performing the puncture a sterile dressing will be applied.
You might also like
- 2W7 Operators Manual - 0M3UC-2W700 Feb2016 - ENDocument70 pages2W7 Operators Manual - 0M3UC-2W700 Feb2016 - ENRAYMULROONEY100% (1)
- A Case Study On Acute AppendicitisDocument56 pagesA Case Study On Acute AppendicitisIvy Mae Evangelio Vios92% (13)
- Compressor Valves and Unloaders For Reciprocating CompressorsDocument19 pagesCompressor Valves and Unloaders For Reciprocating CompressorsGeorge Dom100% (2)
- A Quantum Explanation of Sheldrakes Morphic Resonance by A GoswamiRupert SheldrakeDocument13 pagesA Quantum Explanation of Sheldrakes Morphic Resonance by A GoswamiRupert SheldrakeDavid Jaramillo KlinkertNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Investment Banking in IndiaDocument3 pagesEvolution of Investment Banking in IndiaChsudarshanDhaveji100% (2)
- Emergencies in UrologyDocument112 pagesEmergencies in UrologySusiyadiNo ratings yet
- Emergencies in UrologyDocument112 pagesEmergencies in UrologyafiwahyuNo ratings yet
- Urinary RetentionDocument28 pagesUrinary RetentionSchoeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Urinary RetentionDocument3 pagesAcute and Chronic Urinary RetentionParyNo ratings yet
- Acute Urine RetentionDocument30 pagesAcute Urine Retentiondilekamunasinghe4No ratings yet
- Symptomatology of GUT DisordersDocument75 pagesSymptomatology of GUT DisordersMaraJoRNNo ratings yet
- Elderly Urinary Tract Disorders FixDocument36 pagesElderly Urinary Tract Disorders FixRyan Adi PutraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Retention 2Document3 pagesUrinary Retention 2Agli AdhityaNo ratings yet
- Hydronephrosis & Vesicoureteral Reflux: Dr. Farhanul Huda Associate Professor Dept. of Surgery Aiims RishikeshDocument33 pagesHydronephrosis & Vesicoureteral Reflux: Dr. Farhanul Huda Associate Professor Dept. of Surgery Aiims Rishikeshanjusb712No ratings yet
- Urologic Emergencies: Hakan Koyuncu MD Associate Professor Yeditepe University Medical Faculty Department of UrologyDocument62 pagesUrologic Emergencies: Hakan Koyuncu MD Associate Professor Yeditepe University Medical Faculty Department of UrologycoassrunNo ratings yet
- Acuteurologicalconditions 130121123140 Phpapp01Document58 pagesAcuteurologicalconditions 130121123140 Phpapp01Dr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- Congenital Urological Conditions - Dr. HawkarDocument38 pagesCongenital Urological Conditions - Dr. HawkarBashar KhalilNo ratings yet
- Pitfall in Management of Neonatal Urogenital Disorder 21 08 15Document24 pagesPitfall in Management of Neonatal Urogenital Disorder 21 08 15Marhama FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Im - Uti - Pgi SJ AgbayaniDocument62 pagesIm - Uti - Pgi SJ AgbayaniShareen Joyce AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Urinary & Renal Deviations: Edited By: Cynthia Bartlau, MSN, RN, PHNDocument60 pagesUrinary & Renal Deviations: Edited By: Cynthia Bartlau, MSN, RN, PHNmolyebeedNo ratings yet
- UTI in PregnancyDocument33 pagesUTI in Pregnancyyusufkiduchu8No ratings yet
- History and Examination of Urologenital SystemDocument29 pagesHistory and Examination of Urologenital SystemPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- UTIs 1Document38 pagesUTIs 1Eduardo Valdez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- GU InfectionsDocument33 pagesGU Infectionsxx_caligurl_93xxNo ratings yet
- Types, Causes, Investigtions (UrinaryIncontinence)Document13 pagesTypes, Causes, Investigtions (UrinaryIncontinence)Ashadeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Urethral StrictureDocument43 pagesUrethral StrictureNadila Ayu Putri50% (2)
- Chapter 95 Complications of Urologic Procedures and DevicesDocument39 pagesChapter 95 Complications of Urologic Procedures and DevicesJohn Vincent Dy OcampoNo ratings yet
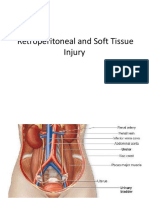
- Retroperitoneal and Soft TissueDocument59 pagesRetroperitoneal and Soft TissueLucas Phi100% (1)
- Urological EmergencyDocument83 pagesUrological EmergencyAlfred LiNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Renal DisordersDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Renal DisordersokaciaNo ratings yet
- Medical SurgicalDocument22 pagesMedical SurgicalGulshad AfridiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument56 pagesUrinary Tract ObstructionMicky FantaNo ratings yet
- Subiecte Studenti 1 1222Document16 pagesSubiecte Studenti 1 1222Andrei GilaNo ratings yet
- Acute ScrotumDocument26 pagesAcute ScrotumkimNo ratings yet
- Renal Notes Step 2ckDocument34 pagesRenal Notes Step 2cksamreen100% (1)
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument50 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Acute Urinary ObstructionDocument34 pagesAcute Urinary ObstructionHafizur RashidNo ratings yet
- History/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyDocument26 pagesHistory/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyDr. NasrumminallahNo ratings yet
- Repro CorrDocument67 pagesRepro CorrsrhmdNo ratings yet
- E. UrinaryDocument16 pagesE. UrinaryGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- EM2 - K12 - Renal and Genitourinary System EmergenciesDocument28 pagesEM2 - K12 - Renal and Genitourinary System EmergenciesrezkadehaNo ratings yet
- UZAIRDocument24 pagesUZAIRUzair AhmadNo ratings yet
- Urinary IncontinenceDocument18 pagesUrinary IncontinenceShatha QudahNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: Tbilisi Referral Hospital, Tbilisi, Georgia Nephrologist Nino MaglakelidzeDocument50 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: Tbilisi Referral Hospital, Tbilisi, Georgia Nephrologist Nino MaglakelidzePayal bhagatNo ratings yet
- PyelonephritisDocument10 pagesPyelonephritisalina abu rumi100% (1)
- Common Symptoms of Kidney Diseases-1Document55 pagesCommon Symptoms of Kidney Diseases-1maruf47774No ratings yet
- 12 Urinary EliminationDocument21 pages12 Urinary EliminationDarla SaulerNo ratings yet
- Testicular and Scrotal DisordersDocument127 pagesTesticular and Scrotal DisordersJean Fatima100% (1)
- Genitourinary Emergency: Prof. Dr. Mostafa Sakr Genitourinary SurgeryDocument83 pagesGenitourinary Emergency: Prof. Dr. Mostafa Sakr Genitourinary SurgeryKeserovic AdmirNo ratings yet
- History/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyDocument25 pagesHistory/Physical and Symptoms and Signs of Different Diseases in UrologyPatrascu CristiNo ratings yet
- Other No Trauma Urological Emergencies GinaDocument53 pagesOther No Trauma Urological Emergencies GinaRwabugili ChrisNo ratings yet
- 4 TraumaDocument52 pages4 TraumaTom perryNo ratings yet
- Urinary IncontinenceDocument3 pagesUrinary Incontinenceខ្ទឹម ក្រហមNo ratings yet
- Back To Medical School: - Anorectal DisordersDocument54 pagesBack To Medical School: - Anorectal DisordersSemSemNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary DisordersDocument134 pagesRenal and Urinary Disordersmirmodepon05100% (1)
- Urology Zusammenfassung 2020 v2Document82 pagesUrology Zusammenfassung 2020 v2Aastha SethNo ratings yet
- Congenital Abnormality copyDocument54 pagesCongenital Abnormality copyOmar KhashashnehNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017Document51 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: DR Badriya Al-Mahrouqi 12/11/2017NinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Dysuria 1Document25 pagesPresentation On Dysuria 1ankur acharyaNo ratings yet
- Repro Female Repro DisordersDocument11 pagesRepro Female Repro Disordersloli popNo ratings yet
- Urinary EliminationDocument71 pagesUrinary EliminationFrances LiqueNo ratings yet
- Female Urinary Retention - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument26 pagesFemale Urinary Retention - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfjqgjwgnnwkNo ratings yet
- IVPDocument48 pagesIVPDini Lintangsari100% (1)
- Microbial Diseases of The Urinary System: Yemane Weldu (MSC., Assistant Professor)Document65 pagesMicrobial Diseases of The Urinary System: Yemane Weldu (MSC., Assistant Professor)Lidiya TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Topical Revision 2 AnswersDocument8 pagesTopical Revision 2 AnswersmichelleNo ratings yet
- Power Apps Deployment Using ADODocument25 pagesPower Apps Deployment Using ADOSameer Wadkar32No ratings yet
- Script For Tablespace Utilization Alert With UTL MAIL Package - Smart Way of TechnologyDocument4 pagesScript For Tablespace Utilization Alert With UTL MAIL Package - Smart Way of TechnologyShivkumar KurnawalNo ratings yet
- Wincor TP06 Printer TicketDocument1 pageWincor TP06 Printer TicketMacTebo EugeneNo ratings yet
- Fueling System of SI and CI Engines: by Zewdie Alemayehu (Automotive Eng.)Document67 pagesFueling System of SI and CI Engines: by Zewdie Alemayehu (Automotive Eng.)ahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Ls STD SLB FPCB A Ro s10 218Document1 pageLs STD SLB FPCB A Ro s10 218Yazer ArafathNo ratings yet
- Bien Prononcer L'anglais: Corrigés Et ScriptsDocument43 pagesBien Prononcer L'anglais: Corrigés Et ScriptsThierry HarmannNo ratings yet
- Circular Functions PDFDocument2 pagesCircular Functions PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Oana Adriana GICADocument42 pagesOana Adriana GICAPhilippe BrunoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Analyer - ConfigDocument23 pagesPortfolio Analyer - Configvikaditya100% (1)
- Sampling PDFDocument45 pagesSampling PDFYousuf AdamNo ratings yet
- Trillion DollarsDocument95 pagesTrillion DollarsVyacheslav GrzhibovskiyNo ratings yet
- ZOOMLION 40T QY40V Tech Specs PDFDocument30 pagesZOOMLION 40T QY40V Tech Specs PDFvikrantathavaleNo ratings yet
- Memorandum Plus 05172024 BOCDocument2 pagesMemorandum Plus 05172024 BOCCath DiversonNo ratings yet
- Daihatsu Gensets Diesel EngineDocument20 pagesDaihatsu Gensets Diesel Enginexyz1002100% (1)
- TLE ICT 10 - Quizalize Pre TestDocument8 pagesTLE ICT 10 - Quizalize Pre TestGioSanBuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Edited - Public EnterpriseDocument9 pagesChapter Three Edited - Public EnterpriseMarah Moses BallaNo ratings yet
- ICOM-CC 2017 Copenhagen 507Document11 pagesICOM-CC 2017 Copenhagen 507Cristi CostinNo ratings yet
- Us Nop Organic Compliant Materials 20171121Document3 pagesUs Nop Organic Compliant Materials 20171121LayfloNo ratings yet
- C37 012-Ieee PDFDocument54 pagesC37 012-Ieee PDFanupama jakka100% (1)
- Creating Delivering: MagnificenceDocument51 pagesCreating Delivering: MagnificencesharmarahulhemantNo ratings yet
- 2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyDocument10 pages2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyNick PopeNo ratings yet
- Python CodeDocument7 pagesPython CodeAmogh VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and MultipathDocument88 pagesMobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and MultipathKhyati ZalawadiaNo ratings yet
- Info 15614 - 2017Document34 pagesInfo 15614 - 2017uğur özdemirNo ratings yet