Professional Documents
Culture Documents
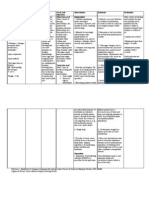
Student Name: Date: Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis (Use PES/PE Format)
Student Name: Date: Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis (Use PES/PE Format)
Uploaded by
Darmatius NambaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Student Name: Date: Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis (Use PES/PE Format)
Student Name: Date: Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis (Use PES/PE Format)
Uploaded by
Darmatius NambaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan Form
Student Name: Date:
Patient Identifier: Patient Medical Diagnosis:
Nursing Diagnosis (use PES/PE format):
Assessment Data Goals & Outcome Nursing Interventions Rationale Outcome Evaluation &
(Include at least three-five (Two statements are required (List at least three nursing or (Provide reason why Replanning
subjective and/or objective for each nursing diagnosis. collaborative interventions with intervention is (Was goal met? How would
pieces of data that lead to the Must be Patient and/or family rationale for each goal & indicated/therapeutic; provide you revise the plan of care
nursing diagnosis) focused; measurable; time- outcome.) references.) according to the patient’s
specific; and reasonable.) response to current plan ?)
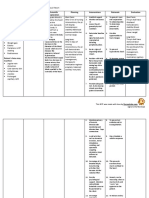
Insufficient fluid volume The patient will maintain Obtain samples according Urine and serum tests can Patient lab result are
associated with nausea, serum sodium, potassium, to instructions to test for provide information on within normal limit
vomiting, and diarrhea, calcium, phosphorus, abnormal potassium levels extracellular potassium
manifested by decreased magnesium and / or pH (for example, potassium levels. There is no practical
urine output, increased within the normal range in serum and urine). way to measure
urine concentration, fever, intracellular K
weakness, decreased
skin/tongue swelling, dry Potassium supplement 2. Low Potassium Levels
mucous membranes, (PO, NG or IV) according Dangerous, Patient May
increased HR, and to policy management Need Supplements.
decreased BP regulations.
Monitor the neurologic and 3. Potassium is an
neuromuscular important electrolyte for
manifestations of
hypokalemia (eg, muscle
bone and smooth muscle Outcome #2
activity
weakness, lethargy,
changes in level of
consciousness).
The patient must have a
normal blood volume, a
urine output greater than 1. Monitor the cardiac 1. Many heart rhythm
30 ml/hour, and a normal manifestations of disorders can be caused
skin elasticity hypokalemia (hypotension, by hypokalemia.
tachycardia, weak pulse, Monitoring heart function
irregular rhythm). during hypokalemia is
essential.
2. Monitor cardiac
manifestations of
hypernatremia (eg, 2. The heart responds to
orthostatic hypotension and fluid loss by increasing its
tachycardia). heart rate to compensate
for the increase in cardiac
output. Low fluid volume
can cause blood pressure
to drop.
3. Monitor the nervous 3. Due to the low volume
system and neuromuscular of body fluids,
manifestations of hypernatremia creates
hypernatremia (for hypertonic vascular
example, lethargy, spaces, causing water to
seizures, hyperreflexia, and move from cells, including
irritability). brain cells. This is the
cause of neurological
symptoms.
The customer will maintain
the fluid volume at a Monitor CVP and vital
Deficient Fluid Volume functional level through signs. Pay attention to
Tachycardia is associated
elevated body temperature
r/t Active fluid loss- stable vital signs, good skin
and orthostatic with varying degrees of
filling, good capillary hypotension, depending on
burns, manifested by hypotension.
filling, moist mucous the degree of fluid
Tachycardia, membranes and sufficient deficiency. CVP
Tachypnea, Weak urine of normal specific measurement helps
gravity. determine the degree of
pulses.
fluid deficiency and
response to alternative
therapies. Fever increases
metabolism and
exacerbates fluid loss
Investigate reports of
sudden or severe chest Increased blood levels
pain, cyanosis, irritability, and platelet aggregation
increased anxiety, and can cause a systemic
difficulty breathing. embolism.
Monitor lab studies, as
ordered. Depending on the degree of
fluid loss, there may be
different electrolyte and
metabolic imbalances that
need to be corrected.
The client will demonstrate
appropriate monitoring
and correction of defects. Assess the client's ability
to manage their own Factors that affect
moisture. customers’ ability to
replenish fluids through
the mouth include
impaired swallowing and
nausea reflexes, anorexia,
oral discomfort, nausea,
and changes in mentality.
Monitor urine output.
Measure or estimate fluid Liquid replacement needs
loss from all sources, such are based on correcting
as sweating, wound current deficiencies and
drainage, and gastric loss. ongoing losses. Decreased
urine output may indicate
insufficient blood volume,
insufficient renal perfusion,
or possible polyuria,
requiring more aggressive
fluid replacement.
Determine the customer's
beverage preferences and Relieves thirst and dry
develop a 24-hour fluid mucosa discomfort and
intake program. Encourage increases parenteral
foods high in liquid replacement.
content.
Deficient Fluid Volume
r/t acute renal failure,
manifested by
Confusion,
restlessness, Dark
concentrated urine,
Decreased urine
volume.
You might also like
- Nixon Nikhil 00761635 Tciq ProjectDocument17 pagesNixon Nikhil 00761635 Tciq ProjectNikhil Nixon100% (4)
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPnj_pink08179456% (9)
- Bender Gestalt Visual Motor TestDocument41 pagesBender Gestalt Visual Motor TestJennifer CaussadeNo ratings yet
- Perception and CoordinationDocument21 pagesPerception and Coordinationsimouny100% (28)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planmanu_gutierrez0891% (11)
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDocument25 pagesNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- NCP For: Hy Pertensio NDocument11 pagesNCP For: Hy Pertensio NFatimah AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Dysfunction and Hypotension: Christopher J. MathiasDocument28 pagesAutonomic Dysfunction and Hypotension: Christopher J. MathiaswaltercarvalhoNo ratings yet
- NCM 106: Self Directed Learning Activity Name and Section: John Michael O. Villanueva BSN 2 ADocument4 pagesNCM 106: Self Directed Learning Activity Name and Section: John Michael O. Villanueva BSN 2 AKaye PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Objective DataDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Planning Rational Objective DataMoonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- ID Pengetahuan Remaja Putri Tentang Cara MeDocument3 pagesID Pengetahuan Remaja Putri Tentang Cara MeAyu Wita DewiNo ratings yet
- KLP3 - NCP For Hypertension - CompressedDocument13 pagesKLP3 - NCP For Hypertension - CompressedFatimah AzzahraNo ratings yet
- 2010 Emergency Nursing Cases Updates - CDH - 10-06-10Document2 pages2010 Emergency Nursing Cases Updates - CDH - 10-06-10shalomNo ratings yet
- NCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountDocument6 pagesNCP PlanningDecreased in Cardiac Output Related To Low Hemoglobin and Hematocrit CountMabelle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Regulation of CVSDocument27 pagesRegulation of CVSvirajmore6222No ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Nursing Management: Patients With Coronary Vascular DisordersDocument13 pagesChapter 14: Nursing Management: Patients With Coronary Vascular DisorderskingNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders and The Neurologic ManifestationsDocument49 pagesEndocrine Disorders and The Neurologic ManifestationsRahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- Nanda NCP BasedDocument14 pagesNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Preeclampsia NCPDocument4 pagesPreeclampsia NCPKhan Hans100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemSheinny Rodriguez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing DiagnosisChe SalveronNo ratings yet
- Approach To ShockDocument28 pagesApproach To ShockSyasya ZulkiffliNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis&Manajemen ShockDocument8 pagesDiagnosis&Manajemen ShockHJKIMNo ratings yet
- NCP KateDor NewDocument6 pagesNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- NCP CPDocument7 pagesNCP CPAllyzah Faith BernalesNo ratings yet
- Mombay 3a Neuman Ncm112 Module 2Document7 pagesMombay 3a Neuman Ncm112 Module 2Xena MombayNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease NCPDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Disease NCPsprrwgoldenNo ratings yet
- NS2881 Renal Revision Worksheet 2022Document10 pagesNS2881 Renal Revision Worksheet 2022Louise GeislerNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisRiska RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Increased ICPDocument22 pagesIncreased ICPCHARLOTTE DU PREEZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HypovolemiaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan HypovolemiaGusmila SariNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia in The Neurologically Ill Patient: A ReviewDocument9 pagesHyponatremia in The Neurologically Ill Patient: A ReviewSerque777No ratings yet
- Neurological Assessment - Romeo RiveraDocument9 pagesNeurological Assessment - Romeo Riveraromeo riveraNo ratings yet
- 11 - ShockDocument30 pages11 - ShockGalassa AbdiNo ratings yet
- Sample: Duquesne University School of Nursing Care Map TemplateDocument6 pagesSample: Duquesne University School of Nursing Care Map TemplateDevin Nikole BlattnerNo ratings yet
- Jade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SDocument5 pagesJade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SJhade Relleta100% (1)
- NCP Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decrease Cardiac OutputAnonymous 2hJKVrNo ratings yet
- Shock: Clinical ManifestationsDocument3 pagesShock: Clinical ManifestationsJean ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Thyroid HormonesDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Thyroid HormonesShenaNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPingridNo ratings yet
- Ijccm 23 s129Document7 pagesIjccm 23 s129Sonu AntonyNo ratings yet
- F.SARAWI NCP SIC Drug StudyDocument30 pagesF.SARAWI NCP SIC Drug StudyaldwinNo ratings yet
- Polycystic NCP1Document4 pagesPolycystic NCP1Mary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- Hypertension TanDocument20 pagesHypertension TanBEA RADANo ratings yet
- IGCSE CoordSci CoordinationAndResponse L3Document28 pagesIGCSE CoordSci CoordinationAndResponse L3Luu ReannaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On HypertensionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan On Hypertensionbhavana100% (1)
- Diagnosis NOC NIC Liquid ManagementDocument3 pagesDiagnosis NOC NIC Liquid ManagementArio SugandaNo ratings yet
- Ario Suganda Epp Fix 2Document3 pagesArio Suganda Epp Fix 2Ario SugandaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiasteffiNo ratings yet
- Kez NCPDocument12 pagesKez NCPShizuka Marycris AmaneNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPDocument6 pagesVehicular Accident (VA) Manifesting Hypovolemic Shock NCPCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsNo ratings yet
- LIVERDocument106 pagesLIVERCurt Leye RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Corticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesCorticospinal Tract Practice QuestionsAlexaNo ratings yet
- UB HSPED Differential Diagnosis of Lower Back PainDocument62 pagesUB HSPED Differential Diagnosis of Lower Back PainJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Document1 pageNutritional Status-Consolidated-2021-2022Laarni Kiamco Ortiz EpanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Suraya's PPT - IPC COVID MX in Private Healthcare PDFDocument40 pagesDr. Suraya's PPT - IPC COVID MX in Private Healthcare PDFFrostz WongNo ratings yet
- Uveitic Glaucoma Management With Recurrent Uveitis EpisodeDocument6 pagesUveitic Glaucoma Management With Recurrent Uveitis EpisodeLina Shabrina QoribNo ratings yet
- Goa University: N.S.S. Work Record CardDocument1 pageGoa University: N.S.S. Work Record Cardraj naikNo ratings yet
- Suvarna H PatilDocument7 pagesSuvarna H Patildaniel_siitompulNo ratings yet
- AAI Pathology of Hematologic MalignanciesDocument2 pagesAAI Pathology of Hematologic MalignanciesHappy Singh100% (1)
- Advances in Intracranial HemorrhageDocument15 pagesAdvances in Intracranial HemorrhageJorge GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Practical - Larval Stages of Taenia Solium - DR Roopa SamalDocument6 pagesPractical - Larval Stages of Taenia Solium - DR Roopa SamalAmishee SoodNo ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument7 pagesWritten ReportChello Ann AsuncionNo ratings yet
- SF South Africa AtlasDocument2 pagesSF South Africa AtlasTrap houseNo ratings yet
- Bone Management in Dental Implantology - Andi Setiawan Budihardja, Thomas Mücke - (2019)Document195 pagesBone Management in Dental Implantology - Andi Setiawan Budihardja, Thomas Mücke - (2019)Neelesh S Jadhav100% (3)
- NMPPDocument19 pagesNMPPaquib89No ratings yet
- OrthorexiaDocument2 pagesOrthorexiaiantracys100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Health, Safety & Environment (HSE)Document23 pagesLecture 1 Health, Safety & Environment (HSE)A to z type videosNo ratings yet
- Classification ParagraphDocument9 pagesClassification Paragraphanwar essahebNo ratings yet
- Stoudt Woman Healers Medieval Germn WomanDocument14 pagesStoudt Woman Healers Medieval Germn WomanAdolfo BaqueiroNo ratings yet
- Adolescents Reproductive Health McqsDocument4 pagesAdolescents Reproductive Health Mcqsrania noorNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Models of Monitoring and Evaluation - Types of Evaluation Process, Outcome and ImpactDocument54 pagesTopic 3 - Models of Monitoring and Evaluation - Types of Evaluation Process, Outcome and Impactmohammadnazar saqi100% (1)
- Problem Statement 5Document17 pagesProblem Statement 5priyankaNo ratings yet
- Kasrp KuisionerDocument12 pagesKasrp KuisionerteguhNo ratings yet
- NURS 406 Concept Map HyperthyroidismDocument1 pageNURS 406 Concept Map HyperthyroidismshyannNo ratings yet
- Funding Vaccines For Emerging Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesFunding Vaccines For Emerging Infectious Diseasesfadfdafade uohdajufadNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis Serologic Testing AlgorithmDocument1 pageToxoplasmosis Serologic Testing AlgorithmHanny Prasetiana YuriantiNo ratings yet
- FQ, Probioticos - CochraneDocument80 pagesFQ, Probioticos - CochraneNoemi MartínezNo ratings yet
- Fields Branches Psychology Definition PDFDocument7 pagesFields Branches Psychology Definition PDFBilal Baig BurlasNo ratings yet