Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIE L A B Color Scale: Background
CIE L A B Color Scale: Background
Uploaded by
rona trisnaningtyasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CIE L A B Color Scale: Background
CIE L A B Color Scale: Background
Uploaded by
rona trisnaningtyasCopyright:
Available Formats
Insight on Color Vol. 8, No.
CIE L*a*b* Color Scale
Background
In 1976, the CIE recommended the CIE L*a*b*, or CIELAB, color scale for use. CIE Publication 15.2
(1986), Section 4.2, contains details on this color scale. It was intended to provide a standard,
approximately uniform color scale which could be used by everyone so that color values could be easily
compared.
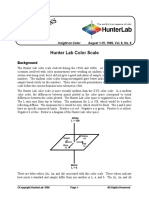
The CIELAB color scale is an approximately uniform color scale. In a uniform color scale, the
differences between points plotted in the color space correspond to visual differences between the colors
plotted. The CIELAB color space is organized in a cube form. The L* axis runs from top to bottom.
The maximum for L* is 100, which represents a perfect reflecting diffuser. The minimum for L* is
zero, which represents black. The a* and b* axes have no specific numerical limits. Positive a* is red.
Negative a* is green. Positive b* is yellow. Negative b* is blue. Below is a diagram representing the
CIELAB color space.
There are delta values associated with this color scale. ∆L*, ∆a*, and ∆b* indicate how much a standard
and sample differ from one another in L*, a*, and b*. These delta values are often used for quality
Page 1 ©Copyright 2008
Applications Note Vol. 8, No. 7
control or formula adjustment. Tolerances may be set for the delta values. Delta values that are out of
the tolerances indicate that there is too much difference between the standard and the sample. The type
of correction needed may be determined by which delta value is out of tolerance. For example, if ∆a* is
out of tolerance, the redness/greenness needs to be adjusted. Whether the sample is redder or greener
than the standard is indicated by the sign of the delta value. For example, if ∆a* is positive, the sample
is redder than the standard.
The total color difference, ∆E*, may also be calculated. The ∆E* is a single value which takes into
account the differences between the L*, a*, and b* of the sample and standard. It does not indicate
which parameter(s) (L*, a*, and/or b*) are out of tolerances if ∆E* is out of tolerance. It may also be
misleading in some cases where ∆L*, ∆a*, or ∆b* is out of tolerance, but ∆E* is still within tolerance.
In addition, there are two other delta values that are related to this scale, ∆C* and ∆H*. The ∆C* is the
difference in chroma between the sample and standard as described in a polar coordinate system. The
∆H* is the difference in hue angle between the sample and standard as described in a polar coordinate
system.
The CIELAB color scale may be used on any object whose color may be measured. It is used
extensively in many industries. As was intended, it provides a standard scale for comparison of color
values.
Conditions for Measurement
Instrumental: Any HunterLab color measurement instrument
Illuminant: Any
Standard Observer Function: 2 or 10 degree
Transmittance and/or Reflectance: Either.
Formulas
If X/Xn, Y/Yn, and Z/Zn are all greater than 0.008856, then
L * = 116 3 Y / Yn - 16
a * = 500 ( 3 X/X n - 3 Y/Yn )
b * = 200 ( 3 Y/Yn - 3 Z/Z n )
If any of X/Xn, Y/Yn, or Z/Zn is equal to or less than 0.008856, then
L * = 903.3 (Y/Yn )
a * = 500 [f (X/X n ) - f (Y/Yn )]
b * = 200 [f (Y/Yn ) - f (Z/Z n )]
where
X, Y, and Z are the CIE Tristimulus Values
Page 2 ©Copyright 2008
Applications Note Vol. 8, No. 7
Xn, Yn, and Zn are the tristimulus values for the illuminant
Yn is 100.00
Xn and Zn are listed in the tables below.
CIE 2 Degree Standard Observer
Illuminant Xn Zn
A 109.83 35.55
C 98.04 118.11
D65 95.02 108.82
F2 98.09 67.53
TL 4 101.40 65.90
UL 3000 107.99 33.91
D50 96.38 82.45
D60 95.23 100.86
D75 94.96 122.53
CIE 10 Degree Standard Observer
Illuminant Xn Zn
A 111.16 35.19
C 97.30 116.14
D65 94.83 107.38
F2 102.13 69.37
TL 4 103.82 66.90
UL 3000 111.12 35.21
D50 96.72 81.45
D60 95.21 99.60
D75 94.45 120.70
f (X/X n ) = 3 X/X n when X/Xn > 0.008856
⎛ X ⎞ 16
f (X/X n ) = 7.87 ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ + when X/Xn < 0.008856
⎝ Xn ⎠ 116
f (Y/Yn ) = 3 Y/Yn when Y/Yn > 0.008856
⎛ Y ⎞ 16
f (Y/Yn ) = 7.87 ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ + when Y/Yn < 0.008856
⎝ Yn ⎠ 116
f (Z/Z n ) = 3 Z/Z n when Z/Zn > 0.008856
⎛ Z ⎞ 16
f (Z/Z n ) = 7.87 ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ + when Z/Zn < 0.008856
⎝ Zn ⎠ 116
∆L* = L*sample - L*standard + ∆L* means sample is lighter than standard
- ∆L* means sample is darker than standard
Page 3 ©Copyright 2008
Applications Note Vol. 8, No. 7
∆a* = a*sample - a*standard + ∆a* means sample is redder than standard
- ∆a* means sample is greener than standard
∆b* = b*sample - b*standard + ∆b* means sample is yellower than standard
- ∆b* means sample is bluer than standard
∆E * = ∆L *2 + ∆a *2 + ∆b *2
∆C* = C*sample - C*standard
where
C* = a *2 + b *2 (this is called metric chroma)
∆H * = ∆E *2 - ∆L *2 - ∆C *2
Typical Applications
This color scale may be used for measurement of the color of any object whose color can be measured.
For Additional Information Contact:
Technical Services Department
Hunter Associates Laboratory, Inc.
11491 Sunset Hills Road
Reston, Virginia 20190
Telephone: 703-471-6870
FAX: 703-471-4237
www.hunterlab.com
06/08
Page 4 ©Copyright 2008
You might also like
- Coulombs Law Online LabDocument9 pagesCoulombs Law Online LabJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 03-Submission FormDocument6 pagesExperiment No 03-Submission FormArjita AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- CIE LCH Color ScaleDocument4 pagesCIE LCH Color ScaleFaisal RehmanNo ratings yet
- Hunter L A B PDFDocument4 pagesHunter L A B PDFSimqrNo ratings yet
- Hunter Lab PDFDocument4 pagesHunter Lab PDFShyam Sundar SahooNo ratings yet
- Measurement Values: Absolute Color Scales (Available When Display Type Is Absolute)Document26 pagesMeasurement Values: Absolute Color Scales (Available When Display Type Is Absolute)rafael_dvgNo ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument13 pagesActivitiesChikun BarikNo ratings yet
- Analisis Elastico e InelasticoDocument41 pagesAnalisis Elastico e InelasticoMario RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 To Study The Measuring Method of Carbon ResistorDocument3 pagesExperiment No 1 To Study The Measuring Method of Carbon ResistorAliNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition Jaeger Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesMicroelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition Jaeger Solutions Manuala851945412No ratings yet
- Line Sizing Calculation 1Document9 pagesLine Sizing Calculation 1SAMUEL UDOHNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor EngineeringDocument12 pagesChemical Reactor EngineeringJavier R- Colina M.No ratings yet
- Opaque or Transparent Coloured Products Calculations of Colorimetric Variations (Cie Lab 1976 System)Document8 pagesOpaque or Transparent Coloured Products Calculations of Colorimetric Variations (Cie Lab 1976 System)Reza AbdolahiNo ratings yet
- Yellowness IndexDocument2 pagesYellowness IndexT AaaNo ratings yet
- Cardines TransDocument6 pagesCardines TransJOHN CARLO CARDINESNo ratings yet
- A) Algorithm Using by Polymath To Solve Part (A) : Homework #9 CHE 354-001 Fall 2020 1Document10 pagesA) Algorithm Using by Polymath To Solve Part (A) : Homework #9 CHE 354-001 Fall 2020 1Daniel Andres Canro CalderónNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument112 pagesElectronicsicti_ku_afNo ratings yet
- Busa5325 SLRtestsDocument10 pagesBusa5325 SLRtestsAnonymous UpDFk5iANo ratings yet
- Understanding Electronics ComponentsDocument101 pagesUnderstanding Electronics Componentsnamemamun50% (4)
- Reinforced Concrete Design For Slab: S - 1 One-Way SlabDocument10 pagesReinforced Concrete Design For Slab: S - 1 One-Way SlabJheo TorresNo ratings yet
- C/a/d Expressing Dollars and Employees in Thousands, The Weighted Mean Expenditure Per Employee IsDocument22 pagesC/a/d Expressing Dollars and Employees in Thousands, The Weighted Mean Expenditure Per Employee Iskdk4916No ratings yet
- Design of Columns2 PDFDocument3 pagesDesign of Columns2 PDFPamela Joanne Falo AndradeNo ratings yet
- Eco No Metrics Assignment 3Document6 pagesEco No Metrics Assignment 3Arpit_Lal_1267No ratings yet
- Barker Microfarads (Radial Thru-Hole) 105RB SeriesDocument6 pagesBarker Microfarads (Radial Thru-Hole) 105RB Seriesester853No ratings yet
- Hunter L-A-BDocument4 pagesHunter L-A-BAsphystraszaNo ratings yet
- DJJ20053 Engineering Laboratory 1 (Electrical Technology) : Experiment 1Document4 pagesDJJ20053 Engineering Laboratory 1 (Electrical Technology) : Experiment 1roslelawati75No ratings yet
- Instant Download PDF Mechanics of Fluids SI Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual Full ChapterDocument70 pagesInstant Download PDF Mechanics of Fluids SI Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual Full Chapterovezowholli6100% (6)
- Pg. 1 DPT of Ece, LbrceDocument21 pagesPg. 1 DPT of Ece, LbrceLenowahira DillemanowaryNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids SI Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument70 pagesMechanics of Fluids SI Edition 5th Edition Potter Solutions Manual instant download all chapterakdevebouadi66100% (5)
- Design of Two Way Slab (With Beams) by DDMDocument23 pagesDesign of Two Way Slab (With Beams) by DDMNafees Imitaz94% (17)
- Ch5 Summary and Exercises Student v3Document41 pagesCh5 Summary and Exercises Student v3Ahmet AydemirNo ratings yet
- Resistor, Capacitor and Inductor: Preferred E12 Values ResistorsDocument3 pagesResistor, Capacitor and Inductor: Preferred E12 Values ResistorsSaroj PurkaitNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Microelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition by JaegerDocument15 pagesSolutions Manual For Microelectronic Circuit Design 5th Edition by JaegerDamnNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On Friction LossesDocument9 pagesLab Report On Friction LossesRicheal OwusuNo ratings yet
- Barker Microfarads (Radial Thru-Hole) 105RG SeriesDocument8 pagesBarker Microfarads (Radial Thru-Hole) 105RG Seriesester853No ratings yet
- 20MBP208Document5 pages20MBP208Nandhini ChandruNo ratings yet
- Resistance Temperature DevicesDocument4 pagesResistance Temperature DevicesMelMaeNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Colour Coding Scheme WaleedDocument5 pagesPhysics Lab Colour Coding Scheme Waleedmehran asimNo ratings yet
- ResiDocument4 pagesResiksjanarthanan_sriNo ratings yet
- Task - 1 - Teoría - Electromagnética - Y - Ondas - Anderson - Julian - Gomez - Velasco1203058A - 1701Document7 pagesTask - 1 - Teoría - Electromagnética - Y - Ondas - Anderson - Julian - Gomez - Velasco1203058A - 1701anderson julian gomez velascoNo ratings yet
- Dielectric ConstantDocument4 pagesDielectric Constantupadhye21No ratings yet
- 2994 - Resistor Colour CodeDocument3 pages2994 - Resistor Colour CodeIruoghene HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - SolutionDocument10 pagesAssignment 2 - SolutionDilum VRNo ratings yet
- Bus Duct-DesignDocument4 pagesBus Duct-Designjaktoms100% (1)
- Worksheet 5 - Compression Member-1Document4 pagesWorksheet 5 - Compression Member-1alwabantsepe529No ratings yet
- Purchased Equipment CostDocument9 pagesPurchased Equipment Costkhawaja danialNo ratings yet
- Chemistry LabDocument6 pagesChemistry LabOmar Khan100% (2)
- Cassette and Ducted Catalogue-Frikool New Modif 2type MedDocument13 pagesCassette and Ducted Catalogue-Frikool New Modif 2type Medanyone can do thisNo ratings yet
- Truss Analysis and DesignDocument14 pagesTruss Analysis and Designraymund baylonNo ratings yet
- Jungreg CDocument7 pagesJungreg CStephen Lloyd GeronaNo ratings yet
- Activity Questions: (Write With Your Own Words)Document9 pagesActivity Questions: (Write With Your Own Words)oswaldo perciaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT No 2Document2 pagesEXPERIMENT No 2Mahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- TyDocument102 pagesTyJay Abainza0% (1)
- Polynomial Curve Fitting - MATLAB & Simulink PDFDocument12 pagesPolynomial Curve Fitting - MATLAB & Simulink PDFAJR365No ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Module 2Document161 pagesDifferential Calculus Module 2sagnikNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE BA201 - Engineering Mathematics DBM1013 PoliteknikDocument5 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE BA201 - Engineering Mathematics DBM1013 PoliteknikFajrul Islam RamdhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter SixDocument30 pagesChapter SixHASEN SEIDNo ratings yet
- UWE Bristol: Lecture 4: Second Order Time Response and The Block Diagram ApproachDocument26 pagesUWE Bristol: Lecture 4: Second Order Time Response and The Block Diagram ApproachYahya NaeemNo ratings yet
- 5.6 Simplifying RadicalsDocument34 pages5.6 Simplifying RadicalsAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Realanal 73 83Document11 pagesRealanal 73 83KowsalyaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Mathematics CompendiumDocument16 pagesClass 10 Mathematics CompendiumApex Institute100% (1)
- Harris-A Combined Corner and Edge DetectorDocument6 pagesHarris-A Combined Corner and Edge DetectorAfortunatovNo ratings yet
- School in DelhiDocument56 pagesSchool in Delhiikrark040No ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 9781605253084 - ch05 (Compatibility Mode)Document34 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - 9781605253084 - ch05 (Compatibility Mode)Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Lorentz Transformation For Frames in Standard ConfigurationDocument19 pagesLorentz Transformation For Frames in Standard ConfigurationhikolNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis - MTH603 Handouts Lecture 9Document11 pagesNumerical Analysis - MTH603 Handouts Lecture 9Niaz Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Week 5: Assignment 5Document3 pagesUnit 6 - Week 5: Assignment 5V I J A Y E D I T ZNo ratings yet
- DIFFYQS PDEs, Separation of Variables, and The Heat EquationDocument12 pagesDIFFYQS PDEs, Separation of Variables, and The Heat EquationLG TVNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra, Vectors, and MatricesDocument6 pagesLinear Algebra, Vectors, and MatricesAriel VenzanoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6 MathematicsDocument218 pagesUnit - 6 MathematicsShrey AnchalNo ratings yet
- Math201 PDFDocument4 pagesMath201 PDFadilNo ratings yet
- 2017 GR 9 MathsDocument1 page2017 GR 9 Mathsrowan chibiNo ratings yet
- Integration Problems Fun Pack !Document2 pagesIntegration Problems Fun Pack !Filip MajstorovićNo ratings yet
- Surfaces of The Second Order: Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum Vol. 2Document25 pagesSurfaces of The Second Order: Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum Vol. 2david.contatos4308No ratings yet
- DMS Assignment 3Document1 pageDMS Assignment 3Hamsa A SNo ratings yet
- PLL Parity CasesDocument2 pagesPLL Parity CasesKattya Enciso Quispe100% (1)
- Analysis HW2 PDFDocument3 pagesAnalysis HW2 PDFAsad QayyumNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear FunctionsDocument27 pagesNonlinear FunctionsJuan David MesaNo ratings yet
- Floyd's Algorithm: All Pairs Shortest PathDocument23 pagesFloyd's Algorithm: All Pairs Shortest PathAshutosh UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY For MEAN, MEDIAN and MODE-1Document6 pagesACTIVITY For MEAN, MEDIAN and MODE-1Estelita ArizalaNo ratings yet
- RE GMAT2111 GEN WPS OfficeDocument17 pagesRE GMAT2111 GEN WPS OfficeVenus CaringalNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The 76th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 5, 2015Document7 pagesSolutions To The 76th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 5, 2015ahmet çolakNo ratings yet
- Ma8251 Unit I Matrices v1Document124 pagesMa8251 Unit I Matrices v1Kousheek VinnakotiNo ratings yet