Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IAL Note
IAL Note
Uploaded by
Alyssa ColeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Emission and Absorption SpectraDocument26 pagesEmission and Absorption SpectraRiriii67% (3)
- L2 Che101Document16 pagesL2 Che101Musa Ahammed MahinNo ratings yet
- 2007 Electrons in AtomsDocument123 pages2007 Electrons in Atomsapi-293306937No ratings yet
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDocument40 pagesThe Development of A New Atomic Modelahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Center of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Document18 pagesCenter of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Sador YonasNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Global IssuesDocument15 pagesContemporary Global IssuesBisrateab FekaduNo ratings yet
- Principle and Working of A Semiconductor LaserDocument16 pagesPrinciple and Working of A Semiconductor LaserAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document19 pagesGroup 5KISAAKYE SIMON PETER KASOZINo ratings yet
- JBAy Q9 Bse 0 Ka Q6 XMN ZW WDocument25 pagesJBAy Q9 Bse 0 Ka Q6 XMN ZW Wsagarshivnathsingh18818No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document9 pagesUnit 2abdulnasim123No ratings yet
- Laser TherapyDocument8 pagesLaser Therapytagewub4No ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect NotesDocument3 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Notessaifi_786No ratings yet
- Topic 7 HandoutDocument7 pagesTopic 7 HandoutnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Principle and Working of A Semiconductor LaserDocument17 pagesPrinciple and Working of A Semiconductor LaserMANISH KUMAR 20SCSE1290075No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences CHE 101: Introduction To Chemistry Dr. Zayed Bin Zakir ShawonDocument13 pagesDepartment of Mathematics and Natural Sciences CHE 101: Introduction To Chemistry Dr. Zayed Bin Zakir ShawonSYEDA UMME SALMANo ratings yet
- CHPTR 11-Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterDocument7 pagesCHPTR 11-Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterDarshanNo ratings yet
- 4.5. Quantum PhysicsDocument4 pages4.5. Quantum PhysicsjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics-104 Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesNuclear Physics-104 Photoelectric EffectshathaNo ratings yet
- Chem U1 M1 1.3 (Electronic Configuration)Document11 pagesChem U1 M1 1.3 (Electronic Configuration)Rachael FooteNo ratings yet
- GRE FactsDocument25 pagesGRE FactsMohamed ElashriNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Solar Energy: What Is It and How Does It Work?Document13 pagesUnit-3 Solar Energy: What Is It and How Does It Work?djkasjdhfNo ratings yet
- Atoms Truc TDocument9 pagesAtoms Truc Tpavi32No ratings yet
- Particle AcceleratorsDocument12 pagesParticle AcceleratorsFavourite MoviesNo ratings yet
- Microwave EngineeringDocument16 pagesMicrowave EngineeringkattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Light From Any Ordinary Source (Such As A Flame) Is Usually: Unpolarized The Wavelength of Red Light Is 700 Nm. Its Frequency IsDocument7 pagesLight From Any Ordinary Source (Such As A Flame) Is Usually: Unpolarized The Wavelength of Red Light Is 700 Nm. Its Frequency IsAbrish AliNo ratings yet
- Principle of Spontaneous and Stimulated Emission - Einstein's Quantum Theory of RadiationDocument43 pagesPrinciple of Spontaneous and Stimulated Emission - Einstein's Quantum Theory of RadiationSksk SkskNo ratings yet
- Phys Sol U08 ReviewDocument25 pagesPhys Sol U08 ReviewmksayshiNo ratings yet
- Wa0016Document103 pagesWa0016sibaranjandash2007No ratings yet
- QuantisationDocument3 pagesQuantisationNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesAtomic StructureThea GermanNo ratings yet
- S.6 Atomic Structur Notes 1 Revision Past PapersDocument12 pagesS.6 Atomic Structur Notes 1 Revision Past PapersMaama PhionaNo ratings yet
- Solar Cells: 1. TheoryDocument26 pagesSolar Cells: 1. TheoryStefan StanescuNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument16 pagesPhotoelectric EffectRushita LingiahNo ratings yet
- Chaper 5Document41 pagesChaper 5gebrewahidbiniam75No ratings yet
- 2020 WTS 12 Photoelectric EffectDocument24 pages2020 WTS 12 Photoelectric EffectlsagadevanNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model and Electron ConfigurationDocument35 pagesBohr Model and Electron ConfigurationJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Cyclotron: A Modern Cyclotron For Radiation TherapyDocument10 pagesCyclotron: A Modern Cyclotron For Radiation TherapyNguyễn Thành Công100% (1)
- Laser PhysicsDocument10 pagesLaser Physicsdc6169564No ratings yet
- Laser System and Application: DirectionalityDocument19 pagesLaser System and Application: DirectionalityajityadavsNo ratings yet
- Electrophysical Agent 1Document209 pagesElectrophysical Agent 1syammptNo ratings yet
- The Bohr Model of The Atom: A Brief DescriptionDocument45 pagesThe Bohr Model of The Atom: A Brief Descriptiondineshk3No ratings yet
- Gen 222 Notes 2 April 2023Document21 pagesGen 222 Notes 2 April 2023Charisse StevensNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Breakdown GasesDocument60 pagesHigh Voltage Breakdown GasesRakesh VasaniNo ratings yet
- Synchrotrons: (A Cyclic Particle Accelerator)Document22 pagesSynchrotrons: (A Cyclic Particle Accelerator)Muhammad Haroon KhanNo ratings yet
- 04 Kimia PlasmaDocument25 pages04 Kimia PlasmaAnggunNo ratings yet
- AccelerototracDocument10 pagesAccelerototracFaijan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Notebook 15 PG 37-38Document2 pagesNotebook 15 PG 37-38api-334252501No ratings yet
- WEEK 4 CDocument13 pagesWEEK 4 CeodurotwumNo ratings yet
- Description: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesDocument8 pagesDescription: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesfaithNo ratings yet
- The Bridge Between Classical and Quantum MechanicsDocument9 pagesThe Bridge Between Classical and Quantum MechanicsGeorge RajnaNo ratings yet
- 2) Atomic ModelsDocument25 pages2) Atomic ModelsShiva Manohar AnanthaNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearDocument52 pagesPresented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearSandeep VermaNo ratings yet
- 5.5. Astrophysics and CosmologyDocument9 pages5.5. Astrophysics and CosmologyjmsonlNo ratings yet
- 32 Bohr S Model OftheatomDocument15 pages32 Bohr S Model OftheatomAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry NotesDocument113 pagesAs Level Chemistry NotesHARIS GAMINGNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Principles of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices: The Role of the PN JunctionFrom EverandPrinciples of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices: The Role of the PN JunctionNo ratings yet
- 07 ScienceinterimreportDocument4 pages07 ScienceinterimreportAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionDocument5 pagesPhysics QuestionAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Velocity / M s1Document4 pagesVelocity / M s1Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument32 pagesPhysics QuestionsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Properties of Gases and The Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Properties of Gases and The Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ForceDocument2 pagesMagnetic ForceAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Current & Charge Calculations Worksheet: Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesCurrent & Charge Calculations Worksheet: Word ProblemsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Document5 pagesGas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Tow Truck Car CableDocument4 pagesTow Truck Car CableAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- SHCDocument6 pagesSHCAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument2 pagesThermalAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Current SolutionDocument2 pagesMagnetism and Current SolutionAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Review WS ANSWERSDocument3 pagesGas Laws Review WS ANSWERSAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Solutions Marks μ IDocument6 pagesSolutions Marks μ IAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field From Current WorksheetDocument2 pagesMagnetic Field From Current WorksheetAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Motion Graph Lesson Plan1819Document5 pagesMotion Graph Lesson Plan1819Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- What Is The Gradient of The Line? What Does This Tell You? Draw The Story of The GraphDocument1 pageWhat Is The Gradient of The Line? What Does This Tell You? Draw The Story of The GraphAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Elevator ProblemsDocument2 pagesElevator ProblemsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesDocument14 pagesLESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Confinement: Jeff Greensite Quarks and Hadrons in Strong QCD St. Goar, GermanyDocument54 pagesSymmetry and Confinement: Jeff Greensite Quarks and Hadrons in Strong QCD St. Goar, Germanycifarha venantNo ratings yet
- The Secret of ManifestationDocument133 pagesThe Secret of ManifestationnepherNo ratings yet
- Quinta Essentia - Part 4Document421 pagesQuinta Essentia - Part 4dgE100% (3)
- Unlocking The Secrets of The Universe PDFDocument37 pagesUnlocking The Secrets of The Universe PDFMacleo BanalNo ratings yet
- Electrogravity Experimental TestsDocument2 pagesElectrogravity Experimental TestsshahidNo ratings yet
- A Dictionary of Scientific QuotationsDocument16 pagesA Dictionary of Scientific Quotationsjpo9No ratings yet
- Econophysics and Capital Asset Pricing: James Ming ChenDocument293 pagesEconophysics and Capital Asset Pricing: James Ming ChenJetzayn CasasNo ratings yet
- Developments in High Energy TheoryDocument58 pagesDevelopments in High Energy TheoryMD2889100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsDocument48 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- ST ND 1 - 7 2 - 7Document10 pagesST ND 1 - 7 2 - 7jatinverma49265No ratings yet
- Phenomenology Particle Physics MartinDocument261 pagesPhenomenology Particle Physics Martincifarha venantNo ratings yet
- Electron Scattering For Nuclear and Nucleon Structure John Dirk Walecka Full ChapterDocument51 pagesElectron Scattering For Nuclear and Nucleon Structure John Dirk Walecka Full Chapterwilliam.mcguire766100% (6)
- Michio Kaku-Quantum Field Theory - A Modern Introduction - Oxford University Press (1993) PDFDocument802 pagesMichio Kaku-Quantum Field Theory - A Modern Introduction - Oxford University Press (1993) PDFjuaco8888100% (10)
- Course:: 1 Elementary ParticlesDocument4 pagesCourse:: 1 Elementary ParticlesJairYesidCoronadoAlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Xing Review 1909.09610Document227 pagesXing Review 1909.09610goforbestNo ratings yet
- 4442 Exam 2007Document7 pages4442 Exam 2007Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Relativistic MechanicsDocument4 pagesRelativistic Mechanicsnikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- Report Phys 06 08Document186 pagesReport Phys 06 08cippolippo123No ratings yet
- Prince Ganai NuclearDocument30 pagesPrince Ganai Nuclearprince_ganaiNo ratings yet
- Type of ForceDocument3 pagesType of ForcePRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- GluonsDocument9 pagesGluonsSwayamtrupta PandaNo ratings yet
- Quark ModelDocument20 pagesQuark ModelMuskan YadavNo ratings yet
- Big Bang TheoryDocument5 pagesBig Bang TheorybsarkarNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.4 Particle InteractionsDocument64 pages3.2.1.4 Particle InteractionseilyaeskandarianNo ratings yet
- The Origin & Structure of The EarthDocument7 pagesThe Origin & Structure of The EarthJasmine LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Particle Physics: Michaelmas Term 2007Document126 pagesSymmetry and Particle Physics: Michaelmas Term 2007Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction For CeeDocument21 pagesAn Introduction For CeeAshik jhaNo ratings yet
- Nucl - Phys.B v.695Document326 pagesNucl - Phys.B v.695buddy72No ratings yet
- 50 Years of Quantum Chromodynamics: A B C DDocument729 pages50 Years of Quantum Chromodynamics: A B C DArchana RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
IAL Note
IAL Note
Uploaded by
Alyssa ColeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IAL Note
IAL Note
Uploaded by
Alyssa ColeCopyright:
Available Formats
Paper 1
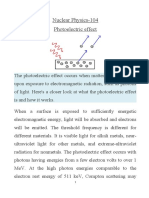
Photoelectric effect
Only one photon can transfer energy to a single electron
Photon energy depends on frequency
Photon energy must be greater than or equal to work function
Light with a greater intensity supplies more photon per second
So more electrons can be emitted per second.
Work function: The minimum energy required for the electron to escape from the metal
Atomic electron energies
Excited atom: Electron gain energy move to higher energy level
Emission: Electrons move to lower energy, emit photons
Only certain frequencies of radiation emit: electrons exist in discrete energy levels
Only certain energy changes are possible.
Energy level: discrete energy of an atom/ allowed energy of electron
Photon: packet of energy
Ground state: the lowest energy level
Ionisation energy: the minimum energy required by an electron in an atom’s ground state in order to
remove the electron completely from the electron.
Fluid flow
Laminar flow is fluid moves with uniform line in which the velocity is constant over time
Turbulent flow is fluid velocity changes over time.
Object falling through a fluid, it moves at a steady speed in a constant direction because the resultant
force acting on it is zero through a fluid.
An object from rest will increases its speed until it reaches terminal velocity.
Paper 2
Proton is accelerated by linac
Proton is accelerated by the electric field
The alternating p.d means that as a proton emerges from one tube the next one is negative.
Length of drift tubes increases because proton travels further during that half period of the cycle
as its speed is grater
p.d must switch at a constant frequency so time in each drift tube is the same
Drift tube length become the same at the end of the of linac
Speed of particles is near the speed of light
Additional energy increases mass
Time spent in each drift tube is constant and speed is constant.
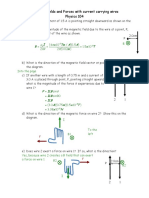
Proton is accelerated by cyclotron
Protons accelerated by electric field between the dees
The magnetic field is perpendicular to proton motion
This causes a centripetal acceleration
The polarity has reverse when the proton reaches the gap again
The path of the proton has larger radius with greater speed
Definition: A standard candle is a stellar known luminosity
The star is view from two position at 6 month intervals
The change in angular position of the star against background of fixed stars is measured.
Trigonometry is used to calculate the distance
Explain how a standard candle can be used to determine distance
Standard candle has a known luminosity
(Radiation) flux/brightness of standard candle is measured at the
Earth
Inverse square law used to calculate distance
Main sequence: A star that is fusing hydrogen in its core
Nuclear fusion energy release:
Hydrogen nuclei combine to form helium
There is loss of mass
This mass loss convert to energy and release
When the star runs out of hydrogen, it becomes a Red giant.
White draft: These stars have small surface area. The have a very high temperature and emit all visible
wavelength so they appear white
Baryon : 3 quarks
Mesons : a quark and an anti quark
Antiparticle : has the same mass but opposite charge
Pion quark composition: π + : u d π 0 : u u or d d π − : d u
Kaon quark composition : K + : u s K 0 : d s and s d K − : s u
Pair production: The photon energy produces an electron and a positron
Annihilation: a particle meets it antiparticle to form 2 photns
You might also like
- Emission and Absorption SpectraDocument26 pagesEmission and Absorption SpectraRiriii67% (3)
- L2 Che101Document16 pagesL2 Che101Musa Ahammed MahinNo ratings yet
- 2007 Electrons in AtomsDocument123 pages2007 Electrons in Atomsapi-293306937No ratings yet
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDocument40 pagesThe Development of A New Atomic Modelahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Center of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Document18 pagesCenter of Biomedical Engineering Medical Radiation Physics (Phys-2223)Sador YonasNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Global IssuesDocument15 pagesContemporary Global IssuesBisrateab FekaduNo ratings yet
- Principle and Working of A Semiconductor LaserDocument16 pagesPrinciple and Working of A Semiconductor LaserAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document19 pagesGroup 5KISAAKYE SIMON PETER KASOZINo ratings yet
- JBAy Q9 Bse 0 Ka Q6 XMN ZW WDocument25 pagesJBAy Q9 Bse 0 Ka Q6 XMN ZW Wsagarshivnathsingh18818No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document9 pagesUnit 2abdulnasim123No ratings yet
- Laser TherapyDocument8 pagesLaser Therapytagewub4No ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect NotesDocument3 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Notessaifi_786No ratings yet
- Topic 7 HandoutDocument7 pagesTopic 7 HandoutnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Principle and Working of A Semiconductor LaserDocument17 pagesPrinciple and Working of A Semiconductor LaserMANISH KUMAR 20SCSE1290075No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences CHE 101: Introduction To Chemistry Dr. Zayed Bin Zakir ShawonDocument13 pagesDepartment of Mathematics and Natural Sciences CHE 101: Introduction To Chemistry Dr. Zayed Bin Zakir ShawonSYEDA UMME SALMANo ratings yet
- CHPTR 11-Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterDocument7 pagesCHPTR 11-Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterDarshanNo ratings yet
- 4.5. Quantum PhysicsDocument4 pages4.5. Quantum PhysicsjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics-104 Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesNuclear Physics-104 Photoelectric EffectshathaNo ratings yet
- Chem U1 M1 1.3 (Electronic Configuration)Document11 pagesChem U1 M1 1.3 (Electronic Configuration)Rachael FooteNo ratings yet
- GRE FactsDocument25 pagesGRE FactsMohamed ElashriNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Solar Energy: What Is It and How Does It Work?Document13 pagesUnit-3 Solar Energy: What Is It and How Does It Work?djkasjdhfNo ratings yet
- Atoms Truc TDocument9 pagesAtoms Truc Tpavi32No ratings yet
- Particle AcceleratorsDocument12 pagesParticle AcceleratorsFavourite MoviesNo ratings yet
- Microwave EngineeringDocument16 pagesMicrowave EngineeringkattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Light From Any Ordinary Source (Such As A Flame) Is Usually: Unpolarized The Wavelength of Red Light Is 700 Nm. Its Frequency IsDocument7 pagesLight From Any Ordinary Source (Such As A Flame) Is Usually: Unpolarized The Wavelength of Red Light Is 700 Nm. Its Frequency IsAbrish AliNo ratings yet
- Principle of Spontaneous and Stimulated Emission - Einstein's Quantum Theory of RadiationDocument43 pagesPrinciple of Spontaneous and Stimulated Emission - Einstein's Quantum Theory of RadiationSksk SkskNo ratings yet
- Phys Sol U08 ReviewDocument25 pagesPhys Sol U08 ReviewmksayshiNo ratings yet
- Wa0016Document103 pagesWa0016sibaranjandash2007No ratings yet
- QuantisationDocument3 pagesQuantisationNarjis FatimaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesAtomic StructureThea GermanNo ratings yet
- S.6 Atomic Structur Notes 1 Revision Past PapersDocument12 pagesS.6 Atomic Structur Notes 1 Revision Past PapersMaama PhionaNo ratings yet
- Solar Cells: 1. TheoryDocument26 pagesSolar Cells: 1. TheoryStefan StanescuNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument16 pagesPhotoelectric EffectRushita LingiahNo ratings yet
- Chaper 5Document41 pagesChaper 5gebrewahidbiniam75No ratings yet
- 2020 WTS 12 Photoelectric EffectDocument24 pages2020 WTS 12 Photoelectric EffectlsagadevanNo ratings yet
- Bohr Model and Electron ConfigurationDocument35 pagesBohr Model and Electron ConfigurationJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Cyclotron: A Modern Cyclotron For Radiation TherapyDocument10 pagesCyclotron: A Modern Cyclotron For Radiation TherapyNguyễn Thành Công100% (1)
- Laser PhysicsDocument10 pagesLaser Physicsdc6169564No ratings yet
- Laser System and Application: DirectionalityDocument19 pagesLaser System and Application: DirectionalityajityadavsNo ratings yet
- Electrophysical Agent 1Document209 pagesElectrophysical Agent 1syammptNo ratings yet
- The Bohr Model of The Atom: A Brief DescriptionDocument45 pagesThe Bohr Model of The Atom: A Brief Descriptiondineshk3No ratings yet
- Gen 222 Notes 2 April 2023Document21 pagesGen 222 Notes 2 April 2023Charisse StevensNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Breakdown GasesDocument60 pagesHigh Voltage Breakdown GasesRakesh VasaniNo ratings yet
- Synchrotrons: (A Cyclic Particle Accelerator)Document22 pagesSynchrotrons: (A Cyclic Particle Accelerator)Muhammad Haroon KhanNo ratings yet
- 04 Kimia PlasmaDocument25 pages04 Kimia PlasmaAnggunNo ratings yet
- AccelerototracDocument10 pagesAccelerototracFaijan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Notebook 15 PG 37-38Document2 pagesNotebook 15 PG 37-38api-334252501No ratings yet
- WEEK 4 CDocument13 pagesWEEK 4 CeodurotwumNo ratings yet
- Description: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesDocument8 pagesDescription: Electromagnetic Radiation Charged ParticlesfaithNo ratings yet
- The Bridge Between Classical and Quantum MechanicsDocument9 pagesThe Bridge Between Classical and Quantum MechanicsGeorge RajnaNo ratings yet
- 2) Atomic ModelsDocument25 pages2) Atomic ModelsShiva Manohar AnanthaNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearDocument52 pagesPresented By-Aarzoo Pathak (Final YearSandeep VermaNo ratings yet
- 5.5. Astrophysics and CosmologyDocument9 pages5.5. Astrophysics and CosmologyjmsonlNo ratings yet
- 32 Bohr S Model OftheatomDocument15 pages32 Bohr S Model OftheatomAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry NotesDocument113 pagesAs Level Chemistry NotesHARIS GAMINGNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Principles of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices: The Role of the PN JunctionFrom EverandPrinciples of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices: The Role of the PN JunctionNo ratings yet
- 07 ScienceinterimreportDocument4 pages07 ScienceinterimreportAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- 2Document3 pages2Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionDocument5 pagesPhysics QuestionAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Velocity / M s1Document4 pagesVelocity / M s1Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument32 pagesPhysics QuestionsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Properties of Gases and The Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Properties of Gases and The Kinetic Molecular Theory of GasesAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic ForceDocument2 pagesMagnetic ForceAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Current & Charge Calculations Worksheet: Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesCurrent & Charge Calculations Worksheet: Word ProblemsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Document5 pagesGas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Tow Truck Car CableDocument4 pagesTow Truck Car CableAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- SHCDocument6 pagesSHCAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument2 pagesThermalAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and Current SolutionDocument2 pagesMagnetism and Current SolutionAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Review WS ANSWERSDocument3 pagesGas Laws Review WS ANSWERSAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Solutions Marks μ IDocument6 pagesSolutions Marks μ IAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field From Current WorksheetDocument2 pagesMagnetic Field From Current WorksheetAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Motion Graph Lesson Plan1819Document5 pagesMotion Graph Lesson Plan1819Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- What Is The Gradient of The Line? What Does This Tell You? Draw The Story of The GraphDocument1 pageWhat Is The Gradient of The Line? What Does This Tell You? Draw The Story of The GraphAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Elevator ProblemsDocument2 pagesElevator ProblemsAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesDocument14 pagesLESSON 2 Atoms, Ions and MoleculesscientistgenerosoNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Confinement: Jeff Greensite Quarks and Hadrons in Strong QCD St. Goar, GermanyDocument54 pagesSymmetry and Confinement: Jeff Greensite Quarks and Hadrons in Strong QCD St. Goar, Germanycifarha venantNo ratings yet
- The Secret of ManifestationDocument133 pagesThe Secret of ManifestationnepherNo ratings yet
- Quinta Essentia - Part 4Document421 pagesQuinta Essentia - Part 4dgE100% (3)
- Unlocking The Secrets of The Universe PDFDocument37 pagesUnlocking The Secrets of The Universe PDFMacleo BanalNo ratings yet
- Electrogravity Experimental TestsDocument2 pagesElectrogravity Experimental TestsshahidNo ratings yet
- A Dictionary of Scientific QuotationsDocument16 pagesA Dictionary of Scientific Quotationsjpo9No ratings yet
- Econophysics and Capital Asset Pricing: James Ming ChenDocument293 pagesEconophysics and Capital Asset Pricing: James Ming ChenJetzayn CasasNo ratings yet
- Developments in High Energy TheoryDocument58 pagesDevelopments in High Energy TheoryMD2889100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsDocument48 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsBibha KumariNo ratings yet
- ST ND 1 - 7 2 - 7Document10 pagesST ND 1 - 7 2 - 7jatinverma49265No ratings yet
- Phenomenology Particle Physics MartinDocument261 pagesPhenomenology Particle Physics Martincifarha venantNo ratings yet
- Electron Scattering For Nuclear and Nucleon Structure John Dirk Walecka Full ChapterDocument51 pagesElectron Scattering For Nuclear and Nucleon Structure John Dirk Walecka Full Chapterwilliam.mcguire766100% (6)
- Michio Kaku-Quantum Field Theory - A Modern Introduction - Oxford University Press (1993) PDFDocument802 pagesMichio Kaku-Quantum Field Theory - A Modern Introduction - Oxford University Press (1993) PDFjuaco8888100% (10)
- Course:: 1 Elementary ParticlesDocument4 pagesCourse:: 1 Elementary ParticlesJairYesidCoronadoAlbarracinNo ratings yet
- Xing Review 1909.09610Document227 pagesXing Review 1909.09610goforbestNo ratings yet
- 4442 Exam 2007Document7 pages4442 Exam 2007Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Relativistic MechanicsDocument4 pagesRelativistic Mechanicsnikita bajpaiNo ratings yet
- Report Phys 06 08Document186 pagesReport Phys 06 08cippolippo123No ratings yet
- Prince Ganai NuclearDocument30 pagesPrince Ganai Nuclearprince_ganaiNo ratings yet
- Type of ForceDocument3 pagesType of ForcePRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- GluonsDocument9 pagesGluonsSwayamtrupta PandaNo ratings yet
- Quark ModelDocument20 pagesQuark ModelMuskan YadavNo ratings yet
- Big Bang TheoryDocument5 pagesBig Bang TheorybsarkarNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.4 Particle InteractionsDocument64 pages3.2.1.4 Particle InteractionseilyaeskandarianNo ratings yet
- The Origin & Structure of The EarthDocument7 pagesThe Origin & Structure of The EarthJasmine LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Particle Physics: Michaelmas Term 2007Document126 pagesSymmetry and Particle Physics: Michaelmas Term 2007Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction For CeeDocument21 pagesAn Introduction For CeeAshik jhaNo ratings yet
- Nucl - Phys.B v.695Document326 pagesNucl - Phys.B v.695buddy72No ratings yet
- 50 Years of Quantum Chromodynamics: A B C DDocument729 pages50 Years of Quantum Chromodynamics: A B C DArchana RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet