Professional Documents
Culture Documents
128 - CREATININE 6x50ml
128 - CREATININE 6x50ml
Uploaded by
Aniket DubeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
128 - CREATININE 6x50ml
128 - CREATININE 6x50ml
Uploaded by
Aniket DubeyCopyright:
Available Formats
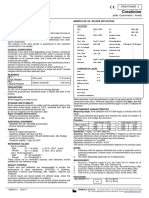
CREATININE
Jaffe’s Kinetic Method 6x50 ml
Quantitative determination of Creatinine in serum or urine by means of 5. Run patients neat serum, 1:50 diluted urine and control samples by
photometric method. following the same procedure.
Only for in vitro use in clinical laboratory (IVD). Calculation
∆A U
Clinical Significance Serum/Plasma Creatinine (mg/dl) = x 2 (Standard Conc.)
Creatinine is the catabolic product of creatinine phosphate, which is used by the ∆A S
skeletal muscle. The daily production depends on muscular mass and it is ∆A U
excreted out of the body entirely by the kidneys. Urine Creatinine (mg/dl) = x 2 x 50 (Dilution Factor for Urine)
Elevated Creatinine levels are found in renal dysfunction reduced renal blood flow ∆A S
(shock, dehydration, congestive heart failure) diabetes acromegaly. Decreased
Creatinine levels are found in muscular dystrophy.
Quality Control
Principle Commercially available normal and pathological control sera are recommended to
monitor the performance of the procedure.
Creatinine reacts with the alkaline picrate (Jaffe reaction) producing a reddish
brown chromogen. The speed of this reaction under controlled conditions is a If control values are found outside the defined range, check the instrument,
measure of the creatinine concentration in the sample, as it behaves as a first reagents and calibrator for problems
order kinetic reaction for creatinine. Besides, it has been proved that non- Serum controls are recommended for internal quality control. Each
creatinine chromogens, which interfere with most of the conventional techniques, laboratory should establish its own Quality Control scheme and corrective
react within 30 seconds from the beginning of the reaction. Thus, the color actions if controls do not meet the acceptable tolerances.
increase there after is only due to creatinine.
Reagents Reference Values
Each Creatinine kit contains Male Serum 0.9 - 1.4 mg/dl
RI - Picric Acid Urine 1000 - 2000 mg/24 hrs.
R II - Alkali Female Serum 0.7 - 1.3 mg/dl
Creatinine STD - Creatinine Standard ( 2 mg/dl) Urine 600 - 1500 mg/24 hrs.
It is suggested that each laboratory establish its own reference range.
Reagent Preparation
Reagents are ready to use.
Mix one Volume of Reagent (R I) with one volume of Reagent (R II) (According to Reagent Performance
the requirement).
Measuring Range
Reaction is linear up to 20 mg/dl of Creatinine under the described assay
Stability conditions.
The provided reagents are stable till the date of expiry when stored as stated on For higher values, dilute sample 1:2 or 1:4 with saline solution and repeat
the labels. testing. Correct calculations multiplying by the dilution factor used.
Working reagent is stable for 30 days at 25o ± 5o C. Do not use the reagent if
turbid. Test Parameters
Visible turbidity in reagent or standard indicates reagent deterioration. Discard in
Mode Two Point Kinetic
such case.
Do not use reagents over the expiration date. Wavelength (nm) 505
Sample Volume (µl) 100
Specimens Working Reagent Volume (µl) 1000
Serum or urine. Lag Time (Sec.) 20
a) Collection: obtain serum in the usual way. 24-hour urine should be Measuring Time(Sec.) 60
collected in a thoroughly cleaned container, which should be refrigerated Standard Conc. (mg/dl) 2
(2°-8° C) during collection. Measure diuresis, take an aliquot and perform Reaction Temperature (° C) 37
a 1:50 dilution. to calculate the amount of creatinine eliminated during 24 Reaction Direction Increasing
hours. Normal Low (mg/dl) 0.9
b) Additives: none required. Normal High (mg/dl) 1.4
c) Known interfering substances: sera with hemoglobin concentration>30 Blank with Reagent
mg/dl or Bilirubin >10 mg/dl yield falsely increased values. No interference Units mg/dl
is observed from mild or moderate hemolysis, hyperlipemia, Linearity Limit 20 mg/dl
disproteinemia or non-creatinine chromogens (such as glucose, ascorbic
acid, ketoacids, glutathione or ergothioneine). For detailed interferences
refer to Young, et. al. 3 .
Literatures
1. Jaffe M. Physiol Chem 10:391, 1886
d) Stability and storage instructions: creatinine in serum is stable up to 24 2. RJ Henry et al, Clin. Chem.- Principles and Technics, 1974, pp 549-550.
hours and in urine upto 4 days, when refrigerated. 3. Young,D.S., et al, Clin.Chem. 21:1D (1975).
Procedure
In three colorimeter test tubes labeled B (Blank), S (Standard) and U
(Unknown), place: Manufactured by
Blank (B) Standard Unknown PRISM DIAGNOSTICS PVT. LTD.
(S) Sample (U) 7&8, Shiv Shakti Laghu Udyog Sankul,
Mumbai – Nashik Road,
Working Reagent 1000 µl 1000 µl 1000 µl Asangaon, Dist. Thane
Dis. Water 100 µl -- --
Standard -- 100 µl -- Marketed by
Unknown Sample -- -- 100 µl SYNERGY BIO, A Division of
Euro Diagnostic Systems Pvt. Ltd.
1. Set photometer cuvette temperature to 30o or 37oC. Zero photometer ‘Millennium House’ M. K. Srinivasan Nagar Main Road
with reagent blank at 505 nm. No. 144, Old Mahabalipuram Road, Perungudi, Chennai-600 096
2. After exactly 20 secs read and record absorbance A1 . Tamil Nadu, India, Phone: 044-2496 1064, 044-2496 0541
3. At exactly 60 secs after A1 , read and record absorbance A2 . Fax: 044-2496 2825 , email: eurods@vsnl.net, www.eurods.in
4. Calculate change in absorbance ∆A by subtracting A2 - A1 .
You might also like
- Nursing Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests DeMYSTiFiedFrom EverandNursing Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests DeMYSTiFiedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 11009001Document1 page11009001Johnmar AquinoNo ratings yet
- URIC ACID LyphoDocument2 pagesURIC ACID LyphoDharmesh Patel50% (2)
- Creatinine: Prepare The Required Quantity of Working Reagent For The Analytical SessionDocument2 pagesCreatinine: Prepare The Required Quantity of Working Reagent For The Analytical SessionTrần Thanh ViệnNo ratings yet
- Principle of The Method Quality Control: Alkaline PicrateDocument1 pagePrinciple of The Method Quality Control: Alkaline PicrateRisqon Anjahiranda Adiputra100% (2)
- Creatinine (Jaffe'S Method) : Alkaline MediumDocument2 pagesCreatinine (Jaffe'S Method) : Alkaline MediumYennySuryaniNo ratings yet
- Clinimate CREDocument2 pagesClinimate CRESinari AlfatNo ratings yet
- Creatinine: (Jaffe (Initial Rate) Method Using Alkaline Picrate)Document2 pagesCreatinine: (Jaffe (Initial Rate) Method Using Alkaline Picrate)Ranjit PathakNo ratings yet
- 11502I CreatinineDocument1 page11502I CreatininemahinNo ratings yet
- Creatinine (Alkaline Picrate) PDFDocument1 pageCreatinine (Alkaline Picrate) PDFatul pandey100% (1)
- Creatinine JaffeDocument2 pagesCreatinine JaffeOsinachi WilsonNo ratings yet
- Insert Kit Kimia KlinikDocument1 pageInsert Kit Kimia Klinikdian saleh100% (1)
- Creatinina PDFDocument2 pagesCreatinina PDFJuniorNo ratings yet
- PI e CREA - JAFFE 20 (1) DikonversiDocument2 pagesPI e CREA - JAFFE 20 (1) DikonversiNonameNo ratings yet
- CreatinineDocument1 pageCreatinineSubodhNo ratings yet
- PI e CREA - JAFFE 20Document2 pagesPI e CREA - JAFFE 20NonameNo ratings yet
- Budi Creatinine - Doc NewDocument3 pagesBudi Creatinine - Doc NewIrvanda ENVIOUSNo ratings yet
- CR510Document4 pagesCR510Benedicta OjoNo ratings yet
- XSYS0024 - XSYS0076 CREA 275 - 564 XL-1000 - J-WUe65cBcT8Document7 pagesXSYS0024 - XSYS0076 CREA 275 - 564 XL-1000 - J-WUe65cBcT8Hùng Hoàng DuyNo ratings yet
- GA4420 00 - Creatinine Enzymatic - 0Document2 pagesGA4420 00 - Creatinine Enzymatic - 0Abdalrhman FarajNo ratings yet
- Wa0056.Document2 pagesWa0056.micklemagdy50No ratings yet
- BSIS77_CREATININA_enzimatica_1001115-17_2011Document2 pagesBSIS77_CREATININA_enzimatica_1001115-17_2011Nghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Qualigent CRPDocument3 pagesQualigent CRPdjebrutNo ratings yet
- CR510 CreatinineDocument2 pagesCR510 CreatinineYurii100% (1)
- IFU - BM6010 e CYSC 1Document3 pagesIFU - BM6010 e CYSC 1Khuon BunthaNo ratings yet
- Creatinine 35 EngDocument6 pagesCreatinine 35 Englilianazar020No ratings yet
- Enzymatic Creatinine: Reagent/ Product Code: Product Code: Product Code: Description Component 11420002 11420003 11420004Document2 pagesEnzymatic Creatinine: Reagent/ Product Code: Product Code: Product Code: Description Component 11420002 11420003 11420004غالب الموسويNo ratings yet
- 31 32 Creatinine EnzymaticDocument2 pages31 32 Creatinine EnzymaticShivpartap SinghNo ratings yet
- WHO GMP Compliance ISO 9001: 2015 & ISO 13485: 2016 Certified CompanyDocument1 pageWHO GMP Compliance ISO 9001: 2015 & ISO 13485: 2016 Certified CompanyRanjit PathakNo ratings yet
- Creatinina SDocument6 pagesCreatinina SLUIS DANIEL VAZQUEZ RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Creatinine: Quantitative Determination of CreatinineDocument3 pagesCreatinine: Quantitative Determination of CreatinineMarcos García RodríguezNo ratings yet
- CT10152 Creatinine EDocument2 pagesCT10152 Creatinine ELaboratorio BianucciNo ratings yet
- KR10150 Rev02Document2 pagesKR10150 Rev02KOUAME EDYMAIN FRANCISNo ratings yet
- CR 0500 CH 4 X 125 ML CR 1000 CH 4 X 250 ML: in Vitro Diagnostic Medical DeviceDocument1 pageCR 0500 CH 4 X 125 ML CR 1000 CH 4 X 250 ML: in Vitro Diagnostic Medical Deviceعصام عبدالهادي العزعزيNo ratings yet
- PI e CREA - JAFFE 19Document2 pagesPI e CREA - JAFFE 19Salsabila Nur OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Direct: 5 X 100/5 X 11 ML 12011005Document1 pageBilirubin Direct: 5 X 100/5 X 11 ML 12011005Ajish joNo ratings yet
- PI e CREA - PAP 18 PDFDocument2 pagesPI e CREA - PAP 18 PDFAPRILLA DENTINo ratings yet
- PI e TPU 11Document2 pagesPI e TPU 11Sinari AlfatNo ratings yet
- Complement C4: N/180/16/A/INT Date of Revision: 27.1.2016Document2 pagesComplement C4: N/180/16/A/INT Date of Revision: 27.1.2016DũngNo ratings yet
- 35.mucoproteinsDocument2 pages35.mucoproteinsHiếu Chí PhanNo ratings yet
- Manuali PDF 405Document1 pageManuali PDF 405Rakib Hossain 3A-159No ratings yet
- GA4256 00 - Direct BilirubinDocument2 pagesGA4256 00 - Direct BilirubinTrần Thanh ViệnNo ratings yet
- PI e CREA - JAFFE 2Document3 pagesPI e CREA - JAFFE 2fitri fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Mi100111 - Creatinina - 2017Document4 pagesMi100111 - Creatinina - 2017Dafne Manrique JerezNo ratings yet
- IFU - R910 e CREA - JAFFE 14Document3 pagesIFU - R910 e CREA - JAFFE 14HaisNo ratings yet
- PI e CYSC 2Document2 pagesPI e CYSC 2sitirahmawatiningsih25No ratings yet
- Triglyceride - SLR INSERTDocument1 pageTriglyceride - SLR INSERTventasmedicarescNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-17 at 11.23.43 AMDocument5 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-17 at 11.23.43 AMs8903082No ratings yet
- 4.estimation of Urinary CreatinineDocument5 pages4.estimation of Urinary Creatinineahteshammirji575No ratings yet
- Randox - Immunoturbidimetric ProteinsDocument32 pagesRandox - Immunoturbidimetric ProteinsCoțovanu IulianNo ratings yet
- Crea 200Document4 pagesCrea 200NonameNo ratings yet
- Urea BLT00060 61Document2 pagesUrea BLT00060 61Vũ Đình DũngNo ratings yet
- IFU - BX e CREA - JAFFE 1Document10 pagesIFU - BX e CREA - JAFFE 1Agnihotram GopinathNo ratings yet
- Bil T Ang 2013 11 14Document2 pagesBil T Ang 2013 11 14yehiwal756No ratings yet
- CreatinineDocument1 pageCreatinineDesiNo ratings yet
- 36.proteins CoomassieDocument2 pages36.proteins CoomassieHiếu Chí PhanNo ratings yet
- PI e CRP 22Document2 pagesPI e CRP 22Hùng Hoàng DuyNo ratings yet
- MEASURE HbA1c (Fixed)Document2 pagesMEASURE HbA1c (Fixed)Trần Văn Bình100% (1)
- Crea 275 - 564 XL-1000 - Xsys0024 - 76 - FDocument4 pagesCrea 275 - 564 XL-1000 - Xsys0024 - 76 - FNonameNo ratings yet
- SOC Regular Savings Account Jan22Document2 pagesSOC Regular Savings Account Jan22Aniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Benef Its: Savings Account Effective January 1, 2022Document2 pagesSchedule of Benef Its: Savings Account Effective January 1, 2022Aniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Charges - Indus Online Savings Account VariantsDocument6 pagesSchedule of Charges - Indus Online Savings Account VariantsAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- M1005-Maglumi 2000Plus-E160922 - ItkDocument7 pagesM1005-Maglumi 2000Plus-E160922 - ItkAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Arigo Troubleshooting ProtocolDocument3 pagesArigo Troubleshooting ProtocolAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification Maglumi 2000Document2 pagesTechnical Specification Maglumi 2000Aniket Dubey100% (1)
- Maglumi 2000 NuevoDocument4 pagesMaglumi 2000 NuevoAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Ins DD en D Dimer Rev.07 150604Document3 pagesIns DD en D Dimer Rev.07 150604Aniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Hot PlatesDocument6 pagesHot PlatesAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- CRP IngDocument2 pagesCRP IngAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Truechemie: Ada Test KitDocument1 pageTruechemie: Ada Test KitAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Erma EL 120 FRONT PAGE PDFDocument2 pagesErma EL 120 FRONT PAGE PDFAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- BC-20s Auto Hematology Analyzer: Minimize Size, Maximize PossibilitiesDocument3 pagesBC-20s Auto Hematology Analyzer: Minimize Size, Maximize PossibilitiesAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Tn-I Plus: Warnings and PrecautionsDocument5 pagesTn-I Plus: Warnings and PrecautionsAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications: System FunctionDocument2 pagesTechnical Specifications: System FunctionAniket dubey0% (1)
- Health Checkup e BrochureDocument12 pagesHealth Checkup e BrochureABHISHEK BOGANo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacy Board Review Module 4Document73 pagesBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacy Board Review Module 4Kate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Farmacia MedicamentosDocument36 pagesFarmacia Medicamentosbayron perezNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - ABG INTERPRETATIONDocument2 pagesGroup 2 - ABG INTERPRETATIONJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- Zulfikar AkbarDocument11 pagesZulfikar AkbarFaiz AnwarNo ratings yet
- System of The Human BodyDocument31 pagesSystem of The Human BodyMari Thomas100% (1)
- 18Document15 pages18saraNo ratings yet
- A Strategic Review On The Involvement of Receptors, Transcription Factors and Hormones in Acne PathogenesisDocument13 pagesA Strategic Review On The Involvement of Receptors, Transcription Factors and Hormones in Acne Pathogenesisoctavio oliveiraNo ratings yet
- What Is Newborn ScreeningDocument2 pagesWhat Is Newborn ScreeningroksanmiNo ratings yet
- Telemed Written Report 4Document5 pagesTelemed Written Report 4Gabriel MillaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Revision Document - FINAL August 2021Document147 pages2021 Revision Document - FINAL August 2021KelsiekhumaloNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules NotesDocument9 pagesBiological Molecules NotesANWESHA BALNo ratings yet
- Jab and Spike Detox For Optimal Health 2021Document23 pagesJab and Spike Detox For Optimal Health 2021Alan N100% (2)
- Diagnostic Problems in Breast Pathology, 2009, PGDocument362 pagesDiagnostic Problems in Breast Pathology, 2009, PGMarin Ionut100% (1)
- Local AnaestheticsDocument27 pagesLocal AnaestheticsRawand Ra'ed D.AlshawabkehNo ratings yet
- Lipids: TEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)Document1 pageLipids: TEST(s) Normal UNIT(s)usman noorNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Keys For Check Your ProgressDocument3 pagesUnit 7 Keys For Check Your ProgressAlfredNo ratings yet
- Compliled DrugstudyDocument15 pagesCompliled DrugstudyApril Jan D. Alagon0% (1)
- Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument59 pagesAcute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Diseasesho bartNo ratings yet
- Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics 8Th Edition Karen Marcdante Full ChapterDocument67 pagesNelson Essentials of Pediatrics 8Th Edition Karen Marcdante Full Chapterclaudia.miser377100% (12)
- Kidney FailureDocument27 pagesKidney FailureKash JamasaliNo ratings yet
- Jurnal - The Role of DIet N The Pathogenesis of Cholesterol GallstonesDocument28 pagesJurnal - The Role of DIet N The Pathogenesis of Cholesterol GallstonesLiaNo ratings yet
- Ispitna Pitanja Farmacija Medicinska BiohemijaDocument2 pagesIspitna Pitanja Farmacija Medicinska BiohemijaTijanaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in RabbitDocument309 pagesRecent Advances in RabbitIvan Graça AraujoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Power PointDocument17 pagesDigestive System Power PointAlyssa Mae DapadapNo ratings yet
- Uma ThapaDocument1 pageUma ThapaBhaktivedanta HospitalNo ratings yet
- Theories of AgingDocument14 pagesTheories of AgingElla Neiza AngelesNo ratings yet
- Gland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical NatureDocument4 pagesGland Hormone Target Tissue Principle Actions Chemical Naturernalfas100% (1)
- 6 HypertensionDocument95 pages6 HypertensionZeleke temechewNo ratings yet
- Menopause DissertationDocument4 pagesMenopause DissertationWriteMyPaperReviewsCanada100% (1)