Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac Circuits
Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac Circuits
Uploaded by
Chaitanya Vivek DeshpandeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac Circuits
Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac Circuits
Uploaded by
Chaitanya Vivek DeshpandeCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Analysis Class/Branch: S.E.
Electrical
Experiment Number: 03
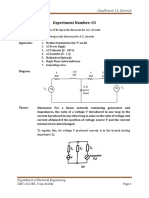
Title: Verification of Reciprocity theorem for A.C. circuits
Aim: To verify Reciprocity theorem for A.C. circuits
Apparatus: 1. Medium transmission line ‘T’ model
2. AC Power Supply
3. AC Voltmeter (0 - 150 V)
4. AC Ammeter (0 - 1 A)
5. Multimeter (Optional)
6. Single Phase Autotransformer
7. Connecting wires
Diagram: 4 110 4 110
ohm mH ohm mH
0.47 V2
V1 micro
farad
Theory: Statement: For a linear network containing generators and
impedances, the ratio of a voltage V introduced in one loop to the
current I produced in any other loop is same as the ratio of voltage and
current obtained if the position of voltage source V and the current
measured are interchanged.
To explain this, let voltage V produced current I3 in the branch having
impedance Z3.
Department of Electrical Engineering
ZES’s ZCOER, Pune-411041 Page 1
Network Analysis Class/Branch: S.E. Electrical
If we just interchange the voltage source and ammeter.
Then as per reciprocity theorem,
𝑉 𝑉
= = 𝑖. 𝑒. 𝐼3 = 𝐼1
𝐼3 𝐼1
Procedure: 1. Construct the circuit as shown in fig.
2. Short circuit the V2 & only V1 is allowed in loop I. Also short circuit
the other source with their internal impedance.
3. Apply 20 V across autotransformer.
4. Measure current I using ammeter.
5. Similarly obtain the value of I2 by short circuiting V1, obtain V2 in
loop 2.
6. Now verify ratio (V1/I1) = (V2/I2) using practical as well as
theoretical value.
Observation
table:
Initial position After interchanging
Sr. No
V I V I
Calculations: Do the calculation on Blank ruled pages.
Conclusion:
=======================================================
Department of Electrical Engineering
ZES’s ZCOER, Pune-411041 Page 2
Network Analysis Class/Branch: S.E. Electrical
Department of Electrical Engineering
ZES’s ZCOER, Pune-411041 Page 3
You might also like
- 2.sumpner's Test On A Pair of Single Phase TransformersDocument5 pages2.sumpner's Test On A Pair of Single Phase Transformerschandrakanth100% (2)
- Virtual Lab Report-1 PDFDocument27 pagesVirtual Lab Report-1 PDFCarlton Lobo0% (1)
- Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Expt - 2 - Verification of Theveninen's Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 2 - Verification of Theveninen's Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande100% (1)
- Expt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande100% (1)
- Expt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- User Manual Machine Lab FullDocument40 pagesUser Manual Machine Lab FullMd. Sojib KhanNo ratings yet
- Open Circuit & Short Open Circuit & Short Circuit Test Single Phase Transformer Tests of RmerDocument14 pagesOpen Circuit & Short Open Circuit & Short Circuit Test Single Phase Transformer Tests of Rmersameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- Model Questions EEE Cat-IDocument4 pagesModel Questions EEE Cat-IIKNo ratings yet
- BEE Lab .Pinku 6Document14 pagesBEE Lab .Pinku 6CHINMAY CHIRANJIB TRIPATHY B.TECHNo ratings yet
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pages1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Experiment No.12 PDFDocument5 pagesExperiment No.12 PDFAlisha AkterNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument23 pagesLaboratory ManualAnmol AhsaasNo ratings yet
- EEE363 (Exp 4) Study of The Current Voltage Relationship and Different Loading Conditions of Single Phase TransformerDocument12 pagesEEE363 (Exp 4) Study of The Current Voltage Relationship and Different Loading Conditions of Single Phase Transformersalad.ass420420No ratings yet
- Be-104 (Beee)Document69 pagesBe-104 (Beee)Sunil NamdevNo ratings yet
- Lab#4 Maxwell BridgeDocument6 pagesLab#4 Maxwell BridgeRehman ButtNo ratings yet
- Verification of Superposition Theorem.Document6 pagesVerification of Superposition Theorem.Apu SarkarNo ratings yet
- PHY547 - LAb Manual-2019Document26 pagesPHY547 - LAb Manual-2019zulhaimirasheedNo ratings yet
- EE2155 Electrical Circuits Lab Manual PDFDocument38 pagesEE2155 Electrical Circuits Lab Manual PDFSymmer CulNo ratings yet
- 1 Prepared by Dr. Joyprokash ChakrabarttyDocument4 pages1 Prepared by Dr. Joyprokash ChakrabarttyShakil Rahman AfidNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.5 Zener Diode Characteristics: ObjectDocument4 pagesExperiment No.5 Zener Diode Characteristics: ObjectEsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Electric Machines LaboratoryDocument44 pagesElectric Machines Laboratory11mustafa.mNo ratings yet
- BEE Lab ExpDocument17 pagesBEE Lab ExpShahid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work 3Document5 pagesLaboratory Work 3Makhmud AssentayNo ratings yet
- Oc SC PDFDocument5 pagesOc SC PDFVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNo ratings yet
- A220Vautomaticvoltagestablizer PDFDocument11 pagesA220Vautomaticvoltagestablizer PDFBhaveen Reddy100% (1)
- Green University of Bangladesh: Faculty of Science and EngineeringDocument3 pagesGreen University of Bangladesh: Faculty of Science and EngineeringHaytham KenwayNo ratings yet
- Machine Lab Manuals Final Modified On 12-2-2019Document67 pagesMachine Lab Manuals Final Modified On 12-2-2019Danyal NasirNo ratings yet
- (EE-111) Lab File For 2nd Semester: Institute of Engineering and TechonologyDocument22 pages(EE-111) Lab File For 2nd Semester: Institute of Engineering and TechonologyDEVIL WISHER YTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 FormatDocument7 pagesExperiment 2 FormatYency TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument40 pagesBee Lab ManualDk gamingNo ratings yet
- 19bei0067 VL2021220100832 Ast03Document12 pages19bei0067 VL2021220100832 Ast03freeretdocsNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument111 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- Exp 1: OC and SC Test Along With Direct Load Test On A Single Phase TransformerDocument7 pagesExp 1: OC and SC Test Along With Direct Load Test On A Single Phase TransformerSumit KatreNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I29012020Document73 pagesElectrical Machines I29012020fake1542002No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 03 Open Circuit Test For Single Phase TransformerDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 03 Open Circuit Test For Single Phase TransformersheherbanoNo ratings yet
- ELEC313 Lab#2Document6 pagesELEC313 Lab#2Ali MoharramNo ratings yet
- Tests of Single-Phase Transformer: October 2019Document11 pagesTests of Single-Phase Transformer: October 2019Walmy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Network Theory Lab ManualDocument31 pagesNetwork Theory Lab ManualkondraguntajbNo ratings yet
- 2 PN in Reverse BiasDocument18 pages2 PN in Reverse Biasdeathride007No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 For CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 For CircuitsAmir EyniNo ratings yet
- Et101 - Electrical Technology Experiment 2 Part A Topic: Ohm'S Law ObjectivesDocument8 pagesEt101 - Electrical Technology Experiment 2 Part A Topic: Ohm'S Law ObjectivesAugustine JR RobertNo ratings yet
- 1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document82 pages1basic Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21roberto carlos roberto carlosNo ratings yet
- Practicals Machine 2Document30 pagesPracticals Machine 2muhammad waseemNo ratings yet
- (291882886) Et-Lab-ManualDocument31 pages(291882886) Et-Lab-ManualvpzfarisNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 2Document7 pagesExperiment No 2Krishnaa SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.2 Ohm's Law For Linear and Nonlinear Circuit: ObjectDocument6 pagesExperiment No.2 Ohm's Law For Linear and Nonlinear Circuit: ObjectBoss barkatNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Thevenin StevensDocument7 pagesLab 4 Thevenin StevenskarthikhrajvNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.9 Superposition Theorems: ObjectDocument5 pagesExperiment No.9 Superposition Theorems: ObjectMahek ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 3.scott Connection of TransformersDocument3 pages3.scott Connection of Transformerschandrakanth100% (2)
- Superposition and Norton TheoremDocument24 pagesSuperposition and Norton TheoremMahmudul AlamNo ratings yet
- Arya Institute of Engineering Technology and Management Subject: Electrical Measurement Code: 4Ee3A Branch: Electrical EngineeringDocument37 pagesArya Institute of Engineering Technology and Management Subject: Electrical Measurement Code: 4Ee3A Branch: Electrical EngineeringSameer GulshanNo ratings yet
- NT Lab MannualDocument31 pagesNT Lab MannualsagarNo ratings yet
- Pa Practical FileDocument28 pagesPa Practical FilevikasNo ratings yet
- Beeme Imp QuesDocument3 pagesBeeme Imp QuesJitheshNo ratings yet
- Online - Bai 2 - Mach Ban DanDocument15 pagesOnline - Bai 2 - Mach Ban DanThất VọngNo ratings yet
- Routine Tests and MeasurementsDocument14 pagesRoutine Tests and MeasurementsAmr IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Thevenin TheoremDocument8 pagesLab 3 - Thevenin TheoremminhtridtaNo ratings yet
- 22dec - S.E. (Electrical Engineering) NETWORK ANALYSIS - 203147Document24 pages22dec - S.E. (Electrical Engineering) NETWORK ANALYSIS - 203147Chaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Imp Video LinkDocument2 pagesImp Video LinkChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals MCQDocument26 pagesAC Fundamentals MCQChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Expt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande100% (1)
- Expt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 3 - Verification of Reciprocity Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Expt - 2 - Verification of Theveninen's Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 2 - Verification of Theveninen's Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek Deshpande100% (1)
- Expt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsDocument3 pagesExpt - 1 - Verification of Superposition Theorem For Ac CircuitsChaitanya Vivek DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Modbus TCP Client V90 enDocument74 pagesModbus TCP Client V90 enGrant Douglas100% (1)
- 1920 Meng Aerospace Electronic Engineering With Industrial Studies 7012Document16 pages1920 Meng Aerospace Electronic Engineering With Industrial Studies 7012muhammad_andinovaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingDocument4 pagesCircuit Switching and Packet SwitchingAwais ShoukatNo ratings yet
- 08 - Parts List 8kV 400HDocument1 page08 - Parts List 8kV 400HHamilton GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Electrical StudentDocument2 pagesElectrical StudentNoel BrhaneNo ratings yet
- 0615 HSBC Initiate On ABF Substrate Sector - As Good As It Gets 3037 TP 170 3189 TP 145 8046 TP 280Document29 pages0615 HSBC Initiate On ABF Substrate Sector - As Good As It Gets 3037 TP 170 3189 TP 145 8046 TP 280Deron LaiNo ratings yet
- 2017 Summer Camp Day4 Part1Document34 pages2017 Summer Camp Day4 Part1gusatNo ratings yet
- 2 - Detection of Digital SignalsDocument19 pages2 - Detection of Digital Signalsتُحف العقولNo ratings yet
- CR ECE Unit 5Document22 pagesCR ECE Unit 5deepas dineshNo ratings yet
- Footprint Naming Convention - Surface MountDocument2 pagesFootprint Naming Convention - Surface MountNeneFINo ratings yet
- Eee Mid 2 Civil IibDocument3 pagesEee Mid 2 Civil IibChintamaneni VijayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: Microwave ComponenetsDocument238 pagesUnit-I: Microwave Componenetspradnya patilNo ratings yet
- VOM Measurement AnalogDocument23 pagesVOM Measurement AnalogMark Philip MarananNo ratings yet
- To Study The Colour Coding of Resistors.Document6 pagesTo Study The Colour Coding of Resistors.Tanzeel UR Rehman0% (1)
- PDH DFE1000 BrochureDocument2 pagesPDH DFE1000 Brochuremajdi1985No ratings yet
- Dabic-5 8-Bit Serial Input Latched Sink Drivers: Description Features and BenefitsDocument8 pagesDabic-5 8-Bit Serial Input Latched Sink Drivers: Description Features and BenefitsMaherNo ratings yet
- Max3080 Max3089Document21 pagesMax3080 Max3089Peter BirdNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language: Overview!: Jennifer Rexford!Document34 pagesAssembly Language: Overview!: Jennifer Rexford!IrishJaneBayotlangWabe100% (1)
- Pe 26 Ee17Document23 pagesPe 26 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Sony Service Manual KV-28WF1xDocument8 pagesSony Service Manual KV-28WF1xTom DickHarryNo ratings yet
- Calibrating A Thermistor CourseworkDocument8 pagesCalibrating A Thermistor Courseworkafjwduenevzdaa100% (2)
- Datasheet 2Document36 pagesDatasheet 2huicholeNo ratings yet
- Cable Fault Locators Easyflex Cable Fault LocatorsDocument1 pageCable Fault Locators Easyflex Cable Fault LocatorsJacek GorączkowskiNo ratings yet
- Datalogic Mémor10Document188 pagesDatalogic Mémor10Jérôme SCHIFFMACHERNo ratings yet
- UA Tech Rider 2018 PDFDocument4 pagesUA Tech Rider 2018 PDFAritra RoyNo ratings yet
- Stick DiagramDocument72 pagesStick DiagramBhanu Bond0% (1)
- ION-M DAS CommissioningDocument23 pagesION-M DAS CommissioningroybutcherNo ratings yet
- AL-74339 Revision AADocument2 pagesAL-74339 Revision AAamahNo ratings yet
- IEEE - IEC - Comparison-OLD of Power TransformerDocument8 pagesIEEE - IEC - Comparison-OLD of Power TransformerJohn Philip ErquizaNo ratings yet
- Infowave PresentationDocument51 pagesInfowave Presentationapi-3807282No ratings yet