Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat-Sink Compound/ Thermal Foam/ Tightening Torque
Heat-Sink Compound/ Thermal Foam/ Tightening Torque
Uploaded by
Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat-Sink Compound/ Thermal Foam/ Tightening Torque
Heat-Sink Compound/ Thermal Foam/ Tightening Torque
Uploaded by
Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat-Sink compound/ Thermal Foam/ Tightening Torque
Heat-sink Compound/ Thermal Grease / Thermal paste are materials that are applied between the
interface of two components to fill up any gaps, ensure smooth contact and allow heat transfer to
occur efficiently. These compounds are thermally conductive but electrically isolating.
Electronic packaging and heat-sink may seemingly have smooth surfaces. However, if one was to
look at them microscopically than surface roughness become apparent. The surface roughness has
ridges and troughs which cause gaps between the two mating surfaces. These gaps are filled up with
air, which is a poor conductor of heat. Therefore, to eliminate these tiny gaps, thermal paste is used.
The thickness of the thermal layer is in the order of microns. A layer of up to 200 microns in the
industrial practice is considered thick.
There are a variety of thermal pastes available. Some have better thermal conductivity than others.
Thermal conductivity depends upon the filler material. The filler materials include particles of
Aluminium oxide, Boron Nitride, Zinc Oxide etc. The higher the amount of filler particles in the base
matrix or the base paste, the higher will be the thermal conductivity. Thermal compounds are
available in thermal conductivity values of 0.8 W/mK to 4.5 W/mK.
The higher thermal conductivity value thermal compounds i.e. 4-8 W/mk normally utilize Silver
nano- particles and are slightly more expensive. Artic Silver 5 is an example of Silver based thermal
paste.
It should be noted that the higher quantity of filler material, the more electrical impedance is
reduced. Furthermore, it becomes difficult to achieve smaller thickness of the thermal paste layer.
Most of the thermal pastes don’t have adhesive quality and therefore the contact pressure has to be
established by means of a clamp or screw etc.
Some thermal compounds require curing time. i.e. They need certain amount of time before they
are fully set to provide best heat transfer. The curing time can be in the order of hours. Other
compounds can be used straight away.
Thermal Foams and Thermal pads are also available that provide the same functionality. They are
less expensive than thermal paste but are also less efficient. Thermal pads allow a certain degree of
compressibility. The advantage is that the foams can be reused if the electronics assembly is
disassembled. Whereas, most thermal pastes solidify and cannot be reused in case of re-assembly.
To maintain a smooth constant, not only thermal compounds are required but also certain amount
of force. The higher the pressure, the better the contact and the lower the interface resistance.
However, there is a limit to how much force can be applied because too much force can also damage
the material. Therefore for most for electronic devices that need to be connected to a heat-sink, the
tightening torque rating is specified.
You might also like
- Principles of Heat Transfer 8th Edition Kreith Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Heat Transfer 8th Edition Kreith Solutions ManualBrianJimenezanco95% (42)
- PD Cen TR 12831-2-2017 PDFDocument34 pagesPD Cen TR 12831-2-2017 PDFMaiDuy100% (2)
- nRF52840 PS v1.5Document631 pagesnRF52840 PS v1.5Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- AMO UWB Module (SR150) : Amosense Co., LTDDocument19 pagesAMO UWB Module (SR150) : Amosense Co., LTDBenyamin Farzaneh Aghajarie100% (1)
- Bs-En 14879-6 - 2009Document56 pagesBs-En 14879-6 - 2009Patricio G. ArrienNo ratings yet
- Lesson 30. Thermoplastic and Thermosetting PolymersDocument11 pagesLesson 30. Thermoplastic and Thermosetting PolymersNizar AbrorNo ratings yet
- Materials and Processes Used For The Manufacturing of Modern Aircraft BrakesDocument9 pagesMaterials and Processes Used For The Manufacturing of Modern Aircraft BrakesZeashaan AkhmedNo ratings yet
- Overview of Refractory MaterialsDocument54 pagesOverview of Refractory MaterialsHenrique Alvr100% (5)
- When Glass meets Pharma: Insights about glass as primary packaging materialFrom EverandWhen Glass meets Pharma: Insights about glass as primary packaging materialNo ratings yet
- Thermal Management of Electronics DevicesDocument4 pagesThermal Management of Electronics Devicesrpselvakumar2008No ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of Thermal Interface MaterialsDocument10 pagesThermal Conductivity of Thermal Interface MaterialsShrestha RishavNo ratings yet
- Resistance Spot WeldingreportDocument12 pagesResistance Spot WeldingreportajaykumarnsitNo ratings yet
- White Paper ACF Bonding Technology 01 2015Document6 pagesWhite Paper ACF Bonding Technology 01 2015RUBEN D. MARIN G.No ratings yet
- 2003 Potting Hillman-BaylakogluDocument9 pages2003 Potting Hillman-BaylakogluVansala GanesanNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument7 pagesPowerKOFI BROWNNo ratings yet
- Artikel TPD 1Document24 pagesArtikel TPD 1anndri wahyuNo ratings yet
- 470F Th-Mech Tutorial PDFDocument5 pages470F Th-Mech Tutorial PDFschmidtsteve7No ratings yet
- RF Sealing TheoryDocument3 pagesRF Sealing Theorykirandasi123No ratings yet
- How To Choose The Right Thermal Interface Materials Types Compounds and Specifications - Tape InnovationsDocument4 pagesHow To Choose The Right Thermal Interface Materials Types Compounds and Specifications - Tape InnovationsAXOX Web SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Gasket Application and Material Selection GuideDocument10 pagesGasket Application and Material Selection GuideTieu KakaNo ratings yet
- Refractories & Insulators UNIT-VIDocument4 pagesRefractories & Insulators UNIT-VIchemistrymasterNo ratings yet
- 2-Final Project ReportDocument134 pages2-Final Project ReportAbhimanyu RanaNo ratings yet
- Nanostructured Fumed Metal Oxides For Thermal Interface PastesDocument12 pagesNanostructured Fumed Metal Oxides For Thermal Interface Pastes3 éme infraNo ratings yet
- 2002 57 ZakDocument8 pages2002 57 ZakAhmet ErecekNo ratings yet
- Cure Matters - Epo-TekDocument4 pagesCure Matters - Epo-TekCelia ThomasNo ratings yet
- Thermal Spray in CFBC BoilerDocument12 pagesThermal Spray in CFBC Boilerssheart_mindNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Sintering Parameter To The Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Cusic Composite For Electronic Packaging ApplicationDocument24 pagesThe Effects of Sintering Parameter To The Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Cusic Composite For Electronic Packaging Applicationshareen tanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Interfacial Materials (Tims) Are Thermally Conductive Materials, Which Are Applied ToDocument24 pagesThermal Interfacial Materials (Tims) Are Thermally Conductive Materials, Which Are Applied ToEllen Kay CacatianNo ratings yet
- PISTONDocument53 pagesPISTONJPPL CHENNAINo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements of Alloys: High-Temperature Strength. The Most Highly StressedDocument11 pagesChemical Elements of Alloys: High-Temperature Strength. The Most Highly StressedalexanderNo ratings yet
- Electronic Materials and Components-Die Bonding MaterialsDocument23 pagesElectronic Materials and Components-Die Bonding MaterialsYue KaiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Barrier Coatings: Seminar Mid Report OnDocument6 pagesThermal Barrier Coatings: Seminar Mid Report OnGanesh NandgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Barrier CoatingDocument16 pagesThermal Barrier CoatingSham Sundar100% (1)
- Question and Answers From Web Seminar: Heatsink 201: Even More About Heatsink DesignDocument10 pagesQuestion and Answers From Web Seminar: Heatsink 201: Even More About Heatsink DesignooqqNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy: F. NashDocument4 pagesPowder Metallurgy: F. NashGouthama KgNo ratings yet
- Plastic WeldingDocument16 pagesPlastic WeldingSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Easa Dgca Module 6Document276 pagesEasa Dgca Module 6kunnann50% (2)
- " Thermal Barrier CoatingDocument6 pages" Thermal Barrier CoatingMohamed AmerNo ratings yet
- SolderingDocument7 pagesSolderingjitendrakitawatNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 AmDocument15 pagesUnit-2 AmSaisurendra VeerlaNo ratings yet
- Heating Element ArticleDocument10 pagesHeating Element ArticleFrea Kent-Dazze D'DrughiNo ratings yet
- Offgrid Rocketstove SweDocument12 pagesOffgrid Rocketstove SwePók hokuszNo ratings yet
- Common Fault Analysis and Solution of ThermocoupleDocument15 pagesCommon Fault Analysis and Solution of ThermocoupleYiDan LiNo ratings yet
- Au/Sn Solder Alloy and Its Applications in Electronics PackagingDocument7 pagesAu/Sn Solder Alloy and Its Applications in Electronics PackagingTeguh Yassi Akasyah PutraNo ratings yet
- Thesis FinalDocument56 pagesThesis Final제너No ratings yet
- Quality Resistance Welding Solutions: Defining The Optimum ProcessDocument10 pagesQuality Resistance Welding Solutions: Defining The Optimum ProcessIsaque PedroNo ratings yet
- Findings (MAT SC)Document4 pagesFindings (MAT SC)silent spritsNo ratings yet
- Polymer: Auguste TrillatDocument8 pagesPolymer: Auguste TrillatMarvin LabajoNo ratings yet
- Joining of PlasticsDocument39 pagesJoining of PlasticsLakshmanan VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Lab D Heat FluxDocument3 pagesLab D Heat FluxSam ShakilNo ratings yet
- Plastic - Joining ProcessesDocument12 pagesPlastic - Joining Processesaditya chouhanNo ratings yet
- P/N Joining Processes, Materials and TechniquesDocument19 pagesP/N Joining Processes, Materials and TechniquesChristian Contreras ArdilesNo ratings yet
- Joint Design - Lap Joints Are Always Preferred Over Butt Designs. When Using A Lap Joint The Amount of Overlap IsDocument11 pagesJoint Design - Lap Joints Are Always Preferred Over Butt Designs. When Using A Lap Joint The Amount of Overlap IsMuhammad AdilNo ratings yet
- All About The Design of HeatsinksDocument40 pagesAll About The Design of Heatsinks조용규No ratings yet
- How Long Should My Thermocouple Last - 2020-03-12 - Industrial HeatingDocument4 pagesHow Long Should My Thermocouple Last - 2020-03-12 - Industrial HeatingTS WongNo ratings yet
- VORTEX Powder Coating For Conductor Insulation of Transformer WindingsDocument4 pagesVORTEX Powder Coating For Conductor Insulation of Transformer WindingsYogesh ChadawatNo ratings yet
- Thermal BondingDocument27 pagesThermal BondingRıdvan ÇıngarNo ratings yet
- Soldering Electronic Components 2nd EditionFrom EverandSoldering Electronic Components 2nd EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Self-healing Ceramic Matrix Composites: A MonographFrom EverandSelf-healing Ceramic Matrix Composites: A MonographNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual of Glass-BlowingFrom EverandLaboratory Manual of Glass-BlowingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Art of Lead Burning: A practical treatise explaining the apparatus and processesFrom EverandThe Art of Lead Burning: A practical treatise explaining the apparatus and processesNo ratings yet
- App PCB Environment v1Document10 pagesApp PCB Environment v1Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- App PolarDocument5 pagesApp PolarBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- En 528035Document31 pagesEn 528035Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Ipc Standard PCB Library Expert Changelogs 2016Document12 pagesIpc Standard PCB Library Expert Changelogs 2016Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- 06 Library Dokumentation v2.0 enDocument13 pages06 Library Dokumentation v2.0 enBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- 07 FAQ v2.0 enDocument4 pages07 FAQ v2.0 enBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2006 027 PDFDocument25 pagesPresentation 2006 027 PDFBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- NXP 8mpluslpd4-Evk QSDocument12 pagesNXP 8mpluslpd4-Evk QSBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Altium To q3d 2020Document8 pagesTutorial Altium To q3d 2020Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- IPC 7351 Pad Stack Naming Convention - 2039898Document6 pagesIPC 7351 Pad Stack Naming Convention - 2039898Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Switched Mode Power SupplyDocument54 pagesSwitched Mode Power SupplyBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Layer 1 Microvia Layer and PTH Nominal Thickness 2 Microvia Layer and PTH 3 Microvia Layer and PTHDocument10 pagesLayer 1 Microvia Layer and PTH Nominal Thickness 2 Microvia Layer and PTH 3 Microvia Layer and PTHBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Plug & Trust Secure Element: Rev. 1.2 - 15 December 2020 Product Data Sheet 577312Document36 pagesPlug & Trust Secure Element: Rev. 1.2 - 15 December 2020 Product Data Sheet 577312Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Five Via-In-Pad Myths: by Duane Benson, Screaming Circuits Marketing ManagerDocument4 pagesFive Via-In-Pad Myths: by Duane Benson, Screaming Circuits Marketing ManagerBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Ces UserDocument445 pagesCes UserBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- LDFO SiP For Wearables IoT With Hetrogeneous IntegrationDocument6 pagesLDFO SiP For Wearables IoT With Hetrogeneous IntegrationBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Dram Controller: Mahdi Nazm BojnordiDocument28 pagesDram Controller: Mahdi Nazm BojnordiBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Ipc 2226Document63 pagesIpc 2226Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Ventec: Professional Manufacturer in Copper Clad LaminatesDocument3 pagesVentec: Professional Manufacturer in Copper Clad LaminatesBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Main Memory System: Mahdi Nazm BojnordiDocument28 pagesMain Memory System: Mahdi Nazm BojnordiBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- BGA Breakout Challenges: by Charles Pfeil, Mentor GraphicsDocument4 pagesBGA Breakout Challenges: by Charles Pfeil, Mentor GraphicsBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Mentor InstroductionDocument200 pagesMentor InstroductionBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Generic Exception CapabilitiesDocument3 pagesGeneric Exception CapabilitiesBenyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
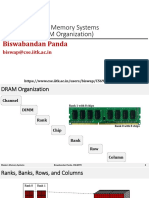
- CS698Y: Modern Memory Systems Lecture-15 (DRAM Organization)Document18 pagesCS698Y: Modern Memory Systems Lecture-15 (DRAM Organization)Benyamin Farzaneh AghajarieNo ratings yet
- Unigraphics NX7.5 - Thermal and Flow AnalysisDocument68 pagesUnigraphics NX7.5 - Thermal and Flow AnalysisBikash Chandra SahooNo ratings yet
- Vitrified Ceramic Materials For Electrical Applications: Standard Test Methods ForDocument5 pagesVitrified Ceramic Materials For Electrical Applications: Standard Test Methods ForRaheelaNo ratings yet
- 17chp06 Process Heat Transfer LabDocument50 pages17chp06 Process Heat Transfer LabpandianvijaybharathiNo ratings yet
- Rotational Flow and Thermal Behavior of Ternary Hybrid Nanomaterials at Small and High Prandtl NumbersDocument17 pagesRotational Flow and Thermal Behavior of Ternary Hybrid Nanomaterials at Small and High Prandtl NumbersprakashjayavelNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: A. Eri, M. Komatina, S. Nemoda, D. Daki, B. RepiDocument9 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: A. Eri, M. Komatina, S. Nemoda, D. Daki, B. RepiViona WidyaNo ratings yet
- Second Edition COSMOS/M 2.0 October 1998Document78 pagesSecond Edition COSMOS/M 2.0 October 1998amokhtaNo ratings yet
- MEC 321 Heat Transfer: Dr. Mohamed Salem ElmnefiDocument13 pagesMEC 321 Heat Transfer: Dr. Mohamed Salem ElmnefiAnonim KopyacıNo ratings yet
- HVAC For Course2Document251 pagesHVAC For Course2Anwar Pariyarath0% (1)
- Calculation of Insulation Thickness For Pipes The Piping Engineering WorldDocument3 pagesCalculation of Insulation Thickness For Pipes The Piping Engineering WorldEddie FongNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of BadDocument3 pagesThermal Conductivity of BadJinorri WilsonNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem Mech Mid Sem Question Bank-1Document14 pages6th Sem Mech Mid Sem Question Bank-1dharmeshNo ratings yet
- Heat NotesDocument216 pagesHeat NotesSaswata Pradhan100% (1)
- COMSOL Introduction ConductionDocument15 pagesCOMSOL Introduction ConductionPatcharapit PromoppatumNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab Experiment Report PDFDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Lab Experiment Report PDFNasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Distortion Control MethodsDocument36 pagesDistortion Control Methodsbmkramesh100% (4)
- Composites: Part B: Chih-Chun Teng, Chen-Chi M. Ma, Kuo-Chan Chiou, Tzong-Ming LeeDocument7 pagesComposites: Part B: Chih-Chun Teng, Chen-Chi M. Ma, Kuo-Chan Chiou, Tzong-Ming LeeamirswtNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Sahimi Heterogeneous Materials I LineaDocument793 pagesMuhammad Sahimi Heterogeneous Materials I LineadashatanliNo ratings yet
- Process Heat TransferDocument327 pagesProcess Heat TransferMartin ZaballaNo ratings yet
- Feap Training ManualDocument203 pagesFeap Training ManualGiorgio ZavariseNo ratings yet
- Thermal PropertiesDocument26 pagesThermal PropertiesChandrahas NarraNo ratings yet
- HMT 2marksDocument85 pagesHMT 2marksyogesh sNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Long AnswerDocument32 pagesHeat Transfer Long Answerdipzbarma5No ratings yet
- Tutorial Material Data InputDocument6 pagesTutorial Material Data InputJavier TrujillanoNo ratings yet
- Two Dim HEDocument25 pagesTwo Dim HEAbhiyanNo ratings yet
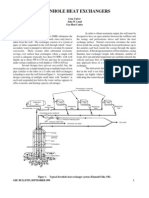
- Down Hole Heat Ex ChangersDocument11 pagesDown Hole Heat Ex ChangersSaudah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument45 pagesSteam Tablesabdalfadel younisNo ratings yet
- Designation: E2113 09Document5 pagesDesignation: E2113 09Lupita RamirezNo ratings yet