Professional Documents
Culture Documents
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
585 viewsAcute Pain Osteosarcoma
Acute Pain Osteosarcoma
Uploaded by
Maryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzThe patient presented with acute right knee pain from bone cancer, with a pain score of 8/10. The pain has both nociceptive and neuropathic components due to tissue damage and nerve injury from the cancer. The plan is for the nurse to assess the patient's pain level, provide comfort measures like heat/cold therapy, encourage rest and hydration, and administer analgesics to reduce the patient's pain score and increase daily activities over 3 days and 3 weeks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Week 8: Ecotourism in The PhilippinesDocument35 pagesWeek 8: Ecotourism in The Philippinesbea krysleen tulio90% (10)
- NCP LymphedemaDocument1 pageNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDocument1 pagePatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (2)
- Spinal Injury Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesSpinal Injury Nursing Care PlanPatricia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileNo ratings yet
- The Real Science Behind Why The COVID Vaccines Are Destroying Organ Function - Dangers of The Spike ProteinDocument40 pagesThe Real Science Behind Why The COVID Vaccines Are Destroying Organ Function - Dangers of The Spike ProteinMara Rebeka Herzog100% (7)
- Why Join PNADocument2 pagesWhy Join PNADarren CariñoNo ratings yet
- I Ching TesseractDocument14 pagesI Ching Tesseractthoth11100% (1)
- NCP Icu-CcuDocument6 pagesNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainDyanne B100% (1)
- Self Care DeficitDocument1 pageSelf Care DeficitPaul Edmer Corcuera RN100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationeihjay-bravo-8041No ratings yet
- Learning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationDocument9 pagesLearning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationNYCA GRACIA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Care DeficitAddie Labitad100% (2)
- NCP BkaDocument4 pagesNCP BkaKeeshia CesnerosNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPyasayayasay yasayNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterAnonymous NZTQVgjaNo ratings yet
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Post-Thyroidectomy FdarDocument1 pagePost-Thyroidectomy FdarKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument3 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNNo ratings yet
- Date Time Focus D-Ata A-Ction R-Esponse D - Patient Verbalized "Sakit Kaau Akong TotoyDocument1 pageDate Time Focus D-Ata A-Ction R-Esponse D - Patient Verbalized "Sakit Kaau Akong TotoyKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Mold: PurposeDocument3 pagesPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- (NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2Document2 pages(NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2roren100% (1)
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Khaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionDocument4 pagesKhaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPnictan 140% (1)
- NCP AlteredDocument3 pagesNCP AlteredShaira TillahNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- NCP - Patient With Endotracheal TubeDocument1 pageNCP - Patient With Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesSubjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermCamille SesaldoNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoDocument1 pageASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceRheegell Ellar-Fuertes50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan DyspneaDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan DyspneaMae JavierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceAce Dioso TubascoNo ratings yet
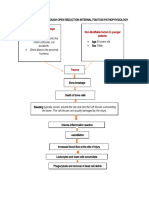
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaDocument1 pageFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Betty Knight's "6F S": FluidsDocument1 pageBetty Knight's "6F S": FluidsESTHER OGODONo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To InjuryDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To InjuryErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNo ratings yet
- NCP For Cervical SpondylosisDocument3 pagesNCP For Cervical Spondylosishannah0% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NCP OsteosarcomaDocument1 pageNCP OsteosarcomaDarylle Hannah De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanice SolamilloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NFc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- OA NCPDocument5 pagesOA NCPsnow.parconNo ratings yet
- Carry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Document8 pagesCarry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Yosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Types and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointDocument3 pagesTypes and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization (EPI) DiseasesDocument12 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization (EPI) DiseasesMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument302 pagesFractureMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Buerger'S Disease: By: Hsu, Hsin-Tan TDocument15 pagesBuerger'S Disease: By: Hsu, Hsin-Tan TMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: By: Glowsy CabralDocument29 pagesOsteomyelitis: By: Glowsy CabralMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus: by Limytch DiazDocument23 pagesHerniated Nucleus Pulposus: by Limytch DiazMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- FRACTUREDocument52 pagesFRACTUREMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue Neoplasms: Mark OlivaDocument33 pagesBone Tissue Neoplasms: Mark OlivaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Series & Parallel PumpsDocument48 pagesSeries & Parallel PumpsMoh AmmNo ratings yet
- 2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmDocument17 pages2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmForu MophiliaNo ratings yet
- Waray PeopleDocument15 pagesWaray PeopleJackie Carlo C. QuilacioNo ratings yet
- XII BIOLOGY Practical 2023-24 NewDocument28 pagesXII BIOLOGY Practical 2023-24 Newpranjal.goswami1830No ratings yet
- Taper Grid H Couplings Range - 2013 PDFDocument1 pageTaper Grid H Couplings Range - 2013 PDFAndres GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDocument24 pages06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- Civil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Document1 pageCivil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Joel AganNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document50 pagesChap 002Eduardo AndradersNo ratings yet
- Axiata Digital Business - Advancing AsiaDocument12 pagesAxiata Digital Business - Advancing AsiaAxiata Group Berhad100% (1)
- Astm D1193Document6 pagesAstm D1193eaarizac100% (7)
- Kantar Worldpanel 5 Key FMCG Trends in Vietnam 2023 ENDocument25 pagesKantar Worldpanel 5 Key FMCG Trends in Vietnam 2023 ENbrianNo ratings yet
- We Were Something DontDocument6 pagesWe Were Something DontmrycovcvzalvwkofgnNo ratings yet
- ARC VisionDocument2 pagesARC VisionmelvincabeNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation: Mark L. Palmeri, M.D., Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering Duke UniversityDocument50 pagesUltrasound Beamforming and Image Formation: Mark L. Palmeri, M.D., Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering Duke UniversitydeepberaNo ratings yet
- TPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3Document88 pagesTPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3DeniMestiWidiantoNo ratings yet
- Test 6Document33 pagesTest 6Балнур АмантайNo ratings yet
- First of All Praise and Gratitude To The Presence of Allah SWTDocument2 pagesFirst of All Praise and Gratitude To The Presence of Allah SWTMuhammad Firmal KusyandiNo ratings yet
- Fault Level CalculationDocument1 pageFault Level Calculationpb21No ratings yet
- Shining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orDocument1,016 pagesShining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orbatiyeNo ratings yet
- "7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofDocument29 pages"7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofOliver Dennis100% (1)
- AppendixDocument5 pagesAppendixAsim IqbalNo ratings yet
- Be The Medicine Latest Version 20-05-2016Document29 pagesBe The Medicine Latest Version 20-05-2016nedux100% (1)
- Obstructive Renal Cyst in A Dog - Ultrasonography-GuidedTreatment Using Puncture Aspiration and Injectionwith 95% EthanolDocument3 pagesObstructive Renal Cyst in A Dog - Ultrasonography-GuidedTreatment Using Puncture Aspiration and Injectionwith 95% EthanolIngrid RamisaNo ratings yet
- 2N60 PDFDocument7 pages2N60 PDFFady HachemNo ratings yet
- Delegate List - 10th IMRC With Contact Details - Removed (1) - RemovedDocument234 pagesDelegate List - 10th IMRC With Contact Details - Removed (1) - RemovedSharon SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares y RegularesDocument2 pagesVerbos Irregulares y RegularesFernando MoraNo ratings yet
- Aip 2023 2 3Document29 pagesAip 2023 2 3menchiemanaloNo ratings yet
Acute Pain Osteosarcoma
Acute Pain Osteosarcoma
Uploaded by
Maryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
585 views8 pagesThe patient presented with acute right knee pain from bone cancer, with a pain score of 8/10. The pain has both nociceptive and neuropathic components due to tissue damage and nerve injury from the cancer. The plan is for the nurse to assess the patient's pain level, provide comfort measures like heat/cold therapy, encourage rest and hydration, and administer analgesics to reduce the patient's pain score and increase daily activities over 3 days and 3 weeks.
Original Description:
nursing
Original Title
ACUTE PAIN OSTEOSARCOMA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient presented with acute right knee pain from bone cancer, with a pain score of 8/10. The pain has both nociceptive and neuropathic components due to tissue damage and nerve injury from the cancer. The plan is for the nurse to assess the patient's pain level, provide comfort measures like heat/cold therapy, encourage rest and hydration, and administer analgesics to reduce the patient's pain score and increase daily activities over 3 days and 3 weeks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
585 views8 pagesAcute Pain Osteosarcoma
Acute Pain Osteosarcoma
Uploaded by
Maryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzThe patient presented with acute right knee pain from bone cancer, with a pain score of 8/10. The pain has both nociceptive and neuropathic components due to tissue damage and nerve injury from the cancer. The plan is for the nurse to assess the patient's pain level, provide comfort measures like heat/cold therapy, encourage rest and hydration, and administer analgesics to reduce the patient's pain score and increase daily activities over 3 days and 3 weeks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
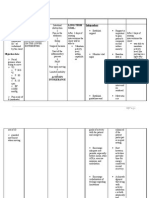
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING IMPLEMENTATION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective Data: Acute Pain There is both a Independent: GOAL MET
related to tissue nociceptive and Measuring pain enables
“Masakit po yung trauma and neuropathic Short term: 1. Assess pain score of the the nurse to assess the Short term:
tuhod ko hanggang effects of cancer component of patient every two hourly amount of pain the patient
sa may bukung- secondary to bone cancer pain. After 3 hours of and on need basis is experiencing. After 3 hours of
bukong. Sobrang disease process nursing interventions, nursing interventio
sakit po para akong as evidenced by The nociceptive the patient will to: 2. Assess muscle strength, Changes or limitation in the patient was ab
kinu-kuryente.” As patient’s pain component is gross and fine motor strength and coordination to:
verbalized by the score 8/10 and caused by bone- Verbalize coordination. serve as an identifier for
patient altered vital destroying decrease of pain and metastasis Verbalize
signs. osteoclasts, and pain from 8/10 decrease of
Objective Data: mechanical to 6/10. Using 3. Provide preventive pain from 8
destabilization the pain scale measures such as Primary function is to to 6/10. Usi
Presented to and fracture of of 0-3 as mild, pillows for cushion and provide direct support for the pain sca
the hospital the bone. 4-6 as support. the affected area and to of 0-3 as m
with right moderate, and minimize pressure. 4-6 as
knee pain The neuropathic 7-10 as severe moderate, a
Patient’s pain component is pain. 7-10 as sev
score 8/10 (10 induced by tumor 4. Provide comfort Pressure, warmth, or cold pain.
being the cell growth which measure such as back is used on the skin, while
highest, 1 injures and Long term: rub or hot or cold the feeling of pain is Long term:
being the destroys the application lessened or blocked.
lowest) distal ends of After 3 days of These can also be used to After 3 days of
Pain on nerve fibers that nursing interventions, stimulate the skin. These nursing interventio
resisted normally the patient will report: techniques also change the patient will rep
flexion and innervate the the flow of blood to the
extension bone. Progressive area that’s stimulated that Progressive decrea
Pain on active decrease may lessen pain during in pain score with
or passive In bone cancer in pain score the stimulation and for increase in activitie
range of pain there is with an hours after it’s finished. of daily living
motion of the frequently a increase in After 3 days of
right ankle peripheral and activities of nursing interventio
Light palpation central daily living. the patient was ab
to the sensitization to report:
proximal fibula resulting in
and tibia primary Progressive
resulted in hyperalgesia 5. Provide quiet To prevent or lessen pain. decrease
severe pain environment and calm in pain scor
VS as follows: activities. with an
increase in
T= 36.9 6. Encourage the patient to Proper hydration can help activities of
PR= 100 increase fluid intake. reduce pain and protect daily living
RR= 24 your joints and muscles by
BP=100/70 keeping the cartilage soft
and pliable. Dehydration
pulls fluid out of your
tissues, which causes
overall body aches and
pain.
7. Teach deep breathing to lessen tension, reduce
exercise and relaxation anxiety, and manage pain
techniques.
Distraction may be used
8. Encourage mind alone to manage mild pain
diversion therapies or used with medicine to
manage brief bouts of
severe pain, such as pain
related to procedures
9. Encourage rest periods Sleep or rest periods, give
to prevent fatigue. more energy, make pt.
less tired, reduce anxiety,
and help other pain-relief
methods work better
Dependent:
1. Administer analgesics as Pain management using
indicated to maximal pharmacologic methods is
dose as ordered. vital in cancer therapy
2. Administer antiemetic to Pain management using
prevent from the pharmacologic methods is
adverse effects of pain vital in cancer therapy
killers as ordered.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING IMPLEMENTATION RATIONALE EVALUATIO
Subjective: Ineffective Chemotherapy
protection related medications work Short term: Independent Short term:
The client stated, to Impairment of by attacking cells,
primary defense or by preventing After 24 hours of 1. Monitor vital signs Provides knowledge on After 24 hours o
“Minsan po parang secondary to cells from growing nursing every 4 hours or a any sign or symptoms nursing
ang bilis ko manghina Antineoplastic drug and dividing. intervention, the ordered. due to bone marrow intervention, the
at mahingal.” therapy as patient will be able suppression and patient will be a
manifested by Cancer cells tend to to Maintain or immunosuppression to Maintain or
Objective: deficient immunity grow and divide improve resulting from improve
and infections rapidly and body’s defences by: chemotherapy. body’s defences
Previous uncontrollably.
episodes Many Patient will Patient will
of infection chemotherapy maintain an 2. Teach patient and Hand hygiene helps maintain an
Receiving drugs are designed infection free family neutropenic prevent infection infection free
antineoplastic to target this type state during precautions to and prevent transmission state during
therapy of rapid cell growth. shift. perform like of microorganisms. shift.
Large Patient will have handwashing Patient will h
exposure of Chemotherapy no episodes of frequently before no episodes
tissues and treatments can’t active bleeding entering and active bleedi
extensive differentiate during shift. leaving the room. during shift.
dissection between cancer Patient will Patient will
across vascular cells and healthy maintain food 3. Inform parents Prevents a highly maintain foo
distributions. cells resulting in safety and and child to avoid susceptible child to safety and
Weakness harming healthy nutrition during exposure to people acquire an infection. nutrition dur
cells, as well as shift. with upper shift.
cancer cells. respiratory infectio
n or any illness.
These medications Long term: Long term:
slow down the 4. Using of protective Prevents transmission of
body's immune After 3 days of gear such as mask a microorganism to a After 3 days of
system and at the nursing and gown when compromised immune nursing
same time reducing intervention, the appropriate, system during intervention, the
inflammation. patient will be able providing a private chemotherapy patient was be a
to: room, monitor for to:
any signs and
Continue to symptoms of Continued to
maintain an infections. maintain an
infection free infection free
state. state.
5. Monitor affected Suppression of bone
Continue to limb for bleeding, marrow and Continued to
have no inflammation of platelet production have no
episodes of the membranes. places pt. at risk for episodes of
active bleeding spontaneous bleeding. active bleedi
during. during.
Continue to 6. Implement Continued to
maintain food measures to Fragile tissues and maintain foo
safety and prevent tissue altered clotting safety and
nutrition. injury or bleeding. mechanisms increase the nutrition.
risk of haemorrhage
following even minor
trauma.
Dependent:
7. Administer Pharmacologic methods
antineoplastic is vital in cancer therapy
medications as
ordered
Collaborative:
8. Ensure that patient A good, well balanced
is well nourished diet will aid in healing
by collaborating and good immunity.
with a nutritionist Protein placed meals or
for the patinet’s drinks will aid in this.
proper diet. Raw foods often carry
bacteria, which could
cause infection.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING IMPLEMENTATION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent GOAL MET
Short term: Short term:
Subjective data: Impaired physical The tumor causes
After 8 hours of nursing Assess the strength to To provide data on After 24 hours of nursing
“Di ko po nailalakad ang mobility related to decreased movement intervention, the patient perform ROM to all extent of any physical intervention, the patient
right leg ko tska will be able to: joints problems was able to:
musculoskeletal in the affected arm or
nahihirapan po ako Demonstrate Assess the need for To avoid weight Demonstrate
gumalaw.” as verbalized damage as manifested leg or nearby joint. measures to increase assistive devices bearing measures to increase
by the patient mobility Demonstrate use of mobility
by inability to bear Patients may limp
Uses safety measures assistive devices To maintain or Uses safety measures
Objective data: weight on the affected because of a tumor in to minimize potential improve an to minimize potential
for injury individual’s for injury
Xray– showed 5x4x4 cm leg the leg or near the
functioning and
lesion in the proximal
knee. Bones affected Provide a safe independence to Long term:
metaphyseal area of
by osteosarcoma are Long term: environment facilitate participation After 3 days of nursing
the R tibia
After 3 days of nursing Encourage participation and to enhance intervention, the patient
Could not bear weight
weakened, and they intervention, the patient in recreational overall well-being was able to:
on the affected leg
may be more likely to will be able to: activities (watching
Presented with a limp
TV, reading To reduce risk for falls Perform physical
Could not flex more fracture or break. Perform physical newspapers, etc.). activity within limits
than 30 degrees
activity within limits To improve the of disease
actively and passively
of disease Execute active assistive patient's sense of self Minimize
Unable to perform
Minimize ROM exercises to all control and help in complications of
resisted
complications of extremities within reducing social immobility
flexion/extensions
immobility limits of disease isolation.
Active/passive ROM of
Turn and position
the right ankle caused
patient every 2 hours. To maintain muscle
pain
strength
Unable to resist
extension of the toes
To promote circulation
and ankle
and relieve pressure
You might also like
- Week 8: Ecotourism in The PhilippinesDocument35 pagesWeek 8: Ecotourism in The Philippinesbea krysleen tulio90% (10)
- NCP LymphedemaDocument1 pageNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Patriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. YingDocument1 pagePatriarca, Janna Mae H. Nursing Care Plan Client: Mr. Yingjanna mae patriarca100% (2)
- Spinal Injury Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesSpinal Injury Nursing Care PlanPatricia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan (ImpairedphyssicalkuroroexileNo ratings yet
- The Real Science Behind Why The COVID Vaccines Are Destroying Organ Function - Dangers of The Spike ProteinDocument40 pagesThe Real Science Behind Why The COVID Vaccines Are Destroying Organ Function - Dangers of The Spike ProteinMara Rebeka Herzog100% (7)
- Why Join PNADocument2 pagesWhy Join PNADarren CariñoNo ratings yet
- I Ching TesseractDocument14 pagesI Ching Tesseractthoth11100% (1)
- NCP Icu-CcuDocument6 pagesNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasNo ratings yet
- Case IcuDocument5 pagesCase IcuTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainDyanne B100% (1)
- Self Care DeficitDocument1 pageSelf Care DeficitPaul Edmer Corcuera RN100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationeihjay-bravo-8041No ratings yet
- Learning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationDocument9 pagesLearning Guide: Ngeles Niversity OundationNYCA GRACIA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesSelf Care DeficitAddie Labitad100% (2)
- NCP BkaDocument4 pagesNCP BkaKeeshia CesnerosNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPyasayayasay yasayNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Orthopedic Philipine CenterAnonymous NZTQVgjaNo ratings yet
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Post-Thyroidectomy FdarDocument1 pagePost-Thyroidectomy FdarKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument3 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNNo ratings yet
- Date Time Focus D-Ata A-Ction R-Esponse D - Patient Verbalized "Sakit Kaau Akong TotoyDocument1 pageDate Time Focus D-Ata A-Ction R-Esponse D - Patient Verbalized "Sakit Kaau Akong TotoyKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Mold: PurposeDocument3 pagesPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- (NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2Document2 pages(NCPS) Impaired Physical Mobility 2roren100% (1)
- NCM 117 Final Exam MamelDocument16 pagesNCM 117 Final Exam MamelJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Khaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionDocument4 pagesKhaye:: Traction: Is The Act of Pulling or Drawing Which Is Associated With Counter TractionChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPnictan 140% (1)
- NCP AlteredDocument3 pagesNCP AlteredShaira TillahNo ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- NCP - Patient With Endotracheal TubeDocument1 pageNCP - Patient With Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesSubjective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermCamille SesaldoNo ratings yet
- Gout N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageGout N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document3 pagesNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoDocument1 pageASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceRheegell Ellar-Fuertes50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data " GoalJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan DyspneaDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan DyspneaMae JavierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesNCP Activity IntoleranceAce Dioso TubascoNo ratings yet
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaDocument1 pageFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Betty Knight's "6F S": FluidsDocument1 pageBetty Knight's "6F S": FluidsESTHER OGODONo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To InjuryDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Related To InjuryErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNo ratings yet
- NCP For Cervical SpondylosisDocument3 pagesNCP For Cervical Spondylosishannah0% (1)
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NCP OsteosarcomaDocument1 pageNCP OsteosarcomaDarylle Hannah De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanice SolamilloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NFc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- OA NCPDocument5 pagesOA NCPsnow.parconNo ratings yet
- Carry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Document8 pagesCarry Out The Doctor's Order (E.g. Kardex, Meds Chart, Tickets)Yosef OxinioNo ratings yet
- Types and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointDocument3 pagesTypes and Causes of Medication Errors From A Nurse'S ViewpointMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Expanded Program On Immunization (EPI) DiseasesDocument12 pagesExpanded Program On Immunization (EPI) DiseasesMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument302 pagesFractureMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Buerger'S Disease: By: Hsu, Hsin-Tan TDocument15 pagesBuerger'S Disease: By: Hsu, Hsin-Tan TMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: By: Glowsy CabralDocument29 pagesOsteomyelitis: By: Glowsy CabralMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus: by Limytch DiazDocument23 pagesHerniated Nucleus Pulposus: by Limytch DiazMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- FRACTUREDocument52 pagesFRACTUREMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue Neoplasms: Mark OlivaDocument33 pagesBone Tissue Neoplasms: Mark OlivaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Series & Parallel PumpsDocument48 pagesSeries & Parallel PumpsMoh AmmNo ratings yet
- 2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmDocument17 pages2G Cluster Optimization Acceptance Report Revised - 20171225pmForu MophiliaNo ratings yet
- Waray PeopleDocument15 pagesWaray PeopleJackie Carlo C. QuilacioNo ratings yet
- XII BIOLOGY Practical 2023-24 NewDocument28 pagesXII BIOLOGY Practical 2023-24 Newpranjal.goswami1830No ratings yet
- Taper Grid H Couplings Range - 2013 PDFDocument1 pageTaper Grid H Couplings Range - 2013 PDFAndres GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDocument24 pages06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- Civil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Document1 pageCivil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Joel AganNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document50 pagesChap 002Eduardo AndradersNo ratings yet
- Axiata Digital Business - Advancing AsiaDocument12 pagesAxiata Digital Business - Advancing AsiaAxiata Group Berhad100% (1)
- Astm D1193Document6 pagesAstm D1193eaarizac100% (7)
- Kantar Worldpanel 5 Key FMCG Trends in Vietnam 2023 ENDocument25 pagesKantar Worldpanel 5 Key FMCG Trends in Vietnam 2023 ENbrianNo ratings yet
- We Were Something DontDocument6 pagesWe Were Something DontmrycovcvzalvwkofgnNo ratings yet
- ARC VisionDocument2 pagesARC VisionmelvincabeNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation: Mark L. Palmeri, M.D., Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering Duke UniversityDocument50 pagesUltrasound Beamforming and Image Formation: Mark L. Palmeri, M.D., Ph.D. Biomedical Engineering Duke UniversitydeepberaNo ratings yet
- TPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3Document88 pagesTPC-1071H - 1271H - 1571H - 1771H - User Manual - Ed3DeniMestiWidiantoNo ratings yet
- Test 6Document33 pagesTest 6Балнур АмантайNo ratings yet
- First of All Praise and Gratitude To The Presence of Allah SWTDocument2 pagesFirst of All Praise and Gratitude To The Presence of Allah SWTMuhammad Firmal KusyandiNo ratings yet
- Fault Level CalculationDocument1 pageFault Level Calculationpb21No ratings yet
- Shining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orDocument1,016 pagesShining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orbatiyeNo ratings yet
- "7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofDocument29 pages"7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofOliver Dennis100% (1)
- AppendixDocument5 pagesAppendixAsim IqbalNo ratings yet
- Be The Medicine Latest Version 20-05-2016Document29 pagesBe The Medicine Latest Version 20-05-2016nedux100% (1)
- Obstructive Renal Cyst in A Dog - Ultrasonography-GuidedTreatment Using Puncture Aspiration and Injectionwith 95% EthanolDocument3 pagesObstructive Renal Cyst in A Dog - Ultrasonography-GuidedTreatment Using Puncture Aspiration and Injectionwith 95% EthanolIngrid RamisaNo ratings yet
- 2N60 PDFDocument7 pages2N60 PDFFady HachemNo ratings yet
- Delegate List - 10th IMRC With Contact Details - Removed (1) - RemovedDocument234 pagesDelegate List - 10th IMRC With Contact Details - Removed (1) - RemovedSharon SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares y RegularesDocument2 pagesVerbos Irregulares y RegularesFernando MoraNo ratings yet
- Aip 2023 2 3Document29 pagesAip 2023 2 3menchiemanaloNo ratings yet