Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Grammer Series
English Grammer Series
Uploaded by
Vingus Rani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesThis document contains questions and multiple choice answers about topics related to cell biology, including mitosis, meiosis, DNA, chromosomes, and genetics. It tests understanding of the stages of mitosis and meiosis, what structures DNA and chromosomes are, how genes and traits are related, types of cell division and their purposes. It also covers concepts like nondisjunction, polyploidy, and genetic modifications like translocations.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains questions and multiple choice answers about topics related to cell biology, including mitosis, meiosis, DNA, chromosomes, and genetics. It tests understanding of the stages of mitosis and meiosis, what structures DNA and chromosomes are, how genes and traits are related, types of cell division and their purposes. It also covers concepts like nondisjunction, polyploidy, and genetic modifications like translocations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesEnglish Grammer Series
English Grammer Series
Uploaded by
Vingus RaniThis document contains questions and multiple choice answers about topics related to cell biology, including mitosis, meiosis, DNA, chromosomes, and genetics. It tests understanding of the stages of mitosis and meiosis, what structures DNA and chromosomes are, how genes and traits are related, types of cell division and their purposes. It also covers concepts like nondisjunction, polyploidy, and genetic modifications like translocations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
THE NAVIGATOR SCIENCE SCHOOL & COLLEGE THATTA
Bio-II/ Chap 6 & 7 Chromosome & DNA, Cell Cycle 22-
10-2020
1. __________ only occur(s) in the gonads to produce gametes.
A) Mitosis B) Meiosis C) Mitosis and meiosis D) Sporogony E) Schizogony
2. Which of the following is mitosis not used for?
A) Repair (of a wound) in multicellular organisms B) Asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms
C) Development (e.g., baby in mother's womb) D) Production of gametes E) All of these use mitosis
3. During which stage of mitosis do the centromeres split?
A) Prophase B) Interphase C) Anaphase D) Telophase E) Synthesis stage
4. after which stage of mitosis does cytokinesis usually occur in animals?
A) Prophase B) Metaphase C) Anaphase D) Telophase E) Interphase
5. What is the correct order of the stages of mitosis? 1-Metaphase 2-Telophase 3-Anaphase 4-Prophase
A) 4,1,2,3 B) 2,3,1,4 C) 1,2,3,4 D) 1,3,2,4
E) 4,1,3,2
6. During which stage of meiosis do the sister chromatids begin to move toward the poles?
A) Prophase I B) Telophase I C) Anaphase II D) Anaphase I E) Telophase II
7. During which stage of meiosis do tetrads line up at the equator?
A) Metaphase I B) Telophase I C) Metaphase II D) Anaphase II E) Anaphase I
8. In both mitosis and meiosis, sister chromatids seperate during anaphase, but there are _____ haploid daughter nuclei produced by meiosis
compared to ______ diploid nuclei by mitosis.
A) 6,3, B) 4,2 C) 2,4 D) 3,6 E) 9,1
9. During which stage of meiosis does the nuclear envelope begin to disappear?
A) Metaphase I B) Telophase I C) Anaphase II D) Prophase I E) Metaphase II
10. When _______________ occurs between nonsister chromatids genetic exchange between chromosomes provides new combination of genes
that are different from either parent.
A) cytokinesis B) crossing-over C) mitosis D) cell division E) centromeres
splitting
Use the following options to answer questions #11 to 13: I. G0 II. G1 III. G2 IV. S V. Mitosis VI.
Cytokinesis
11. The cell cycle is divided into several distinct sub phases. Which sub phases occur during interphase?
A) I, II, and III B) II, III, and IV C) I, II, III, and IV D) V and VI E) none of these
12. Similarly to interphase, the mitotic phase includes different sub phases, including which of the following?
A) V B) IV, V, and VI C) V and VI D) I, V, and VI E) none of these
13. The cell cycle is regulated by several factors. Cell cycle checkpoints exist during which of the following processes?
A) I, II, and III B) V and VI C) II, III, and IV D) II, III, and V E) none of these
14. Which of the following is not something that occurs before metaphase?
A) Sister chromatids separate. B) Nuclear envelope fragments.
C) Chromosomes become tightly coiled. D) Centrosomes align on opposite sides of the cell.
15. Meiosis is broken down into two separate processes: meiosis I and meiosis II. Which of the following statements incorrectly pairs an event
that occurs in each process?
A) Meiosis I: separates homologous chromosomes B) Meiosis II: creates haploid cells with duplicated chromosomes
C) Meiosis I: independent assortment along metaphase plate D) Meiosis II: separates sister chromatids
16. What event would cause Turner’s syndrome?
A) The joining of two gametes that are each missing a sex chromosome. B) The joining of a gamete with a somatic cell.
C) The joining of a normal gamete with a gamete missing a sex chromosome. D) The joining of two polyploid gametes.
17. Gametes and meiosis are related in the same way as which of the following pairs?
A) Meiosis: haploid B) Chromosomes: alleles C) Somatic cells: mitosis D) Mitosis: Binary fission E) none of
these
18. interphase
19. G1 phase
20. G2 phase
21. Mitosis
22. S phase
23. Identify two stages of the mitotic phase.
A) prophase and metaphase B) cytokinesis and interphase
C) mitosis and interphase D) interphase and metaphase
24. The DNA in a eukaryotic chromosome is best described as:
A) a single circular double-helical molecule.
B) a single linear double-helical molecule. C) a single linear single-stranded molecule.
D) multiple linear double-helical molecules. E) multiple linear single-stranded molecules.
25. The most precise modern definition of a gene is a segment of genetic material that:
A) codes for one polypeptide. B) codes for one polypeptide or RNA product. C) determines one phenotype.
D) determines one trait. E) that codes for one protein.
26. The fundamental repeating unit of organization in a eukaryotic chromosome is:
A) the centrosome. B) the lysosome. C) the microsome. D) the nucleosome. E) the polysome
27. If the sequence of bases in DNA is TACCGACCA, then the sequence of codons on the transcript will be
A) ATGGCTGGT B) ATCCGAACU C) AUGGCUGGU D) AUGGACUAA
28. this is a _______ nitrogenous base
A) adenine B) guanine C) thymine D) cytosine
29. What are the repeating units of nucleic acids?
A) phosphate molecules B) nucleotides C) bases D) sugar molecules
30. Cancer cells are
A) Unlimited number of cell divisions B) Growth without external signals C) Avoidance of cell death D) All of these
31. Which of the following helps maintain the structure of chromosomes and control the activity of genes?
A) the nuclear membrane B) proteins C) centromeres D) ribosomes E) none of these
32. Sister chromatids are
A) found right after a cell divides. B) joined together at a centromere. C) made only of DNA. D) unique to prokaryotes
33. Looking into your microscope, you spot an unusual cell. Instead of the typical rounded cell shape, the cell has a very narrow middle
separating two bulging ends. It sort of looks like the number 8! Then you realize that this cell is
A) undergoing cytokinesis. B) in the S phase of interphase. C) in the G1 phase of interphase. D) about to undergo mitosis
34. Which of the following statements is false?
A) Gametes are haploid cells. B) Two haploid cells fuse during fertilization. C) An X chromosome is an autosome.
D) A zygote is a fertilized egg. E) none of these
35. Karyotyping
A) shows chromosomes as they appear in metaphase of meiosis II. B) can reveal alterations in chromosome number.
C) examines points of crossing over. D) reveals the presence of cancerous genes.
36. Nondisjunction occurs when
A) a portion of a chromosome breaks off and is lost. B) two chromosomes fuse into one.
C) members of a chromosome pair fail to separate. D) an entire pair of chromosomes is lost during meiosis I.
37. Which of the following statements about nondisjunction is false?
A) Nondisjunction in meiosis can affect autosomes and sex chromosomes.
B) In mammals, extra copies of the Y chromosome are typically inactivated.
C) In general, a single Y chromosome is enough to produce "maleness."
D) Women with a single X chromosome have Turner syndrome and are sterile.
38. Which of the following types of organisms commonly demonstrates polyploidy?
A) mammals B) reptiles C) flowering plants D) fish E) none of these
39. How many generations does it take to develop a new plant species by polyploidy?
A) one B) two C) ten D) about twenty E) five
40. If a chromosome fragment breaks off and then reattaches to the original chromosome, but in the reverse direction, it is
A) deletion. B) inversion. C) translocation. D) reciprocal translocation. E) none of suits
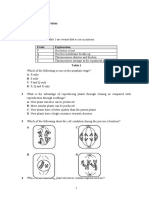
41. If these four cells resulted from cell division of a single cell with diploid chromosome number 2n = 4, what best describes what just
occurred?
A) normal meiosis B) translocation C) inversion D) nondisjunction
42. In trying to determine whether DNA or protein is the genetic material,
Hershey and Chase made use of which of the following facts?
A) DNA contains sulfur, whereas protein does not.
B) DNA contains phosphorus, whereas protein does not.
C) DNA contains nitrogen, whereas protein does not. D) DNA contains purines, whereas protein includes pyrimidines.
43. Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this
sample will be thymine?
A) 8% B) 16% C) 31% D) 42% E) 100%
44. Which of the following can be determined directly from X-ray diffraction photographs of crystallized DNA?
A) the diameter of the helix B) the rate of replication C) the sequence of nucleotides
D) the bond angles of the subunits E) the frequency of A vs. T nucleotides
45. What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the strands that make up DNA?
A) The twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands. B) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands
C) The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
D) One strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged.
46. Which of the following help(s) to hold the DNA strands apart while they are being replicated?
A) primase B) ligase C) DNA polymerase D) exonuclease E) none of
these
47. Why do histones bind tightly to DNA?
A) Histones are positively charged, and DNA is negatively charged. B) Histones are negatively charged, and DNA is positively charged.
C) Both histones and DNA are strongly hydrophobic. D) Histones are covalently linked to the DNA.
48. Once the pattern found after one round of replication was observed, Meselson and Stahl could be confident of which of the following
conclusions?
A) Replication is semi-conservative. B) Replication is not dispersive. C) Replication is not semi-conservative.
D) Replication is not conservative. E) Replication is neither dispersive nor conservative
49. In analyzing the number of different bases in a DNA sample, which result would be consistent with the base-pairing rules?
A) A = G B) A + G = C + T C) A + T = G + T D) A = C E) G = T
50. Which choice best describes the cell cycle?
A) Cells grow and develop during interphase. Cells reproduce during the mitotic phase.
B) Cells grow and develop during the mitotic phase. Cells reproduce during interphase.
C) The nucleus of a cell divides during interphase. The cytoplasm of a cell divides during the mitotic phase.
D) The nucleus of a cell divides during the mitotic phase. The cytoplasm of a cell divides interphase.
You might also like
- Ebook Campbell Essential Biology With Physiology 4Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEbook Campbell Essential Biology With Physiology 4Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFMichaelCarrollmnzq100% (14)
- Ebook Campbell Essential Biology 5Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEbook Campbell Essential Biology 5Th Edition Simon Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (17)
- Concepts of Genetics 3rd Edition Brooker Test BankDocument22 pagesConcepts of Genetics 3rd Edition Brooker Test BankChristianBrownxmstk100% (16)
- Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles For RNA DeliveryDocument11 pagesChemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles For RNA DeliveryJohnNo ratings yet
- Ap Cell Division and Reproduction MCDocument6 pagesAp Cell Division and Reproduction MCapi-522349089No ratings yet
- Exercise On Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesExercise On Cell DivisionNorliyana Ali100% (1)
- Test Bank - 1Document18 pagesTest Bank - 1Bai GraceNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Cell Reproduction Practice ExamDocument5 pagesCell Reproduction Practice Examjacky qianNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition by Pierce Isbn 1319050964 978131905096 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition by Pierce Isbn 1319050964 978131905096 Full Chapter PDFdavid.caple542100% (14)
- Biology Paper 04.07.2022 KeyDocument14 pagesBiology Paper 04.07.2022 Keymocoking007No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division-1Document35 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division-1shaikh mohammadNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell Division PEARSONDocument6 pagesCell and Cell Division PEARSONSujata UpadhyeNo ratings yet
- RWS Term I Grade X Bio Structure of ChromosomeDocument3 pagesRWS Term I Grade X Bio Structure of Chromosomesuyashb1003No ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument19 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questionkavianr0% (1)
- DPP 2 10Document3 pagesDPP 2 10MahakNo ratings yet
- CellCycle90QuestionsTest PDFDocument92 pagesCellCycle90QuestionsTest PDFArshia PatniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Division MCQDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Cell Division MCQCarin TanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell Cycle - QuestionsDocument6 pagesLecture 3 Cell Cycle - Questions中华雅思王No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Divisons - AglaSem Schools PDFDocument29 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisons - AglaSem Schools PDFEunice LimNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarterly Unit Test in General BiologyDocument5 pages2nd Quarterly Unit Test in General BiologySir Josh100% (1)
- Unit - III Chapter-13. Cell Cycle and Cell Divisions: Important PointsDocument19 pagesUnit - III Chapter-13. Cell Cycle and Cell Divisions: Important PointsLokender KumarNo ratings yet
- Sci.8 4th Term - Test QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesSci.8 4th Term - Test QuestionnaireJENIVIEVE DELARMENTENo ratings yet
- Cuestionario2 TestBank - Basics - Bio10a - Chapter9 División Celular (Kelly Merchán)Document8 pagesCuestionario2 TestBank - Basics - Bio10a - Chapter9 División Celular (Kelly Merchán)Kelly MerchánNo ratings yet
- Kvpy 1 Cell Cycle Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesKvpy 1 Cell Cycle Cell DivisionBHARTENDU TIWARINo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division Practice TestDocument12 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division Practice TestIndu Yadav100% (1)
- Pre Board Botany IIDocument2 pagesPre Board Botany IISyed Raza Hassan GardeziNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10 ch10 Class 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 10 ch10 Class 11akilapaul17682No ratings yet
- Cell Division 111 MCQSDocument113 pagesCell Division 111 MCQSAnik RoyNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesMitosis Meiosis DNA ReplicationJon HosmerNo ratings yet
- MCQ Cell Cycle N ChromosomeDocument3 pagesMCQ Cell Cycle N ChromosomeHenary Chongtham100% (2)
- Question Bank - Introduction To Computational Biology - Unit 1 - Cell and EvolutionDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank - Introduction To Computational Biology - Unit 1 - Cell and EvolutionMadhav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Zoology McqsDocument6 pagesZoology McqsPrime RoseNo ratings yet
- Test-7 Cell Cycle (Key)Document4 pagesTest-7 Cell Cycle (Key)arehmanmalik619No ratings yet
- Origami Works of Satoshi Kamiya PDF FreeDocument19 pagesOrigami Works of Satoshi Kamiya PDF FreeAdam LameyNo ratings yet
- Biology Question For ExamDocument6 pagesBiology Question For ExamIsmail HossainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Division - Print - QuizizzDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Cell Division - Print - QuizizzCarin TanNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16Document32 pagesAP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16EUNAH LimNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument7 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionSANDRA BENAVIDESNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 Exam 2 Print To Be SendDocument4 pagesGenbio1 Exam 2 Print To Be SendMohammad Rex MuharramNo ratings yet
- Neet Quiz Cell Division 2022Document7 pagesNeet Quiz Cell Division 2022Kiruthika RNo ratings yet
- Ans Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument22 pagesAns Chapter 6 Cell Division汪楷熙No ratings yet
- Practice Exam 3 CH 11-15 QuestionsDocument6 pagesPractice Exam 3 CH 11-15 QuestionsJeff SandersNo ratings yet
- Cell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Document5 pagesCell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Risti SFNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 5Document10 pagesBio Chapter 5Rosfaizzati MarnunNo ratings yet
- Cell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Document6 pagesCell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwk100% (1)
- 00 .Cell The Unit of Life A-R Questions and Statement WiseDocument10 pages00 .Cell The Unit of Life A-R Questions and Statement Wisem4vsn7zqytNo ratings yet
- Meosis TestDocument3 pagesMeosis TestMark FuntinillaNo ratings yet
- Document 2242 8139Document54 pagesDocument 2242 8139slypesecularjgi77No ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis TestDocument4 pagesMitosis Meiosis TestCarla MinghettiNo ratings yet
- Biology: Concept Booster MCQ Sheet - 8Document10 pagesBiology: Concept Booster MCQ Sheet - 8Yousra SamreenNo ratings yet
- Xi Biology Term 2 MCQDocument94 pagesXi Biology Term 2 MCQkiruthikpranav46No ratings yet
- Cell Division Objective QuestionsDocument10 pagesCell Division Objective QuestionsSUREINTHARAAN A/L NATHAN Moe100% (1)
- E Cell and Nuclear DivisionDocument18 pagesE Cell and Nuclear DivisionKai JieNo ratings yet
- General Biology First PerioDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology First PerioJay-Ar MalanaNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION Q and ADocument2 pagesCELL DIVISION Q and AMariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- C C C D: ELL Ycle AND ELL IvisionDocument5 pagesC C C D: ELL Ycle AND ELL IvisionBur ChattaNo ratings yet
- 12 BiologyDocument9 pages12 BiologysohiniNo ratings yet
- Questions OnlehDocument13 pagesQuestions OnlehElcei LazoNo ratings yet
- 620biology QB Xii 23-24 Term 1Document23 pages620biology QB Xii 23-24 Term 1Jiya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 4 4 Electron Transport ChainDocument2 pages4 4 Electron Transport ChainKai JieNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Biotechnology: (4 - Semesters W.E.F. July 2004) Outlines of Syllabus (Total Credits-90)Document8 pagesM.Sc. Biotechnology: (4 - Semesters W.E.F. July 2004) Outlines of Syllabus (Total Credits-90)Pradeep KhandaitNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and Pathology of Radical-Mediated Protein OxidationDocument18 pagesBiochemistry and Pathology of Radical-Mediated Protein OxidationSams SriningsihNo ratings yet
- TMP A7 DEDocument26 pagesTMP A7 DEFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Cloning and Vector: Instructor: Prof. Myoung-Dong Kim T: 6458, Mdkim@kangwon - Ac.kr Room 411, Ag. BLD #3Document41 pagesCloning and Vector: Instructor: Prof. Myoung-Dong Kim T: 6458, Mdkim@kangwon - Ac.kr Room 411, Ag. BLD #3ferinarzNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cancer MetabolismDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Cancer MetabolismAlvaro Cano TortajadaNo ratings yet
- Article - 4 ImpDocument26 pagesArticle - 4 ImpSai BhagavathulaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1&3 No Lec or Lab Week 2Document41 pagesLec 1&3 No Lec or Lab Week 2joshNo ratings yet
- Declaration: Annexure-2 (Declaration To Be Filled by PHD Student)Document16 pagesDeclaration: Annexure-2 (Declaration To Be Filled by PHD Student)avnishNo ratings yet
- MitochondriaDocument13 pagesMitochondriamariemmohamed200713No ratings yet
- Acjc H2 Bio P2Document16 pagesAcjc H2 Bio P2DD97No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Immunology - Death by Friendly FireDocument145 pagesFundamentals of Immunology - Death by Friendly FireAngel FeresiaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-NrmfDocument24 pagesChromosomes: Magdalena F. Natividad, PHD Dean, School of Medical Lab Science Feu-NrmfCharm AngelesNo ratings yet
- MCB 251 Lab PCRDocument8 pagesMCB 251 Lab PCRDan BorsNo ratings yet
- A227 RuBP CarboxylaseDocument4 pagesA227 RuBP Carboxylaseramloghun veer100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Gene Transfer in BacteriaDocument52 pagesLecture 1 - Gene Transfer in BacteriaAbraham Kang0% (1)
- Isolation of Rna and Uv MeasurementDocument5 pagesIsolation of Rna and Uv MeasurementDanAdamL33% (3)
- 11handbook of Detection of Enzyme On Electrophoret GelsDocument570 pages11handbook of Detection of Enzyme On Electrophoret GelsOsama Abdulkareem100% (2)
- 6 Mcq2 Enzymes 130107225709 Phpapp02Document14 pages6 Mcq2 Enzymes 130107225709 Phpapp02Dawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- June 2017 QP p3Document32 pagesJune 2017 QP p3RS JNo ratings yet
- Mb044 - Nzydna Ladder IIIDocument2 pagesMb044 - Nzydna Ladder IIIKimShannayNo ratings yet
- Rt-Quic: A New Test For Sporadic CJD: Alison J E GreenDocument7 pagesRt-Quic: A New Test For Sporadic CJD: Alison J E GreenAliciaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Insulin SecretionDocument8 pagesPhysiology of Insulin SecretionChenai04No ratings yet
- ATOH7 Mutations Cause Autosomal Recessive Persistent Hyperplasia of The Primary VitreousDocument14 pagesATOH7 Mutations Cause Autosomal Recessive Persistent Hyperplasia of The Primary VitreousAmilaNo ratings yet
- BAB 2 Principle of Cellular LifeDocument49 pagesBAB 2 Principle of Cellular LifeMuhammad Dalili Al FarisNo ratings yet
- Recent Research Paper On Gene TherapyDocument6 pagesRecent Research Paper On Gene Therapyafnkfgvsalahtu100% (1)
- Matta Et Al. - 2018 - Development and Characterization of A Novel LucifeDocument14 pagesMatta Et Al. - 2018 - Development and Characterization of A Novel LucifeRaghav VijNo ratings yet
- Western Blot (Brochure)Document2 pagesWestern Blot (Brochure)Anonymous SwrYcKuXNo ratings yet
- Nociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and InflammationDocument15 pagesNociceptor Sensory Neuron-Immune Interactions in Pain and InflammationRogerio MachadoNo ratings yet