Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter-3: Business F (Nance
Chapter-3: Business F (Nance
Uploaded by
Shahid MahmudCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Gumbaynggirr Dreaming UnitDocument19 pagesGumbaynggirr Dreaming Unitapi-355090152No ratings yet
- Making Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)From EverandMaking Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)No ratings yet
- 2.2organisational StructureDocument34 pages2.2organisational StructurecarolinaNo ratings yet
- Oam Topic 3Document20 pagesOam Topic 3mwagadijohnathan65No ratings yet
- Organizational StructureDocument6 pagesOrganizational StructureKumkum SultanaNo ratings yet
- Osd Notes 1Document37 pagesOsd Notes 1yogendra choukikerNo ratings yet
- Management and EntrepreneurshipDocument27 pagesManagement and Entrepreneurshipashika nayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23-: Organisation Structure and EmployeesDocument21 pagesChapter 23-: Organisation Structure and Employeessk001No ratings yet
- CHP 4 Foundation of Organizational StructureDocument46 pagesCHP 4 Foundation of Organizational StructureSanjida Ahmed PipoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLDocument23 pagesUnit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLAmbar DunskiNo ratings yet
- iMBA MAN7039 Strategic Human Resource Management: Week 9 Organisational StructureDocument33 pagesiMBA MAN7039 Strategic Human Resource Management: Week 9 Organisational StructureYash BajajNo ratings yet
- Organization Structure & DesignDocument37 pagesOrganization Structure & Designmridsinghster64No ratings yet
- Organisation Structure: UNIT:2Document28 pagesOrganisation Structure: UNIT:2S. B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Organizational Struc-Ture and Design - : UmmaryDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - Organizational Struc-Ture and Design - : UmmaryUrs AteequeNo ratings yet
- HBO - Organizational StructureDocument35 pagesHBO - Organizational StructureDewdrop Mae RafananNo ratings yet
- Designing Adaptive Organization and Managing Change and InnovationDocument27 pagesDesigning Adaptive Organization and Managing Change and InnovationRobert John PerezNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Oganization Theory and DesignDocument51 pagesConcepts in Oganization Theory and DesignKishan MadhooNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Related To Organisation: Organisational HierarchyDocument7 pagesBasic Concepts Related To Organisation: Organisational HierarchySpandana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Business Notes (Unt 2)Document21 pagesBusiness Notes (Unt 2)Azar Anjum RiazNo ratings yet
- Topic Three Organizing FunctionDocument10 pagesTopic Three Organizing Functionstill earvinNo ratings yet
- Organising Human ResourcesDocument4 pagesOrganising Human ResourcesmariadelafuentejimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Complete Notes - 21694911 - 2024 - 04 - 11 - 15 - 41Document30 pagesUnit - 4 Complete Notes - 21694911 - 2024 - 04 - 11 - 15 - 41sampurnav6No ratings yet
- Managing Org StructureDocument63 pagesManaging Org StructureAbhyudaya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - OrganizingDocument12 pagesChapter 6 - OrganizingMy KiềuNo ratings yet
- Departmentation 2020 1Document16 pagesDepartmentation 2020 1malcomNo ratings yet
- Principles OF Management: OrganizingDocument52 pagesPrinciples OF Management: OrganizingVigil J VijayanNo ratings yet
- Handout-04 OrganizingDocument4 pagesHandout-04 OrganizingncncNo ratings yet
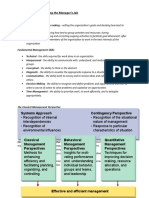
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Document36 pagesStrategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Vignesh VSNo ratings yet
- #4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6) #4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6)Document5 pages#4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6) #4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6)Minh Anh HoangNo ratings yet
- B.m-Private Answer Key - July-2022Document13 pagesB.m-Private Answer Key - July-2022adhuNo ratings yet
- Adm650 Chapter 6 Strategy Implementation Orperational Structure & Management - Operation May Sapura Revised Mac2023Document28 pagesAdm650 Chapter 6 Strategy Implementation Orperational Structure & Management - Operation May Sapura Revised Mac2023Arya zllkaNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document44 pagesCH 5TamiratNo ratings yet
- Gate 3 - Execution - Machinery, Methods, and Management SkillsDocument35 pagesGate 3 - Execution - Machinery, Methods, and Management SkillsJohn Nelo MorataNo ratings yet
- Strategyimplementation 4Document36 pagesStrategyimplementation 4Eunice Eidelwiess AraniegoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Basic Organizational DesignDocument26 pagesChapter 10 - Basic Organizational DesignSaira Khan100% (1)
- Structural ImplementationDocument12 pagesStructural ImplementationSiddhartha Singhal057No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document22 pagesUnit 1ashish198722No ratings yet
- Daniels Ib11 ch15Document32 pagesDaniels Ib11 ch15Niki NicolaouNo ratings yet
- Full RevisionDocument57 pagesFull Revisionmariamessamqatar1No ratings yet
- L5 - OrganisingDocument13 pagesL5 - OrganisingAnonymous 8ooQmMoNs1No ratings yet
- Daniels15 - The Organization of International BusinessDocument32 pagesDaniels15 - The Organization of International BusinessHuman Resource ManagementNo ratings yet
- Organization 11Document22 pagesOrganization 11Ravi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerDharnel Jude EpeNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument41 pagesOrganization StructureMiddle BenchersNo ratings yet
- PM Unit 1 NotesDocument113 pagesPM Unit 1 NotesSaish SawantNo ratings yet
- ACCA SBL Unit of Innovation, Performance Excellence and Change Management 2021Document255 pagesACCA SBL Unit of Innovation, Performance Excellence and Change Management 2021Quensteen LimNo ratings yet
- HRM 370-Materials For Review-71-Managerial Basics-Survival SkillsDocument18 pagesHRM 370-Materials For Review-71-Managerial Basics-Survival SkillsRushat OrchiNo ratings yet
- IG Chapter 7 Part 1. 2.2.1 Draw, Interpret and Understand Simple Organisational ChartsDocument8 pagesIG Chapter 7 Part 1. 2.2.1 Draw, Interpret and Understand Simple Organisational ChartsJuné MaraisNo ratings yet
- BBA110 Business Administration Module 7Document80 pagesBBA110 Business Administration Module 7pphiriemmanuel888No ratings yet
- Reportmodule6 120508034134 Phpapp01 PDFDocument76 pagesReportmodule6 120508034134 Phpapp01 PDFdingdong magandiaNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Organizational StructureDocument6 pagesOrganizing and Organizational Structuretemesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- Soc. Sci 1 Chapter 2Document126 pagesSoc. Sci 1 Chapter 2Lailanie FortuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Topic OutlineLovely JillNo ratings yet
- Management Asia-Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument56 pagesManagement Asia-Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual instant download all chapterladimshoki100% (3)
- Organization and Management Lesson 2Document115 pagesOrganization and Management Lesson 2destinybond69420No ratings yet
- Module 8.org and MGTDocument25 pagesModule 8.org and MGTMaria Katriel TejadaNo ratings yet
- Management Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesManagement Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFirisdavid3n8lg100% (14)
- PART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Document4 pagesPART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Hillary CanlasNo ratings yet
- COM Unit 3Document16 pagesCOM Unit 3Ammar AhsanNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering ActivitiesDocument3 pagesData Gathering ActivitiesKyla PapaNo ratings yet
- Eng Sales Manual PBPDocument16 pagesEng Sales Manual PBPCoara OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Bruma Lake - More Than An Environmental Upgrade FinalDocument5 pagesBruma Lake - More Than An Environmental Upgrade FinalElishaNo ratings yet
- Part4-Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument151 pagesPart4-Object Oriented Programminganhtrang_181289No ratings yet
- Reading 3Document5 pagesReading 3Aileen Mae E. MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument6 pages7 PDFjoseNo ratings yet
- Datasheet (Signal Booster)Document4 pagesDatasheet (Signal Booster)Shrisha BhatNo ratings yet
- MAS24118 SolutionDocument15 pagesMAS24118 SolutionAditiNo ratings yet
- Non-Nutritive Sucking Habit Breakers Carlos Loza and Christina Rodriguez NutritionDocument6 pagesNon-Nutritive Sucking Habit Breakers Carlos Loza and Christina Rodriguez Nutritionapi-421866375No ratings yet
- APICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesDocument11 pagesAPICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesvayugaramNo ratings yet
- Berglihn - Ecosystem Services From Urban Forests The Case of Oslomarka, NorwayDocument11 pagesBerglihn - Ecosystem Services From Urban Forests The Case of Oslomarka, NorwayQuentin LempereurNo ratings yet
- Grand Central Terminal Mep Handbook 180323Document84 pagesGrand Central Terminal Mep Handbook 180323Pete A100% (1)
- Quarterly English 10Document6 pagesQuarterly English 10Edel Mae OpenaNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Formulation Technologies and Novel Strategies For The Design of Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms: A Comprehensive Industrial ReviewDocument13 pagesInsights Into Formulation Technologies and Novel Strategies For The Design of Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms: A Comprehensive Industrial ReviewROBINNo ratings yet
- Policy Guideliness For Community Radio in KenyaDocument36 pagesPolicy Guideliness For Community Radio in KenyaAmos Ochieng100% (1)
- Notice: Meetings: California Independent System Operator Corp. Post-Technical Conference Comments Period RescindedDocument1 pageNotice: Meetings: California Independent System Operator Corp. Post-Technical Conference Comments Period RescindedJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Jewma2Document15 pagesJewma2Riston SinagaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document27 pagesModule 5Labour lawNo ratings yet
- 8 Answer Key A Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationDocument6 pages8 Answer Key A Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationPatinéNo ratings yet
- Buzan 1993Document27 pagesBuzan 1993Paula CordobaNo ratings yet
- Feynman's Invaluable Advice For StudentsDocument7 pagesFeynman's Invaluable Advice For StudentsJerome Rafael100% (1)
- Stress Due To Surface LoadDocument7 pagesStress Due To Surface LoadDesalegn TamirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TestDocument3 pagesChemistry TestAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- PICA Hose Problem - Sept-Nov 2012Document20 pagesPICA Hose Problem - Sept-Nov 2012Edwin FitrianNo ratings yet
- Customer Pricelist General 06-2015Document21 pagesCustomer Pricelist General 06-2015ilayyinan50% (2)
- Naruto's Rise Chapter 6 - Let's Be Friends, A Naruto Fanfic - FanFictionDocument1 pageNaruto's Rise Chapter 6 - Let's Be Friends, A Naruto Fanfic - FanFictionyukilatsu999No ratings yet
- BankingDocument99 pagesBankingNamrata KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 25274Document93 pages25274prnjanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Instrumentation Assesment 1 Copy 1Document11 pagesIndustrial Instrumentation Assesment 1 Copy 1MARVIN NAMANDANo ratings yet
Chapter-3: Business F (Nance
Chapter-3: Business F (Nance
Uploaded by
Shahid MahmudOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter-3: Business F (Nance
Chapter-3: Business F (Nance
Uploaded by
Shahid MahmudCopyright:
Available Formats
Business & F[nance
Chapter-3
Organizational structure and business forms
organizational structure: Formed by the grouping by of people into departments or sections and the
allocation of responsibility and authority, organizational structure sets out how the various functions are
[ormally arranged.
Organizational structure is a frameworl< intended to
The buildine blocl( of orsanizational structure:
Operating core: People directly involved in the process of obtaining inputs and
4"
converting them into outputs.
r Middle line: Conveys the goals set by the strategic apex and controls of the operating
4.- core in pursuit of those goals.
->" Strategic apex: Ensure the organization follows its mission. Manages the organization's
4 ffivith the environment. Top managers.
. Support staff: support staff do not plan or standardize operations. They function
z' - --i--
' independently of the operating core.
->" Techno-structure: analysts determine and standardize worl< processes and techniques.
'-'7
' Planners determine and standardize outputs. Personnel analysts standardize skills.
ldeology: values, believes and traditions.
4 "
ed an allocated rationally.
2@Authorityshouldflowverticallydownaclearchainofcommandfrom
highest to lowest ranl<.
3. of authority and responsibility:The holder of an office should have
-Correspondence
enough authority to cffities assigned to them.
4. Appropriateate centralization: Decision should be taken at the top of the organization
where appropriate.
5. Unity of directions:There should be one head and one plan for activity.
6. Unity of command: For any action a subordinate should receive orders from one boss
onlY-
1. lnitiative: Employees should be encouraged to use direction within the bounds of their
a uthority.
Md. Mahedi Masud ACA
8. Subordination of individual interests: lnterest of the employees should not prevail over
that of the general interest of the organization.
9. Discipline: A fair disciplinary system can be strength in an organization. Organizailon's
member should behave in agreed ways.
l-0. Order: people and resources should be reliably be where they are supposed to be.
11. Stability of personnel:There should be continuity of employment where possible.
12. Equity: Organizational policies should be just.
13. Remuneration: Rewards should be fatr.
14. Esprit de corps: Harmony and teamworl< are essentialto promote discipline and
co nte n tme nt.
Structu res:
1, Entrepreneurial structure:Entrepreneur has specialist knowledge of product/service and has
totalcontrol over running of the business. The entrepreneurialstructure is most suitable where
there is one product or a group of similar products-
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
the entrepreneur does not have specialist sl<ill/knowledge;
2. Functional structure:Jobs grouped by common feature and ranl<ed in hierarchy. Clear lines of
reporting and authority are existing. The functional bureaucratic structure is most suitable
where there is single product/closely-related product form.
Advantages:
can progress up through the ranl<s;
Disadvantaqes:
--Growth;
--Dive rsificatio n;
3. Divisionalstructure:
Divisionalisation:The division of a business into autonomous regions or product businesses,
each with its own revenues, expenditures and capitalasset purchase programs, and therefore
each with its own profit responsibility. ln divisionalstructure business is split into divisions
(division is usually by product or location).
Md. Malredi Masud RCA
Advantages:
p rof it;
Reduces the number of levels of management;
Encourages to greater attention to efficiency, lower cost and higher profit;
Better performance decisions made by managers;
Releases top management to concentrate on strategtc tssues;
Reduces tlie likelihood of unprofitable products and activities being continued.
for which separate divisions can be set up.
4' Matrix structure:is more suitable to complex/hi-tech industry, R&D departments, educational
establishment where there may be lecturers reporting to both subject and course heads. This
structure formalizes vertical and latqral lines of communications. lt may be temporary.
AdvantaRes:
Reflects importance of project or customer, so may improve relationships and
sa les;
Business co-ordinated with regard to technology, information etc.
r Corrfricting demand over ailocation of other resources;
centralized structure:upper levels retain authority to mal<e decisions.
Decentralized structure: Authority to mal<e decision is passed to lower levels of the
hierarchy.
centralized orqanization: one in which decision making authority is concentrated in
one place, that is
\z lhe strategic apex. We can lool< at centralization in 2 ways- Geography and Authority.
Factor affectine the amount of decentralization in a business:
r Leadership style;
r Extent of activity diversification;
Effectiveness of com m u nication'
':
Ability of management;
r Speed of technological advancement;
r Geogra phy of location;
r Extend of a local l<nowledge needed.
Md. Mahedi Masud RCA
\
\ ')
Span of control:The number of people reporting to one person.
lnfluences on the span of control:
Scalar chain:The chain of command from the most senior to the most junior.
Tall business:One which, in relation to its size, has a large number of levels in its management hierarchy,
normally because there are narrow Span of control.
Flat business: One which, in relation to its size, has a small number of hierarchical Ievels, normally
because there are wide span of control.
Are tall or flat businesses better?
Ta ll business:
For Aga inst
Narrow control spans _l tnhipLttlS]_uer!9lt _
Small groups enable team members to participate Rigid supervision can be imposed, blocl<ing
in decision initiative
A large number of steps on the promotional The same worl< passes through too many hands
ladder-assists management training and career
planning
lncreases administration and overhead costs
Slow decision mal<ing and responses, as the
strategic apex is further away
Flat business:
For Aga i nst
More opportunity for delegation Requires that jobs can be delegated. lf managers
are overworl<ed they are more lil<ely to be involved
in crisis management
Managers may only get a superficial idea of'whait
goes on
Re latively chea p Sacrifices control
ln theorv, speeds up communications between Middle managers are often necessary to co nve rt
strategic apex and operatrng core the gra nd visio n of the strategic a pex tnto
o p e ra t io n a I te rm s
Mld. Mahedi lVlasud RCA
You might also like
- Gumbaynggirr Dreaming UnitDocument19 pagesGumbaynggirr Dreaming Unitapi-355090152No ratings yet
- Making Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)From EverandMaking Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)No ratings yet
- 2.2organisational StructureDocument34 pages2.2organisational StructurecarolinaNo ratings yet
- Oam Topic 3Document20 pagesOam Topic 3mwagadijohnathan65No ratings yet
- Organizational StructureDocument6 pagesOrganizational StructureKumkum SultanaNo ratings yet
- Osd Notes 1Document37 pagesOsd Notes 1yogendra choukikerNo ratings yet
- Management and EntrepreneurshipDocument27 pagesManagement and Entrepreneurshipashika nayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23-: Organisation Structure and EmployeesDocument21 pagesChapter 23-: Organisation Structure and Employeessk001No ratings yet
- CHP 4 Foundation of Organizational StructureDocument46 pagesCHP 4 Foundation of Organizational StructureSanjida Ahmed PipoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLDocument23 pagesUnit 2.2 - Organizational Structure - Business IB HLAmbar DunskiNo ratings yet
- iMBA MAN7039 Strategic Human Resource Management: Week 9 Organisational StructureDocument33 pagesiMBA MAN7039 Strategic Human Resource Management: Week 9 Organisational StructureYash BajajNo ratings yet
- Organization Structure & DesignDocument37 pagesOrganization Structure & Designmridsinghster64No ratings yet
- Organisation Structure: UNIT:2Document28 pagesOrganisation Structure: UNIT:2S. B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Organizational Struc-Ture and Design - : UmmaryDocument8 pagesChapter 10 - Organizational Struc-Ture and Design - : UmmaryUrs AteequeNo ratings yet
- HBO - Organizational StructureDocument35 pagesHBO - Organizational StructureDewdrop Mae RafananNo ratings yet
- Designing Adaptive Organization and Managing Change and InnovationDocument27 pagesDesigning Adaptive Organization and Managing Change and InnovationRobert John PerezNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Oganization Theory and DesignDocument51 pagesConcepts in Oganization Theory and DesignKishan MadhooNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Related To Organisation: Organisational HierarchyDocument7 pagesBasic Concepts Related To Organisation: Organisational HierarchySpandana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Business Notes (Unt 2)Document21 pagesBusiness Notes (Unt 2)Azar Anjum RiazNo ratings yet
- Topic Three Organizing FunctionDocument10 pagesTopic Three Organizing Functionstill earvinNo ratings yet
- Organising Human ResourcesDocument4 pagesOrganising Human ResourcesmariadelafuentejimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Complete Notes - 21694911 - 2024 - 04 - 11 - 15 - 41Document30 pagesUnit - 4 Complete Notes - 21694911 - 2024 - 04 - 11 - 15 - 41sampurnav6No ratings yet
- Managing Org StructureDocument63 pagesManaging Org StructureAbhyudaya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - OrganizingDocument12 pagesChapter 6 - OrganizingMy KiềuNo ratings yet
- Departmentation 2020 1Document16 pagesDepartmentation 2020 1malcomNo ratings yet
- Principles OF Management: OrganizingDocument52 pagesPrinciples OF Management: OrganizingVigil J VijayanNo ratings yet
- Handout-04 OrganizingDocument4 pagesHandout-04 OrganizingncncNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveDocument13 pagesCHAPTER 1: Understanding The Manager's Job: Systems Approach Contingency PerspectiveNina ManginsayNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Document36 pagesStrategy Implementation: HCAD 5390Vignesh VSNo ratings yet
- #4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6) #4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6)Document5 pages#4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6) #4 - Organizational Structure and Design (Chapter 6)Minh Anh HoangNo ratings yet
- B.m-Private Answer Key - July-2022Document13 pagesB.m-Private Answer Key - July-2022adhuNo ratings yet
- Adm650 Chapter 6 Strategy Implementation Orperational Structure & Management - Operation May Sapura Revised Mac2023Document28 pagesAdm650 Chapter 6 Strategy Implementation Orperational Structure & Management - Operation May Sapura Revised Mac2023Arya zllkaNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document44 pagesCH 5TamiratNo ratings yet
- Gate 3 - Execution - Machinery, Methods, and Management SkillsDocument35 pagesGate 3 - Execution - Machinery, Methods, and Management SkillsJohn Nelo MorataNo ratings yet
- Strategyimplementation 4Document36 pagesStrategyimplementation 4Eunice Eidelwiess AraniegoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Basic Organizational DesignDocument26 pagesChapter 10 - Basic Organizational DesignSaira Khan100% (1)
- Structural ImplementationDocument12 pagesStructural ImplementationSiddhartha Singhal057No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document22 pagesUnit 1ashish198722No ratings yet
- Daniels Ib11 ch15Document32 pagesDaniels Ib11 ch15Niki NicolaouNo ratings yet
- Full RevisionDocument57 pagesFull Revisionmariamessamqatar1No ratings yet
- L5 - OrganisingDocument13 pagesL5 - OrganisingAnonymous 8ooQmMoNs1No ratings yet
- Daniels15 - The Organization of International BusinessDocument32 pagesDaniels15 - The Organization of International BusinessHuman Resource ManagementNo ratings yet
- Organization 11Document22 pagesOrganization 11Ravi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Finals ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinals ReviewerDharnel Jude EpeNo ratings yet
- Organization StructureDocument41 pagesOrganization StructureMiddle BenchersNo ratings yet
- PM Unit 1 NotesDocument113 pagesPM Unit 1 NotesSaish SawantNo ratings yet
- ACCA SBL Unit of Innovation, Performance Excellence and Change Management 2021Document255 pagesACCA SBL Unit of Innovation, Performance Excellence and Change Management 2021Quensteen LimNo ratings yet
- HRM 370-Materials For Review-71-Managerial Basics-Survival SkillsDocument18 pagesHRM 370-Materials For Review-71-Managerial Basics-Survival SkillsRushat OrchiNo ratings yet
- IG Chapter 7 Part 1. 2.2.1 Draw, Interpret and Understand Simple Organisational ChartsDocument8 pagesIG Chapter 7 Part 1. 2.2.1 Draw, Interpret and Understand Simple Organisational ChartsJuné MaraisNo ratings yet
- BBA110 Business Administration Module 7Document80 pagesBBA110 Business Administration Module 7pphiriemmanuel888No ratings yet
- Reportmodule6 120508034134 Phpapp01 PDFDocument76 pagesReportmodule6 120508034134 Phpapp01 PDFdingdong magandiaNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Organizational StructureDocument6 pagesOrganizing and Organizational Structuretemesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- Soc. Sci 1 Chapter 2Document126 pagesSoc. Sci 1 Chapter 2Lailanie FortuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Topic OutlineDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Topic OutlineLovely JillNo ratings yet
- Management Asia-Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument56 pagesManagement Asia-Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual instant download all chapterladimshoki100% (3)
- Organization and Management Lesson 2Document115 pagesOrganization and Management Lesson 2destinybond69420No ratings yet
- Module 8.org and MGTDocument25 pagesModule 8.org and MGTMaria Katriel TejadaNo ratings yet
- Management Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument44 pagesManagement Asia Pacific 6th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFirisdavid3n8lg100% (14)
- PART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Document4 pagesPART 4 Chapters 8 To 10Hillary CanlasNo ratings yet
- COM Unit 3Document16 pagesCOM Unit 3Ammar AhsanNo ratings yet
- Data Gathering ActivitiesDocument3 pagesData Gathering ActivitiesKyla PapaNo ratings yet
- Eng Sales Manual PBPDocument16 pagesEng Sales Manual PBPCoara OvidiuNo ratings yet
- Bruma Lake - More Than An Environmental Upgrade FinalDocument5 pagesBruma Lake - More Than An Environmental Upgrade FinalElishaNo ratings yet
- Part4-Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument151 pagesPart4-Object Oriented Programminganhtrang_181289No ratings yet
- Reading 3Document5 pagesReading 3Aileen Mae E. MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument6 pages7 PDFjoseNo ratings yet
- Datasheet (Signal Booster)Document4 pagesDatasheet (Signal Booster)Shrisha BhatNo ratings yet
- MAS24118 SolutionDocument15 pagesMAS24118 SolutionAditiNo ratings yet
- Non-Nutritive Sucking Habit Breakers Carlos Loza and Christina Rodriguez NutritionDocument6 pagesNon-Nutritive Sucking Habit Breakers Carlos Loza and Christina Rodriguez Nutritionapi-421866375No ratings yet
- APICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesDocument11 pagesAPICS BSCM Chapter 1 NotesvayugaramNo ratings yet
- Berglihn - Ecosystem Services From Urban Forests The Case of Oslomarka, NorwayDocument11 pagesBerglihn - Ecosystem Services From Urban Forests The Case of Oslomarka, NorwayQuentin LempereurNo ratings yet
- Grand Central Terminal Mep Handbook 180323Document84 pagesGrand Central Terminal Mep Handbook 180323Pete A100% (1)
- Quarterly English 10Document6 pagesQuarterly English 10Edel Mae OpenaNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Formulation Technologies and Novel Strategies For The Design of Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms: A Comprehensive Industrial ReviewDocument13 pagesInsights Into Formulation Technologies and Novel Strategies For The Design of Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms: A Comprehensive Industrial ReviewROBINNo ratings yet
- Policy Guideliness For Community Radio in KenyaDocument36 pagesPolicy Guideliness For Community Radio in KenyaAmos Ochieng100% (1)
- Notice: Meetings: California Independent System Operator Corp. Post-Technical Conference Comments Period RescindedDocument1 pageNotice: Meetings: California Independent System Operator Corp. Post-Technical Conference Comments Period RescindedJustia.comNo ratings yet
- Jewma2Document15 pagesJewma2Riston SinagaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document27 pagesModule 5Labour lawNo ratings yet
- 8 Answer Key A Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationDocument6 pages8 Answer Key A Grammar, Vocabulary, and PronunciationPatinéNo ratings yet
- Buzan 1993Document27 pagesBuzan 1993Paula CordobaNo ratings yet
- Feynman's Invaluable Advice For StudentsDocument7 pagesFeynman's Invaluable Advice For StudentsJerome Rafael100% (1)
- Stress Due To Surface LoadDocument7 pagesStress Due To Surface LoadDesalegn TamirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TestDocument3 pagesChemistry TestAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- PICA Hose Problem - Sept-Nov 2012Document20 pagesPICA Hose Problem - Sept-Nov 2012Edwin FitrianNo ratings yet
- Customer Pricelist General 06-2015Document21 pagesCustomer Pricelist General 06-2015ilayyinan50% (2)
- Naruto's Rise Chapter 6 - Let's Be Friends, A Naruto Fanfic - FanFictionDocument1 pageNaruto's Rise Chapter 6 - Let's Be Friends, A Naruto Fanfic - FanFictionyukilatsu999No ratings yet
- BankingDocument99 pagesBankingNamrata KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 25274Document93 pages25274prnjanNo ratings yet
- Industrial Instrumentation Assesment 1 Copy 1Document11 pagesIndustrial Instrumentation Assesment 1 Copy 1MARVIN NAMANDANo ratings yet