Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V Best Chapter 1.1 Quadratics - ONLINE PDF
V Best Chapter 1.1 Quadratics - ONLINE PDF
Uploaded by
Medical ReviewOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V Best Chapter 1.1 Quadratics - ONLINE PDF
V Best Chapter 1.1 Quadratics - ONLINE PDF
Uploaded by
Medical ReviewCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.
my
Pure Mathematics 1.1: Quadratics
You should be able to learn:
1.1.1 Completing the square and use a completed square form
1.1.2 Find and use the discriminant of a quadratic polynomial
1.1.3 Solve quadratic equations, quadratic inequalities, in one unknown
1.1.4 Solve simultaneous equations of which one is linear and one is quadratic
1.1.5 Recognise and solve equations in ! which are quadratic in some function of !
1.1.1 Completing the square and use a completed square form
Types of Completing the Square
When " = 1 When " ≠ 1
General Form: %(!) = ! ! + )! + * General Form: %(!) = "! ! + )! + *
Completed Square Form: %(!) = (! + +)! + , Completed Square Form: %(!) = "(! + +)! + ,
Techniques: Techniques:
" ! "
1. Divide b by 2 and put into bracket -! + !. 1. Factorize " and you get " -! ! + !. + *
&
!
" ! " ! " "
2. Add − -!. to -! + !. 2. Divide & by 2 and put into bracket -! + !&.
! !
" ! "
3. Add − - . to -! +
"
.
3. Simplify − - . + * using calculator !& !&
!
" ! " !
4. Multiply " into the bracket 4-! + !& . − -!&. 5
# $ #!
Outcome: 0(1) = -1 + $. − +2
% ""
5. Simplify − + * using calculator
'&
# $ #!
Outcome: 0(1) = 6 -1 + . − +2
$( %(
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 1
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
Exercise – Completing the Square
1. %(!) = ! ! + 4! + 2 2. %(!) = 2 + ! − ! !
3. %(!) = 1 + ! − 3! ! 4. %(!) = 6! ! − 29! − 5
5. %(!) = −! ! + 5! + 9 6. %(!) = 3 + 13! + 12! !
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 2
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
Sketching Graph and Finding Range/Equation of Axis of Symmetry
%(!) = "(! + +)! + ,, the values of ", + "?@ , will determine the position and shape of graph.
a) Value of " will determine if the shape of graph and if graph is narrower or broader.
6 > B, graph is minimum (happy face) and 6 < B, graph is maximum (sad face)
%(!) = ! ! %(!) = −! !
6 > D, graph is narrower and 6 < D, graph is broader
%(!) = 2! ! 1
%(!) = ! !
3
b) Value of p will determine if the graph is shifted left or right
***Equation of axis of symmetry: 1 = −E
E > B, graph is shifted to left and E < B, graph is shifted to right
%(!) = (! + 2)! %(!) = (! − 2)!
c) Value of q will determine if the graph is shifted up or down
F > B, graph is shifted up and F < B, graph is shifted down
%(!) = ! ! + 2 %(!) = ! ! − 2
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 3
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
Find maximum or minimum points and Equation of Axis of Symmetry
1. %(!) = (! − 3)! + 5 2. %(!) = −(! + 3)! − 7
3. %(!) = −2(! + 1)! + 4 4. %(!) = −2(! − 1)! + 3
5. %(!) = 2! ! + 3! 6. %(!) = 5! ! + 9! − 2
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 4
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
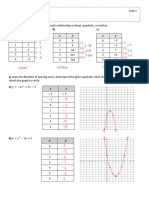
Sketching Quadratic Function Graph (Using Completing the Square Method)
%(!) = ! ! − 4! + 3
Shape of the graph:
Step 1: Completing the Square to find Maximum/Minimum point
Step 2: Find the y-intercept
Step 3: Find the x-intercept (if necessary)
Step 4: Plot graph
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 5
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
Sketching Quadratic Function Graph (Using the intersection Points Method)
%(!) = (! + 2)(6 − !)
Shape of graph:
Step 1: Find the x-intercept
Step 2: Determine the Maximum/Minimum point
Step 3: Find y-intercept
Step 4: Plot graph
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 6
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
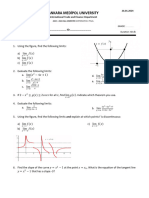
1. Plot the graph for the equation below
%(!) = 7 + 2! − 5! !
2. Plot the graph for the equation below
%(!) = 4! ! + ! − 1
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 7
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
1.1.2 Find and use the discriminant of a quadratic polynomial
Discriminant: H$ − I62, where it determines the nature of the roots
) ! − 4"* > 0
) ! − 4"* = 0
) ! − 4"* < 0
) ! − 4"* ≥ 0
Example:
Find the range of values of k if the graph %(!) = ! ! − L! + L + 8 intersects the x-axis at two points.
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 8
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
1. The roots of ! ! + +! + (+ − 1) = 0 are equal. Find p.
2. Find the range of values of m if the graph of the quadratic function N(!) = ! ! + O! + 16 does not
meet the x-axis.
3. Prove that the roots of the equation L! ! + (2L + 4)! + 8 = 0 are real for all values of L.
4. Show that the equation ! ! + 2(+ − 1)! + + = 0 always has real roots.
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 9
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
1.1.3 Solve quadratic equations, quadratic inequalities, in one unknown
Skills to solve quadratic equations
1. Factorisation
2. Completing the Square
3. Formula to find roots
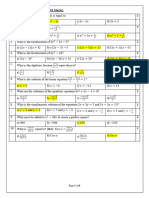
1. Solve the following equations using Formula to find roots
a. 4! ! + 3! = 5 b. 1 = 5! − 5! !
c. 8! − ! ! = 1 c. 5! ! + 9! + 2 = 0
2. Find the range of values of x if 7! + 4 ≤ 5! ! − 2
3. Solve the inequality 2(! − 3)! < 8
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 10
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
4. Solve the inequality 3! ! − ! < 2
5. Given that %(!) = 5! ! − 4! − 1, find the range of values of x so that %(!) is positive.
6. Given that %(!) = ! ! + 4! − 1 and N(!) = 6! + 2, find the range of values of x if %(!) > N(!).
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 11
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
1.1.4 Solve simultaneous equations of which one is linear and one is quadratic
***We use the linear equation express one unknown in terms of the other and substitute this in the quadratic
equation.
Example:
Solve the equation
!−Q =2
2! ! − 3Q ! = 15
Solve the following pairs of equations
!! + Q! = 5
Q−! =1
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 12
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
! ! + 4Q ! = 2
2Q + ! + 2 = 0
! ! − !Q = 14
Q =3−!
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 13
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
1.1.5 Recognise and solve equations in ! which quadratic in some function of !
An equation that is quadratic in a function of x can be reduced to a quadratic equation in x by replacing the
function of x by y.
Example
! ' + ! ! − 12 = 0
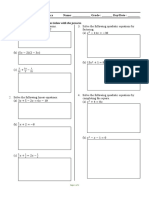
Solve the equations below
1.
)
−
)+
+ 36 = 0 2. (4! ! − 5)(! ! − 2) = 10
*" *
3. 8! ' − 4! ! = 0 , )
4. 9 = * " − * #
5. 2! + 5√! − 12 = 0 6. (! ! − 1)! − 5(! ! − 1) + 4 = 0
1st Edition: Mr Zi Yao
Producer: Mr Austin Lau & Jack
Copyright by VBest. All right reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or
transmitted in any form by any means, including photocopying, recording, or other electronic or mechanical
methods, without prior written permission of the publisher. Legal actions could be taken if there is a breach
in copyrights of notes.
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 14
Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709) vbest.edu.my
Pure mathematics 1.1 Quadratics | Google: VBEST | Notes Version 1.0 15
You might also like
- Section 4 Homework!: - Develop An Iterative Solver For!Document24 pagesSection 4 Homework!: - Develop An Iterative Solver For!tienkhoaNo ratings yet
- WPH12 01 MSC 20210517Document19 pagesWPH12 01 MSC 20210517Medical ReviewNo ratings yet
- QQQ - Pureyr2 - Chapter 3 - Sequences & Series (V1) : Total Marks: 48Document5 pagesQQQ - Pureyr2 - Chapter 3 - Sequences & Series (V1) : Total Marks: 48Medical Review100% (1)
- James Ruse 2019 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument24 pagesJames Ruse 2019 3U Prelim Yearly & SolutionsHazard Messi100% (1)
- Systems of Inequalities Study GuideDocument2 pagesSystems of Inequalities Study Guideapi-470562131No ratings yet
- (P) Add Maths Formula 2.0Document20 pages(P) Add Maths Formula 2.0suruli thandiramNo ratings yet
- 23 24 No MCQ SBQ 2 Polar and ComplexDocument7 pages23 24 No MCQ SBQ 2 Polar and Complexxffns4ffrcNo ratings yet
- FE Practice 1 Completed PDFDocument20 pagesFE Practice 1 Completed PDFkittttNo ratings yet
- FE Practice 1 CompletedDocument20 pagesFE Practice 1 CompletedkittttNo ratings yet
- MI Vol 2Document515 pagesMI Vol 2Quang Trần MinhNo ratings yet
- Sarp Ankara Calculus İskenderunDocument2 pagesSarp Ankara Calculus İskenderunMurat SahilliogluNo ratings yet
- Advanced Assessor TestDocument8 pagesAdvanced Assessor Testnathan.lee80No ratings yet
- 160.103 Methods of Mathematics - 2006 - Semester 3 - Final Exam - SolnsDocument7 pages160.103 Methods of Mathematics - 2006 - Semester 3 - Final Exam - SolnsDonNo ratings yet
- 00 - Unit 2 Course PackDocument19 pages00 - Unit 2 Course Packgameredi1234No ratings yet
- Grade 7 SeatWork 3Document2 pagesGrade 7 SeatWork 3jgalut611No ratings yet
- Jensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewDocument11 pagesJensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewKarma TenzinNo ratings yet
- AF12 Chapter 5 SolutionsDocument111 pagesAF12 Chapter 5 SolutionssupremeNo ratings yet
- 160.103 Methods of Mathematics - 2005 - Semester 3 - Final Exam-SolnsDocument6 pages160.103 Methods of Mathematics - 2005 - Semester 3 - Final Exam-SolnsDonNo ratings yet
- Precalculus 02 Polynomial FunctionsDocument64 pagesPrecalculus 02 Polynomial FunctionssandiodjimelijulioarmelNo ratings yet
- 7 TestDocument9 pages7 TestЕралы БегалыNo ratings yet
- Classwork-1 Mathematics Grade XDocument2 pagesClasswork-1 Mathematics Grade XRasendriya AdindaNo ratings yet
- Algebra Problems: 1. (4 MarksDocument15 pagesAlgebra Problems: 1. (4 Marksirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- MI1046 Midterm 20182 QuestionDocument1 pageMI1046 Midterm 20182 QuestionTùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 160.103 Methods of Mathematics - 2006 - Semester 1-Final Exam-SolnsDocument7 pages160.103 Methods of Mathematics - 2006 - Semester 1-Final Exam-SolnsDonNo ratings yet
- Ready, Set, Go!Document2 pagesReady, Set, Go!Nadya JamulaNo ratings yet
- Parametric FormDocument2 pagesParametric FormAlexander XieNo ratings yet
- Midterm PHYS102 SolutionsDocument4 pagesMidterm PHYS102 Solutionsatakanozcan2004No ratings yet
- Logartihm HWDocument6 pagesLogartihm HWDemir BasaktarNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Final Exam ADocument29 pagesPrecalculus Final Exam Ashenglan fangNo ratings yet
- 34 Slope Field - 230313 - 173727 PDFDocument8 pages34 Slope Field - 230313 - 173727 PDFŞilayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 (Indices)Document2 pagesWorksheet 4 (Indices)chân trầnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Integration by Parts & Algebraic SubstitutionDocument19 pagesLesson 8 Integration by Parts & Algebraic SubstitutionMarvin James JaoNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Crash Course 2022Document16 pagesAdd Maths Crash Course 2022Raveena SinghNo ratings yet
- The Way of The World Guide-CompressedDocument50 pagesThe Way of The World Guide-CompressedNajam Khan MahsudNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods 3&4 CAS: Total Time: 45 Mins Total Marks: 20Document6 pagesMathematical Methods 3&4 CAS: Total Time: 45 Mins Total Marks: 20Gina OhNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review - ฉบับจริงDocument6 pagesFinal Exam Review - ฉบับจริงGreat-Pattadol PannsumneangNo ratings yet
- PCT Chapter 10 SolutionsDocument26 pagesPCT Chapter 10 SolutionsecamodeoNo ratings yet
- GeomDocument148 pagesGeomspecialuses351No ratings yet
- How Do I Solve This EquationDocument6 pagesHow Do I Solve This EquationkinglerNo ratings yet
- Zekolah CIS Year End Junior 1 MM 8h7p5yDocument15 pagesZekolah CIS Year End Junior 1 MM 8h7p5yJacky SowNo ratings yet
- Introduction Pack v2Document31 pagesIntroduction Pack v2dadajee420No ratings yet
- Summer Entering Algebra2Document31 pagesSummer Entering Algebra2Ross HamiltonNo ratings yet
- SecondPartial 2018-01-30 C SolutionsDocument6 pagesSecondPartial 2018-01-30 C SolutionsfabriNo ratings yet
- Topical Practice Chap 1Document1 pageTopical Practice Chap 1Lee JunNo ratings yet
- E-Book: Managerial Accounting Test Paper Questions On BudgetingDocument26 pagesE-Book: Managerial Accounting Test Paper Questions On BudgetingbhalaNo ratings yet
- Vectors (PPD)Document11 pagesVectors (PPD)Fazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Final Exam ADocument13 pagesPrecalculus Final Exam AEdal SantosNo ratings yet
- Precalculus Final Exam A PDFDocument13 pagesPrecalculus Final Exam A PDFMelissa OrozcoNo ratings yet
- (Maximum Marks: 15)Document2 pages(Maximum Marks: 15)ZEEL PATELNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Mathematics Yearly Teaching Scheme 2012Document11 pagesForm 2 Mathematics Yearly Teaching Scheme 2012iazs3028No ratings yet
- Problems October 2023Document3 pagesProblems October 2023woboc79249No ratings yet
- Some Extra Questions FunctionsDocument7 pagesSome Extra Questions FunctionsDemir BasaktarNo ratings yet
- PC End of Year Exam PracticeDocument12 pagesPC End of Year Exam Practice40687No ratings yet
- Hw3bs-Multiplying and Dividing Rational ExpressionsDocument2 pagesHw3bs-Multiplying and Dividing Rational ExpressionsDhaval PatelNo ratings yet
- 485 ReviewDocument8 pages485 Reviewdaksh22pNo ratings yet
- Venn DiagramsDocument14 pagesVenn DiagramsjoNo ratings yet
- S3 Indices Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesS3 Indices Revision WorksheetbrendanchanzhiquanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Math Year End Review 2015: Unit 1: Square Root and Pythagorean TheoremDocument8 pagesGrade 8 Math Year End Review 2015: Unit 1: Square Root and Pythagorean TheoremJenny ZhangNo ratings yet
- Promo. Exam Amath Paper 1 (Suggested Answers)Document14 pagesPromo. Exam Amath Paper 1 (Suggested Answers)legacyNo ratings yet
- COPADS, I: Distance Coefficients Between Two Lists or Sets: Maurice HT LingDocument31 pagesCOPADS, I: Distance Coefficients Between Two Lists or Sets: Maurice HT LingDauji SahaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Microsoft ExcelDocument45 pagesMicrosoft Excel Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Microsoft Excel Microsoft ExcelAziz ZazzaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Department of Engineering: LegendDocument1 pageDepartment of Engineering: LegendMedical ReviewNo ratings yet
- If Wrong No Marks in (I) : 4.2 Answers To Exam Questions 1Document3 pagesIf Wrong No Marks in (I) : 4.2 Answers To Exam Questions 1Medical ReviewNo ratings yet
- Journal 1 Future of Medicine Real-Life TricorderDocument2 pagesJournal 1 Future of Medicine Real-Life TricorderMedical ReviewNo ratings yet
- 307C Operations ResearchDocument25 pages307C Operations ResearchBasant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Density Functionals For Couiomb Systems: Departments New Jersey 08544, U.S.ADocument35 pagesDensity Functionals For Couiomb Systems: Departments New Jersey 08544, U.S.ARamon FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Math in The Modern WorldDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam Math in The Modern WorldJoana Marie DeontoyNo ratings yet
- Cauchy Integral Formula PDFDocument7 pagesCauchy Integral Formula PDFbhabapradhan5572No ratings yet
- 01 - REAL NUMBERS - MCQsDocument25 pages01 - REAL NUMBERS - MCQsjellohuman127No ratings yet
- (Made Simple Books) William R. Gondin, Bernard Sohmer - Advanced Algebra and Calculus Made Simple (1959, Doubleday) - Libgen - LiDocument228 pages(Made Simple Books) William R. Gondin, Bernard Sohmer - Advanced Algebra and Calculus Made Simple (1959, Doubleday) - Libgen - LiRodrigoNo ratings yet
- A Math Summary BookletDocument113 pagesA Math Summary BookletbusinessNo ratings yet
- Trapezoidal Rule NotesDocument3 pagesTrapezoidal Rule NotesAmbreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Desrosiers, Lübbecke - A Primer in Column GenerationDocument32 pagesDesrosiers, Lübbecke - A Primer in Column Generationmundocientifico78No ratings yet
- The Rise of Axiomatic MethodDocument26 pagesThe Rise of Axiomatic MethodMichael Bahian Dodongan100% (1)
- Relation Between Difference OperatorsDocument8 pagesRelation Between Difference OperatorsS AdilakshmiNo ratings yet
- I Integration-02 - Solved ExampleDocument23 pagesI Integration-02 - Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- HSC Maths Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesHSC Maths Questions and AnswersNithya VasuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sets: (Socks, Shoes, Watches, Shirts, ... ) (Index, Middle, Ring, Pinky)Document8 pagesIntroduction To Sets: (Socks, Shoes, Watches, Shirts, ... ) (Index, Middle, Ring, Pinky)Mark Wesly RequirmeNo ratings yet
- Constrained Minimization Using The Genetic AlgorithmDocument5 pagesConstrained Minimization Using The Genetic AlgorithmJoãoEdgarNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Summative Test: - Read The Questions Carefully. Choose The Letter of Your Answer and Write It in YourDocument4 pagesMath 7 Summative Test: - Read The Questions Carefully. Choose The Letter of Your Answer and Write It in Youretheljoy agpaoaNo ratings yet
- Lattice Solution PDFDocument142 pagesLattice Solution PDFhimanshu Arya100% (1)
- 7 1Document30 pages7 1Ben Joseph CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Algebra 80308Document10 pagesAlgebra 80308Nie Anggraeni RiniNo ratings yet
- Exercises Modelica TutorialDocument3 pagesExercises Modelica Tutorialrodiboss99No ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 6Document10 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 6ESTER ENGANANo ratings yet
- 2023 HSC Maths Ext 1Document20 pages2023 HSC Maths Ext 1n4eel3shNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-II (MATH F112) : Linear Algebra and Complex AnalysisDocument70 pagesMathematics-II (MATH F112) : Linear Algebra and Complex AnalysisReetik RanjanNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent Relay Coordination in A Grid-Connected Microgrid SystemDocument5 pagesOvercurrent Relay Coordination in A Grid-Connected Microgrid SystemWirangga Septiano PutraNo ratings yet
- 2 Zero Exponent and Powers of 10Document3 pages2 Zero Exponent and Powers of 10Salma SaderNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Paper 4H Higher TierDocument28 pagesMathematics A: Paper 4H Higher Tiermanz 123No ratings yet
- ENAT Class Grade 10 PreTest FAITHDocument32 pagesENAT Class Grade 10 PreTest FAITHJEREMY FOLLERONo ratings yet
- MITx SCX KeyConcept SC0x FV PDFDocument61 pagesMITx SCX KeyConcept SC0x FV PDFJoao CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- TSTDocument26 pagesTSThuyhoangkobeNo ratings yet