Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4
Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4
Uploaded by
Diệp Đỗ Ngọc0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageMars is the fourth planet from the Sun and has notable geological features including the largest volcano and canyon in the solar system. It has a thin atmosphere and reddish appearance due to iron oxide on its surface. Mars has been explored by numerous uncrewed spacecraft starting in 1964. In recent years, spacecraft from multiple space agencies including NASA, ESA, ISRO, and the UAE have visited Mars to study its climate and geology.
Original Description:
Original Title
no
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMars is the fourth planet from the Sun and has notable geological features including the largest volcano and canyon in the solar system. It has a thin atmosphere and reddish appearance due to iron oxide on its surface. Mars has been explored by numerous uncrewed spacecraft starting in 1964. In recent years, spacecraft from multiple space agencies including NASA, ESA, ISRO, and the UAE have visited Mars to study its climate and geology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4
Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4
Uploaded by
Diệp Đỗ NgọcMars is the fourth planet from the Sun and has notable geological features including the largest volcano and canyon in the solar system. It has a thin atmosphere and reddish appearance due to iron oxide on its surface. Mars has been explored by numerous uncrewed spacecraft starting in 1964. In recent years, spacecraft from multiple space agencies including NASA, ESA, ISRO, and the UAE have visited Mars to study its climate and geology.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
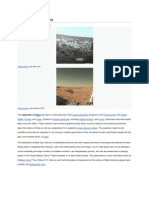
Mars
is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, being
larger than only Mercury. In English, Mars carries the name of the Roman god of war and is often
referred to as the "Red Planet".[16][17] The latter refers to the effect of the iron oxide prevalent on
Mars's surface, which gives it a reddish appearance distinctive among the astronomical bodies
visible to the naked eye.[18] Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, with surface features
reminiscent of the impact craters of the Moon and the valleys, deserts and polar ice caps of Earth.
The days and seasons are comparable to those of Earth, because the rotational period as well as
the tilt of the rotational axis relative to the ecliptic plane are similar. Mars is the site of Olympus
Mons, the largest volcano and highest known mountain on any planet in the Solar System, and
of Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The smooth Borealis basin in
the Northern Hemisphere covers 40% of the planet and may be a giant impact feature.[19][20] Mars
has two moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are small and irregularly shaped. These may be
captured asteroids, similar to 5261 Eureka, a Mars trojan.[21][22]
Mars has been explored by several uncrewed spacecraft. Mariner 4 was the first spacecraft to visit
Mars; launched by NASA on 28 November 1964, it made its closest approach to the planet on 15
July 1965. Mariner 4 detected the weak Martian radiation belt, measured at about 0.1% that of Earth,
and captured the first images of another planet from deep space.[23] The Soviet Mars 3 mission
included a lander, which achieved a soft landing in December 1971; however, contact was lost
seconds after touchdown.[24] On 20 July 1976, Viking 1 performed the first successful landing on the
Martian surface.[25] On 4 July 1997, the Mars Pathfinder spacecraft landed on Mars and on 5 July
released its rover, Sojourner, the first robotic rover to operate on Mars.[26] The Mars Express orbiter,
the first European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft to visit Mars, arrived in orbit on 25 December
2003.[27] In January 2004, NASA's Mars Exploration Rovers, named Spirit and Opportunity, both
landed on Mars; Spirit operated until 22 March 2010 and Opportunity lasted until 10 June 2018.
[28]
NASA landed its Curiosity rover on August 6, 2012, as a part of its Mars Science Laboratory
(MSL) mission to investigate Martian climate and geology.[29] On 24 September 2014, the Indian
Space Research Organisation (ISRO) became the fourth space agency to visit Mars when its
maiden interplanetary mission, the Mars Orbiter Mission spacecraft, arrived in orbit.[30] The United
Arab Emirates became the fifth to successfully undertake a mission to Mars, having inserted an
orbiter in to the Martian atmosphere on 9 February 2021.[31] NASA's Perseverance rover
and Ingenuity helicopter successfully landed on Mars on 18 February 2021.
You might also like
- The UniverseDocument15 pagesThe Universenidarsena2004No ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - The Solar SystemDocument36 pagesChapter 24 - The Solar SystemHeather Blackwell100% (1)
- Mars Surface Outpost-Mission ReportDocument14 pagesMars Surface Outpost-Mission ReportRyan Holloway100% (1)
- Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4Document1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4Heh MehNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4Document1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4LT ExtraNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4Document1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4robertoNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4Document1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4Carlos GomezNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument1 pageMarssoham limayeNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument23 pagesMarsPrajwal SNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second Smallest Planet in The Solar SystemDocument1 pageMars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second Smallest Planet in The Solar Systempress_jakeNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4 Viking 1 Sojourner Zhurong Rosalind Franklin Rover MissionDocument1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Mariner 4 Viking 1 Sojourner Zhurong Rosalind Franklin Rover MissionjdkfdbNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second Smallest Planet in The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesMars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second Smallest Planet in The Solar SystemLak DavisNo ratings yet
- Planet Mars OverviewDocument2 pagesPlanet Mars OverviewsoftwareanpNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The FourthDocument1 pageMars Is The FourthANMOLNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument7 pagesMarsRachna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The FourthDocument1 pageMars Is The FourthSaad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Historical Observations: Mars Is The FourthDocument18 pagesHistorical Observations: Mars Is The FourthLakshmish GopalNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument9 pagesEarthHaider AbbasNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second-Smallest Planet in The SolarDocument3 pagesMars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second-Smallest Planet in The SolarEdgar Vega AragónNo ratings yet
- MarsDocument6 pagesMarsjennysardonaNo ratings yet
- Exploration of MarsDocument30 pagesExploration of MarsHaris Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- The History of Going To MarsDocument1 pageThe History of Going To MarsAngelie AngelidouNo ratings yet
- JupiterDocument2 pagesJupiterAnonymous Xak6PI3YNo ratings yet
- Planets 23Document7 pagesPlanets 23clinkx drewNo ratings yet
- MARSDocument5 pagesMARSAnchyNo ratings yet
- Solar System by Harsh MandhianDocument10 pagesSolar System by Harsh MandhianHarsh MandhianNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentJo JsNo ratings yet
- Mercury Is The InnermostDocument4 pagesMercury Is The InnermostAbbasali AsamdiNo ratings yet
- Grade V-Gumamela Damilag Elementary School: John Paul C. CuynoDocument1 pageGrade V-Gumamela Damilag Elementary School: John Paul C. CuynoLen Cen YnoNo ratings yet
- Jupiter: Jupiter Is The FifthDocument4 pagesJupiter: Jupiter Is The FifthSahil NaikNo ratings yet
- Inner Planets:: MercuryDocument10 pagesInner Planets:: MercuryRekha Raghavan NandakumarNo ratings yet
- Balba Chrislyn B Solar System ProjectDocument15 pagesBalba Chrislyn B Solar System ProjectBalba ChrislynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Robotic ExplorationDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Robotic ExplorationJillKellyNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth: 134340 PlutoDocument1 pageMars Is The Fourth: 134340 Plutopatilamol019No ratings yet
- Planet MarsDocument2 pagesPlanet Marsmarolien.swartNo ratings yet
- The Latest: Insight Mission Elysium PlanitiaDocument7 pagesThe Latest: Insight Mission Elysium PlanitiaUnbeeNo ratings yet
- Hanshan Mathieesan - Wed May 1Document9 pagesHanshan Mathieesan - Wed May 1mathihanshanNo ratings yet
- The Nine PlanetsDocument2 pagesThe Nine PlanetsbabucpyNo ratings yet
- Solar System Paper-MarsDocument7 pagesSolar System Paper-Marsapi-255137286No ratings yet
- Scrapbook in Science: Venus Is The SecondDocument4 pagesScrapbook in Science: Venus Is The SecondAngela Halasan HinautanNo ratings yet
- Mars A Brief History of All Missions To The Red PlanetDocument8 pagesMars A Brief History of All Missions To The Red PlanetVirtuous RenaissanceNo ratings yet
- MoonDocument2 pagesMoonYounes BajdaNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth: Planet Sun Solar SystemDocument1 pageMars Is The Fourth: Planet Sun Solar SystemRega DasNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument8 pagesEarthKhent NatzNo ratings yet
- Planets 4Document2 pagesPlanets 4PRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Mars Facts: Mars Was Formed Approximately 4.6 Billion Years AgoDocument7 pagesMars Facts: Mars Was Formed Approximately 4.6 Billion Years AgoLV MartinNo ratings yet
- MarssssDocument1 pageMarssssTheo lolNo ratings yet
- Solar System PlanetsDocument6 pagesSolar System PlanetsAbida AzizNo ratings yet
- UniverseDocument13 pagesUniverseMini RobertNo ratings yet
- Mars Exploration Current MissionsDocument6 pagesMars Exploration Current MissionsrathanNo ratings yet
- MoonDocument2 pagesMoonAvram AvramovNo ratings yet
- About Planets - Vaishali's ProjectDocument3 pagesAbout Planets - Vaishali's ProjectRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Planets 5Document4 pagesPlanets 5PRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Mars Exploration: 1. Mars - The Red PlanetDocument5 pagesMars Exploration: 1. Mars - The Red PlanetDrGnome BloxNo ratings yet
- The Sun Terrestrial Planets The Solar System EarthDocument6 pagesThe Sun Terrestrial Planets The Solar System EarthJackie DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second-Smallest Planet inDocument26 pagesMars Is The Fourth Planet From The Sun and The Second-Smallest Planet inAnishNo ratings yet
- Venus Is The Second: Planet Sun Earth Roman Goddess Moon Apparent Magnitude Inferior Planet ElongationDocument3 pagesVenus Is The Second: Planet Sun Earth Roman Goddess Moon Apparent Magnitude Inferior Planet ElongationEva Michelle Tolentino DatoNo ratings yet
- Planet Mars: By: Thomas Samuel P. MataDocument7 pagesPlanet Mars: By: Thomas Samuel P. MataSteffane MataNo ratings yet
- Mars Is The fou-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageMars Is The fou-WPS OfficeIan Rex DesolocNo ratings yet
- Planets in Our Solar SystemDocument10 pagesPlanets in Our Solar SystemSamir BelkarNo ratings yet
- NASA Vision and MissionDocument26 pagesNASA Vision and MissionFajar NdoluNo ratings yet
- Exploring Universe Video WorksheetDocument2 pagesExploring Universe Video WorksheetDaniel PayerasNo ratings yet
- All About The USA by Emily WinstonDocument13 pagesAll About The USA by Emily WinstonДавид ПустельникNo ratings yet
- Using A Robotic Helicopter To Fuel Interest in and Augment The HumanDocument11 pagesUsing A Robotic Helicopter To Fuel Interest in and Augment The Human枪手瞎炳No ratings yet
- Space ExplorationDocument15 pagesSpace Explorationt_ql2010No ratings yet
- The Future of The Mars RoverDocument4 pagesThe Future of The Mars RoverJosh PillitiereNo ratings yet
- Bricks+Reading+240+Nonfiction L2 Word+ListDocument16 pagesBricks+Reading+240+Nonfiction L2 Word+ListLingoes Wy KimNo ratings yet
- Life On Mars Final ReportDocument27 pagesLife On Mars Final Reportahmedxahmed100% (1)
- Reading About Mars - Comprehension Grades 3 - 6Document16 pagesReading About Mars - Comprehension Grades 3 - 6Matilda El HageNo ratings yet
- Astronomy, Vol. 51.08 (August 2023)Document80 pagesAstronomy, Vol. 51.08 (August 2023)georgetacaprarescuNo ratings yet
- 2022.3.31 - MSR Overview - ASTR Presentation 2Document16 pages2022.3.31 - MSR Overview - ASTR Presentation 2Anonymous Wu14iV9dqNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentJo JsNo ratings yet
- Mars Global Surveyor FactsDocument36 pagesMars Global Surveyor FactsAviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet
- The Mars EnigmaDocument89 pagesThe Mars Enigmasithusoemoe100% (1)
- Mars Science Laboratory - Curiosity Rover - NASADocument3 pagesMars Science Laboratory - Curiosity Rover - NASAsandamaliNo ratings yet
- RevisedessayDocument4 pagesRevisedessayapi-609945085No ratings yet
- A Mars Rover Is An Automated Motor Vehicle Which Propels Itself Across The Surface of The Planet Mars After LandingDocument5 pagesA Mars Rover Is An Automated Motor Vehicle Which Propels Itself Across The Surface of The Planet Mars After Landingsasanka9No ratings yet
- Complete RISE The Journey of A Young EntrepreneurDocument56 pagesComplete RISE The Journey of A Young EntrepreneursatNo ratings yet
- Tianwen 1Document13 pagesTianwen 1gewoce9355No ratings yet
- Types of TextDocument13 pagesTypes of TextPauline Diane PresenteNo ratings yet
- A Hypothesis: The Opportunity and Curiosity Mars RoversDocument55 pagesA Hypothesis: The Opportunity and Curiosity Mars Roversm_tOm100% (1)
- Mars Program - WikipediaDocument6 pagesMars Program - WikipediazentropiaNo ratings yet
- The Hope Probe's SuccessDocument3 pagesThe Hope Probe's SuccessSkygazers' Society100% (1)
- The Exploration of Mars - Crew Surface ActivitiesDocument19 pagesThe Exploration of Mars - Crew Surface ActivitiesngibbinsNo ratings yet
- Avanthi's Scientific Technological and Research Academy.: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument25 pagesAvanthi's Scientific Technological and Research Academy.: Department of Mechanical EngineeringSampath Kumar PesaramelliNo ratings yet
- 2022年中考英语必读时事热点 (学生版)Document13 pages2022年中考英语必读时事热点 (学生版)PeggyNo ratings yet
- MarCO - CubeSats To Mars in 2016Document7 pagesMarCO - CubeSats To Mars in 2016Ahmed FalihNo ratings yet