Professional Documents
Culture Documents
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
709 viewsDaily Management Quiz: 2007: SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
Daily Management Quiz: 2007: SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
Uploaded by
Prakash KumarThis document contains a 30 question quiz about various terms and concepts related to total productive maintenance (TPM). The questions cover topics such as the full forms of acronyms like TPM, JIPM, TQM, OEE; concepts like autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, 5S; pioneers of TPM like Seichi Nakajima; and which country introduced certain concepts. The quiz provides multiple choice answers for identifying the correct response for each question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Audit Checklist - JH Steps 1-3Document13 pagesAudit Checklist - JH Steps 1-3Shantanu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Shut Down Procedure (Tata Steel)Document19 pagesShut Down Procedure (Tata Steel)Prakash Kumar100% (2)
- 5 KK PillarDocument54 pages5 KK Pillarazadsingh183% (6)
- Slide TPM SHEDocument14 pagesSlide TPM SHEhdjdjNo ratings yet
- E & Tpillar: Education & Training Pillar ActivitiesDocument21 pagesE & Tpillar: Education & Training Pillar Activitiessamkaria rajesh100% (1)
- JIPM TPM AwardsDocument23 pagesJIPM TPM AwardspreethishNo ratings yet
- CII JH Step 4Document4 pagesCII JH Step 4Kumar Swami0% (1)
- SFM Tmmin Otics PDFDocument40 pagesSFM Tmmin Otics PDFAgung IndriantoNo ratings yet
- JH Step 1 Audit SheetDocument2 pagesJH Step 1 Audit SheetSwayambhar Majumder75% (4)
- CQI-09.Ver 4Document128 pagesCQI-09.Ver 4Nethaji MettNo ratings yet
- Training ON TPM: Rapl Production SystemDocument25 pagesTraining ON TPM: Rapl Production Systemabhijit bhattacherjeENo ratings yet
- TPMDocument42 pagesTPMSrinivasan VenkatNo ratings yet
- Pillar: Initial Control or Development ManagementDocument7 pagesPillar: Initial Control or Development ManagementNavneet SharmaNo ratings yet
- JH Step-1 & 2activitiesDocument34 pagesJH Step-1 & 2activitiesGREENEXE BUSINESS CONSULTANTNo ratings yet
- JH PPT 18.12.20Document46 pagesJH PPT 18.12.20MAngesh Gade0% (1)
- TPM Over ViewDocument37 pagesTPM Over ViewHarshad_SNo ratings yet
- Kobetsu Kaizen Pillar: Training Program OnDocument51 pagesKobetsu Kaizen Pillar: Training Program OnNeeraj SethyNo ratings yet
- Q Star - (Waste Management)Document14 pagesQ Star - (Waste Management)Anonymous Y5cnLVYMGNo ratings yet
- JH PillarDocument39 pagesJH PillarshaktiNo ratings yet
- KK Pillar PDFDocument91 pagesKK Pillar PDFdiwesh26decNo ratings yet
- CPCL TPM AnalysisDocument67 pagesCPCL TPM AnalysisKhader HussainNo ratings yet
- Focused Improvement PillarDocument19 pagesFocused Improvement PillarDkhissene Imad100% (1)
- Chapter 7. QM PILLAR PDFDocument60 pagesChapter 7. QM PILLAR PDFNARENDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Education & Training ManualDocument23 pagesChapter 6. Education & Training ManualVivek Kumar100% (1)
- TPM JH PPT 01 JH AwarenessDocument28 pagesTPM JH PPT 01 JH AwarenessLakshmanan Venkatesan100% (1)
- MT QM PillarDocument71 pagesMT QM Pillarazadsingh1No ratings yet
- Six Sigma - Reduction of Downtime - RE Mill-2 - NewDocument76 pagesSix Sigma - Reduction of Downtime - RE Mill-2 - NewKiruthiga VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- Quality CricleDocument22 pagesQuality CricleQSSD ENTERPRISES100% (1)
- Stage Step (Nakajima's 12 Steps) : Decision To Introduce TPMDocument16 pagesStage Step (Nakajima's 12 Steps) : Decision To Introduce TPMKarisma Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- Study of JH Implementation ReadyDocument27 pagesStudy of JH Implementation ReadyNaveen Jangid100% (1)
- QM Pillar Training CIIDocument76 pagesQM Pillar Training CIINARENDER SINGH100% (1)
- Standard Reaction Plan To Abnormal Situation: Restart ProcessDocument1 pageStandard Reaction Plan To Abnormal Situation: Restart ProcessDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- 02 TVS Motor Co. LTDDocument127 pages02 TVS Motor Co. LTDRaj Rudrapaa100% (2)
- For Cii On TPM - Jun '10 v3Document54 pagesFor Cii On TPM - Jun '10 v3outline35No ratings yet
- KK PillarDocument117 pagesKK PillarMAngesh Gade100% (1)
- 08.DM Pillar FCDocument67 pages08.DM Pillar FCashutoshpal21No ratings yet
- 5.6 Office TPM and Concept of PQCDSMDocument9 pages5.6 Office TPM and Concept of PQCDSMvenkata_776555228100% (1)
- 4M Change Management PresentationDocument42 pages4M Change Management PresentationSARAI MARINNo ratings yet
- DWM Overview RIBDocument43 pagesDWM Overview RIBAshokNo ratings yet
- Jishu Hozen Audit Sheet: Step 1: Initial Cleaning Department: Area: Circle Name: Circle LeaderDocument7 pagesJishu Hozen Audit Sheet: Step 1: Initial Cleaning Department: Area: Circle Name: Circle LeaderharshavardhanNo ratings yet
- Kaizen in JIT Production SystemDocument51 pagesKaizen in JIT Production SystemLlehk FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Blue 7 TPM Part 1 of 2Document30 pagesBlue 7 TPM Part 1 of 2shamelnaNo ratings yet
- 01.sundram Fasteners LTDDocument60 pages01.sundram Fasteners LTDTapash Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Improvement KaizenDocument11 pagesImprovement KaizenAnkur DhirNo ratings yet
- Kaizen KobetDocument19 pagesKaizen KobetShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomous MaintenanceDocument38 pagesAutonomous Maintenancechusz100% (1)
- Non Conformity Report: Part Name:-Clamp Bolt Model: M4 Clamp Bolt Supplier:-Paradise Indus. Customer: PICLDocument1 pageNon Conformity Report: Part Name:-Clamp Bolt Model: M4 Clamp Bolt Supplier:-Paradise Indus. Customer: PICLAyush Narang100% (1)
- Sona GroupDocument56 pagesSona GroupbrindatammaNo ratings yet
- SKILL MATRIX StaffDocument3 pagesSKILL MATRIX StaffMAHIPAL baseraNo ratings yet
- Concept Diagram - Figure of 8': Quality Kaizen Quality MaintenanceDocument41 pagesConcept Diagram - Figure of 8': Quality Kaizen Quality MaintenanceNARENDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- Example of TPM in Office EuropeDocument53 pagesExample of TPM in Office Europekingathur26681No ratings yet
- WCM ChecklistDocument13 pagesWCM ChecklistYurdun OrbakNo ratings yet
- Lost Cost MatrixDocument2 pagesLost Cost Matrixrecep1100% (5)
- Professional MaintenanceDocument391 pagesProfessional MaintenanceAimar Vanderlei Ferreira Filho100% (1)
- STEP1MANDocument101 pagesSTEP1MANRPM28XI100% (1)
- Kaizen EventDocument22 pagesKaizen EventRibmanNo ratings yet
- Red Bin AnalysisDocument5 pagesRed Bin AnalysisDINESHCHOUDHARY88No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Total Pr...Document9 pagesAn Introduction To Total Pr...Abhinav JainNo ratings yet
- Total Productive Maintenance: Production Production Maintenance MaintenanceDocument42 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance: Production Production Maintenance Maintenance123456789No ratings yet
- FI Training WorkshopDocument17 pagesFI Training WorkshopRajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Reports in TQMDocument1 pageReports in TQMJean LeonorNo ratings yet
- Effective Maintenance Introduction 1712885423Document29 pagesEffective Maintenance Introduction 1712885423Rogério Andrade Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- PcbridgeDocument4 pagesPcbridgePrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Download CoprocessorDocument2 pagesHow To Download CoprocessorPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProceduresDocument4 pagesStandard Operating ProceduresPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Automatio N Pyramid?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Automatio N Pyramid?Prakash KumarNo ratings yet
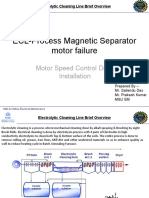
- ECL-Process Magnetic Separator Motor Failure: Motor Speed Control Drive InstallationDocument7 pagesECL-Process Magnetic Separator Motor Failure: Motor Speed Control Drive InstallationPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Reactions Under Anodic and Cathodic PolarizationDocument4 pagesReactions Under Anodic and Cathodic PolarizationPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- # 6030 PEN OIL: Grade: Industrial Grade Heavy Duty Penetrating OilDocument3 pages# 6030 PEN OIL: Grade: Industrial Grade Heavy Duty Penetrating OilPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Cable Maintenance: Study Material OnDocument54 pagesFiber Optics Cable Maintenance: Study Material OnPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- BAF - SOP - 04 Maintenance of Emerson UPSDocument12 pagesBAF - SOP - 04 Maintenance of Emerson UPSPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Ultraware FaultdetailsDocument14 pagesUltraware FaultdetailsPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Seat BeltDocument2 pagesSeat BeltPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Valid Standard: Approved Vendor List For Electrical and ElectronicsDocument12 pagesValid Standard: Approved Vendor List For Electrical and ElectronicsPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- 8376 Electronic Component CleanerDocument3 pages8376 Electronic Component CleanerPrakash Kumar100% (1)
- Electrical SafetyDocument16 pagesElectrical SafetyPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Gas SafetyDocument1 pageHydrogen Gas SafetyPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Track Line Safety Inside Tata Steel Works SS/GEN-24: by Sachin ParanjapeDocument14 pagesTrack Line Safety Inside Tata Steel Works SS/GEN-24: by Sachin ParanjapePrakash Kumar100% (1)
- Valid Standard: Power Cutting Tracking FormDocument1 pageValid Standard: Power Cutting Tracking FormPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Safety Shower Eye WashDocument10 pagesSafety Shower Eye WashPrakash Kumar100% (1)
- SpeedingDocument3 pagesSpeedingPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Seat BeltDocument2 pagesSeat BeltPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Power TransformerDocument55 pagesPower TransformerPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Selection and Maintenance of AC MotorDocument29 pagesSelection and Maintenance of AC MotorPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Check List For Fire Hydrant Safety StandardDocument3 pagesCheck List For Fire Hydrant Safety StandardPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Dakota Office Products Case StudyDocument12 pagesDakota Office Products Case StudyAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- 2.8 - ICR Aug 06 - Mill PerformanceDocument2 pages2.8 - ICR Aug 06 - Mill PerformanceKreshnik StratiNo ratings yet
- Acrydur 116 ENG US 20 10 2022Document4 pagesAcrydur 116 ENG US 20 10 2022Volkmar LullNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints Limited:: Management As A Tool For Higher ProductivityDocument26 pagesAsian Paints Limited:: Management As A Tool For Higher ProductivityAditi NigamNo ratings yet
- Slides Erp - SCMDocument79 pagesSlides Erp - SCMMAI NGUYỄN XUÂNNo ratings yet
- Client CV - Account Manager (MY)Document2 pagesClient CV - Account Manager (MY)SAIHA AZIZNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Pharma: January 2014Document8 pagesCustomer Relationship Management (CRM) in Pharma: January 2014Uchenna 'Bonex' OgbonnaNo ratings yet
- Marriott: Subject: Marketing Research MBA (Agribusiness Management) Batch: 2021-23Document10 pagesMarriott: Subject: Marketing Research MBA (Agribusiness Management) Batch: 2021-23SOMYA RANJAN NANDANo ratings yet
- Quality Gurus: (The Correct Options Have Been Marked in Red) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuality Gurus: (The Correct Options Have Been Marked in Red) Multiple Choice QuestionsRanbir KapoorNo ratings yet
- AAR Hotels & Resorts - Company ProfileDocument14 pagesAAR Hotels & Resorts - Company ProfileRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Business - Riverview Trial With SolutionsDocument31 pages2012 Business - Riverview Trial With SolutionsArpit KumarNo ratings yet
- PCN Analysis Exercise 2012 With Airline ExampleDocument16 pagesPCN Analysis Exercise 2012 With Airline ExampleQuick StarNo ratings yet
- DAILY WELD FIT-UP and PRODUCTION REPORT (Field Weld) - PIPELINE-SATR-W-2007Document2 pagesDAILY WELD FIT-UP and PRODUCTION REPORT (Field Weld) - PIPELINE-SATR-W-2007smdriyazbashaNo ratings yet
- Amazon Fba Guide 2021Document116 pagesAmazon Fba Guide 2021Nabil MehibelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementJohanna VidadNo ratings yet
- 12th All Komatsu Indonesia Technical Olympic 2022 Official ResultDocument2 pages12th All Komatsu Indonesia Technical Olympic 2022 Official ResultMarchal KawengianNo ratings yet
- On Customer Relationship ManagementDocument17 pagesOn Customer Relationship ManagementSandip Chaudhari96% (28)
- Topic 1: E-Commerce Business Models and ConceptsDocument10 pagesTopic 1: E-Commerce Business Models and Conceptsmaria lailanie bautistaNo ratings yet
- PIZZA ZONE BBA ProjectDocument76 pagesPIZZA ZONE BBA ProjectPrince RamoliyaNo ratings yet
- B2B Case Study On Voltas & EELDocument11 pagesB2B Case Study On Voltas & EELDebasis PrustyNo ratings yet
- Contractor Vendor Audit ChecklistDocument4 pagesContractor Vendor Audit ChecklistMandy NormanNo ratings yet
- AJMAAR Vol 6 (1) - ArifDocument10 pagesAJMAAR Vol 6 (1) - ArifProf. Bilal Mustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Proses BisnisDocument65 pagesProses BisnisCrio Binratman Tripatmono50% (2)
- Inventory and PurchasingDocument71 pagesInventory and PurchasingMikail MpuNo ratings yet
- Abm and AbcDocument25 pagesAbm and AbcMs. FitNo ratings yet
- Marketing Seminar 17th March 2023 Notice To StudentsDocument2 pagesMarketing Seminar 17th March 2023 Notice To StudentsAyush MundNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Assignment - 2Document5 pagesSupply Chain Assignment - 2Madhavi TakNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Submit Team Culminating Project Milestone 1Document7 pagesModule 3 Submit Team Culminating Project Milestone 1api-622172809No ratings yet
- Product Management MHM-614 / W-10227Document21 pagesProduct Management MHM-614 / W-10227Aisha KhanNo ratings yet
Daily Management Quiz: 2007: SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
Daily Management Quiz: 2007: SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
Uploaded by
Prakash Kumar50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
709 views5 pagesThis document contains a 30 question quiz about various terms and concepts related to total productive maintenance (TPM). The questions cover topics such as the full forms of acronyms like TPM, JIPM, TQM, OEE; concepts like autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, 5S; pioneers of TPM like Seichi Nakajima; and which country introduced certain concepts. The quiz provides multiple choice answers for identifying the correct response for each question.
Original Description:
Original Title
TPMquiz2007
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a 30 question quiz about various terms and concepts related to total productive maintenance (TPM). The questions cover topics such as the full forms of acronyms like TPM, JIPM, TQM, OEE; concepts like autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, 5S; pioneers of TPM like Seichi Nakajima; and which country introduced certain concepts. The quiz provides multiple choice answers for identifying the correct response for each question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xls, pdf, or txt
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
709 views5 pagesDaily Management Quiz: 2007: SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
Daily Management Quiz: 2007: SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
Uploaded by
Prakash KumarThis document contains a 30 question quiz about various terms and concepts related to total productive maintenance (TPM). The questions cover topics such as the full forms of acronyms like TPM, JIPM, TQM, OEE; concepts like autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, 5S; pioneers of TPM like Seichi Nakajima; and which country introduced certain concepts. The quiz provides multiple choice answers for identifying the correct response for each question.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as xls, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
DAILY MANAGEMENT QUIZ : 2007
SN Question Option A Option B Option C Option D Answer
1 What is the full form of TPM? Total Profit Management Total Productive Maintenance Total Profit Maintenance Total Productive Management B
2 What is the full form of JIPM Japan Institute Of Preventive Maintenance Japan Industrial Preventive Maintenance Japan Institute Of Plant Maintenance Japan Industrial Plant Maintenance C
3 TPM philosophy entails Improving people Improving publicity Improving equipment Both A & C D
4 Basic objective of TPM Maximize OEE Improve equipment reliability Economical life cycle cost All of the above D
5 What is the full form of TQM Toyota Quality Management Total Quality Maintenance Total Quality Management Toyota Quality Maintenance C
6 What is it the full form of OEE Optimum Equipment Efficiency Overall Equipment Effectiveness Overall Engineering Efficiency All of the above B
7 What is the meaning of “efu” Pen Improvement Abnormality Tag D
8 Who is the father of TPM Tomayo atonable Seichi Nakajima Saguira Yamaguchi B
9 TPM initiated by which country America Japan India UK B
10 TPM concept was first initiated by Suzuki Nippon Denso TOYOTA Ford Automobiles B
11 Total productive maintenance carried out by the involvement of Managers and supervisors only Supervisors and workers All employees Only workers C
12 Choose wrong one, in TPM ‘T’ stand for total which means Total improvement of efficiency Total department involvement Total managers participation Total life cycle of production system C
13 This is used as the mark of calling for rectification by operators them selves Yellow tag White tag Red tag Black tag B
This is an indication of the need to call on specialists such as maintenance men
14 as correction Yellow tag White tag Red tag Black tag C
15 What is the meaning of ‘Jishu hozen’ Planned Maintenance Autonomous Maintenance Quality Maintenance Focused Improvement B
16 What is the full form of “MP” sheet Management Protection Management Prevention Maintenance Prevention All of the above C
17 The principle activities of TPM consists of how many pillars 5 6 7 8 D
18 What is the full form of VWM Visionary Welfare Management Visual Work Place Management Visionary Work Place Management Visual Welfare Management B
19 What is full form of ‘MTTR’ Modern Technique To Failure Maintenance Technique To Failure Mean Time To Repair All of the above C
20 What is full form of ‘MTBF’ Maintenance Technique Between Failure Maintenance Technique Before Failure Mean Time Between Failure Maintenance Time Between Failure C
21 TPM circles are part of which pillar? Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Quality Maintenance Focused Improvement A
22 SEIRI means Sorting Systematizing Shining Standardization A
23 SEITON means Sorting Systematizing Shining Standardization B
24 SEISO means Sorting Systematizing Shining Standardization C
25 SEIKETSU Sorting Systematizing Shining Standardization D
26 SHITSUKE Self Discipline Shining Standardization Sorting A
27 Which country introduced the 5S concept USA INDIA JAPAN CHINA C
28 Jishu hozen pillar having how many steps 5 6 7 8 C
29 What is the full form of TBM Total Business Management Time Based Maintenance Total Break Down Maintenance All of the above B
30 What is the full form of CBM Culture Based Maintenance Condition Based Maintenance Challenged Break Down Maintenance Condition Break Down Maintenance B
31 What is step #1 of Jishu hozen Improve hard to access areas Thorough Initial cleaning Counter measures for the causes of forced deterioration Preparation of tentative standards B
32 What is step #2 of Jishu hozen Improve hard to access areas Counter measures for the causes of forced deteriorati Preparation of tentative standards Both A & B D
33 What is step #0 of Jishu hozen Initial cleaning Improve hard to access areas Awareness of people why Jishu hozen Both A & B C
34 What is step #3 of Jishu hozen Improve hard to access areas Thorough Initial cleaning Preparation of tentative standards for cleaning, lubrication,inspecBoth A & B C
35 Meaning of Jishu hozen Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Quality Maintenance Focused Improvement A
36 Meaning of ‘Keikaku Hozen’ Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Quality Maintenance Focused Improvement B
37 According to TPM, how many types of major losses there in a system 10 7 16 5 C
38 According to TPM, abnormalities are how many types 10 7 16 5 B
39 Full form of ‘FMEA’ Failure Method And Efficiency Analysis Failure Mode And Effect Analysis Failure Method And Engineering Analysis Failure Mode And Engineering Analysis B
40 Full form of ‘RCM’ Reliability Cantered Measurement Reliability Cantered Maintenance Reliability Conditioned Maintenance Reason Cantered Maintenance B
41 TPM excellence award administered by CII JIPM TOYOTA SUZUKI B
42 In P, Q, C, D, S, M what is P Profit Productivity Performance Both A & B B
43 In P, Q, C, D, S, M what is C Customer Compliance Cost Control C
44 Poka-yoke Waste Stress-Strain Fool proof Strain free C
45 What is step #4 of Jishu Hozen Preparation of tentative J.H standards General inspection Autonomous inspection Standardization B
46 Keikaku Hozen means Policy Deployment Planned Maintenance Quality Maintenance Development Management B
47 OPL stands for One Page Lesson One Project Lesson Open Page Lesson One Point Lesson D
48 MOU stands for Margins Of Understanding Memorandum Over Understanding Memorandum Of Understanding Margins Over Understanding C
49 (GOD hours- planned & un planned Stoppage hours) / GOD hours is Availability Performance Rate Rate Efficiency Operating Efficiency A
50 (Available hours- non machine related losses) / Available hours is Availability Performance Rate Rate Efficiency Operating Efficiency D
51 Actual out put / designed out put is Availability Performance Rate Rate Efficiency Operating efficiency C
52 (Availability) x (Performance rate) x (Quality rate) Operating efficiency Rate Efficiency Overall Equipment Effectiveness Reliability C
53 In PQCDSM targets P indicator includes Productivity Overall Equipment Effectiveness Failure Rate All Of The Above D
54 In PQCDSM targets Q indicator includes Defect rate Quality Lead time Both A& B B
55 In PQCDSM targets C indicator includes Cost of Manufacturing Cost of Maintenance Customer Complaints Both A& B D
56 In PQCDSM targets D indicator includes Delivery Lead time Defect rate Both A& B D
57 Identical phenomenon occurs with a certain variation is called Sporadic Chronic Both None B
58 Deteriorations are how many types 2 3 4 5 A
59 “Forced Deterioration” minimized with which pillar activities Jishu Hozen Planned Maintenance Focused Improvement Development Management A
60 “Natural Deterioration” deals with which pillar activities Jishu Hozen Planned Maintenance Focused Improvement Development Management B
61 In Heinrich triangle the ratio of various types of causes is 1: 300:1000:3000 1: 29:1000:3000 1: 29:300:3000 1: 29:300:1000 C
62 The primary analysis methodology for availability of the equipment is MTBF MTTR Delay analysis All of the above D
In TPM for "Shabashi" award minimum how many number of kaizens required in
63 a quarter 4 3 2 1 C
64 OHSAS stands for Occupational Health & Safety . Assessment sy Occupational Health & Safety Assessment series Occupational Hygiene & Safety. . Assessment series Occupational Hygiene & Safety. . . Assessment system B
65 “SHE” in its expanded form Safety Health And Ergonomics Safety Health And Environment Safety Hygiene And Environment Safety Hygiene And Ergonomics B
66 PDCA is also known as Kaizen wheel Quality wheel Deming wheel Juran wheel C
67 Kanban stands for Work place Mistake proofing Just in time Ergonomics C
68 Expanded form of QFD Quality Function Delegation Quality Function Deployment Quality For Development All Of The Above B
69 Expanded form of COPQ Cost Of Perfect Quality Cost Of Poor Quality Cost Of Poor Quantity Cut On Poor Quality B
70 Other name of cause and effect diagram Watanabe Diagram Ishikawa Diagram Yamaguchi Diagram Taguchi Diagram B
71 In Control Charts "UCL" stands for Un Controlled Line Upper Control Limit Un Controlled Limit Upper Cost Limit B
72 In Control Charts "LCL" stands for Level Cost Limit Lower Control Limit Level Control Limit Lower Cost Limit B
73 Pareto principle can be applied for Root cause Vital few Useful Many Both B & C D
74 ASPIRE stands for Aspirational Improvements To Retain Excellence ) Ambitious Improvements To Retain Excellence Aspirational Initiatives To Retain Excellence Ambitious Initiatives To Retain Excellence C
75 Hoshin Kanri means Mistake Proofing Policy Deployment Improvement Initiative Individual Improvement B
76 Which concept was introduced in Toyota Production System for eliminating 5s Total productive maintenance (TPM) Just in time (JIT) None C
77 DMAIC stands for Design, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control Define, Monitor, Analyze, Improve, Control Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control Design, Measure, Act, Improve, Control C
78 In 1950 after world war II statistical quality control was taught in to Japan by Dr. W.A.Shewart Dr. W.E.Deming Dr. A.Feingbaum Dr. J.M.Juran B
79 Quality is “conformation to specifications, fitness for use” Who defined in this way Dr. W.A.Shewart Dr. W.E.Deming Dr. J.M.Juran Dr. K.Ishikawa C
Quality Planning, Quality Control, Quality Improvement, the elements given in
80 one word Quality Triple Quality Tripod Quality Trilogy Quality Triplet C
81 PDCA cycle named after Dr. J.M.Juran Dr. K.Ishikawa Dr. W.E.Deming Dr. W.A.Shewart C
82 The originator of modern graphic method M.C.Lorenz S.Oaklando T.H.Lambert W.Pareto C
83 Pareto diagram is a Bar Graph Pie Graph Compound Graph Line Graph C
84 What is 1S & 2S Sorting & Sweeping Sorting & Systematizing Sweeping & Self Discipline Sorting & Shining B
85 Main objective of Jishu Hozen is Operators to have proficient skill Ownership of his own equipment To eliminate major losses Both A & B D
86 Main objective of Planned Maintenance Operators to have proficient skill Ownership of his own equipment Zero breakdowns with minimum cost Both A & B C
What is the minimum score required to cross autonomous audit (stage #1 audit)
87 in Jishu Hozen step #1 91 86 81 76 A
What is the minimum score required to cross Jishu Hozen subcommittee (stage#
88 2) audit is 91 86 81 76 B
What is the minimum score required to cross management audit (stage# 3) in
89 Jishu hozen 91 86 81 76 C
“Enhancement of maintenance technologies and skills” is the responsibility of
90 which pillar Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Focused Improvement Development Management B
Which pillar helps TPM circles in eliminating hard to access areas and source of
91 contamination and their countermeasures Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Focused Improvement TPM in Office A
92 Condition of zero failure at minimum possible maintenance cost is responsibility Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Education And Training Focused Improvement B
93 Which pillar responsible for the White tag management Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Education And Training Focused Improvement A
94 Which pillar responsible for the Red tag management Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Education And Training Focused Improvement B
95 Standardization of spares is the responsibility of which pillar Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Education And Training Focused Improvement B
96 Objective of TPM is Zero accidents Zero defects Zero breakdowns All of the above D
97 Philosophy of TPM is Improving people Improving equipment Improving company All of the above D
98 Benefits of TPM is Reduce breakdowns Improve skill of people Improve morale all of the above D
99 How we can stop the accelerated deterioration? Clean the equipment Identify the problem and rectify Develop / implement standards All of the above D
100 In phase zero of Jishu Hozen, which activities are required 1S & 2S around the equipment Understanding of Forced Deterioration Safety of the equipment All of the above D
101 In the following activities which is not step #1 of Jishu Hozen activity Initial Cleaning Discovery of equipment defects Removal of un necessary things Preparation of standards D
102 In the following activities which is not Planned Maintenance pillar activity Support to jishu hozen Lubrication management Preparation of loss structure Spare parts management C
103 Planned Maintenance and Autonomous Maintenance are parallel activities 0 1 Partially true Independent activities B
104 As per “watanabe’s model of failure analysis” What is the full form of CMNT Condition Monitoring Not Taken Counter Measures Not Taken Critical Measures Not Taken Critical Monitoring Not Taken B
105 As per “watanabe’s model of failure analysis” What is the full form of CMNE Critical Maintenance Not Effective Condition Maintenance Not Effective Counter Measures Not Effective Critical Measures Not Effective C
106 As per “watanabe’s model of failure analysis” What is the full form of CMNM Counter Measures Taken But Not Maintained Critical Maintenance Not Monitored Critical Measures Not Maintained Condition Measures Not Maintained A
Right product first time, every time in the shortest possible time is the objective
107 of which pillar Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Focused Maintenance Development Management D
108 Vertical start up of the new equipment is the objective of which pillar Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Focused Maintenance Development Management D
109 Capturing of “MP sheet” information is the responsibility of which pillar Autonomous Maintenance Planned Maintenance Focused Maintenance Development Management D
An equipment availability is 80%, performance rate is 90%, quality rate is 95 %
110 what is the OEE 92% 88% 78% 68% D
111 What is the full for of SOP Self Operating Procedure Safe Operating Program Standard Operating Procedure Self Operating Program C
112 What is the full for of OCP Occupational Control Procedure Operational Control Procedure Operational Control Program Occupational Control Program B
113 Objective of the Development Management Pillar Right product first time, every time Vertical start up of the equipment Shortest possible cycle time All of the above D
114 Which technique is used to separate the vital few from the useful many Stratification Pareto Diagram Spider Chart Scatter Diagram B
115 Pareto Diagram is Percentage Graph Cumulative Percentage Graph Number Of Defects Graph All of the above B
116 Pareto Analysis is used for Prioritizing the problem Analyzing the symptoms Root cause analysis Both A & B D
117 Who introduced the Cause & Effect Diagram Dr. J.M.Juran Kaoru Ishikawa Tomoya Watanabe Alfred pareto B
118 This diagram gives the theories about the causes that results in a specific effect Ishikawa Diagram Cause & Effect Diagram Fish Bone Diagram All of the above D
119 The cause & effect diagram first introduced in which organization Toyota Motors Kawasaki Iron Works Suzuki Motors Nippon Iron & Steel B
120 In the following which is the Cause & Effect Diagram Dispersion analysis Production process classification Cause enumeration type All of the above D
121 This is a graphical representation of frequency distribution Histogram Scatter diagram Pareto diagram Control chart A
122 This is a graphic summary of variation in a product or process Pareto diagram Scatter diagram Histogram Control chart C
123 Who introduced Histograms Dr. J.M.Juran A.M. Guerry Tomoya Watanabe Y.Kondu B
124 In a table (higher value- lower value) is called Cell width Range Frequency All of the above B
Two different processes or two different machines in that case which type of
125 histogram appears Skewed Type Double Peak Type Comb Type Plateau Type B
126 There is a possible error in the data collection which type of histogram appears Skewed Type Double Peak Type Comb Type Plateau Type C
127 The samples are from different processes which type of histogram appears Skewed Type Double Peak Type Comb Type Plateau Type D
128 Who introduced brain storming technique J.M.Juran Alex Osbon T.H.Lambert M.C.Lorenge B
129 Who introduced the curve (cumulative percentage) in the pareto diagram J.M.Juran M.C.Lorenge Alex Osbon T.H.Lambert B
130 Technique for unlocking the creative power of people by simulating useful ideas Cause & Effect Diagram Brain Storming Flow Diagram Decision Matrix B
131 In Brainstorming session the participants should be preferably less than 20 10 15 5 D
132 The other name of “un-structured” brain storming technique Free wheeling Slip method Round robin method None A
133 The other name of “Round robin” brain storming technique Free wheeling method Slip method Un structured method Structured method D
134 In which type of brain storming no limit on number of ideas at a time Free wheeling method Slip method Un structured method Structured method A
135 Which type of brain storming technique used for involvement of large group Free wheeling method Slip method Un structured method Structured method B
136 As per Mr.J.P.Gulfords, capability of producing maximum ideas in a given time is Fluency Flexibility Originality Awareness A
137 As per Mr.J.P.Gulfords, ability for the mind to move from one aspect to another is Fluency Flexibility Originality Awareness B
138 Separation of data in to suitable categories is called Scattering Brain storming Stratification Histogram C
139 Graphical representation of relationship between two variables is called Bar diagram Scatter diagram Histogram Line diagram B
140 Who developed the printed graph paper Alex Osborn Dr.Burton T.H.Lambert S.Oaklando B
141 Who introduced the scatter diagram J.F.W.Horschel Dr.Burton T.H.Lambert S.Oaklando A
In a scatter diagram, the value of Y clearly increases as the value of X increases
142 the relationship is Strong negative correlation Strong positive correlation No correlation Weak negative correlation B
In a scatter diagram, the value of Y clearly decreases as the value of X
143 increases the relationship is Strong negative correlation Strong positive correlation No correlation Weak negative correlation A
In a scatter diagram, any value of X, Y can have both large and small values the
144 relationship is Strong negative correlation Strong positive correlation No correlation Weak negative correlation C
145 In a detailed flow diagram, the oval symbol used for Start & stop Decision Activity Connector A
146 In a detailed flow diagram, the rectangle symbol used for Start & stop Decision Activity Connector C
147 In a detailed flow diagram, the diamond symbol used for Start & stop Decision Activity Connector B
148 In a detailed flow diagram, the circle symbol used for Start & stop Decision Activity Connector D
149 The flow diagrams are drawn for Defining the process flow Defining the problem Defining the root cause all of the above D
150 Which diagram is used to plan the activities of known but complex tasks or flow diagram cause & effect diagram Arrow diagram Tree diagram C
151 The arrow diagram traced back from the which graph Line graph Harmony graph Spider graph Bar graph B
152 What is the full form of SGA Small gathering achievements Small Group Activities Small gathering activities Small group achievements B
153 For annual shutdown/implementation of new projects which diagram is more Bar diagram Line diagram Spider diagram Arrow diagram D
Which diagram is used for organizing the verbal data into groups based on
154 natural relation ship Tree diagram Arrow diagram Flow diagram Affinity diagram D
155 Who introduced the affinity diagram T.H.Lambert Dr.Burton Kawakita jiro S.Oaklando C
156 What is the full form of PDPC Program decision process chart Process Decision Program Chart Preventive decision process chart Process decision prevention chart B
157 Who developed the PDPC method T.H. Lambert Dr. Burton Y.Kondo S.Oaklando C
158 In an arrow diagram “nodes” are used to represent Activity Event Decision Storage B
159 In an arrow diagram “arrows” are used to represent Decision Event Activity Storage C
160 Matrix data analysis is also called FME analysis Principle compound analysis Root cause analysis PM analysis B
161 Is 2004 how many departments in Tata steel awarded JIPM award 2 3 4 5 C
162 (Total operating time / number of breakdowns) x 100 is called MTBF MTTR Availability PM task rate A
163 (Total repair time/ total number of failures) is called MTTR MTBF Availability PM task rate A
164 What is the full form of SIP Small initiated project Self Initiated Project Self interested project Self improvement project B
165 What is the full form of “CTQ” Crisis To Quality Crisis To Quantity Critical To Quality Critical To Quantity C
166 In problem solving approach this is very important Brain storming Why-why analysis Pareto analysis Phenomenon observation D
167 What is Step # 4 of Jishu Hozen (Autonomous Maintenance) Preparation of CLIT Standards Equipment General inspection Process General Inspection Both A & B B
168 What is the objective of Step # 4 of Jishu Hozen (Autonomous Maintenance) Mastering in preparation of standards Develop more number of kaizens Develop equipment competent operator Develop power of observation C
169 In Step # 4 (Autonomous Maintenance) training, which one is basic training TPM over view Lubrication system Pillar Activities problem analysis B
170 Methodology to provide step 4 training. 25 % class room, 25 % training, 50 % on job 50% training Center, 50 % on job 100% on job. 100% class Room A
171 After step # 4 training (Basic/ specific) the number of fuguais should ?? Increase Reduce No relation Remain same A
172 The step # 4 Jishu Hozen audit should be done in following stages. Only by central group By JH Self, JH and Central Group Only by JH committee. C
173 What is the full form of PDCA ? Plan do check act Prepare, do, calculate, access Plan do clarify act Prepare do check act A
______________ is always a deviation from same standard or norm of desired
174 performance. Improvement. Problem Decision Kaizen B
In Ideal view “Our _______________ shows us how much room for
175 improvement we have Problems Kaizens Gemba kaizens All. A
176 What is the full form of JDI? Just do it Job done immediately Job do it None A
177 What is TOYOTA’s secret weapon TPM Six Sigma Lean production system All C
178 In a vertical flange joints generally the bolt should be inserted from Top Side Bottom Side Both A & B None of the above B
179 While making a flange joint this is important All the bolts should be in same size 50% bolts one direction, remaining 50% in opposite dir All the bolts are in same direction A and C D
180 Role of Lubrication Control the Temp Eliminate abrasion Reduce the friction All of the Above D
181 In lubricating oils what is the full form of SAE Society of Automotive Engineers Standards of automobile engineers Standards of automobile engineers Society of Aeronautic Engineers A
182 The Deming prize is administrated by the which organisation JIPM JUSE CII B
183 Name the tool use for separating the data in to groups Histogram Stratification Scatter diagram pareto diagram A
184 In X chart what is the full form of UCL Unique control level Upper control limit under control level Unique control limit B
185 In X chart what is the full form of LCL Lower control limit Linear control limit Longitudinal control limit All of the above A
186 What is the full form of “TOC” Theory of Controls Total Operational Control Techniques Of Control Theory of Constraints D
187 Who is the consultant for TOC programme in Tata Steel Eliyahu – Goldratt Kepner T- atonable Ando A
188 The book “The Goal” Written by Henn Goldratt Kepner Goldratt Eliyahu Goldratt Alex Goldratt C
189 In TPM/SGA circles the team facilitator can be a person of Managers Supervisors Workers Any of them D
190 In TPM/SGA circles the team leader and member can be a Managers Supervisors Workers both B& C D
In Tata Steel Small Group Activities competition) all circles are divided in to how
191 many bands. 2 3 4 1 C
192 In Tata Steel Small Group Activities competition is held in how many levels? 2 3 4 1 B
The SGA teams with 3 or more kaizens in a year will enter in to the competition
193 at_____level? Apex level Sponsor level Champion level None C
SGA Teams who participated in the previous year Apex level competition and
194 are not in black band the remaining are in____ band. Yellow Green White Any one A
SGA Teams who participated in the previous year Apex level competition and
are in top 25 % of the 3 streams subjected to a minimum of 75 % marks will be
195 in____ band. Yellow Green White Black D
SGA Teams who have made less than 3 kaizens/projects in a year are in
196 _____band. Yellow Green White Red C
197 SGA Teams who have made 3 or more kaizens/projects in a year are in Yellow Green White Red B
In Tata Steel Small Group Activities competition, as per the guide lines how
198 many marks allocated for Jishu Hozen & 1S /2S activities. 10 15 20 30 C
199 "1S" of "5S" methodology means Systemisation Sorting Self Discipline Shining B
200 "2S" of "5S" methodology means Systemisation Sorting Self Discipline Shining A
201 "3S" of "5S" methodology means Systemisation Sorting Self Discipline Shining D
202 "4S" of "5S" methodology means Systemisation Sorting Standardisation Shining C
203 "5S" of "5S" methodology means Systemisation Sorting Self Discipline Shining C
204 Which one of the following is not a part of "5S" methodology Shining Sorting Self Discipline Sharing D
205 "VWM" stands for Waste Management Visual Work Place Management Water Management Visual Work Maintenance B
206 "1S/2S & Visual Workplace Management" assessment is conducted by JWQC Every Quarter Every Month Once in 6 Months Once in a Year A
207 " Kaizen" means Just in Time Breakthrough Improvement Small Improvement Customer Focussed C
208 "Jishu Hozen" which is one of the pillar of TPM Methodology means Planned Maintenance Autonomous Maintenance Quality Maintenance Focused Improvement B
209 "Deming Application Prize" is administered by which institution of Japan JIPM JUSE JIST JUSL B
210 "Deming Application Prize" is given to a company which practices philosophy of TQM TPM TOC SIX SIGMA A
211 "Deming Application Prize" is given to a company every Year Month Once in 2 Years Once in 5 years A
212 Which one of the following is not a part of ASPIRE"T3" TQM Training Technology TOC B
213 TQM philosophy gives maximum focus on which activities Cost Reduction Customer Focussed Profit Improvement Productivity Improvement B
214 What is the " First Level of Quality" as per Dr. N.Kano's competitive advantage Meeting Basic Requirements Meeting Expressed Requirements Customer 's Delight Meeting Customer's Quality Requirements A
215 What is the "Second Level of Quality" as per Dr. N.Kano's competitive advantage Meeting Basic Requirements Meeting Expressed Requirements Customer 's Delight Meeting Customer's Quality Requirements B
216 What is the " Third Level of Quality" as per Dr. N.Kano's competitive advantage Meeting Basic Requirements Meeting Expressed Requirements Customer 's Delight Meeting Customer's Quality Requirements C
217 Which one is not a component of TQM Problem Solving Daily Management Inventory Management Policy Management C
218 " Breakthrough Improvement" is covered under which component of TQM Daily Management Autonomous Maintenance Policy Management Planned Maintenance C
219 "Incremental Improvement" is covered under which component of TQM Daily Management Autonomous Maintenance Policy Management Planned Maintenance A
220 Daily Management Covers sustenance of routine activities done on a Daily Basis Weekly Basis Shift Basis All of the above D
221 Daily Management doesn't include Maintenance Activities Incremental Improvement Activities Breakthrough Improvement Activities All of the above C
222 Policy Management doesn't include Breakthrough Improvement Activities Incremental Improvement Activities Problem Solving Activities All of the above B
223 "TA" activities of the TQM philosophy stands for Task Achieving Team Achieving Team Ability Task Addressing A
224 TQM stands for Total Quality Maintenance Total Quantity Management Tata Quality Management Total Quality Movement C
225 A Company must focus on Internal Customers only External Customers only Both Internal & External Customers None of these C
226 Daily Management involves managing Daily Activities only Regular Activities only Regular/Routine/Transactional Activities Hourly Activities C
227 Breakthrough improvements are related to Daily Management Policy Management Total Productive Maintenance None of these B
228 Daily Management activities help in Achieving Breakthrough Results Maintaining and Sustaining current level of performance Achieving 20% improvement in performance Maintaining and Sustaining current level of performance with gradual im D
229 Daily Management Activities will always include daily jobs only may include hourly,daily,weekly jobs . never include Yearly jobs None of these B
230 Stretched Targets set by Management are to be achieved by Daily Management Policy Management Small Group Activities Cross Functional Management B
231 P-D-C-A stands for Plan,Do,Check,Adjust Please do not change anything Plan,Do,Change,Adjust Plan,Do,Check.Act D
232 Policy Management Activities are done for "Changing the Business" whereas Daily "Running the Business" "Changing the Direction of the Business" "Acquiring a New Business" None of these A
233 Management
S-D-C-A standsActivities
for are for Systematize-Do-Check-Act Simplify-Do-Check-Act Standardize-Do- Check-Act Standardize-Do-Check-Adjust C
234 Daily Management activities can be done: To control performance parameters To monitor performance parameters To monitor and control performance parameters None of these C
235 What is not expected outcome of Daily Management Unstable Operations Predictable Operations Reduced Process Variations Consistent Quality of Products A
236 Which is not applicable for Daily Management ? Variability Control Continual Improvement Breakthrough Improvements Process Capability Analysis C
237 SPC stands for Standard Practice and Control Systematic Procedure and Control Statistical Process Control None of these C
238 SOP stands for Standard Operating Practice Standard Operating Procedure Simplified Opportunity Practice Standard Operating Plan B
239 Preferably SOPs should be written in text and kept in office. visual and displayed near workstation written in English Language only Visual and displayed at Visitors Gallery B
240 Which is a part of TQM? Policy Management Daily Management Task Achieving All of the Above D
241 The term "DRIP" used in Daily Management stands for Data Rich And Information Poor Doing Regular and Interesting Projects Development of Regular Information process None of these A
242 Objectives are stated in terms of QCD PQCSM PQCDSM QCDSM C
243 Daily Management helps in spotting the defects at Process Level Inspection Level Customer Level None of these A
244 SOPs are more useful for Senior Level Managers Middle Level Managers Front Line Operators Customers C
245 Fire Fighting is mainly an outcome of Bad Workplace Bad Policy Management Poor Daily Management Bad Environment C
246 Daily Management calls for Routine Management by Front Line Operators only by Front Line Operators and Managers only by Front Line and Middle Level Managers only by all levels. D
247 Which is a part of Daily Management? Suggestion Management SGA Jishu Hozen of TPM All of the above D
248 Any Process is defined by its Input and output Measures its Input, in-process and output measures its in-process Measures only None of these B
249 Answering "Dr. Kano's Questions " gives clarity on" Roles and Objetives" of a department idea about critical concerns related to objective finalisation of action points related to critical concerns All of the above D
250 "Dr. Kano's Questions on Roles and Objectives "to be answered by Operation Deptt. Only Maint. Deptt. Only Service Deptt. only Operation, Maint. & Service Deptts. D
251 Who is Dr. N Kano? An American TQM Expert A Japanese TQM Expert A Japanese TPM Expert None of these B
252 What is the prime objective of "Daily Management"? To enhance Process Capability To reduce Cost To ascertain Process Stability None of these C
A Company has achieved 5 MT production in 2005-06.In 2006-07,they set a target of 5.2
253 MT .This may be achieved by Policy Management Daily Management Both Policy and Daily Management Neither Policy nor Daily Management is required B
254 Which is less applicable to Daily Management in Operation Function? Process Flow Control Plan Management System Chart PFMEA C
255 Which is less applicable to Daily Management in Service Function? Dr. Kano's Questions on "Roles & Objectives" Process Flow Management System Chart SOPs B
256 FMEA stands for Failure Mode & Effect Analysis Failure Method & Effect Analysis Fast Method & Effective Analysis None of these A
257 FMEA is a tool which gives an idea about: What can go right? What can go wrong? What will not change? What will improve? B
258 What is not true for FMEA? It takes care of severity of effects of potential failure mode It takes care of occurrence frequency of potential causes It takes care of prevention/detection Method of Potential Causes. All of the above D
259 RPN stands for : Risk Probability Number Risk Priority Number Risk Preference Number None of these B
260 The RPN in FMEA is calculated by: Severity*occurrence/Detectibility Severity* Occurrence Severity*Occurrence*Detectibility Severity*Detectibility C
261 Severity Rating in FMEA corresponds to seriousness of an effect of a potential failure mode on a scale o seriousness of an effect of a potential causes on a scale of seriousness of an effect of a potential failure mode on a scale of 1-5 None of these A
262 Occurrence Rating in FMEA corresponds to Occurrence of Potential causes on a scale of 1-10 Occurrence of Potential failure mode on a scale of 1-10 Occurrence of Potential causes on a scale of 1-5 None of these A
263 Detectibility Rating in FMEA corresponds to Probability of detection of Potential causes on a scale of 1-10 Probability of detection of Potential causes on a scale of 1-5 Probability of detection of Potential effects on a scale of 1-10 None of these A
264 Control Chart was developed by Dr Graham Bells Dr. W A Shewart Dr. Suda Dr. N Kano B
265 What is not true ? Specification Limit and Control Limits are the same. Specification Limit is given by Customer Control Limit is internal to process None of these A
266 Control Limits are determined statistically from probability distribution of the sample statistic by calculating specification limits by regression analysis None of these A
267 Temperature is a Discrete Data Variable Data Random Data None of these B
268 Length is a Discrete Data Variable Data Random Data None of these B
269 Which Control Chart is not applicable to discrete data? c chart np chart X-MR chart None of these C
270 Which Control Chart is not applicable to continuous data? X-MR Chart X bar-R Chart c Chart All of the above C
271 If data volume is large, which control chart is used for variable data? X-MR Chart X bar- R Chart c Chart np chart B
272 If data volume is small, which control chart is used for X-MR Chart X bar- R Chart c Chart np chart A
273 Which Control Chart is applicable to discrete data? X-MR Chart X bar- R Chart c Chart None of these C
274 What is first step for plotting a control chart? Control Data Collection Analysis Improvement B
275 One or more data points above Upper Control Limits indicate that Process is capable Process is not capable Process may be capable Process is unstable. D
276 One or more data points lower than Lower Control Limits indicate that Process is capable Process is not capable Process may be capable Process is unstable. D
In Control Chart, Data trending Downward or Upward Seven or more data points in a
277 row indicate Process is stable Process is capable Process is unstable Process is just capable C
278 Cp Value is related to Process Stability Process Capability Process Suitability None of these B
279 Cpk Value is related to Process Stability Process Capability Process Suitability None of these B
280 If Value of Cp <1 then Process is capable Process is just capable Process is not capable Process is Unstable C
281 If Value of Cp =1 then Process is capable Process is just capable Process is not capable Process is Unstable B
282 If Value of Cp >1 then Process is capable Process is just capable Process is not capable Process is Unstable A
283 The Value of Cpk should be less than 1 equal to1 as less as possible >1.33 D
284 What is difficult to know? Chance Cause Special Cause Random Cause None of these A
285 What is easy to detect? Chance Cause Special Cause Random Cause None of these B
286 Chance Cause is also known as Common Cause Assignable cause Special Cause None of these A
287 Special Cause is also known as Common Cause Assignable cause Special Cause None of these B
288 Common Causes are normally inherent causes of variation Assignable cause May be inherent or assignable None of these A
289 Special Causes are normally inherent causes of variation Assignable cause May be inherent or assignable None of these B
290 Common Causes normally follows a specific pattern does not follow a specific pattern May or May not follow a specific pattern None of these A
291 Control Chart is normally used to differentiate common cause and special cause put a chart in a nice manner differentiate between specification and control limits All of the above A
292 Dr W A Shewart worked in GE Motors Nippon Steel Bell Telephone Industries Nokia Telephone C
293 A Company Produces a product consistently within control limits, it indicates Process is capable Process is just capable Process is stable Process is Unstable C
294 Senior/Top Management spends more time on which component of TQM Daily Management Policy Management Problem Solving Task Achieving B
295 Front Line Employees should spend more time on which component of TQM Daily Management Policy Management Problem Solving Task Achieving A
296 P-D-C-A stands for Plan-Do- Check -Act Plan-Do-Check-Adjust Plan-Do-Change-Adjust Plan-Do-Control -Act A
297 In "S-D-C-A" Cycle of TQM, 'S' stands for Simplify Standardize Stratification Systematise B
298 " Four Student Model " of Dr. Kano is a tool to assess the effectiveness of Daily Management Policy Management Problem Solving Task Achieving B
Daily Management Assessment Criteria for a department in our company
299 consists of 3-Stages 4-Stages 5-Stages 6-Stages C
300 TQM Diagnosis of our company by JUSE was done in the year 2003 2003 2004 2005 D
301 Methodology followed for doing a " Problem Solving" exercise in our company is DMADIC DMAIC SDCA DMPAC B
302 Methodology followed for doing a " Task Achieving" exercise in our company is DMADIC DMAIC SDCA DMPAC A
303 D ' in DMAIC stands for Design Define Deliver Derive B
304 'C' in DMAIC stands for Check Control Combine Correct B
305 M' in DMAIC stands for Measure Move Make Mean A
Which one of the following activities are not part of Daily Management Activities
306 in our company Small Group Activity Suggestion Management TPM JH & Planed Maint. ASPIRE Projects D
Incremental improvements achieved through Kaizens & suggestion scheme is a
307 part of Daily Management Policy Management Problem Solving Task Achieving A
In our company, Daily Management activities have been categorised into 3
308 Functions. Which is not a part of this: Operation Function Maint. Function Marketing Function Service Function C
309 Dr. Kano's questions are aimed at defining roles and objectives Monitoring critical performance indicators Initiating Improvement Projects None of these A
310 "Process Flow Chart" is a tool to identify Input Sources of Variation Process Characteristics Product Characteristics All of the above D
311 Process FMEA is made for a process in order to Identify Indicators Prioritise Indicators Monitor Indicators Analyse indicators B
312 Which one is not a part of RPN Calculation Severity Occurrence Criticality Detectibility C
313 Control Plan' is a document under DM in operation area showing a plan to monitor/control performance indicator Preventive actions taken Identification of abnormalities All of the above A
314 "Control Plan" of DM addresses which part of PDCA rotation P D C A A
315 " Control Chart" of DM addresses which part of PDCA rotation P D C A C
316 "Corrective and Preventive Actions" of DM addresses which part of PDCA P D C A D
317 Process Flow Chart-PFMEA-Control Plan addresses which part of PDCA P D C A A
A Process Performance Indicator such as "Steam Temperature" should be
318 monitored using Trend Chart Run Chart Control Chart Check Sheet C
A Process Performance Indicator such as "No. of Failures" should be monitored
319 using Trend Chart Run Chart Control Chart Check Sheet A
320 "MSC" under Daily Management in Service Function stands for Maintenance Schedule Chart Management System Chart Maintenance System Code Management Standardisation Code B
321 Variability of any process happens due to Common Cause Special Cause Both A & B None of the above C
322 "Assignable causes" for a variation can be identified and reduced not be identified and reduced not be identified None of the above A
323 Chance or Common Causes of a variation can be be identified be reduced not be identified All of the above C
324 Control Chart is a tool to differentiate between Common Cause & Assignable Cause Common Cause & Chance Cause Special Cause & Assignable Cause None of the above A
325 A process is under control (or stable) when no chance causes are present no special causes are present Only Chance causes are present Only special causes are present B
If a process is under the influence of only common causes of variation, the
326 process is said to be Capable Stable Capable & Stable None of the above B
If a process is under the influence of only special causes of variation, the
327 process is said to be not stable not capable stable but not capable neither capable nor stable A
328 A Control Chart should necessarily have Control Limits Mean Specification Limits Both A & B D
329 "UCL" in a control chart stands for Upper Control Limit Upper check limit Unwanted Control Limit None of the above A
330 Customer of a process provides information on Control Limit Specification Limit Both A & B None of the above B
331 "Control Limits" for a process indicator is calculated based on past data given by customer decided by the process owner Either of the above A
332 A Variation in a process will be called due to special/assignable cause if Value is beyond control limits Value is beyond specification limits Value is within control limits Value is within specification limits A
333 Which one of the following is special cause of variation All points within control limits 5 Consecutive points going up 6 Consecutive Points one side of mean 7 Consecutive points going down D
334 Any data can be classified into Continuous data Attribute data both A & B None of the above C
335 Which of the following is not a type of control chart used for variable data X-MR Chart Xbar-R c Chart Xbar-S Chart C
336 What is full form of "SGA" Similar Group Activity Small Group Activities Similar Grade Activity Small Grade Activity B
337 Which are the part of SGA teams in our company TPM Circles Quality Circles Both A & B None of the above C
In our company, A SGA team can be formed with how many members including
338 facilitator) Any number 1 to 10 3 to 8 5 to 8 C
339 The leader and members of any SGA team can be officer only supervisor only Worker only Non Officers Only D
340 Facilitator of any SGA team can be a officer only supervisor only Worker only Any Employee D
341 A "TPM Circle" normally performs the following activities 1S/2S in the workplace Autonomous Maintenance on an equipment Kaizens (Small improvement) All of the above D
342 As on date, how many SGA teams are registered in our company less than 3000 3000-4000 4000-5000 More than 5000 D
During the year 2006(Jan- Dec), how many kaizens were completed by the SGA
343 teams of our company upto 5000 5001-8000 8000-11000 More than 11000 C
In order to become eligible for receiving "Shabashi Reward", how many kaizens
344 should a SGA team must do 3 in a year 2 in a year 2 in a quarter 3 in a quarter C
In order to become eligible for participating SGA Competition, a SGA team must
345 complete a minimum of kaizens 2 Kaizens in each quarter 3 Kaizens in a year 2 Kaizens in a year None of the above B
346 A SGA team is called a "Green Band" team if it completes 3 Kaizens in a colander year 6 Kaizens in a colander year 3 Kaizens in a financial year 2 Kaizens in a colander year A
As per our company's suggestion scheme, maximum how many persons
347 together can submit a suggestion 3 5 4 2 C
As per our company's suggestion scheme, who out of followings are not eligible
348 to submit a suggestion Officer in any level Officer in IL3 & above Officers in R&D None of the above B
What is the highest award which can be received by suggestor for one time
349 saving as per our company's suggestion scheme Rs.25000 Rs.50000 Rs.40000 Rs.2.5 lakh B
What is the highest award which can be received by a suggestor for a recurring
350 saving type of suggestion as per our suggestion scheme Rs.1.0 Lakh Rs.50000 Rs.2.5 Lakh Rs.5.0 Lakh B
What is the name of Joint Management Union Body who decides high value
351 suggestion for rewards Joint Works Quality Committee Suggestion Box Committee Joint Works Council Any of the above B
As per our company's suggestion scheme, a suggestor will be awarded only
352 after its submission implementation acceptance Any of the above B
Implemented Suggestions with tangible benefits can be awarded with a
353 maximum amount of Rs.1000 Rs.50000 Rs.5000 Rs.10000 B
A JDC Suggestion subcommittee can reward any suggestion with a maximum
354 reward value of Rs.1000 Rs.50000 Rs.5000 Rs.10000 A
In our Company, for the year 2006,number of suggestions generated per year
355 was in the range of 5-10 2-5 11-15 Less than 2 B
356 Suggestion Box Committee of our Company consists of Management Representative only Union Representative only Both Management & Union Representative Head of Departments C
357 In our Company, Annual SGA Competition are organised at how many levels 4 Levels 3 Levels 2 Levels 5 Levels B
358 At the Apex Level Competition, the evaluation is done based on Team Presentation Site Evaluation Both A & B Only Team Presentation B
Out of the following, which activity will be a Daily Management activity for a SGA
359 team (TPM related) Maintenance of CLIT standards Identify abnormalities & do kaizens Both A & B None of the above C
360 Teen Se Jeet' is related to Q3 R3 S3 T3 D
361 Which is a part of T3? Temperature Technology Training None of the above B
362 Knowledge Management is now a part of R&D Technology Scientific Services None of the above B
363 Policy Management is a part of TOC TQM Technology All of the Above B
364 Critical Chain Project Management is a part of TOC TQM Technology All of the Above A
365 "Learning from Failures" and "Self Confidence" are important elements of TOC TQM Technology All of the Above C
366 Which of the following company is Deming Winning Company in India? Tata Motors Sona Koyo Steering Ashok Leyland None of the Above B
367 Which of the following company is not a Deming Winning Company in India? Sona Koyo Steering SRF Limited Rane Brake Hindustan Motors D
368 What is full form of DTQMP? Descriptive Translation of Quality Management and PrescrDescription of TQM Practices Description of TQM Procedures None of the Above B
370 Who of the following Japanese Expert is connected with TPM? Dr. Kano Prof. Ando Prof. Su Yamada Mr. Watanabe D
371 Who of the following Japanese Expert is connected with TQM? Dr. Kano Prof. Ando Prof. Su Yamada All of the Above D
Which of the following TPM activities to be adopted for Daily Management in
373 Maintenance Function? Quality Maintenance SHE Planned Maintenance Office in TPM C
374 MTTR may be a key performance indicator of Operation Maintenance Services None of the above B
375 Which of the following tool is used for "Daily Management in Service Function" Process Flow Chart Management System Chart Customer Flow Chart All of the Above B
376 MTBF' may be a performance indicator of Operation Maintenance Services None of the above B
377 TBM is Total Buy Management Time Based Maintenance Time Before Maint. Toyota Based Maintenance B
378 CBM is Conditional Buy Management Condition Based Maintenance Condition Before Maintenance None of the Above B
380 SPC is related to Quality Assurance Quality Control Process Control All of the Above C
390 In X-MR chart, MR is Mean of Range Moving Range Mean Regression Moving Ratio B
391 If sampling of a variable data is done once in a shift, which control chart to be X Bar-R X-MR Xbar-S C chart B
392 A variable data is monitored online continuously. Which control chart to be used? X Bar-R X-MR Xbar-S C chart A
393 Which of the following methodology is not adopted in Tata Steel? Suggestion Management TPM TPS TOC C
394 Suggestion Management, TPM and SGA are part of Daily Management Policy Management TOC Problem Solving A
395 Number of Near Miss' is a performance indicator related to which objective Quality Cost Delivery Safety Hygiene And Ergonomics D
396 "No. of Suggestions/employee" is a performance indicator related to which Quality Cost Delivery Morale D
398 Which type of methodology to be used for chronic problems? JDI KKD QC Story None of the above C
399 Process Capability is denoted by UCL, LCL USL. LSL Cp,Cpk None of the Above C
Which of the following is shown as Foundation of Aspire T3-TQM Working Model
400 at Tata Steel? Daily Management Policy Management Cross Functional Management Environment Management A
You might also like
- Audit Checklist - JH Steps 1-3Document13 pagesAudit Checklist - JH Steps 1-3Shantanu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Shut Down Procedure (Tata Steel)Document19 pagesShut Down Procedure (Tata Steel)Prakash Kumar100% (2)
- 5 KK PillarDocument54 pages5 KK Pillarazadsingh183% (6)
- Slide TPM SHEDocument14 pagesSlide TPM SHEhdjdjNo ratings yet
- E & Tpillar: Education & Training Pillar ActivitiesDocument21 pagesE & Tpillar: Education & Training Pillar Activitiessamkaria rajesh100% (1)
- JIPM TPM AwardsDocument23 pagesJIPM TPM AwardspreethishNo ratings yet
- CII JH Step 4Document4 pagesCII JH Step 4Kumar Swami0% (1)
- SFM Tmmin Otics PDFDocument40 pagesSFM Tmmin Otics PDFAgung IndriantoNo ratings yet
- JH Step 1 Audit SheetDocument2 pagesJH Step 1 Audit SheetSwayambhar Majumder75% (4)
- CQI-09.Ver 4Document128 pagesCQI-09.Ver 4Nethaji MettNo ratings yet
- Training ON TPM: Rapl Production SystemDocument25 pagesTraining ON TPM: Rapl Production Systemabhijit bhattacherjeENo ratings yet
- TPMDocument42 pagesTPMSrinivasan VenkatNo ratings yet
- Pillar: Initial Control or Development ManagementDocument7 pagesPillar: Initial Control or Development ManagementNavneet SharmaNo ratings yet
- JH Step-1 & 2activitiesDocument34 pagesJH Step-1 & 2activitiesGREENEXE BUSINESS CONSULTANTNo ratings yet
- JH PPT 18.12.20Document46 pagesJH PPT 18.12.20MAngesh Gade0% (1)
- TPM Over ViewDocument37 pagesTPM Over ViewHarshad_SNo ratings yet
- Kobetsu Kaizen Pillar: Training Program OnDocument51 pagesKobetsu Kaizen Pillar: Training Program OnNeeraj SethyNo ratings yet
- Q Star - (Waste Management)Document14 pagesQ Star - (Waste Management)Anonymous Y5cnLVYMGNo ratings yet
- JH PillarDocument39 pagesJH PillarshaktiNo ratings yet
- KK Pillar PDFDocument91 pagesKK Pillar PDFdiwesh26decNo ratings yet
- CPCL TPM AnalysisDocument67 pagesCPCL TPM AnalysisKhader HussainNo ratings yet
- Focused Improvement PillarDocument19 pagesFocused Improvement PillarDkhissene Imad100% (1)
- Chapter 7. QM PILLAR PDFDocument60 pagesChapter 7. QM PILLAR PDFNARENDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Education & Training ManualDocument23 pagesChapter 6. Education & Training ManualVivek Kumar100% (1)
- TPM JH PPT 01 JH AwarenessDocument28 pagesTPM JH PPT 01 JH AwarenessLakshmanan Venkatesan100% (1)
- MT QM PillarDocument71 pagesMT QM Pillarazadsingh1No ratings yet
- Six Sigma - Reduction of Downtime - RE Mill-2 - NewDocument76 pagesSix Sigma - Reduction of Downtime - RE Mill-2 - NewKiruthiga VelmuruganNo ratings yet
- Quality CricleDocument22 pagesQuality CricleQSSD ENTERPRISES100% (1)
- Stage Step (Nakajima's 12 Steps) : Decision To Introduce TPMDocument16 pagesStage Step (Nakajima's 12 Steps) : Decision To Introduce TPMKarisma Lumban GaolNo ratings yet
- Study of JH Implementation ReadyDocument27 pagesStudy of JH Implementation ReadyNaveen Jangid100% (1)
- QM Pillar Training CIIDocument76 pagesQM Pillar Training CIINARENDER SINGH100% (1)
- Standard Reaction Plan To Abnormal Situation: Restart ProcessDocument1 pageStandard Reaction Plan To Abnormal Situation: Restart ProcessDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- 02 TVS Motor Co. LTDDocument127 pages02 TVS Motor Co. LTDRaj Rudrapaa100% (2)
- For Cii On TPM - Jun '10 v3Document54 pagesFor Cii On TPM - Jun '10 v3outline35No ratings yet
- KK PillarDocument117 pagesKK PillarMAngesh Gade100% (1)
- 08.DM Pillar FCDocument67 pages08.DM Pillar FCashutoshpal21No ratings yet
- 5.6 Office TPM and Concept of PQCDSMDocument9 pages5.6 Office TPM and Concept of PQCDSMvenkata_776555228100% (1)
- 4M Change Management PresentationDocument42 pages4M Change Management PresentationSARAI MARINNo ratings yet
- DWM Overview RIBDocument43 pagesDWM Overview RIBAshokNo ratings yet
- Jishu Hozen Audit Sheet: Step 1: Initial Cleaning Department: Area: Circle Name: Circle LeaderDocument7 pagesJishu Hozen Audit Sheet: Step 1: Initial Cleaning Department: Area: Circle Name: Circle LeaderharshavardhanNo ratings yet
- Kaizen in JIT Production SystemDocument51 pagesKaizen in JIT Production SystemLlehk FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Blue 7 TPM Part 1 of 2Document30 pagesBlue 7 TPM Part 1 of 2shamelnaNo ratings yet
- 01.sundram Fasteners LTDDocument60 pages01.sundram Fasteners LTDTapash Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Improvement KaizenDocument11 pagesImprovement KaizenAnkur DhirNo ratings yet
- Kaizen KobetDocument19 pagesKaizen KobetShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomous MaintenanceDocument38 pagesAutonomous Maintenancechusz100% (1)
- Non Conformity Report: Part Name:-Clamp Bolt Model: M4 Clamp Bolt Supplier:-Paradise Indus. Customer: PICLDocument1 pageNon Conformity Report: Part Name:-Clamp Bolt Model: M4 Clamp Bolt Supplier:-Paradise Indus. Customer: PICLAyush Narang100% (1)
- Sona GroupDocument56 pagesSona GroupbrindatammaNo ratings yet
- SKILL MATRIX StaffDocument3 pagesSKILL MATRIX StaffMAHIPAL baseraNo ratings yet
- Concept Diagram - Figure of 8': Quality Kaizen Quality MaintenanceDocument41 pagesConcept Diagram - Figure of 8': Quality Kaizen Quality MaintenanceNARENDER SINGHNo ratings yet
- Example of TPM in Office EuropeDocument53 pagesExample of TPM in Office Europekingathur26681No ratings yet
- WCM ChecklistDocument13 pagesWCM ChecklistYurdun OrbakNo ratings yet
- Lost Cost MatrixDocument2 pagesLost Cost Matrixrecep1100% (5)
- Professional MaintenanceDocument391 pagesProfessional MaintenanceAimar Vanderlei Ferreira Filho100% (1)
- STEP1MANDocument101 pagesSTEP1MANRPM28XI100% (1)
- Kaizen EventDocument22 pagesKaizen EventRibmanNo ratings yet
- Red Bin AnalysisDocument5 pagesRed Bin AnalysisDINESHCHOUDHARY88No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Total Pr...Document9 pagesAn Introduction To Total Pr...Abhinav JainNo ratings yet
- Total Productive Maintenance: Production Production Maintenance MaintenanceDocument42 pagesTotal Productive Maintenance: Production Production Maintenance Maintenance123456789No ratings yet
- FI Training WorkshopDocument17 pagesFI Training WorkshopRajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Reports in TQMDocument1 pageReports in TQMJean LeonorNo ratings yet
- Effective Maintenance Introduction 1712885423Document29 pagesEffective Maintenance Introduction 1712885423Rogério Andrade Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- PcbridgeDocument4 pagesPcbridgePrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Download CoprocessorDocument2 pagesHow To Download CoprocessorPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating ProceduresDocument4 pagesStandard Operating ProceduresPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Automatio N Pyramid?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Automatio N Pyramid?Prakash KumarNo ratings yet
- ECL-Process Magnetic Separator Motor Failure: Motor Speed Control Drive InstallationDocument7 pagesECL-Process Magnetic Separator Motor Failure: Motor Speed Control Drive InstallationPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Reactions Under Anodic and Cathodic PolarizationDocument4 pagesReactions Under Anodic and Cathodic PolarizationPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- # 6030 PEN OIL: Grade: Industrial Grade Heavy Duty Penetrating OilDocument3 pages# 6030 PEN OIL: Grade: Industrial Grade Heavy Duty Penetrating OilPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Cable Maintenance: Study Material OnDocument54 pagesFiber Optics Cable Maintenance: Study Material OnPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- BAF - SOP - 04 Maintenance of Emerson UPSDocument12 pagesBAF - SOP - 04 Maintenance of Emerson UPSPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Ultraware FaultdetailsDocument14 pagesUltraware FaultdetailsPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Seat BeltDocument2 pagesSeat BeltPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Valid Standard: Approved Vendor List For Electrical and ElectronicsDocument12 pagesValid Standard: Approved Vendor List For Electrical and ElectronicsPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- 8376 Electronic Component CleanerDocument3 pages8376 Electronic Component CleanerPrakash Kumar100% (1)
- Electrical SafetyDocument16 pagesElectrical SafetyPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Gas SafetyDocument1 pageHydrogen Gas SafetyPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Track Line Safety Inside Tata Steel Works SS/GEN-24: by Sachin ParanjapeDocument14 pagesTrack Line Safety Inside Tata Steel Works SS/GEN-24: by Sachin ParanjapePrakash Kumar100% (1)
- Valid Standard: Power Cutting Tracking FormDocument1 pageValid Standard: Power Cutting Tracking FormPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Safety Shower Eye WashDocument10 pagesSafety Shower Eye WashPrakash Kumar100% (1)
- SpeedingDocument3 pagesSpeedingPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Seat BeltDocument2 pagesSeat BeltPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Power TransformerDocument55 pagesPower TransformerPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Selection and Maintenance of AC MotorDocument29 pagesSelection and Maintenance of AC MotorPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Check List For Fire Hydrant Safety StandardDocument3 pagesCheck List For Fire Hydrant Safety StandardPrakash KumarNo ratings yet
- Dakota Office Products Case StudyDocument12 pagesDakota Office Products Case StudyAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- 2.8 - ICR Aug 06 - Mill PerformanceDocument2 pages2.8 - ICR Aug 06 - Mill PerformanceKreshnik StratiNo ratings yet
- Acrydur 116 ENG US 20 10 2022Document4 pagesAcrydur 116 ENG US 20 10 2022Volkmar LullNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints Limited:: Management As A Tool For Higher ProductivityDocument26 pagesAsian Paints Limited:: Management As A Tool For Higher ProductivityAditi NigamNo ratings yet
- Slides Erp - SCMDocument79 pagesSlides Erp - SCMMAI NGUYỄN XUÂNNo ratings yet
- Client CV - Account Manager (MY)Document2 pagesClient CV - Account Manager (MY)SAIHA AZIZNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Pharma: January 2014Document8 pagesCustomer Relationship Management (CRM) in Pharma: January 2014Uchenna 'Bonex' OgbonnaNo ratings yet
- Marriott: Subject: Marketing Research MBA (Agribusiness Management) Batch: 2021-23Document10 pagesMarriott: Subject: Marketing Research MBA (Agribusiness Management) Batch: 2021-23SOMYA RANJAN NANDANo ratings yet
- Quality Gurus: (The Correct Options Have Been Marked in Red) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuality Gurus: (The Correct Options Have Been Marked in Red) Multiple Choice QuestionsRanbir KapoorNo ratings yet
- AAR Hotels & Resorts - Company ProfileDocument14 pagesAAR Hotels & Resorts - Company ProfileRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Business - Riverview Trial With SolutionsDocument31 pages2012 Business - Riverview Trial With SolutionsArpit KumarNo ratings yet
- PCN Analysis Exercise 2012 With Airline ExampleDocument16 pagesPCN Analysis Exercise 2012 With Airline ExampleQuick StarNo ratings yet
- DAILY WELD FIT-UP and PRODUCTION REPORT (Field Weld) - PIPELINE-SATR-W-2007Document2 pagesDAILY WELD FIT-UP and PRODUCTION REPORT (Field Weld) - PIPELINE-SATR-W-2007smdriyazbashaNo ratings yet
- Amazon Fba Guide 2021Document116 pagesAmazon Fba Guide 2021Nabil MehibelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementJohanna VidadNo ratings yet
- 12th All Komatsu Indonesia Technical Olympic 2022 Official ResultDocument2 pages12th All Komatsu Indonesia Technical Olympic 2022 Official ResultMarchal KawengianNo ratings yet
- On Customer Relationship ManagementDocument17 pagesOn Customer Relationship ManagementSandip Chaudhari96% (28)
- Topic 1: E-Commerce Business Models and ConceptsDocument10 pagesTopic 1: E-Commerce Business Models and Conceptsmaria lailanie bautistaNo ratings yet
- PIZZA ZONE BBA ProjectDocument76 pagesPIZZA ZONE BBA ProjectPrince RamoliyaNo ratings yet
- B2B Case Study On Voltas & EELDocument11 pagesB2B Case Study On Voltas & EELDebasis PrustyNo ratings yet
- Contractor Vendor Audit ChecklistDocument4 pagesContractor Vendor Audit ChecklistMandy NormanNo ratings yet
- AJMAAR Vol 6 (1) - ArifDocument10 pagesAJMAAR Vol 6 (1) - ArifProf. Bilal Mustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- Proses BisnisDocument65 pagesProses BisnisCrio Binratman Tripatmono50% (2)
- Inventory and PurchasingDocument71 pagesInventory and PurchasingMikail MpuNo ratings yet
- Abm and AbcDocument25 pagesAbm and AbcMs. FitNo ratings yet
- Marketing Seminar 17th March 2023 Notice To StudentsDocument2 pagesMarketing Seminar 17th March 2023 Notice To StudentsAyush MundNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Assignment - 2Document5 pagesSupply Chain Assignment - 2Madhavi TakNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Submit Team Culminating Project Milestone 1Document7 pagesModule 3 Submit Team Culminating Project Milestone 1api-622172809No ratings yet
- Product Management MHM-614 / W-10227Document21 pagesProduct Management MHM-614 / W-10227Aisha KhanNo ratings yet