Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology:: Disruption To The Formation of The Lip and Palate During Organogesis
Pathophysiology:: Disruption To The Formation of The Lip and Palate During Organogesis
Uploaded by
3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hematological Disorders ErythropoiesisDocument4 pagesHematological Disorders Erythropoiesis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Intro High Risk NewbornDocument40 pagesIntro High Risk Newborn3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- EstradiolDocument1 pageEstradiol3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Stretching and Tearing of of The Muscle, Ligaments and Fibrious TissueDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Stretching and Tearing of of The Muscle, Ligaments and Fibrious Tissue3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- OxybutyninDocument2 pagesOxybutynin3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis NCPDocument2 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis NCP3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology:: Hormonal Imbalance Due To PregnancyDocument1 pagePathophysiology:: Hormonal Imbalance Due To Pregnancy3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis NCPDocument2 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis NCP3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
Pathophysiology:: Disruption To The Formation of The Lip and Palate During Organogesis
Pathophysiology:: Disruption To The Formation of The Lip and Palate During Organogesis
Uploaded by
3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology:: Disruption To The Formation of The Lip and Palate During Organogesis
Pathophysiology:: Disruption To The Formation of The Lip and Palate During Organogesis
Uploaded by
3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.Copyright:
Available Formats
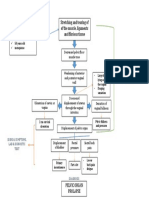
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
NON-MODIFIABLE
MODIFIABLE
Disruption to the Family history of Cleft
Alcohol use
formation of the lip lip and cleft palate
Cigarette smoking
and palate during (Genetic disorder)
organogesis
Failure fusion of the Failure of the tongue to
maxillary process and move downward to
medial nasal process undergo palatine
formation process
Bilateral cleft lip The primary and DISEASE
secondary palatal PROCESS
tissues and nasal septum
unable to fuse to form
Complete cleft palate definitive palate.
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS,
LAB & DIGNOSTIC TEST Intrauterine
development of the hard
Inspection of the oral and soft palate, and lips
cavity and structures is incomplete.
reveals that cleft extends
from soft to hard palate
exposing the nasal
cavity.
DIAGNOSIS
CLEFT LIP AND
CLEFT PALATE
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hematological Disorders ErythropoiesisDocument4 pagesHematological Disorders Erythropoiesis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Intro High Risk NewbornDocument40 pagesIntro High Risk Newborn3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- EstradiolDocument1 pageEstradiol3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Stretching and Tearing of of The Muscle, Ligaments and Fibrious TissueDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Stretching and Tearing of of The Muscle, Ligaments and Fibrious Tissue3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- OxybutyninDocument2 pagesOxybutynin3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis NCPDocument2 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis NCP3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology:: Hormonal Imbalance Due To PregnancyDocument1 pagePathophysiology:: Hormonal Imbalance Due To Pregnancy3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Path o Physiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePath o Physiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of SyphilisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Syphilis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Trichomonas Vaginalis NCPDocument2 pagesTrichomonas Vaginalis NCP3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet