Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9b Plants
9b Plants
Uploaded by
Oneth RajapakseCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Catalogue Magicfarmers Info enDocument74 pagesCatalogue Magicfarmers Info enakfbw2000No ratings yet
- 9a Mark SchemesDocument6 pages9a Mark Schemesobomar2010No ratings yet
- Pastel Spells PDFDocument94 pagesPastel Spells PDFlaura garcia ortiz50% (4)
- 7ge Air PressureDocument25 pages7ge Air PressureSapphire BlueNo ratings yet
- Name Class Date: G - N/KGDocument4 pagesName Class Date: G - N/KGDelosh TNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument2 pages9B Summary Sheetsameema80% (5)
- Summary Sheets: Cells and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesSummary Sheets: Cells and Their FunctionsLola Smith0% (1)
- Algae Water Flea Stickleback: ProtoctistsDocument2 pagesAlgae Water Flea Stickleback: Protoctistsghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- Proposed A Drip Irrigation Water System Design in Mantalongon, Dalaguete, Cebu CityDocument51 pagesProposed A Drip Irrigation Water System Design in Mantalongon, Dalaguete, Cebu CityAnsil Jane Gonzales100% (3)
- Dukan Diet SummaryDocument6 pagesDukan Diet SummaryLavinia DumitruNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Term 1 Test (Revision)Document10 pagesYear 8 Term 1 Test (Revision)A.K MonNo ratings yet
- 141L69P4MW5UVDocument2 pages141L69P4MW5UVSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesis Questionsnyonika chandak100% (1)
- Light 4 QPDocument9 pagesLight 4 QPHabibullah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument8 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomEngy AlasutyNo ratings yet
- InspireEnglish Y9 StudentBookAnswersDocument96 pagesInspireEnglish Y9 StudentBookAnswersPwintNo ratings yet
- 8i - Word - Sheets FluidsDocument2 pages8i - Word - Sheets FluidsJoshua ChungNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 9f Word SheetsDocument2 pages9f Word SheetsbanaliaNo ratings yet
- 8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersDocument1 page8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersClaire LNo ratings yet
- 8A Summary SheetDocument2 pages8A Summary Sheetishaan surapaneniNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Going For Gold!Document2 pagesSummary Sheets: Going For Gold!chan myae100% (1)
- Grade7 Geograpy ADocument264 pagesGrade7 Geograpy AJannet YangNo ratings yet
- Science 8G Metals and Their UsesDocument2 pagesScience 8G Metals and Their UsesHeba AwadNo ratings yet
- Igcse: Art and Design: Fine Art, Graphic Design, Photography, TextilesDocument24 pagesIgcse: Art and Design: Fine Art, Graphic Design, Photography, TextilesSabsNo ratings yet
- Es Int 9e QQ AspDocument3 pagesEs Int 9e QQ AspRifaa WidasmaraNo ratings yet
- 8a Food Digestion Science QuizDocument42 pages8a Food Digestion Science QuizahmerjamilNo ratings yet
- 8A B C D Summary SheetsDocument13 pages8A B C D Summary SheetsFaheem BhaimedNo ratings yet
- 7I Energy ResourcesDocument17 pages7I Energy ResourcesNemoOshiNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and WavesDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and Waves박찬우No ratings yet
- Book and Work Sheet Answers Year 7Document100 pagesBook and Work Sheet Answers Year 7reetiNo ratings yet
- KS3 7E Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesKS3 7E Acids and AlkalisG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 8g Summary SheetsDocument3 pages8g Summary SheetszunairaNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 1 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesQuick Quiz: 1 Page 1 of 2Arjun Kalyan's Private accountNo ratings yet
- Question 8KdDocument5 pagesQuestion 8KdShihabsirNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes Grade 7Document4 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes Grade 7HansyNo ratings yet
- Biology PracticeDocument4 pagesBiology PracticeVishva Atma100% (1)
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 14 - EcosystemsDocument4 pagesIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 14 - EcosystemsKim GuermacheNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Practice TestDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions Practice TestShemy RajNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Int Esws at 7e Unit TTPPDocument30 pagesInt Esws at 7e Unit TTPPHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproduction: I CanDocument1 pageTypes of Reproduction: I CanazharNo ratings yet
- Density Worksheet HADocument2 pagesDensity Worksheet HALê Phạm Ngọc KhánhNo ratings yet
- Term Test QP 1Document9 pagesTerm Test QP 1sollu786_889163149No ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetslNo ratings yet
- 8I Fluids Revision - Worksheet - Answers 660Document1 page8I Fluids Revision - Worksheet - Answers 660gbqwzy56fzNo ratings yet
- Acids and AlkalisDocument6 pagesAcids and AlkalisAmarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Year - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesYear - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeChuanthing TeeNo ratings yet
- 7h Summary Sheets PDFDocument3 pages7h Summary Sheets PDFAghaanaa JaiganeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper For Virtual Classes JUNE IG 1Document12 pagesBiology Paper For Virtual Classes JUNE IG 1Ruqia ZahraNo ratings yet
- Assessment For Learning Year: 8... Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesAssessment For Learning Year: 8... Mark SchemeprincesstraillNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructurebilalNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes Part5Document10 pagesBiology Revision Notes Part5volvanskyNo ratings yet
- Energy From Food Resources 2023-10-20 07 - 26 - 20Document4 pagesEnergy From Food Resources 2023-10-20 07 - 26 - 20steckova.lindaNo ratings yet
- 8e Combustion Scheme of LearningDocument4 pages8e Combustion Scheme of LearningJude HassanNo ratings yet
- Summary 7KDocument2 pagesSummary 7KTHJNo ratings yet
- 9J Summary SheetsDocument2 pages9J Summary SheetsFar ZNo ratings yet
- Unit of Work - Summative Information - Science Unit 7G - Year 7Document4 pagesUnit of Work - Summative Information - Science Unit 7G - Year 7Amir AminiNo ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetsSelena Alsrouri100% (1)
- 8F QPDocument7 pages8F QPsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Stage 9 Chemistry Pe1Document8 pagesStage 9 Chemistry Pe1sneakyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology IGCSE: 2.12: Enzymes and TemperatureDocument3 pagesEdexcel Biology IGCSE: 2.12: Enzymes and TemperatureahmedNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument5 pages9B Summary SheetsNafiul Munsur Year 7No ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant ProcessesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Plant ProcessesRajiv SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Alliteration and OnomatopoeiaDocument21 pages1.6 Alliteration and OnomatopoeiaOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- 9J Quick QuizDocument2 pages9J Quick QuizOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 9ba 9BbDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: 9ba 9BbOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Tle 09Document15 pagesTle 09Lance GabrielNo ratings yet
- Seed Testing - Purity and GerminationDocument8 pagesSeed Testing - Purity and GerminationMahathir Mohmed100% (1)
- Arhitect Parcuri NebbienDocument20 pagesArhitect Parcuri NebbienIleana BurnichioiuNo ratings yet
- Prep Plant/tipple PermitsDocument3 pagesPrep Plant/tipple PermitsRishiraj SahooNo ratings yet
- Untuk Latihan Soal Menghadapi Ulangan Tengah SemesterDocument4 pagesUntuk Latihan Soal Menghadapi Ulangan Tengah SemesterTikuss OutsiderNo ratings yet
- Breakfast PDFDocument23 pagesBreakfast PDFAleksa Malicar100% (3)
- Coffee Tea and Spice Handout EndestDocument128 pagesCoffee Tea and Spice Handout EndestHailu Hameso100% (5)
- SMP - Bahasa Inggris 1999Document7 pagesSMP - Bahasa Inggris 1999manip saptamawati100% (4)
- Stelechocarpus Burahol: Scientific NameDocument4 pagesStelechocarpus Burahol: Scientific NameShania Astanti SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- LifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionDocument174 pagesLifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionSatyam SoniNo ratings yet
- 2367-Article Text-18832-2-10-20210820Document8 pages2367-Article Text-18832-2-10-20210820desy meilinda putri firdauziNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids FDocument147 pagesAlkaloids FAirthSpark3000100% (1)
- Gulf of Mexico: Central America and The CaribbeanDocument1 pageGulf of Mexico: Central America and The CaribbeanAlexandra VartolomeiNo ratings yet
- Flower and Plant Care ManualDocument213 pagesFlower and Plant Care ManualPanait Alina100% (1)
- Soal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5 SD MI Dan Kunci JawabnyaDocument3 pagesSoal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5 SD MI Dan Kunci JawabnyaRidwan AlgoniNo ratings yet
- MANGO - Asean StandardDocument8 pagesMANGO - Asean StandardDenis Salvatierra100% (1)
- Sample Answer:: Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesSample Answer:: Mark SchemeKatherinaNo ratings yet
- Book Information - Singaporean & Malaysian Kuih Cookbook, Aromas of KuihsDocument3 pagesBook Information - Singaporean & Malaysian Kuih Cookbook, Aromas of KuihsBrowncookie.comNo ratings yet
- Travelling Water ScreenDocument11 pagesTravelling Water ScreenAnirban SinhaNo ratings yet
- Copy of Pharmacognosy-and-Plant-ChemistryDocument25 pagesCopy of Pharmacognosy-and-Plant-ChemistryDecemae FuentesNo ratings yet
- SauerkrautDocument2 pagesSauerkrautRoger AugeNo ratings yet
- Food and Cooking Vocabulary Jeopardy Game Fun Activities Games Games 93474Document57 pagesFood and Cooking Vocabulary Jeopardy Game Fun Activities Games Games 93474Diana Estefania Elescano RojasNo ratings yet
- Urban Forestry: Greening A Highway in Nairobi For People and NatureDocument56 pagesUrban Forestry: Greening A Highway in Nairobi For People and NaturecathyhwatsonNo ratings yet
- J Fluid 2005 12 045Document10 pagesJ Fluid 2005 12 045Azar DeenNo ratings yet
- UMUTOBE W'IGITANGAZA CFR NUFOTEC BURUNDIDocument27 pagesUMUTOBE W'IGITANGAZA CFR NUFOTEC BURUNDINyandwi LeonardNo ratings yet
- Common Plants Animals: Project Study OFDocument17 pagesCommon Plants Animals: Project Study OFGöùräv ÇhäkräbørtýNo ratings yet
9b Plants
9b Plants
Uploaded by
Oneth RajapakseOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9b Plants
9b Plants
Uploaded by
Oneth RajapakseCopyright:
Available Formats
9 BL8a
Summary Sheets
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a series of chemical reactions that we can summarise using a word
equation. Energy and chlorophyll are needed for it to happen. The energy is transferred by
light (usually from the Sun) and becomes stored in glucose.
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
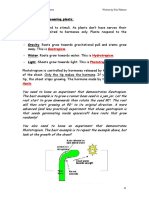
Getting water
Water is taken out of the soil by the
roots. Roots are adapted to their
function by being branched and spread
out to help them to absorb water from a
large volume of soil. They also have root
hair cells, which have a large surface
area to help them absorb water quickly.
The water flows up xylem vessels
(made of hollow cells) to the leaf.
Water is also needed because mineral salts are dissolved in it. These keep plants healthy.
For instance, plants need nitrates to make proteins. Water also stops plants wilting by filling
up their cells, and it can keep their leaves cool.
Getting carbon dioxide
Air, containing carbon dioxide,
diffuses into leaves through
small holes called stomata.
Leaves are thin so that the
carbon dioxide does not need to
go very far before reaching the
cells that need it. Increasing the
amount of carbon dioxide
around a plant can often speed
up photosynthesis.
Getting light
Many leaves are wide so that they have a large surface area to trap as much light as possible.
They are also arranged so that they do not shade one another.
Most photosynthesis happens in the palisade cells, which are found near the upper surface of
leaves. Palisade cells are packed with chloroplasts. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green
chemical that absorbs energy transferred by light and uses it to power photosynthesis. Increasing
the amount of light can often speed up photosynthesis.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 15 Page 1 of 2
9 BL8a
Summary Sheets
Aerobic respiration
Plant cells release the energy stored in glucose using aerobic respiration (another series of
chemical reactions):
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
All living cells need energy and so all living cells respire. Aerobic respiration happens all the time,
but photosynthesis can only happen when there is light.
Uses of glucose
Glucose is a type of sugar. It is used for three things:
● respiration to release energy
● making other substances that act as stores of energy (e.g. starch), which can be turned back
into glucose for respiration when needed
● making new materials for growth, e.g. cellulose (for cell walls), lipids (e.g. for cell membranes)
and proteins (e.g. for enzymes). To make proteins, mineral salts called nitrates are needed.
New substances made by a plant are carried around the plant in phloem vessels.
Farming
Modern farming methods can cause environmental problems.
What is done Why it is done Problems this causes
land is cleared of hedges and to create more land for crops and Destroys habitats. Lack of roots
trees make it easier for machinery to can cause soil erosion.
move around
pesticides (e.g. herbicides, to kill pests that compete with or Can kill useful organisms as well
insecticides) are used harm the crops as pests. Damages food webs.
fertilisers are used they contain mineral salts that Can wash into streams and rivers
help plants to grow and increase and cause pollution so that the
the yield organisms in the water die.
varieties varieties of plants are chosen that The planting of huge areas of a
produce the highest yield single variety reduces
biodiversity.
Breeding varieties
Farmers and plant breeders may choose or ‘select’ a plant with certain characteristics.
This organism is then used to breed from. The offspring that have the best of these characteristics
are then bred from again. This is called selective breeding and is how many varieties are created.
Sometimes two different varieties are bred together to try to produce offspring with characteristics
from both varieties. This is called cross-breeding.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 16 Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Catalogue Magicfarmers Info enDocument74 pagesCatalogue Magicfarmers Info enakfbw2000No ratings yet
- 9a Mark SchemesDocument6 pages9a Mark Schemesobomar2010No ratings yet
- Pastel Spells PDFDocument94 pagesPastel Spells PDFlaura garcia ortiz50% (4)
- 7ge Air PressureDocument25 pages7ge Air PressureSapphire BlueNo ratings yet
- Name Class Date: G - N/KGDocument4 pagesName Class Date: G - N/KGDelosh TNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument2 pages9B Summary Sheetsameema80% (5)
- Summary Sheets: Cells and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesSummary Sheets: Cells and Their FunctionsLola Smith0% (1)
- Algae Water Flea Stickleback: ProtoctistsDocument2 pagesAlgae Water Flea Stickleback: Protoctistsghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- Proposed A Drip Irrigation Water System Design in Mantalongon, Dalaguete, Cebu CityDocument51 pagesProposed A Drip Irrigation Water System Design in Mantalongon, Dalaguete, Cebu CityAnsil Jane Gonzales100% (3)
- Dukan Diet SummaryDocument6 pagesDukan Diet SummaryLavinia DumitruNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Term 1 Test (Revision)Document10 pagesYear 8 Term 1 Test (Revision)A.K MonNo ratings yet
- 141L69P4MW5UVDocument2 pages141L69P4MW5UVSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesis Questionsnyonika chandak100% (1)
- Light 4 QPDocument9 pagesLight 4 QPHabibullah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument8 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomEngy AlasutyNo ratings yet
- InspireEnglish Y9 StudentBookAnswersDocument96 pagesInspireEnglish Y9 StudentBookAnswersPwintNo ratings yet
- 8i - Word - Sheets FluidsDocument2 pages8i - Word - Sheets FluidsJoshua ChungNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 9f Word SheetsDocument2 pages9f Word SheetsbanaliaNo ratings yet
- 8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersDocument1 page8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersClaire LNo ratings yet
- 8A Summary SheetDocument2 pages8A Summary Sheetishaan surapaneniNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Going For Gold!Document2 pagesSummary Sheets: Going For Gold!chan myae100% (1)
- Grade7 Geograpy ADocument264 pagesGrade7 Geograpy AJannet YangNo ratings yet
- Science 8G Metals and Their UsesDocument2 pagesScience 8G Metals and Their UsesHeba AwadNo ratings yet
- Igcse: Art and Design: Fine Art, Graphic Design, Photography, TextilesDocument24 pagesIgcse: Art and Design: Fine Art, Graphic Design, Photography, TextilesSabsNo ratings yet
- Es Int 9e QQ AspDocument3 pagesEs Int 9e QQ AspRifaa WidasmaraNo ratings yet
- 8a Food Digestion Science QuizDocument42 pages8a Food Digestion Science QuizahmerjamilNo ratings yet
- 8A B C D Summary SheetsDocument13 pages8A B C D Summary SheetsFaheem BhaimedNo ratings yet
- 7I Energy ResourcesDocument17 pages7I Energy ResourcesNemoOshiNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and WavesDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Sound Vibrations and Waves박찬우No ratings yet
- Book and Work Sheet Answers Year 7Document100 pagesBook and Work Sheet Answers Year 7reetiNo ratings yet
- KS3 7E Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesKS3 7E Acids and AlkalisG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- 8g Summary SheetsDocument3 pages8g Summary SheetszunairaNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 1 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesQuick Quiz: 1 Page 1 of 2Arjun Kalyan's Private accountNo ratings yet
- Question 8KdDocument5 pagesQuestion 8KdShihabsirNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes Grade 7Document4 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts Notes Grade 7HansyNo ratings yet
- Biology PracticeDocument4 pagesBiology PracticeVishva Atma100% (1)
- IGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 14 - EcosystemsDocument4 pagesIGCSE - Bio - Lesson Plan 14 - EcosystemsKim GuermacheNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Practice TestDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions Practice TestShemy RajNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Int Esws at 7e Unit TTPPDocument30 pagesInt Esws at 7e Unit TTPPHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproduction: I CanDocument1 pageTypes of Reproduction: I CanazharNo ratings yet
- Density Worksheet HADocument2 pagesDensity Worksheet HALê Phạm Ngọc KhánhNo ratings yet
- Term Test QP 1Document9 pagesTerm Test QP 1sollu786_889163149No ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetslNo ratings yet
- 8I Fluids Revision - Worksheet - Answers 660Document1 page8I Fluids Revision - Worksheet - Answers 660gbqwzy56fzNo ratings yet
- Acids and AlkalisDocument6 pagesAcids and AlkalisAmarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Year - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesYear - 9 Photosynthesis - Mark SchemeChuanthing TeeNo ratings yet
- 7h Summary Sheets PDFDocument3 pages7h Summary Sheets PDFAghaanaa JaiganeshNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper For Virtual Classes JUNE IG 1Document12 pagesBiology Paper For Virtual Classes JUNE IG 1Ruqia ZahraNo ratings yet
- Assessment For Learning Year: 8... Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesAssessment For Learning Year: 8... Mark SchemeprincesstraillNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructurebilalNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision Notes Part5Document10 pagesBiology Revision Notes Part5volvanskyNo ratings yet
- Energy From Food Resources 2023-10-20 07 - 26 - 20Document4 pagesEnergy From Food Resources 2023-10-20 07 - 26 - 20steckova.lindaNo ratings yet
- 8e Combustion Scheme of LearningDocument4 pages8e Combustion Scheme of LearningJude HassanNo ratings yet
- Summary 7KDocument2 pagesSummary 7KTHJNo ratings yet
- 9J Summary SheetsDocument2 pages9J Summary SheetsFar ZNo ratings yet
- Unit of Work - Summative Information - Science Unit 7G - Year 7Document4 pagesUnit of Work - Summative Information - Science Unit 7G - Year 7Amir AminiNo ratings yet
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument2 pages8c Summary SheetsSelena Alsrouri100% (1)
- 8F QPDocument7 pages8F QPsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Stage 9 Chemistry Pe1Document8 pagesStage 9 Chemistry Pe1sneakyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology IGCSE: 2.12: Enzymes and TemperatureDocument3 pagesEdexcel Biology IGCSE: 2.12: Enzymes and TemperatureahmedNo ratings yet
- 9B Summary SheetsDocument5 pages9B Summary SheetsNafiul Munsur Year 7No ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant ProcessesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Plant ProcessesRajiv SinghNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Alliteration and OnomatopoeiaDocument21 pages1.6 Alliteration and OnomatopoeiaOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- 9J Quick QuizDocument2 pages9J Quick QuizOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 9ba 9BbDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: 9ba 9BbOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Tle 09Document15 pagesTle 09Lance GabrielNo ratings yet
- Seed Testing - Purity and GerminationDocument8 pagesSeed Testing - Purity and GerminationMahathir Mohmed100% (1)
- Arhitect Parcuri NebbienDocument20 pagesArhitect Parcuri NebbienIleana BurnichioiuNo ratings yet
- Prep Plant/tipple PermitsDocument3 pagesPrep Plant/tipple PermitsRishiraj SahooNo ratings yet
- Untuk Latihan Soal Menghadapi Ulangan Tengah SemesterDocument4 pagesUntuk Latihan Soal Menghadapi Ulangan Tengah SemesterTikuss OutsiderNo ratings yet
- Breakfast PDFDocument23 pagesBreakfast PDFAleksa Malicar100% (3)
- Coffee Tea and Spice Handout EndestDocument128 pagesCoffee Tea and Spice Handout EndestHailu Hameso100% (5)
- SMP - Bahasa Inggris 1999Document7 pagesSMP - Bahasa Inggris 1999manip saptamawati100% (4)
- Stelechocarpus Burahol: Scientific NameDocument4 pagesStelechocarpus Burahol: Scientific NameShania Astanti SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- LifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionDocument174 pagesLifeSciencesPart-2 FifthEditionSatyam SoniNo ratings yet
- 2367-Article Text-18832-2-10-20210820Document8 pages2367-Article Text-18832-2-10-20210820desy meilinda putri firdauziNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids FDocument147 pagesAlkaloids FAirthSpark3000100% (1)
- Gulf of Mexico: Central America and The CaribbeanDocument1 pageGulf of Mexico: Central America and The CaribbeanAlexandra VartolomeiNo ratings yet
- Flower and Plant Care ManualDocument213 pagesFlower and Plant Care ManualPanait Alina100% (1)
- Soal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5 SD MI Dan Kunci JawabnyaDocument3 pagesSoal UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 5 SD MI Dan Kunci JawabnyaRidwan AlgoniNo ratings yet
- MANGO - Asean StandardDocument8 pagesMANGO - Asean StandardDenis Salvatierra100% (1)
- Sample Answer:: Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesSample Answer:: Mark SchemeKatherinaNo ratings yet
- Book Information - Singaporean & Malaysian Kuih Cookbook, Aromas of KuihsDocument3 pagesBook Information - Singaporean & Malaysian Kuih Cookbook, Aromas of KuihsBrowncookie.comNo ratings yet
- Travelling Water ScreenDocument11 pagesTravelling Water ScreenAnirban SinhaNo ratings yet
- Copy of Pharmacognosy-and-Plant-ChemistryDocument25 pagesCopy of Pharmacognosy-and-Plant-ChemistryDecemae FuentesNo ratings yet
- SauerkrautDocument2 pagesSauerkrautRoger AugeNo ratings yet
- Food and Cooking Vocabulary Jeopardy Game Fun Activities Games Games 93474Document57 pagesFood and Cooking Vocabulary Jeopardy Game Fun Activities Games Games 93474Diana Estefania Elescano RojasNo ratings yet
- Urban Forestry: Greening A Highway in Nairobi For People and NatureDocument56 pagesUrban Forestry: Greening A Highway in Nairobi For People and NaturecathyhwatsonNo ratings yet
- J Fluid 2005 12 045Document10 pagesJ Fluid 2005 12 045Azar DeenNo ratings yet
- UMUTOBE W'IGITANGAZA CFR NUFOTEC BURUNDIDocument27 pagesUMUTOBE W'IGITANGAZA CFR NUFOTEC BURUNDINyandwi LeonardNo ratings yet
- Common Plants Animals: Project Study OFDocument17 pagesCommon Plants Animals: Project Study OFGöùräv ÇhäkräbørtýNo ratings yet