Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ring Design Chapter08
Ring Design Chapter08
Uploaded by
ismail güleç0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageThis document discusses compression squeeze and ratio recommendations for static o-ring seals. It defines compression squeeze and ratio, and provides minimum, target, and maximum recommended ratio ranges of 5-30% for rod/piston seals and 10-35% for static axial seals. It also explains that gland dimensions refer to the height and width of the rectangular space that contains the o-ring, and that the height must be less than the o-ring diameter to create compression, while the width only serves to contain the o-ring. Formulas for calculating gland dimensions for different seal types are referenced on the next page.
Original Description:
O-RING DESIGN GUIDE FOR BEGINNERS.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses compression squeeze and ratio recommendations for static o-ring seals. It defines compression squeeze and ratio, and provides minimum, target, and maximum recommended ratio ranges of 5-30% for rod/piston seals and 10-35% for static axial seals. It also explains that gland dimensions refer to the height and width of the rectangular space that contains the o-ring, and that the height must be less than the o-ring diameter to create compression, while the width only serves to contain the o-ring. Formulas for calculating gland dimensions for different seal types are referenced on the next page.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageRing Design Chapter08
Ring Design Chapter08
Uploaded by
ismail güleçThis document discusses compression squeeze and ratio recommendations for static o-ring seals. It defines compression squeeze and ratio, and provides minimum, target, and maximum recommended ratio ranges of 5-30% for rod/piston seals and 10-35% for static axial seals. It also explains that gland dimensions refer to the height and width of the rectangular space that contains the o-ring, and that the height must be less than the o-ring diameter to create compression, while the width only serves to contain the o-ring. Formulas for calculating gland dimensions for different seal types are referenced on the next page.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
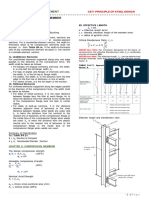
Compression Squeeze
𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑝𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑆𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑒𝑧𝑒
CS Height Ratio= x 100
𝐶𝑆
Recommended Value
See Below
Figure 2.1: Important measurements in relation
Compression Ratio
to compression squeeze Recommendations
Compression Squeeze Rod or Piston O-ring seal
Squeeze = CS – Height
Recommended Minimum Value Min: 5% Target: 20% Max: 30%
Squeeze > 0.1 mm (0.005 in)
Static Axial O-ring Seal
Min: 10% Target: 25% Max: 35%
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio recommendations seen Gland Dimension Calculations
below are for Static sealing applications only.
Although each physical arrangement is different,
When dealing with dynamic sealing applications
each involves the O-ring being captured in a
you would want to use tighter tolerances on the
rectangular gland which has two sets of opposing
mating components, as well as target a
surfaces. The first set of opposing surfaces is
compression ratio range in the lower half of the
sealing surfaces, in that the distance between
static sealing recommended range (5% to 20%). A
them, the gland height, is less than the O-ring
smaller compression squeeze is recommended
cross-section (CS) so that the installed O-ring is
die to friction and wear considerations.
compressed resulting in a sealing force.
Compression Squeeze The second set of opposing surfaces is
containing surfaces, in that the distance between
X%
them, the gland width, is larger than the O-ring
cross-section so that they only serve to keep the
100% O-ring in place.
Gland height and width are used for compression
and fill calculations. The formulas for calculating
these gland dimensions for piston glands, rod
glands and face seals are shown on the next
Figure 2.2: Important
measurements in relation to
page.
compression ratio
You might also like
- CH 17Document183 pagesCH 17Neerom Baldemoro100% (1)
- Chapter III: Metal Fits and Tolerances DR: Ramadan El Soudy Done By: Group 1Document15 pagesChapter III: Metal Fits and Tolerances DR: Ramadan El Soudy Done By: Group 1Karim MagdyNo ratings yet
- Lab 321 #1 VVVDocument12 pagesLab 321 #1 VVVSamNo ratings yet
- O-Rings For Low-Pressure Service: Machine DesignDocument7 pagesO-Rings For Low-Pressure Service: Machine DesignWin AsharNo ratings yet
- 5.3 ConstructionDocument45 pages5.3 Constructionprakashbudha8848No ratings yet
- O-Ring Design - Best PracticeDocument7 pagesO-Ring Design - Best PracticeJnanesh K SNo ratings yet
- General Design Information - Cam-Mechanism Design - Force-Analysis - Cam - Contact-StressDocument6 pagesGeneral Design Information - Cam-Mechanism Design - Force-Analysis - Cam - Contact-Stresssanthoshkumar.sNo ratings yet
- Section3 o Ring BasicsDocument4 pagesSection3 o Ring Basicssteve@air-innovations.co.zaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2-System of Limits, Fits, TolerancesDocument18 pagesMODULE 2-System of Limits, Fits, TolerancesjishnushankarNo ratings yet
- Leс3Document22 pagesLeс3PaulNo ratings yet
- Influence of Surface Roughness On Press FitsDocument13 pagesInfluence of Surface Roughness On Press FitsHuiFrankyNo ratings yet
- GD & TDocument43 pagesGD & TMahender Kumar100% (1)
- Compresión O-Rings PDFDocument12 pagesCompresión O-Rings PDFEdwin Patricio Taco ChuseteNo ratings yet
- RC Design - ACIDocument41 pagesRC Design - ACIAbebe WoldeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial of Hertzian Contact Stress Analysis: Nlecain@optics - Arizona.eduDocument8 pagesTutorial of Hertzian Contact Stress Analysis: Nlecain@optics - Arizona.edugego2No ratings yet
- Slender ColumnsDocument50 pagesSlender ColumnsSYEDHASSAN RAZANo ratings yet
- Ch6 Transverse ShearDocument33 pagesCh6 Transverse ShearDoğukan KurtuluşNo ratings yet
- Ce150 Steel 4.1 Tension Members Tensile Strength 01Document3 pagesCe150 Steel 4.1 Tension Members Tensile Strength 01Jhan SeenNo ratings yet
- Bosses: Figure 7: Boss Design GuidelinesDocument5 pagesBosses: Figure 7: Boss Design GuidelinesAaselNo ratings yet
- Fretting Simulation For Crankshaft-Counterweight Contact: A. Mäntylä and C. LönnqvistDocument17 pagesFretting Simulation For Crankshaft-Counterweight Contact: A. Mäntylä and C. LönnqvistPravinkumarGhodakeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Almen Strip Selection: Academic StudyDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Almen Strip Selection: Academic StudyUmit AytarNo ratings yet
- 5dimensioning and TolerancingDocument43 pages5dimensioning and TolerancingPavan RaghavNo ratings yet
- Product Design Mold DesignDocument19 pagesProduct Design Mold Designajithp_kvr100% (1)
- Module 2 - Sizing and DimensioningDocument13 pagesModule 2 - Sizing and Dimensioningfoj90532No ratings yet
- RC Cantilever DeflectionDocument1 pageRC Cantilever Deflectionklára LudínováNo ratings yet
- Compression MembersDocument4 pagesCompression Membersvincent mark garridoNo ratings yet
- Tolerance and Fits (Adjustments)Document13 pagesTolerance and Fits (Adjustments)Brown MeshNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design DrawingDocument41 pagesAnalysis and Design DrawingBrown MeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Design of Special BeamsDocument15 pagesChapter 1 - Design of Special BeamsSine EntertaimentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Analysis and Design of Tension Members (Part 1)Document6 pagesChapter 3 - Analysis and Design of Tension Members (Part 1)John Philip NuñezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Compression On T H E Shear Modulus of Rubber: of of of of of of ofDocument3 pagesEffect of Compression On T H E Shear Modulus of Rubber: of of of of of of ofstefan.vince536No ratings yet
- Module3 Design of Tension MembersDocument33 pagesModule3 Design of Tension MembersPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- On The Fretting Fatigue Crack Nucleation of Complete, Almost Complete and Incomplete Contacts Using An Asymptotic MethodDocument41 pagesOn The Fretting Fatigue Crack Nucleation of Complete, Almost Complete and Incomplete Contacts Using An Asymptotic MethodMAZOUZI AbdelhamidNo ratings yet
- Metrology & Mech. Measurement Ch. 02 System of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and GaugingDocument20 pagesMetrology & Mech. Measurement Ch. 02 System of Limits, Fits, Tolerance and GaugingAjij MujawarNo ratings yet
- Fits and TolerenceDocument34 pagesFits and Tolerencerana__singhNo ratings yet
- GD & T Notes PDFDocument44 pagesGD & T Notes PDFRoshan GajeenkarNo ratings yet
- Madhav Institute OF Technology and Science Gwalior: "Limits Fits and Tolerance"Document18 pagesMadhav Institute OF Technology and Science Gwalior: "Limits Fits and Tolerance"Jaideep SinghNo ratings yet
- Statically Loaded Weld Joint CalculatorDocument2 pagesStatically Loaded Weld Joint CalculatorM Jobayer AzadNo ratings yet
- Middle Third Rule For Rectangular Section - Engineering ApplicationsDocument4 pagesMiddle Third Rule For Rectangular Section - Engineering ApplicationsShivamKumarNo ratings yet
- FMD GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-10 06042020020009PMDocument37 pagesFMD GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-10 06042020020009PMKotadia ShivamNo ratings yet
- Stress Concentration Numerical Analysis of A Panel With Big GroovesDocument4 pagesStress Concentration Numerical Analysis of A Panel With Big GroovesKilian MartenNo ratings yet
- Bearing: A Device That Supports, Guides, and Reduces The Friction of Motion Between Fixed and Moving Machine PartsDocument8 pagesBearing: A Device That Supports, Guides, and Reduces The Friction of Motion Between Fixed and Moving Machine PartsankitsarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Tension MemberDocument75 pagesTension Memberalan saeed AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Tension Members-BDocument124 pagesTension Members-Balqazi.designerNo ratings yet
- Stress Concentration and FatigueDocument22 pagesStress Concentration and FatiguelosoceNo ratings yet
- Fukuoka 1992Document6 pagesFukuoka 1992Suissi AnisNo ratings yet
- 2.A Study On Stress ConcentrationDocument27 pages2.A Study On Stress ConcentrationRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- Spardha Mehta SP16Document7 pagesSpardha Mehta SP16Spradha MehtaNo ratings yet
- Limits, Fits and TolerancesDocument81 pagesLimits, Fits and TolerancesSaYed RaDyNo ratings yet
- Tension Member DesignDocument97 pagesTension Member DesignJm CampitanNo ratings yet
- MMEN 326 - Torsion of Non-CircularDocument23 pagesMMEN 326 - Torsion of Non-CircularchegedennNo ratings yet
- 6 Restrained Beams HandoutDocument2 pages6 Restrained Beams HandoutEng TrNo ratings yet
- Common Composite Layup RulesDocument1 pageCommon Composite Layup Rulessnappish1No ratings yet
- Spur and Helical Gear DesignDocument45 pagesSpur and Helical Gear Designkibromgidey12No ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter033Document1 pageRing Design Chapter033ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2000 Primer Continued : ST NDDocument1 pageASTM D2000 Primer Continued : ST NDismail güleçNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter032Document1 pageRing Design Chapter032ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- O-Ring Size Reference Guide: SAE AS568Document1 pageO-Ring Size Reference Guide: SAE AS568ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter017Document1 pageRing Design Chapter017ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter015Document1 pageRing Design Chapter015ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter016Document1 pageRing Design Chapter016ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- Ring Design Chapter010Document1 pageRing Design Chapter010ismail güleçNo ratings yet
- Lorus Watch Manual PDFDocument2 pagesLorus Watch Manual PDFDave Long100% (1)
- Lorenz 1986Document10 pagesLorenz 1986Jessica Lienlaf RojasNo ratings yet
- Motivation: Archit GuptaDocument19 pagesMotivation: Archit GuptaArchit GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc.: Publisher Tinley Park, IllinoisDocument23 pagesThe Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc.: Publisher Tinley Park, IllinoisSaurav ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Emf Values of Organic CompoundsDocument34 pagesEmf Values of Organic CompoundsPrabir SahaNo ratings yet
- SCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020Document11 pagesSCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020JoanNo ratings yet
- Elhai Và C NG S (2020)Document10 pagesElhai Và C NG S (2020)Ánh Ngọc Đỗ TrầnNo ratings yet
- Nuusbrief - Newsletter 4 of 2022Document20 pagesNuusbrief - Newsletter 4 of 2022augustina gaiceanuNo ratings yet
- MechanismsDocument22 pagesMechanismssilva, april joy c.No ratings yet
- (Bradford Books) Sidney I. Wiener, Jeffrey S. Taube - Head Direction Cells and The Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Orientation-The MIT Press (2005)Document503 pages(Bradford Books) Sidney I. Wiener, Jeffrey S. Taube - Head Direction Cells and The Neural Mechanisms of Spatial Orientation-The MIT Press (2005)Víctor FuentesNo ratings yet
- Heat of Vaporization and Heat of FusionDocument17 pagesHeat of Vaporization and Heat of FusionJASIS JULIA NOELYN V.No ratings yet
- Hjørland, B. (1998) Theory and Metatheory of Information Science. A New Interpretation. Journal of Documentation 54 (5) 606-621.Document17 pagesHjørland, B. (1998) Theory and Metatheory of Information Science. A New Interpretation. Journal of Documentation 54 (5) 606-621.Raul TorresNo ratings yet
- Examen de Ingles b1Document13 pagesExamen de Ingles b1GIANN CARLO GUTIERREZ GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Microchip FabricationDocument39 pagesChapter1 Microchip Fabrication吳文嘉100% (1)
- Sameh Gamal Saad (Final PHD)Document321 pagesSameh Gamal Saad (Final PHD)Remon SamirNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationDocument11 pages1.2 Bus Admittance Matrix: FormulationMohamed Elsir100% (1)
- Consumer Behavior and Sustainable MarketingDocument14 pagesConsumer Behavior and Sustainable Marketinglon choNo ratings yet
- Badminton Lesson Plan Backhand Net ShotDocument3 pagesBadminton Lesson Plan Backhand Net ShotFreddie MoatNo ratings yet
- 4k Solar Camera FlyerDocument4 pages4k Solar Camera FlyerElvis EmilianoNo ratings yet
- MKTG 2P52 Chapter 2Document41 pagesMKTG 2P52 Chapter 2Jeffrey O'LearyNo ratings yet
- BNN-Orientierungswert EN 22122021Document4 pagesBNN-Orientierungswert EN 22122021MOhamedNo ratings yet
- Duke Decompression Risk Analysis Comparing Oxygen and 50 Nitrox Decompression StopsDocument1 pageDuke Decompression Risk Analysis Comparing Oxygen and 50 Nitrox Decompression StopsBenoit BruhmullerNo ratings yet
- Castrol Enduron 10W-40Document2 pagesCastrol Enduron 10W-40Chun-Nien LaiNo ratings yet
- Defence Presentation - Ekaterina NazarenkoDocument44 pagesDefence Presentation - Ekaterina NazarenkoЕкатерина НазаренкоNo ratings yet
- CFDLV13 N12 P32 44Document13 pagesCFDLV13 N12 P32 44Rahmat Azis NabawiNo ratings yet
- Single Cell AnalysisDocument22 pagesSingle Cell AnalysisJonathan MilhomensNo ratings yet
- Toray TM810 Sea Water RO Element LDocument2 pagesToray TM810 Sea Water RO Element LMohamad JammalNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
- Carbonate ClassificationDocument5 pagesCarbonate ClassificationArpit UpadhyayNo ratings yet