Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 viewsNursing Care Plan 1
Nursing Care Plan 1
Uploaded by
kuro hanabusa Provide Provide reassurance and Provide information about Provide support and Provide a caring, non-
reassurance and support. support. Explain that treatment and recovery encouragement to seek judgmental environment.
Address anxiety and anxiety and withdrawal programs. Refer to further help. Collaborate Address physical and
withdrawal symptoms. symptoms are normal appropriate resources as with other providers as emotional needs. Refer to
Refer to treatment as and will subside with needed. needed. appropriate resources.
appropriate. time and treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Cruz - BSN 3 - Section 2 - Sybil Reaction PaperDocument1 pageCruz - BSN 3 - Section 2 - Sybil Reaction PaperMingoy, CarlosNo ratings yet
- 057608komatsu Hydraulic Oil HO 46-HMDocument5 pages057608komatsu Hydraulic Oil HO 46-HMrolex21No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPAnne De VeraNo ratings yet
- Case Write Up-DengueDocument16 pagesCase Write Up-DengueSyafi'ie Syukri100% (1)
- Free Preview - The Stall Slayer PDFDocument9 pagesFree Preview - The Stall Slayer PDFRohit RumadeNo ratings yet
- CVL Consent PDFDocument5 pagesCVL Consent PDFGolam SarwarNo ratings yet
- Know Your Soil PDFDocument20 pagesKnow Your Soil PDFbpcdivNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations NCP PDFDocument3 pagesHallucinations NCP PDFANGELA ERES BALINGBING100% (2)
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPchiki08No ratings yet
- Nusing CareplanDocument3 pagesNusing Careplanardec_143No ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument32 pagesPsychiatric NursingPinky Cuaresma100% (1)
- Case Report No1Document9 pagesCase Report No1Menn PetchuayNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT REPORT (Confidential Material) : September 2018Document12 pagesPSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT REPORT (Confidential Material) : September 2018manar 9939No ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument4 pagesPsych NCPnoman-053No ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2ampalNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyRizzi DeveraNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia An OverviewDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia An OverviewEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument10 pagesAcute PancreatitisCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanTenth Ann ModanzaNo ratings yet
- NCP TetanusDocument2 pagesNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- NCM117Document20 pagesNCM117Marie Isabelle HerveraNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument3 pagesNCP FinalCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- Drug Study East AveDocument15 pagesDrug Study East AveSean Philippe CabralNo ratings yet
- PATIENT AmeliaDocument3 pagesPATIENT AmeliaPao DelossantosNo ratings yet
- The Magic Pill ReactionDocument2 pagesThe Magic Pill ReactionShannen PondocNo ratings yet
- Qi NCPDocument5 pagesQi NCPJesse Israel TadenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FluoxetineDocument2 pagesDrug Study of FluoxetineLance De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Com/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewDocument2 pagesCom/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewCharles Belonio Dorado100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Personality Disorders: College of Nursing Psychiatric NursingDocument2 pagesCase Study - Personality Disorders: College of Nursing Psychiatric NursingCamille SindayNo ratings yet
- Counselling LetterDocument1 pageCounselling LetterSeann LorescoNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Drug Induced-PsychosisDocument3 pagesNcp-Drug Induced-PsychosisMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryKyla ToledoNo ratings yet
- CLUBFOOTDocument19 pagesCLUBFOOTKaryn Joy LamisNo ratings yet
- NCP Format Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Format Acute PainRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDocument2 pagesConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationLi Luren Raphaelle TanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Document6 pagesNursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Elaine Dionisio TanNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care: Prepare The (Sterile) Hypo Tray-The Inner Side Is Considered SterileDocument5 pagesNewborn Care: Prepare The (Sterile) Hypo Tray-The Inner Side Is Considered Sterileallkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- GRP 3 2 Renal Nephrectomy NCPDocument6 pagesGRP 3 2 Renal Nephrectomy NCPPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- 13 Surgery (Perioperative Client) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument31 pages13 Surgery (Perioperative Client) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsRena SafitriNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument3 pagesOlanzapineLeris Luigi VictorioNo ratings yet
- Quiz Process RecordingDocument7 pagesQuiz Process RecordingDewley Guevarra MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Geria Nursing: Activity 1.1: Grandparents' LoveDocument11 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Geria Nursing: Activity 1.1: Grandparents' LoveMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- A.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionDocument4 pagesA.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionKate Aenyle AgsoyNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristDocument22 pagesNursing TheoristG a i l R i c h w e l lNo ratings yet
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Document2 pagesDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaNo ratings yet
- 7 Midazozalam Drug StudyDocument3 pages7 Midazozalam Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Jenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesJenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated BibliographyEmergencyPlanning101No ratings yet
- NCM 117 Psychiatric Nursing MODULE 3Document13 pagesNCM 117 Psychiatric Nursing MODULE 3Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Potential Nursing Care Plan SchizopremiaDocument1 pagePotential Nursing Care Plan SchizopremiaopxNo ratings yet
- CHN ReflectionDocument1 pageCHN ReflectionKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Context: NCM 116 RleDocument1 pageContext: NCM 116 RleTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis NCPDocument5 pagesAppendicitis NCPEarl Joseph DezaNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument2 pagesNCP RiskNura ZeinNo ratings yet
- NCP Depression1Document1 pageNCP Depression1kyreNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reviseddd (Mia)Document16 pagesReviseddd (Mia)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- MSE Research 1Document11 pagesMSE Research 1kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing - Assessment - (Mse) (Josol)Document5 pagesNursing - Assessment - (Mse) (Josol)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Date Identified: July 13, 2021 Date Evaluated: July 20, 2021 TetengDocument5 pagesDate Identified: July 13, 2021 Date Evaluated: July 20, 2021 Tetengkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Quiz (Perfect)Document3 pagesQuiz (Perfect)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)kuro hanabusa100% (2)
- Program Design (Dance Therapy)Document3 pagesProgram Design (Dance Therapy)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic TherapiesDocument51 pagesPsychoanalysis and Psychodynamic Therapieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reflection On Therapeutic ModalitiesDocument23 pagesJournal Reflection On Therapeutic Modalitieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test (B)Document7 pagesPre-Test (B)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic TherapiesDocument51 pagesPsychoanalysis and Psychodynamic Therapieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reflection On Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesJournal Reflection On Nursing Care Plankuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reflection On Mental Status Examination 1Document9 pagesJournal Reflection On Mental Status Examination 1kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination: Concerns and AddictionDocument2 pagesMental Status Examination: Concerns and Addictionkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument53 pagesDocxkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Francisco Arcellana: 4 Life Lessons That Can Be Derived From The StoryDocument1 pageFrancisco Arcellana: 4 Life Lessons That Can Be Derived From The Storykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature During American RegimeDocument13 pagesPhilippine Literature During American Regimekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank EquipmentsDocument12 pagesBlood Bank EquipmentsJomar100% (1)
- Diet For Patient With Parkinson's DiseaseDocument2 pagesDiet For Patient With Parkinson's DiseaseNuzulina SafiraNo ratings yet
- 3) Z. 10.1016@j.jcrc.2020.06.005 (Alexis Tabah)Document18 pages3) Z. 10.1016@j.jcrc.2020.06.005 (Alexis Tabah)Mastifa HanasitaNo ratings yet
- B. VinothDocument5 pagesB. VinothBilal HassanNo ratings yet
- Development of Push-Pull Osmotic Pump Tablets For A SlightlyDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Push-Pull Osmotic Pump Tablets For A SlightlyphamuyenthuNo ratings yet
- PacemakersDocument69 pagesPacemakersdocjeevan89100% (1)
- Hyperworks Technology Conference (HTC) 2011: Optimization of PMH StructuresDocument25 pagesHyperworks Technology Conference (HTC) 2011: Optimization of PMH StructuresgiakovidNo ratings yet
- Knowledge ManagementDocument63 pagesKnowledge Managementrahul-singh-6592No ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument5 pagesCase StudiesPou PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Applied PsychologyDocument362 pagesApplied Psychologyprajjwal100% (1)
- November 2009 Final EditionDocument45 pagesNovember 2009 Final Editionaajo136No ratings yet
- Medicare Enrollment TipsDocument34 pagesMedicare Enrollment TipsdaringdreuNo ratings yet
- PREGNANCYDocument4 pagesPREGNANCYShaileeNo ratings yet
- Newborn ReflexesDocument41 pagesNewborn ReflexesUmairah Bashir100% (5)
- MSPG Infographic 2Document9 pagesMSPG Infographic 2Norzaherawati Aryani Md TahirNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument11 pagesDental MaterialsShweta RangharNo ratings yet
- Prevention & Management of Sports Injuries: Quimcy Dsouza Fybms-Sm (B) 75Document26 pagesPrevention & Management of Sports Injuries: Quimcy Dsouza Fybms-Sm (B) 75Quimcy100% (1)
- HypothermiaDocument5 pagesHypothermiaMRS CHAKRAPANINo ratings yet
- IS 501 2021-2022 Spring Assignment #4: Part-1: Can The National Health Service Go Paperless?Document3 pagesIS 501 2021-2022 Spring Assignment #4: Part-1: Can The National Health Service Go Paperless?adsfNo ratings yet
- Community Resilience: Integrating Hazard Management and Community EngagementDocument21 pagesCommunity Resilience: Integrating Hazard Management and Community EngagementJavier Gonzales IwanciwNo ratings yet
- HOLANDA ALEX CFE103 Module4 ContextEngageActivitiesDocument4 pagesHOLANDA ALEX CFE103 Module4 ContextEngageActivitiesAsus LaptopNo ratings yet
- Lab Report For ParacetamolDocument5 pagesLab Report For Paracetamol9gcfz8zf9xNo ratings yet
- Section 8 The CTA Written Examination PDFDocument10 pagesSection 8 The CTA Written Examination PDFBojana VulasNo ratings yet
- Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesCrossword PuzzleJohn Patric Plaida100% (1)
- Activity #1: ETHICAL CASE Name: Date: Year/Section: Grade/scoreDocument4 pagesActivity #1: ETHICAL CASE Name: Date: Year/Section: Grade/scoreJovie FabrosNo ratings yet
Nursing Care Plan 1
Nursing Care Plan 1
Uploaded by
kuro hanabusa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views5 pages Provide Provide reassurance and Provide information about Provide support and Provide a caring, non-
reassurance and support. support. Explain that treatment and recovery encouragement to seek judgmental environment.
Address anxiety and anxiety and withdrawal programs. Refer to further help. Collaborate Address physical and
withdrawal symptoms. symptoms are normal appropriate resources as with other providers as emotional needs. Refer to
Refer to treatment as and will subside with needed. needed. appropriate resources.
appropriate. time and treatment.
Original Description:
Original Title
Ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Provide Provide reassurance and Provide information about Provide support and Provide a caring, non-
reassurance and support. support. Explain that treatment and recovery encouragement to seek judgmental environment.
Address anxiety and anxiety and withdrawal programs. Refer to further help. Collaborate Address physical and
withdrawal symptoms. symptoms are normal appropriate resources as with other providers as emotional needs. Refer to
Refer to treatment as and will subside with needed. needed. appropriate resources.
appropriate. time and treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views5 pagesNursing Care Plan 1
Nursing Care Plan 1
Uploaded by
kuro hanabusa Provide Provide reassurance and Provide information about Provide support and Provide a caring, non-
reassurance and support. support. Explain that treatment and recovery encouragement to seek judgmental environment.
Address anxiety and anxiety and withdrawal programs. Refer to further help. Collaborate Address physical and
withdrawal symptoms. symptoms are normal appropriate resources as with other providers as emotional needs. Refer to
Refer to treatment as and will subside with needed. needed. appropriate resources.
appropriate. time and treatment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
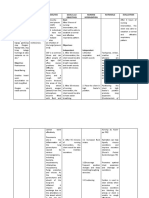
NURSING CARE PLAN 1
Date identified: July 16, 2021
Date evaluated: July 18, 2021
CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective cue: Anxiety related to Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term Goal:
cessation of alcohol
Objective cues: intake, physiological Within 4 hours of Identify cause of anxiety, Persons in acute phase of Goal met. Within 4 hours of
withdrawal as evidenced nursing interventions, involving client in the withdrawal may be nursing interventions,
-fear by increased the patient will be able process. Explain that unable to identify and/or patient was able to
helplessness, fear, to verbalize reduction of alcohol withdrawal accept what is demonstrate participation
-helplessness tension, hopelessness fear and anxiety to an increases anxiety and happening. Anxiety may in interaction with the
with loss of control of acceptable and uneasiness. Reassess be physiologically or student nurse in a calmer
-tension own life. manageable level. level of anxiety on an environmentally caused. manner and was able to
ongoing basis. verbalize acceptance of
- nausea and vomiting Long Term Goal: need for treatment and
Develop a trusting Provides client with a awareness that willpower
-loss of appetite Within 3 days of nursing relationship through sense of humanness, alone cannot control
interventions, the frequent contact and helping to decrease abstinence.
-insomnia patient will be able to being honest and paranoia and distrust.
regain and maintain nonjudgmental. Project Client will be able to Long Term Goal:
healthy state with a drug an accepting attitude detect biased or
and alcohol-free lifestyle. about alcoholism. condescending attitude Goal met. Within 3 days of
of caregivers. nursing interventions,
patient was able to engage
Inform client about what Enhances sense of trust, in peer support and
you plan to do and why. and explanation may demonstrate active
Include client in planning increase cooperation and participation in program.
process and provide reduce anxiety. Provides “With the support I have
choices when possible sense of control over self now I feel like I’m regaining
in circumstance where my healthy living. Though
loss of control is a I’m still working on to be a
significant factor. drug and alcohol-free
person,” as verbalized by
Assist patient to In the precontemplation the patient…………………….....
recognize problem exists. phase, the patient has K.P.Josol,FSUU/SN(7/16/21)
Discuss in a caring, non- not yet identified that
judgmental manner how drug use is problematic.
drug has interfered with While patient is hurting,
life; it is easier to admit
substance use has
created negative
consequences.
Encourage verbalization May help patient begin
of feelings, fears, and to come to terms with
anxiety. long-unresolved issues.
Reorient frequently Client may experience
periods of confusion,
resulting in increased
anxiety
Guide and assist patient Although not mandatory
in self-examination of for recovery,
spirituality, faith. surrendering to and faith
in a power greater than
oneself has been found
to be effective for many
individuals in substance
recovery; may decrease
sense of powerlessness.
This also helps client to
meditate and achieve
Dependent: better sleep.
Administer medications, Anti-anxiety agents are
as indicated, for given during acute
example: withdrawal to help client
Benzodiazepines, such as relax, be less
chlordiazepoxide hyperactive, and feel
(Librium), and diazepam more in control.
(Valium).
Administer Barbiturates, These drugs are
such as phenobarbital, or sometimes used to treat
possibly secobarbital or prevent alcohol
(Seconal) or withdrawal seizures, but
pentobarbital need to be used with
(Nembutal) caution because they are
respiratory depressants.
Collaborative:
Provide consultation or Client is more likely to
referral to detoxification contract for treatment
or crisis center for while still hurting and
ongoing treatment experiencing fear and
program as soon as anxiety from last drinking
medically stable episode. Motivation
decreases as well-being
increases and person
again feels able to
control the problem.
Explore support in peer Patient may need
group. Encourage sharing assistance in expressing
about drug hunger, self, speaking about
situations that increase powerlessness, admitting
the desire to indulge, need for help in order to
ways that substance has face up to problem and
influenced life. begin resolution.
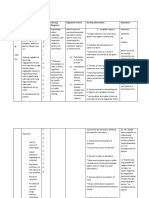
NURSING CARE PLAN 2
Date identified: July 16, 2021
Date evaluated: July 18, 2021
CUES NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective cue: Ineffective individual Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term Goal:
coping related to
Objective cues: personal vulnerability as Within 2 hours of nursing Complete an initial client This information can Goal not met. After 2 hours
evidenced by decreased interventions, the patient assessment; ask what help you anticipate the of nursing interventions,
- Impaired nutrition ability to handle will be able to identify and how much the client onset and severity of patient was still believing
pressure/stress ineffective coping usually drinks, as well as withdrawal symptoms. that only in alcohol and
- Physical exhaustion behaviors/consequences, the time and amount of The client’s memory may drugs she can feel
including use of alcohol the last drink of alcohol. be impaired or he or she contented. “Alcohol and
- Sleep disturbances and substances as a may not reveal the drugs are my only saviors
method of coping. actual extent of alcohol when I’m pressured,” as
- Dependence on intake. verbalized by the patient.
alcohol/drugs Long Term Goal:
Long Term Goal:
Within 3 days of nursing Provide food or Many clients who use
interventions, the patient nourishing fluids as soon alcohol heavily Goal partially met. After 3
will be able to establish a as the client can tolerate experience gastritis or days of nursing
balance of rest, sleep, eating; have something anorexia. It is important interventions, patient was
and activity available at night. (Bland to reestablish nutritional able to verbalize having
food usually is tolerated intake as soon as the enough sleep but still
more easily at first.) client tolerates food. experiencing the urge to go
back to the dependency of
Determine Provides information alcohol and drugs. “I’m still
understanding of current about degree of denial, working on it,” as
situation, previous, and acceptance of personal verbalized by the
other methods of coping responsibility and patient………………………………
with life’s problems. commitment to change; K.P.Josol,FSUU/SN(7/16/21)
identifies coping skills
that may be used in
present situation.
Encourage verbalization May help patient begin
of feelings, fears, and to come to terms with
anxiety. long-unresolved issues.
Assist patient to learn Helps patient relax,
and encourage use of develop new ways to
relaxation skills, guided deal with stress,
imagery, visualizations. problem-solve.
Encourage involvement Therapeutic writing or
in therapeutic writing. journaling can enhance
Have patient begin participation in
journaling or writing treatment; serves as a
autobiography. release for grief, anger,
and stress; provides a
useful tool for
monitoring patient’s
safety; and can be used
to evaluate patient’s
progress.
Autobiographical activity
provides an opportunity
for patient to remember
and identify sequence of
events in his or her life
that relate to current
situation.
Maintain a quiet, safe Helps patient to have a
environment during relaxing rest and sleep.
withdrawal from any Excessive noise may
drug. agitate the patient.
Dependent:
Administer medications Used to suppress craving
as indicated: such as for opioids and may help
Naltrexone (Trexan), prevent relapse in the
nalmefene (Revex). patient abusing alcohol.
Current research
suggests that naltrexone
suppresses urge to
continue drinking by
interfering with alcohol-
induced release of
Collaborative: endorphins.
Structure diversional Discovery of alternative
activity that relates to methods of coping with
recovery (social activity drug hunger can remind
within support group), patient that addiction is
wherein issues of being a lifelong process and
chemically free are opportunity for changing
examined. patterns is available.
Use peer support to Self-help groups are
examine ways of coping valuable for learning and
with drug hunger. promoting abstinence in
each member, using
understanding and
support as well as peer
pressure.
You might also like
- Cruz - BSN 3 - Section 2 - Sybil Reaction PaperDocument1 pageCruz - BSN 3 - Section 2 - Sybil Reaction PaperMingoy, CarlosNo ratings yet
- 057608komatsu Hydraulic Oil HO 46-HMDocument5 pages057608komatsu Hydraulic Oil HO 46-HMrolex21No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPAnne De VeraNo ratings yet
- Case Write Up-DengueDocument16 pagesCase Write Up-DengueSyafi'ie Syukri100% (1)
- Free Preview - The Stall Slayer PDFDocument9 pagesFree Preview - The Stall Slayer PDFRohit RumadeNo ratings yet
- CVL Consent PDFDocument5 pagesCVL Consent PDFGolam SarwarNo ratings yet
- Know Your Soil PDFDocument20 pagesKnow Your Soil PDFbpcdivNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations NCP PDFDocument3 pagesHallucinations NCP PDFANGELA ERES BALINGBING100% (2)
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPchiki08No ratings yet
- Nusing CareplanDocument3 pagesNusing Careplanardec_143No ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument32 pagesPsychiatric NursingPinky Cuaresma100% (1)
- Case Report No1Document9 pagesCase Report No1Menn PetchuayNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT REPORT (Confidential Material) : September 2018Document12 pagesPSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT REPORT (Confidential Material) : September 2018manar 9939No ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument4 pagesPsych NCPnoman-053No ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2ampalNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyRizzi DeveraNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia An OverviewDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia An OverviewEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nikolai P. Funcion, FSUU-SNNikolai FuncionNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument10 pagesAcute PancreatitisCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanTenth Ann ModanzaNo ratings yet
- NCP TetanusDocument2 pagesNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis GOALS and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GoalMonica Angelique SalayoNo ratings yet
- NCM117Document20 pagesNCM117Marie Isabelle HerveraNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument3 pagesNCP FinalCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- Drug Study East AveDocument15 pagesDrug Study East AveSean Philippe CabralNo ratings yet
- PATIENT AmeliaDocument3 pagesPATIENT AmeliaPao DelossantosNo ratings yet
- The Magic Pill ReactionDocument2 pagesThe Magic Pill ReactionShannen PondocNo ratings yet
- Qi NCPDocument5 pagesQi NCPJesse Israel TadenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FluoxetineDocument2 pagesDrug Study of FluoxetineLance De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Com/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewDocument2 pagesCom/4-Cholecystitis - Cholelithiasis - Nursing-Care - Plans/2/ 6-OverviewCharles Belonio Dorado100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Personality Disorders: College of Nursing Psychiatric NursingDocument2 pagesCase Study - Personality Disorders: College of Nursing Psychiatric NursingCamille SindayNo ratings yet
- Counselling LetterDocument1 pageCounselling LetterSeann LorescoNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Drug Induced-PsychosisDocument3 pagesNcp-Drug Induced-PsychosisMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With Musculoskeletal InjuryKyla ToledoNo ratings yet
- CLUBFOOTDocument19 pagesCLUBFOOTKaryn Joy LamisNo ratings yet
- NCP Format Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Format Acute PainRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDocument2 pagesConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationLi Luren Raphaelle TanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Document6 pagesNursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Elaine Dionisio TanNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care: Prepare The (Sterile) Hypo Tray-The Inner Side Is Considered SterileDocument5 pagesNewborn Care: Prepare The (Sterile) Hypo Tray-The Inner Side Is Considered Sterileallkhusairy6tuansiNo ratings yet
- GRP 3 2 Renal Nephrectomy NCPDocument6 pagesGRP 3 2 Renal Nephrectomy NCPPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- 13 Surgery (Perioperative Client) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument31 pages13 Surgery (Perioperative Client) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsRena SafitriNo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument3 pagesOlanzapineLeris Luigi VictorioNo ratings yet
- Quiz Process RecordingDocument7 pagesQuiz Process RecordingDewley Guevarra MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Introduction To Geria Nursing: Activity 1.1: Grandparents' LoveDocument11 pagesTopic 1: Introduction To Geria Nursing: Activity 1.1: Grandparents' LoveMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- A.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionDocument4 pagesA.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionKate Aenyle AgsoyNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristDocument22 pagesNursing TheoristG a i l R i c h w e l lNo ratings yet
- Dela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Document2 pagesDela Rosa 2A MCN-Module 05Atsu MiyaNo ratings yet
- 7 Midazozalam Drug StudyDocument3 pages7 Midazozalam Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Jenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesJenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated BibliographyEmergencyPlanning101No ratings yet
- NCM 117 Psychiatric Nursing MODULE 3Document13 pagesNCM 117 Psychiatric Nursing MODULE 3Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Potential Nursing Care Plan SchizopremiaDocument1 pagePotential Nursing Care Plan SchizopremiaopxNo ratings yet
- CHN ReflectionDocument1 pageCHN ReflectionKen SimonNo ratings yet
- Context: NCM 116 RleDocument1 pageContext: NCM 116 RleTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis NCPDocument5 pagesAppendicitis NCPEarl Joseph DezaNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument2 pagesNCP RiskNura ZeinNo ratings yet
- NCP Depression1Document1 pageNCP Depression1kyreNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Reviseddd (Mia)Document16 pagesReviseddd (Mia)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- MSE Research 1Document11 pagesMSE Research 1kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing - Assessment - (Mse) (Josol)Document5 pagesNursing - Assessment - (Mse) (Josol)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Date Identified: July 13, 2021 Date Evaluated: July 20, 2021 TetengDocument5 pagesDate Identified: July 13, 2021 Date Evaluated: July 20, 2021 Tetengkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Quiz (Perfect)Document3 pagesQuiz (Perfect)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Loxapine, Haloperidol)kuro hanabusa100% (2)
- Program Design (Dance Therapy)Document3 pagesProgram Design (Dance Therapy)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic TherapiesDocument51 pagesPsychoanalysis and Psychodynamic Therapieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reflection On Therapeutic ModalitiesDocument23 pagesJournal Reflection On Therapeutic Modalitieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test (B)Document7 pagesPre-Test (B)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalysis and Psychodynamic TherapiesDocument51 pagesPsychoanalysis and Psychodynamic Therapieskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reflection On Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesJournal Reflection On Nursing Care Plankuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Journal Reflection On Mental Status Examination 1Document9 pagesJournal Reflection On Mental Status Examination 1kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination: Concerns and AddictionDocument2 pagesMental Status Examination: Concerns and Addictionkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument53 pagesDocxkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Francisco Arcellana: 4 Life Lessons That Can Be Derived From The StoryDocument1 pageFrancisco Arcellana: 4 Life Lessons That Can Be Derived From The Storykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Literature During American RegimeDocument13 pagesPhilippine Literature During American Regimekuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank EquipmentsDocument12 pagesBlood Bank EquipmentsJomar100% (1)
- Diet For Patient With Parkinson's DiseaseDocument2 pagesDiet For Patient With Parkinson's DiseaseNuzulina SafiraNo ratings yet
- 3) Z. 10.1016@j.jcrc.2020.06.005 (Alexis Tabah)Document18 pages3) Z. 10.1016@j.jcrc.2020.06.005 (Alexis Tabah)Mastifa HanasitaNo ratings yet
- B. VinothDocument5 pagesB. VinothBilal HassanNo ratings yet
- Development of Push-Pull Osmotic Pump Tablets For A SlightlyDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Push-Pull Osmotic Pump Tablets For A SlightlyphamuyenthuNo ratings yet
- PacemakersDocument69 pagesPacemakersdocjeevan89100% (1)
- Hyperworks Technology Conference (HTC) 2011: Optimization of PMH StructuresDocument25 pagesHyperworks Technology Conference (HTC) 2011: Optimization of PMH StructuresgiakovidNo ratings yet
- Knowledge ManagementDocument63 pagesKnowledge Managementrahul-singh-6592No ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument5 pagesCase StudiesPou PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Applied PsychologyDocument362 pagesApplied Psychologyprajjwal100% (1)
- November 2009 Final EditionDocument45 pagesNovember 2009 Final Editionaajo136No ratings yet
- Medicare Enrollment TipsDocument34 pagesMedicare Enrollment TipsdaringdreuNo ratings yet
- PREGNANCYDocument4 pagesPREGNANCYShaileeNo ratings yet
- Newborn ReflexesDocument41 pagesNewborn ReflexesUmairah Bashir100% (5)
- MSPG Infographic 2Document9 pagesMSPG Infographic 2Norzaherawati Aryani Md TahirNo ratings yet
- Dental MaterialsDocument11 pagesDental MaterialsShweta RangharNo ratings yet
- Prevention & Management of Sports Injuries: Quimcy Dsouza Fybms-Sm (B) 75Document26 pagesPrevention & Management of Sports Injuries: Quimcy Dsouza Fybms-Sm (B) 75Quimcy100% (1)
- HypothermiaDocument5 pagesHypothermiaMRS CHAKRAPANINo ratings yet
- IS 501 2021-2022 Spring Assignment #4: Part-1: Can The National Health Service Go Paperless?Document3 pagesIS 501 2021-2022 Spring Assignment #4: Part-1: Can The National Health Service Go Paperless?adsfNo ratings yet
- Community Resilience: Integrating Hazard Management and Community EngagementDocument21 pagesCommunity Resilience: Integrating Hazard Management and Community EngagementJavier Gonzales IwanciwNo ratings yet
- HOLANDA ALEX CFE103 Module4 ContextEngageActivitiesDocument4 pagesHOLANDA ALEX CFE103 Module4 ContextEngageActivitiesAsus LaptopNo ratings yet
- Lab Report For ParacetamolDocument5 pagesLab Report For Paracetamol9gcfz8zf9xNo ratings yet
- Section 8 The CTA Written Examination PDFDocument10 pagesSection 8 The CTA Written Examination PDFBojana VulasNo ratings yet
- Crossword PuzzleDocument2 pagesCrossword PuzzleJohn Patric Plaida100% (1)
- Activity #1: ETHICAL CASE Name: Date: Year/Section: Grade/scoreDocument4 pagesActivity #1: ETHICAL CASE Name: Date: Year/Section: Grade/scoreJovie FabrosNo ratings yet