Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resources To Support Online Learning 2021 April (Grade 12) Chapter-2: Electrostatc Potential & Capacitance
Resources To Support Online Learning 2021 April (Grade 12) Chapter-2: Electrostatc Potential & Capacitance
Uploaded by
Athiya ZainabCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chem Investegatory ProjectDocument18 pagesChem Investegatory ProjectAthiya Zainab94% (17)
- Mobile Phone Signal JammerDocument97 pagesMobile Phone Signal JammerAmol Bengiri100% (1)
- Electromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Document18 pagesElectromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Minh Trương PhúcNo ratings yet
- Practice Assignment-3 Electrostatic Potential: Corporate Office: A-1/169, Main Najafgarh Road, JanakpuriDocument7 pagesPractice Assignment-3 Electrostatic Potential: Corporate Office: A-1/169, Main Najafgarh Road, JanakpuriAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CbseDocument9 pagesChapter 1 CbseAbhinav YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PP Xii PhysicsDocument4 pagesChapter 01 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77No ratings yet
- Electrostatics - ALP3Document7 pagesElectrostatics - ALP3Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- REVISION WORKSHEET MID TERM Answer KerDocument11 pagesREVISION WORKSHEET MID TERM Answer Kermansi8861040066No ratings yet
- Subjective Paper 2023Document2 pagesSubjective Paper 2023hridhaananand896No ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS-Rev Pract-2Document2 pagesELECTROSTATICS-Rev Pract-2bys628h8skNo ratings yet
- Physics Rmning HHWDocument14 pagesPhysics Rmning HHWnipundayalan12345No ratings yet
- ExamDocument6 pagesExamsdasNo ratings yet
- 01-Electrostatics PyqDocument10 pages01-Electrostatics PyqgudiNo ratings yet
- ELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Document4 pagesELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- Classical ElectromanDocument1 pageClassical Electromanayush kumarNo ratings yet
- Electricity & MagnetismDocument39 pagesElectricity & MagnetismAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Assignment: Gravity ClassesDocument6 pagesElectrostatics Assignment: Gravity Classesjagan9912342495No ratings yet
- Tutorial ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageTutorial ElectrostaticsRavi NasitNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Electrostatics: One Mark QuestionsDocument20 pagesUnit - 1 Electrostatics: One Mark QuestionsNIKSHAYNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument92 pagesClass 12 Physicsniyatigupta5623No ratings yet
- Xii Phy Holidayhomework 2Document13 pagesXii Phy Holidayhomework 2Amar Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISEDocument32 pagesCLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISERohan SNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document21 pagesCH 2terasaini77No ratings yet
- Questions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayDocument4 pagesQuestions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayFirdous ANo ratings yet
- Assnment GausslawDocument2 pagesAssnment GausslawforillegaluNo ratings yet
- Physics - XII (Holiday Home Work)Document10 pagesPhysics - XII (Holiday Home Work)VIVAAS .SNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Chapter Wise Question BankDocument87 pagesPhysics XII Chapter Wise Question BankAdiba khanNo ratings yet
- WorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & FieldDocument3 pagesWorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & Fieldgkgthe1No ratings yet
- PHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Document11 pagesPHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Agag HsgsNo ratings yet
- Potential AssignmentDocument2 pagesPotential AssignmentdhananjayajainNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy CH1&2Document3 pagesXii Phy CH1&2DEVIKAA ARUNNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapascitanceDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapascitancemapuclouddigitalworldNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: (Physics)Document6 pagesElectrostatics: (Physics)Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- MCQ - 1Document3 pagesMCQ - 1Harish KarthikNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS HARD Question Paper With SolutionDocument30 pagesELECTROSTATICS HARD Question Paper With SolutionArvita KaurNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Unit 3 Objective QuestionDocument12 pagesApplied Physics Unit 3 Objective QuestionNitin YogeshNo ratings yet
- Xii Assign - Unit 1Document5 pagesXii Assign - Unit 1devendrak189No ratings yet
- (IITExp1) - (JLD 3.0) - Electrostatics - 14th August.Document43 pages(IITExp1) - (JLD 3.0) - Electrostatics - 14th August.Debi prasad jenaNo ratings yet
- Phy ppr 2024-2025Document4 pagesPhy ppr 2024-2025astrophysicistharshit2007No ratings yet
- Gauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46Document7 pagesGauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46parasbhardwaj52159No ratings yet
- Xii Physics - Chapter 2term 1Document17 pagesXii Physics - Chapter 2term 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics AssignmentDocument6 pagesElectrostatics AssignmentsamahadadilkhanNo ratings yet
- CAPACITANCE With Checkpoint 1-18Document40 pagesCAPACITANCE With Checkpoint 1-18chirayuaggarwal2006No ratings yet
- Wa0024.Document6 pagesWa0024.bt21 rjsjmvkNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Phaseiv El 3 Lecture-3 Final PDFDocument8 pagesSankalp Phaseiv El 3 Lecture-3 Final PDFArnav SNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 SAQsDocument38 pagesChapter-01 SAQsHrgamersNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetism Spring 2007 PROBLEM SET 7 SolutionsDocument7 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetism Spring 2007 PROBLEM SET 7 SolutionsByron AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument54 pagesProblem SetXyNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics WDocument25 pagesXii Physics WFree Fire KingNo ratings yet
- 110-Electric Charges & FieldsDocument11 pages110-Electric Charges & FieldsHanzalaNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asngmt CH - 01Document5 pagesAissce Asngmt CH - 016pqq745bq2No ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1and 2Document8 pagesElectrostatics 1and 2maheruakhanNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: Physics I-Mid Term Examination - 2021 Max Marks: 35 Class: Xii DURATION: 90minDocument3 pagesSUBJECT: Physics I-Mid Term Examination - 2021 Max Marks: 35 Class: Xii DURATION: 90minmano17 ShinNo ratings yet
- Ha3 Phy113 103 180423Document2 pagesHa3 Phy113 103 180423TigerNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - JEE Main 2020-22 PYQDocument255 pagesElectrostatics - JEE Main 2020-22 PYQfsqf41No ratings yet
- Sheet - 01-Pages-27-72Document46 pagesSheet - 01-Pages-27-72Hemant KumarNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION Cyclic I Class XII PhysicsDocument8 pagesSOLUTION Cyclic I Class XII PhysicsRizwana RNo ratings yet
- Em Bank10 16 0Document20 pagesEm Bank10 16 0ArUn KuMarNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Assignment..2024-25 NewDocument27 pagesXii Physics Assignment..2024-25 Newabcx87380No ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument10 pagesElectric Chargesradhasumanpradhan9593No ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential 1Document2 pagesElectrostatic Potential 1Athiya ZainabNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerDocument24 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerAthiya Zainab100% (1)
- Cell Therapy For HIV: Investigatory Project byDocument18 pagesCell Therapy For HIV: Investigatory Project byAthiya ZainabNo ratings yet
- ANT-AMB452000-1502 DatasheetDocument2 pagesANT-AMB452000-1502 Datasheetpenglean heanNo ratings yet
- 150 sg009 - en PDocument54 pages150 sg009 - en PDaniel Andres Silva AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Integrated CircuitDocument7 pagesComparison and Simulation of Integrated Circuitapi-744376938No ratings yet
- Fujitsu General Manual de ServicioDocument31 pagesFujitsu General Manual de ServicioTomás ArrebolaNo ratings yet
- Maglev Trains - How Maglev Trains Work - by Alex Landovskis & Veronique RondeaDocument3 pagesMaglev Trains - How Maglev Trains Work - by Alex Landovskis & Veronique RondeaarnavraizadakhushiNo ratings yet
- Rexroth HCS01Document5 pagesRexroth HCS01TFNo ratings yet
- Power Purchase During FY 2018-19Document75 pagesPower Purchase During FY 2018-19Piya MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Eaton 269471 Emt6 KDB en GBDocument4 pagesEaton 269471 Emt6 KDB en GBAriel TorresNo ratings yet
- 7sj63 Catalog Sip E7Document39 pages7sj63 Catalog Sip E7alexns84No ratings yet
- Beee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017Document4 pagesBeee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017upender raoNo ratings yet
- 2CNM203002R2001 m2m BasicDocument3 pages2CNM203002R2001 m2m BasicHuy Hồ PhướcNo ratings yet
- EE2402 PROTECTION AND SWITCHGEAR Syllabus Regulation 2008Document1 pageEE2402 PROTECTION AND SWITCHGEAR Syllabus Regulation 2008Muruga Raj0% (1)
- I Eee FlickerDocument8 pagesI Eee FlickerErmin FazlicNo ratings yet
- FP We3a2 A YadavDocument6 pagesFP We3a2 A Yadavİbrahim KozatNo ratings yet
- Wireless Digital Stethoscope Using Bluetooth TechnDocument10 pagesWireless Digital Stethoscope Using Bluetooth TechnHitesh DammuNo ratings yet
- Pico - SERIES SA - 2024-01-04Document8 pagesPico - SERIES SA - 2024-01-04Giap LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 FSK DemodDocument25 pagesChapter 14 FSK DemodberkahNo ratings yet
- The TL431 in The Control of Switching Power SuppliesDocument63 pagesThe TL431 in The Control of Switching Power Suppliesrangerford0% (1)
- ESU-400 ENG-SPA Rev00Document2 pagesESU-400 ENG-SPA Rev00grupomedibuyNo ratings yet
- Mje 13003Document3 pagesMje 13003Hatem AissaouiNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Rectification With Flyback and Forward ConvertersDocument26 pagesSynchronous Rectification With Flyback and Forward ConverterszwolfNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Cascode Distributed LNA With Gain and Noise Improvement in 0.15-m GaAs pHEMT TechnologyDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Cascode Distributed LNA With Gain and Noise Improvement in 0.15-m GaAs pHEMT Technologyسري صالحNo ratings yet
- Developments in Electric Power Supply Configurations For Electrical-Discharge-Machining (EDM)Document6 pagesDevelopments in Electric Power Supply Configurations For Electrical-Discharge-Machining (EDM)فایلجو پروژه و مقالهNo ratings yet
- Automático Schneider Ic60 - A9F44340Document2 pagesAutomático Schneider Ic60 - A9F44340jorgeNo ratings yet
- Group-16 - CSTH in SeriesDocument53 pagesGroup-16 - CSTH in SeriesRuchita LaswanteNo ratings yet
- How Magnetic Induction Lamps WorkDocument4 pagesHow Magnetic Induction Lamps WorkMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Transistor ApproximationsDocument5 pagesTransistor ApproximationsGlenn D. KleinNo ratings yet
- Class AB Push-Pull Vacuum Tube Guitar Amplifier Analysis, Design, and ConstructionDocument14 pagesClass AB Push-Pull Vacuum Tube Guitar Amplifier Analysis, Design, and ConstructiontekellamerZ aka tekellamer100% (2)
- 48V DC - DC Converter - Mild Hybrid DC - DC Converter - EatonDocument3 pages48V DC - DC Converter - Mild Hybrid DC - DC Converter - EatonShubham KaklijNo ratings yet
Resources To Support Online Learning 2021 April (Grade 12) Chapter-2: Electrostatc Potential & Capacitance
Resources To Support Online Learning 2021 April (Grade 12) Chapter-2: Electrostatc Potential & Capacitance
Uploaded by
Athiya ZainabOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resources To Support Online Learning 2021 April (Grade 12) Chapter-2: Electrostatc Potential & Capacitance
Resources To Support Online Learning 2021 April (Grade 12) Chapter-2: Electrostatc Potential & Capacitance
Uploaded by
Athiya ZainabCopyright:
Available Formats
RESOURCES TO SUPPORT ONLINE LEARNING 2021 APRIL (GRADE 12)
CHAPTER–2: ELECTROSTATC POTENTIAL & CAPACITANCE
LESSON 2
Relation between E and V, Electric potential due to a sphere
1. Obtain a relation between E and V in (a) integral form (b) differential form.
2. Write expressions for electric potential due to a sphere at a point outside on the
surface and at a point inside the sphere.
3. Draw a graph to show the variation of V with r for a charged conducting sphere
and explain why the potential is constant inside the sphere and is same as that on
the surface.
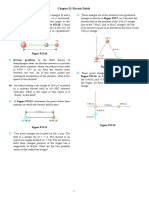
4. Two spherical conductors of A and B radii R 1 and R2 (R2 > R1) are charged. If they
are connected by a conducting wire, find out the ratio of the (a) Electric potential of
A to B (b) surface charge density of A to B and (c) Electric field intensity of A to B
𝑉𝐴 𝜎𝐴 𝐸𝐴 𝑅2
(Ans: = 1, = = )
𝑉𝐵 𝜎𝐵 𝐸𝐵 𝑅1
5. A small conducting sphere of radius r is carrying a charge +q is surrounded by
large conducting shell of radius R on which a charge +Q is given. Show that if you
connect the smaller sphere and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the
former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
𝐾𝑄 𝑘𝑞 𝐾𝑄 𝑘𝑞
(Ans: 𝑉(𝑟) = + & 𝑉𝑅) = + , 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑟 < 𝑅, the
𝑅 𝑟 𝑅 𝑅
outer sphere is always at a higher potential compared
to the inner sphere and hence charge flows from inner
to outer sphere.)
6. Three concentric metallic spheres A, B and C have radii
a,b and c(a<b<c) and surface charge densities on them are
σ,−σ, and σ respectively. Calculate the values of V at the
surfaces of each sphere. If the potential on the surface of
inner sphere is equal to that on the surface of the outer
sphere, find a relation between a, b and c.
𝜎 𝜎 𝑎2 𝜎 𝑎2 𝑏2
( Ans: 𝑉𝑎 = [𝑎 − 𝑏 + 𝑐], 𝑉𝑏 = [ − 𝑏 + 𝑐], 𝑉𝑐 = [ − + 𝑐] & a +b = c]
𝜀 𝜀 𝑏 𝜀 𝑐 𝑐
7. A hollow metal sphere of radius 5 cm is charged such that the potential on its
surface is 10 V. What is the potential at the centre of the sphere? What will be the
potential at a point (a) 15cm (b) 3cm from the center of the sphere?
10
(Ans: 10V, 𝑉, 10V.)
3
8. Eight identical spherical drops, each carrying a charge 1 nC are at a potential of
900 V each. All these drops combine together to form a single large drop. Calculate
the potential of this large drop. (Assume no wastage of any kind).
(Ans: 3600V)
1|page1
You might also like
- Chem Investegatory ProjectDocument18 pagesChem Investegatory ProjectAthiya Zainab94% (17)
- Mobile Phone Signal JammerDocument97 pagesMobile Phone Signal JammerAmol Bengiri100% (1)
- Electromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Document18 pagesElectromagnetism Practice Problems 1 4Minh Trương PhúcNo ratings yet
- Practice Assignment-3 Electrostatic Potential: Corporate Office: A-1/169, Main Najafgarh Road, JanakpuriDocument7 pagesPractice Assignment-3 Electrostatic Potential: Corporate Office: A-1/169, Main Najafgarh Road, JanakpuriAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CbseDocument9 pagesChapter 1 CbseAbhinav YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PP Xii PhysicsDocument4 pagesChapter 01 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77No ratings yet
- Electrostatics - ALP3Document7 pagesElectrostatics - ALP3Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- REVISION WORKSHEET MID TERM Answer KerDocument11 pagesREVISION WORKSHEET MID TERM Answer Kermansi8861040066No ratings yet
- Subjective Paper 2023Document2 pagesSubjective Paper 2023hridhaananand896No ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS-Rev Pract-2Document2 pagesELECTROSTATICS-Rev Pract-2bys628h8skNo ratings yet
- Physics Rmning HHWDocument14 pagesPhysics Rmning HHWnipundayalan12345No ratings yet
- ExamDocument6 pagesExamsdasNo ratings yet
- 01-Electrostatics PyqDocument10 pages01-Electrostatics PyqgudiNo ratings yet
- ELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Document4 pagesELETROSTATICS - Advanced Level Problems (ALP) - 2Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- Classical ElectromanDocument1 pageClassical Electromanayush kumarNo ratings yet
- Electricity & MagnetismDocument39 pagesElectricity & MagnetismAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Assignment: Gravity ClassesDocument6 pagesElectrostatics Assignment: Gravity Classesjagan9912342495No ratings yet
- Tutorial ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageTutorial ElectrostaticsRavi NasitNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Electrostatics: One Mark QuestionsDocument20 pagesUnit - 1 Electrostatics: One Mark QuestionsNIKSHAYNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument92 pagesClass 12 Physicsniyatigupta5623No ratings yet
- Xii Phy Holidayhomework 2Document13 pagesXii Phy Holidayhomework 2Amar Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISEDocument32 pagesCLASS XII - CH - 2 - ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAlAND CAPACITANCE (COMPETENCY - BASED TEST ITEMS) MARKS WISERohan SNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document21 pagesCH 2terasaini77No ratings yet
- Questions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayDocument4 pagesQuestions: D or 2d As Drawn, and A Central Point Is Shown MidwayFirdous ANo ratings yet
- Assnment GausslawDocument2 pagesAssnment GausslawforillegaluNo ratings yet
- Physics - XII (Holiday Home Work)Document10 pagesPhysics - XII (Holiday Home Work)VIVAAS .SNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Chapter Wise Question BankDocument87 pagesPhysics XII Chapter Wise Question BankAdiba khanNo ratings yet
- WorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & FieldDocument3 pagesWorkSheet 1 - Chapter1 - Elecrtic Charge & Fieldgkgthe1No ratings yet
- PHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Document11 pagesPHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Agag HsgsNo ratings yet
- Potential AssignmentDocument2 pagesPotential AssignmentdhananjayajainNo ratings yet
- Xii Phy CH1&2Document3 pagesXii Phy CH1&2DEVIKAA ARUNNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapascitanceDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapascitancemapuclouddigitalworldNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: (Physics)Document6 pagesElectrostatics: (Physics)Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- MCQ - 1Document3 pagesMCQ - 1Harish KarthikNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS HARD Question Paper With SolutionDocument30 pagesELECTROSTATICS HARD Question Paper With SolutionArvita KaurNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Unit 3 Objective QuestionDocument12 pagesApplied Physics Unit 3 Objective QuestionNitin YogeshNo ratings yet
- Xii Assign - Unit 1Document5 pagesXii Assign - Unit 1devendrak189No ratings yet
- (IITExp1) - (JLD 3.0) - Electrostatics - 14th August.Document43 pages(IITExp1) - (JLD 3.0) - Electrostatics - 14th August.Debi prasad jenaNo ratings yet
- Phy ppr 2024-2025Document4 pagesPhy ppr 2024-2025astrophysicistharshit2007No ratings yet
- Gauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46Document7 pagesGauss Theorem - WORKSHEET - 17869718 - 2024 - 03 - 03 - 15 - 46parasbhardwaj52159No ratings yet
- Xii Physics - Chapter 2term 1Document17 pagesXii Physics - Chapter 2term 1RahulNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics AssignmentDocument6 pagesElectrostatics AssignmentsamahadadilkhanNo ratings yet
- CAPACITANCE With Checkpoint 1-18Document40 pagesCAPACITANCE With Checkpoint 1-18chirayuaggarwal2006No ratings yet
- Wa0024.Document6 pagesWa0024.bt21 rjsjmvkNo ratings yet
- Sankalp Phaseiv El 3 Lecture-3 Final PDFDocument8 pagesSankalp Phaseiv El 3 Lecture-3 Final PDFArnav SNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01 SAQsDocument38 pagesChapter-01 SAQsHrgamersNo ratings yet
- Physics: Electromagnetism Spring 2007 PROBLEM SET 7 SolutionsDocument7 pagesPhysics: Electromagnetism Spring 2007 PROBLEM SET 7 SolutionsByron AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument54 pagesProblem SetXyNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics WDocument25 pagesXii Physics WFree Fire KingNo ratings yet
- 110-Electric Charges & FieldsDocument11 pages110-Electric Charges & FieldsHanzalaNo ratings yet
- Aissce Asngmt CH - 01Document5 pagesAissce Asngmt CH - 016pqq745bq2No ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1and 2Document8 pagesElectrostatics 1and 2maheruakhanNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: Physics I-Mid Term Examination - 2021 Max Marks: 35 Class: Xii DURATION: 90minDocument3 pagesSUBJECT: Physics I-Mid Term Examination - 2021 Max Marks: 35 Class: Xii DURATION: 90minmano17 ShinNo ratings yet
- Ha3 Phy113 103 180423Document2 pagesHa3 Phy113 103 180423TigerNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - JEE Main 2020-22 PYQDocument255 pagesElectrostatics - JEE Main 2020-22 PYQfsqf41No ratings yet
- Sheet - 01-Pages-27-72Document46 pagesSheet - 01-Pages-27-72Hemant KumarNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION Cyclic I Class XII PhysicsDocument8 pagesSOLUTION Cyclic I Class XII PhysicsRizwana RNo ratings yet
- Em Bank10 16 0Document20 pagesEm Bank10 16 0ArUn KuMarNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Assignment..2024-25 NewDocument27 pagesXii Physics Assignment..2024-25 Newabcx87380No ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument10 pagesElectric Chargesradhasumanpradhan9593No ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential 1Document2 pagesElectrostatic Potential 1Athiya ZainabNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerDocument24 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: Study On CancerAthiya Zainab100% (1)
- Cell Therapy For HIV: Investigatory Project byDocument18 pagesCell Therapy For HIV: Investigatory Project byAthiya ZainabNo ratings yet
- ANT-AMB452000-1502 DatasheetDocument2 pagesANT-AMB452000-1502 Datasheetpenglean heanNo ratings yet
- 150 sg009 - en PDocument54 pages150 sg009 - en PDaniel Andres Silva AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Integrated CircuitDocument7 pagesComparison and Simulation of Integrated Circuitapi-744376938No ratings yet
- Fujitsu General Manual de ServicioDocument31 pagesFujitsu General Manual de ServicioTomás ArrebolaNo ratings yet
- Maglev Trains - How Maglev Trains Work - by Alex Landovskis & Veronique RondeaDocument3 pagesMaglev Trains - How Maglev Trains Work - by Alex Landovskis & Veronique RondeaarnavraizadakhushiNo ratings yet
- Rexroth HCS01Document5 pagesRexroth HCS01TFNo ratings yet
- Power Purchase During FY 2018-19Document75 pagesPower Purchase During FY 2018-19Piya MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Eaton 269471 Emt6 KDB en GBDocument4 pagesEaton 269471 Emt6 KDB en GBAriel TorresNo ratings yet
- 7sj63 Catalog Sip E7Document39 pages7sj63 Catalog Sip E7alexns84No ratings yet
- Beee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017Document4 pagesBeee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017upender raoNo ratings yet
- 2CNM203002R2001 m2m BasicDocument3 pages2CNM203002R2001 m2m BasicHuy Hồ PhướcNo ratings yet
- EE2402 PROTECTION AND SWITCHGEAR Syllabus Regulation 2008Document1 pageEE2402 PROTECTION AND SWITCHGEAR Syllabus Regulation 2008Muruga Raj0% (1)
- I Eee FlickerDocument8 pagesI Eee FlickerErmin FazlicNo ratings yet
- FP We3a2 A YadavDocument6 pagesFP We3a2 A Yadavİbrahim KozatNo ratings yet
- Wireless Digital Stethoscope Using Bluetooth TechnDocument10 pagesWireless Digital Stethoscope Using Bluetooth TechnHitesh DammuNo ratings yet
- Pico - SERIES SA - 2024-01-04Document8 pagesPico - SERIES SA - 2024-01-04Giap LeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 FSK DemodDocument25 pagesChapter 14 FSK DemodberkahNo ratings yet
- The TL431 in The Control of Switching Power SuppliesDocument63 pagesThe TL431 in The Control of Switching Power Suppliesrangerford0% (1)
- ESU-400 ENG-SPA Rev00Document2 pagesESU-400 ENG-SPA Rev00grupomedibuyNo ratings yet
- Mje 13003Document3 pagesMje 13003Hatem AissaouiNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Rectification With Flyback and Forward ConvertersDocument26 pagesSynchronous Rectification With Flyback and Forward ConverterszwolfNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of A Cascode Distributed LNA With Gain and Noise Improvement in 0.15-m GaAs pHEMT TechnologyDocument5 pagesDesign and Analysis of A Cascode Distributed LNA With Gain and Noise Improvement in 0.15-m GaAs pHEMT Technologyسري صالحNo ratings yet
- Developments in Electric Power Supply Configurations For Electrical-Discharge-Machining (EDM)Document6 pagesDevelopments in Electric Power Supply Configurations For Electrical-Discharge-Machining (EDM)فایلجو پروژه و مقالهNo ratings yet
- Automático Schneider Ic60 - A9F44340Document2 pagesAutomático Schneider Ic60 - A9F44340jorgeNo ratings yet
- Group-16 - CSTH in SeriesDocument53 pagesGroup-16 - CSTH in SeriesRuchita LaswanteNo ratings yet
- How Magnetic Induction Lamps WorkDocument4 pagesHow Magnetic Induction Lamps WorkMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Transistor ApproximationsDocument5 pagesTransistor ApproximationsGlenn D. KleinNo ratings yet
- Class AB Push-Pull Vacuum Tube Guitar Amplifier Analysis, Design, and ConstructionDocument14 pagesClass AB Push-Pull Vacuum Tube Guitar Amplifier Analysis, Design, and ConstructiontekellamerZ aka tekellamer100% (2)
- 48V DC - DC Converter - Mild Hybrid DC - DC Converter - EatonDocument3 pages48V DC - DC Converter - Mild Hybrid DC - DC Converter - EatonShubham KaklijNo ratings yet