Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types Description Graphics: Types of Pile Foundations Based On Construction Method
Types Description Graphics: Types of Pile Foundations Based On Construction Method
Uploaded by
04BHANDIWAD SANJANAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types Description Graphics: Types of Pile Foundations Based On Construction Method
Types Description Graphics: Types of Pile Foundations Based On Construction Method
Uploaded by
04BHANDIWAD SANJANACopyright:
Available Formats
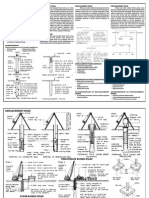
➢ Types of Pile Foundations Based on Construction Method:
Types Description Graphics
➢ Cast-in-situ piles are concrete pile. These piles are
constructed by drilling holes in the ground to the
Cast-in-situ required depth and then filling the hole with
Pile concrete.
Foundations ➢ Reinforcements are also used in the concrete as per
the requirements. These piles are of small diameter
compared to drilled piers.
➢ Cast-in-situ piles are straight bored piles or with one
or more bulbs at intervals are casted.
➢ The piles with one or more bulbs are called as under-
reamed piles.
➢ Driven and Cast-in-situ Piles -
o Driven and cast-in-situ piles have the advantages of
both driven and cast-in-situ piles.
o The procedure of installing a driven and cast-in-situ
pile is as follows:
o A steel shell of diameter of pile is driven into the
ground with the aid of a mandrel inserted into the
shell.
o After driving the shell, the mandrel is removed and
concrete is poured in the shell.
o The shell is made of corrugated and reinforced thin
sheet steel (monotube piles) or pipes (Armco welded
pipes or common seamless pipes). The piles of this
type are called a shell type piles.
o The shell-less type is formed by withdrawing the shell
while the concrete is being placed.
o In both the types of piles the bottom of the shell is
closed with a conical tip which can be separated from
the shell.
o By driving the concrete out of the shell an enlarged
bulb may be formed in both the types of piles.
o Franki piles are of this type. In some cases the shell
will be left in place and the tube is concreted.
o This type of pile is very much used in piling over
water.
➢ Bored cast in situ concrete pile
o Applications of bored cast in situ concrete pile
o bored cast in situ pile is a strong choice in the
following conditions:
o If noise prevention to the buildings located around
the construction is mandatory or undesired, then the
construction of bored cast in situ pile is the most
suitable option.
o Bored cast in situ pile is ideal as end bearing pile,
exclusively when it need to be socketed into rock.
o When high capacity pile is required, then this type of
pile is an ideal choice. According to IS 2911 part 01-
Section 02- 2010, such type of pile preferred for
weights ranges from 150tonnes to 300tonnes.
➢ Advantages of Cast-in- situ Concrete Piles
o The shells are light weighted, so they are easy to
handle.
o Length of piles can be varied easily.
o The shells may be assembled at sight.
o No excess enforcement is required only to prevent
damage from handling.
o No possibility of breaking during installation.
o Additional piles can be provided easily if required.
➢ Disadvantages of Cast-in- situ Concrete Piles
o Installation requires careful supervision and quality
control.
o Needs sufficient place on site for storage of the
materials used for construction.
o It is difficult to construct cast in situ piles where the
underground water flow is heavy.
o Bottom of the pile may not be symmetrical.
o If the pile is un-reinforced and uncased, the pile can
fail in tension if there acts and uplifting force.
Pre – cast and ➢ Driven precast concrete piles are constructed by
Driven Pile hammering the piles into the soil to a depth greater
Foundations than 40m by an adjustable hydraulic or diesel
hammer.
➢ Driven precast concrete piles are widely used
because of their versatility and suitability for most
ground conditions. These piles can be used for the
foundation of all types of engineering structures
under nearly every soil condition.
➢ Driven pile foundations can be made from concrete,
steel or timber.
➢ Driven precast concrete piles are particularly suited
where the founding stratum is overlain by soft
deposits and aggressive or contaminated soils. Piles
are manufactured in factories under high-quality
control, and consist of segmental lengths of
reinforced concrete sections of lengths between 3m
and 15m with required or standard cross-section.
➢ These piles are prefabricated before placing at the
construction site.
➢ When driven piles are made of concrete, they are
precast. These piles are driven using a pile hammer.
➢ When these piles are driven into the granular soils,
they displace the equal volume of soil.
➢ This helps in compaction of soil around the sides of
piles and results in the densification of soil.
➢ The piles which compact the soil adjacent to it is also
called as compaction pile.
➢ This compaction of soil increases its bearing
capacity.
➢ Saturated silty soils and cohesive soils have poor
drainage capability. Thus these soils are not
compacted when driven piles are drilled through it.
➢ The water have to be drained for the soil to be
compacted. Thus stresses are developed adjacent to
the piles have to be borne by pore water only.
➢ This results in increase in pore water pressure and
decrease in bearing capacity of the soil
➢ Advantages of Pre-cast Piles -
o Provides high resistance to chemical and biological
cracks.
o They are usually of high strength.
o To facilitate driving, a pipe may be installed along the
center of the pile.
o If the piles are cast and ready to be driven before the
installation phase is due, it can increase the pace of
work.
o The confinement of the reinforcement can be
ensured.
o Quality of the pile can be controlled.
o F any fault is identified, it can be replaced before
driving.
o Pre-cast piles can be driven under the water.
o The piles can be loaded immediately after it is driven
up to the required length.
➢ Disadvantages of Pre-cast Piles -
o Once the length of the pile is decided, it is difficult to
increase or decrease the length of the pile afterward.
o They are difficult to mobilize.
o Needs heavy and expensive equipment to drive.
o As they are not available for readymade purchase, it
can cause a delay in the project.
o There is a possibility of breakage or damage during
handling and driving of piles.
➢ Classification of pile foundation w.r.t function or use -
Types Description Graphics
Sheet Piles
➢ This type of pile is mostly used to provide lateral
support.
➢ Usually, they resist lateral pressure from loose soil,
the flow of water, etc.
➢ They are usually used for cofferdams, trench
sheeting, shore protection, etc.
➢ They are not used for providing vertical support to
the structure.
➢ They are usually used to serve the following
purpose-
o Construction of retaining walls.
o Protection from river bank erosion.
o Retain the loose soil around foundation trenches.
o For isolation of foundation from adjacent soils.
o For confinement of soil and thus increase the
bearing capacity of the soil
Bearing Piles ➢ Load Bearing Piles
o This type of pile foundation is mainly used to
transfer the vertical loads from the structure to the
soil.
o These foundations transmit loads through the soil
with poor supporting property onto a layer which
is capable of bearing the load.
o Depending on the mechanism of load transfer
from pile to the soil, load-bearing piles can be
further classified as flowed.
➢ End Bearing Piles
o In this type of pile, the loads pass through the lower
tip of the pile.
o The bottom end of the pile rests on a strong layer
of soil or rock.
o Usually, the pile rests at a transition layer of a weak
and strong slayer.
o As a result, the pile acts as a column and safely
transfers the load to the strong layer.
o The total capacity of end bearing pile can be
calculated by multiplying the area of the tip of the
pile and the bearing capacity of at that particular
depth of soil at which the pile rests.
o Considering a reasonable factor of safety, the
diameter of the pile is calculated.
Friction ➢ Friction pile transfers the load from the structure
Pile to the soil by the frictional force between the
surface of the pile and the soil surrounding the pile
such as stiff clay, sandy soil, etc.
➢ Friction can be developed for the entire length of
the pile or a definite length of the pile, depending
on the strata of the soil.
➢ In friction pile, generally, the entire surface of the
pile works to transfer the loads from the structure
to the soil.
➢ The surface area of the pile multiplied by the safe
friction force developed per unit area determines
the capacity of the pile.
➢ While designing skin friction pile, the skin friction
to be developed at a pile surface should be
sincerely evaluated and a reasonable factor of
safety should be considered.
➢ Besides this one can increase the pile diameter,
depth, number of piles and make pile surface rough
to increase the capacity of friction pile.
Soil ➢ Sometimes piles are driven at placed closed
Compacto intervals to increase the bearing capacity of soil by
r Piles compacting.
➢ Classification of Piles Based on Materials -
• Primarily piles can be classified into two parts.
1. Displacement piles Non-displacement
2. Replacement piles.
• Piles which causes the soil to be displaced vertically and radially as they are driven to the ground is known as
Displacement piles.
• In case of Replacement piles, the ground is bored and the soil is removed and then the resulting hole is either
filled with concrete or a pre-cast concrete pile is inserted.
• On the basis of materials of pile construction and their installation process load-bearing piles can be classified as
follows:
Materials Description Graphics
Timber ➢ Timber piles are placed under the water level.
Piles ➢ They last for approximately about 30 years.
➢ They can be rectangular or circular in shape.
➢ Their diameter or size can vary from 12 to 16
inches.
➢ The length of the pile is usually 20 times of the
top width.
➢ They are usually designed for 15 to 20 tons.
Additional strength can be obtained by bolting
fish plates to the side of the pile
➢ Advantages of Timber Piles-
o Timber piles of regular size are available.
o Economical.
o Easy to install.
o Low possibility of damage.
o Timber piles can be cut off at any desired
length after they are installed.
o If necessary, timber piles can be easily pulled
out.
o Disadvantages of Timber Piles-
o Piles of longer lengths are not always available.
o It is difficult to obtain straight piles if the
length is short.
o It is difficult to drive the pile if the soil strata
are very hard.
o Spicing of timber pile is difficult.
o Timber or wooden piles are not suitable to be
used as end-bearing piles.
o For durability of timber piles, special measures
have to be taken. For example- wooden piles
are often treated with preservative.
Concrete ➢ Pre-cast Concrete Pile
Piles o The precast concrete pile is cast in pile bed in
the horizontal form if they are rectangular in
shape.
o Usually, circular piles are cast in vertical
forms.
o Precast piles are usually reinforced with steel
to prevent breakage during its mobilization
from casting bed to the location of the
foundation.
o After the piles are cast, curing has to be
performed as per specification.
o Generally curing period for pre-cast piles is 21
to 28 days.
➢ Cast-in-Palace Concrete Piles
o This type of pile is constructed by boring of soil
up to the desired depth and then, depositing
freshly mixed concrete in that place and letting
it cure there.
o This type of pile is constructed either by
driving a metallic shell to the ground and filling
it with concrete and leaves the shell with the
concrete or the shell is pulled out while
concrete is poured.
Steel Piles ➢ Steel piles may be of I-section or hollow pipe.
They are filled with concrete.
➢ The size may vary from 10 inches to 24 inches
in diameter and thickness is usually ¾ inches.
➢ Because of the small sectional area, the piles
are easy to drive.
➢ They are mostly used as end-bearing piles.
➢ Advantages of Steel Piles
o They are easy to install.
o They can reach a greater depth comparing to
any other type of pile.
o Can penetrate through the hard layer of soil
due to the less cross-sectional area.
o It is easy to splice steel piles
o Can carry heavy loads.
➢ Disadvantage of Steel Piles
o Prone to corrosion and expensive
o Has a possibility of deviating while driving.
Pile Accessories
Accessory Description Graphics
Pile cap
➢ A pile cap is defined as a concrete block cast
on the head of a group of piles, to transmit
the load from the structure to the group of
piles.
➢ To protect the top of pile from blow of
hammer on top, pile cap is provided.
➢ Generally, pile cap transfers the load form the
structures to a pile group, then the load
further transfers to firm soil.
➢ External pressures on a pile are likely to be
greatest near the ground surface. Ground
stability increases with depth and pressure.
➢ The top of the pile therefore, is more
vulnerable to movement and stress than the
base of the pile.
➢ Pile caps are thus incorporated in order to tie
the pile heads together so that individual pile
movement and settlement is greatly reduced.
➢ Thus stability of the pile group is greatly
increased
➢ The functions of a pile cap are:
o To distribute a single load equally over the
pile group and thus over a greater area of
bearing potential.
o To laterally stabilise individual piles thus
increasing overall stability of the group.
o To provide the necessary combined
resistance to stresses set up by the
superstructure and/or ground movement
Pile shoe ➢ Pile shoe is fitted at bottom end of pile to
protect the pile and to facilitate easy pile
driving.
➢ Pile shoe is made of cast iron, steel or
wrought iron.
➢ Types of pile shoe:
o Square pile shoe
o Wedged shaped pile shoe
o Round pile shoe
o Steel trap pile shoe for timber pile
o Socket type pile shoe for timber pile
o closed end shoe for pipe piles
Sayali Said | 04
You might also like
- Pile Vs WellDocument16 pagesPile Vs Wellgvgbabu100% (4)
- Email Contacts For Steel Company in IndiaDocument3 pagesEmail Contacts For Steel Company in Indiazukmos67% (3)
- Precedent Report Final ExamDocument18 pagesPrecedent Report Final ExamExaudi SitumorangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basement: PurposeDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Basement: Purpose04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- History of Architecture PDFDocument22 pagesHistory of Architecture PDFViệt Vớ Vẩn63% (8)
- W3 Deep FoundationDocument42 pagesW3 Deep FoundationTeoh Zhi TongNo ratings yet
- Building Construction I-Lecture 5B (Deep Foundation)Document27 pagesBuilding Construction I-Lecture 5B (Deep Foundation)Pradip PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Foundation Engineering: Introduction To Deep FoundationDocument17 pagesGeotechnical Foundation Engineering: Introduction To Deep FoundationQaisar KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pile Foundations 01Document60 pagesIntroduction To Pile Foundations 01Sivaathmiga RangeswaranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Chapter 1 IntrodiuctionDocument9 pagesLecture 1 Chapter 1 Introdiuctionsnc.miccpNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering-IiDocument45 pagesFoundation Engineering-IiDaniel SolomonNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationDocument20 pagesPile FoundationAlcohol You LaterNo ratings yet
- Abc-Sem7: Pile FoundationDocument21 pagesAbc-Sem7: Pile Foundationshreeyya nairNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations PDFDocument15 pagesDeep Foundations PDFGaddam Padmaja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7.PILEFOUNDDocument42 pagesChapter 7.PILEFOUNDZsoloa adamNo ratings yet
- CE325 - 15 Pile FoundationsDocument31 pagesCE325 - 15 Pile Foundationsfaizankhan23No ratings yet
- Advance Building ConstructionDocument23 pagesAdvance Building ConstructionGagandeepNo ratings yet
- CE 324 - Lec 06 Pile Foundations PDFDocument93 pagesCE 324 - Lec 06 Pile Foundations PDFAli BajwaNo ratings yet
- Piled Foundation ReportDocument7 pagesPiled Foundation ReportDijo Mathews100% (1)
- PilingDocument30 pagesPilingChinnu NinanNo ratings yet
- DSCRHT 206 Lecture-5Document22 pagesDSCRHT 206 Lecture-5Sadik SaikatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Pile - 22Document158 pagesChapter 2 - Pile - 22gediongatzNo ratings yet
- Deep FoundationDocument74 pagesDeep FoundationShantanu PaulNo ratings yet
- 01 - Deep FoundationDocument14 pages01 - Deep FoundationRekha ojhaNo ratings yet
- Footing (Anmol)Document16 pagesFooting (Anmol)Anmol ChughNo ratings yet
- 2 Deep Foundations R1 PDFDocument39 pages2 Deep Foundations R1 PDFAayisha MNo ratings yet
- Foundation 2Document34 pagesFoundation 2aamaniammuNo ratings yet
- Piling Tugasan1Document29 pagesPiling Tugasan1MDanish AimanNo ratings yet
- PilesDocument47 pagesPilesnurulselangorNo ratings yet
- I. Deep Foundation: A. PileDocument7 pagesI. Deep Foundation: A. PileNikol CapulongNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV. Design of Deep FoundationDocument91 pagesUnit-IV. Design of Deep FoundationRwagatare civilcontractorsNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document82 pagesModule 2Nishan K NichuNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationsDocument30 pagesPile FoundationsUsman HakimNo ratings yet
- Pilefoundations 180502041727Document60 pagesPilefoundations 180502041727Kiprono VincentNo ratings yet
- 02 - Displacement PileDocument71 pages02 - Displacement Pilesolehahnasir15No ratings yet
- Pile FoundationDocument23 pagesPile Foundationshafeeq KoottayiNo ratings yet
- DCQ10033 - TOPIC 3 SUBSTRUCTURE Vol 1 PILINGDocument75 pagesDCQ10033 - TOPIC 3 SUBSTRUCTURE Vol 1 PILINGMohamad HaniffNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations 14-10-19Document45 pagesPile Foundations 14-10-19Goutam NandiNo ratings yet
- Pile Foun PDF - RemovedDocument26 pagesPile Foun PDF - Removedsrishtisonkar15No ratings yet
- Pile Foundation: For More Log On ToDocument35 pagesPile Foundation: For More Log On ToBRAIN OF AN ARCHITECT100% (1)
- 03 - Driven Cast in PlaceDocument27 pages03 - Driven Cast in Placesolehahnasir15No ratings yet
- Bearing Piles and GroupsDocument36 pagesBearing Piles and Groupsjologscresencia100% (1)
- Deep FoundationsDocument15 pagesDeep FoundationsSanjit BadgujarNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Piles N Cement Concrete PilesDocument18 pagesCast Iron Piles N Cement Concrete PilesAditya Dinesh BhagatNo ratings yet
- Different Types of PileDocument16 pagesDifferent Types of PileBayu Suprayogi100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Sheet PileDocument93 pagesChapter 1 - Sheet PilegediongatzNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundation: When Do We Use Deep Foundations?Document7 pagesDeep Foundation: When Do We Use Deep Foundations?Cadfiles aasthaNo ratings yet
- Driven Cast in Situ PilesDocument17 pagesDriven Cast in Situ PilesSonu KumawatNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations Ii - CHP3-1Document37 pagesPile Foundations Ii - CHP3-1Uveys kavakliNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations: MR Mohd Faiz B Mohammad ZakiDocument24 pagesPile Foundations: MR Mohd Faiz B Mohammad ZakiMohammad Hafiz MahadzirNo ratings yet
- Pile FoundationDocument33 pagesPile FoundationAvantika DhimanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8. Pile FoundationsDocument30 pagesLecture 8. Pile FoundationsMmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.PILEFOUND - ModfDocument32 pagesChapter 5.PILEFOUND - ModfnahomdemelashNo ratings yet
- Pile and Mat FoundationDocument9 pagesPile and Mat FoundationMuhamad SafeenNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation - Based On MaterialDocument36 pagesPile Foundation - Based On MaterialAvani JNo ratings yet
- Purpose of JettiesDocument16 pagesPurpose of JettiesPriyanka FulpagareNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations: Kaidy DuarteDocument22 pagesDeep Foundations: Kaidy DuarteCynthia XiuNo ratings yet
- 2 SubstructureDocument37 pages2 SubstructureMartin NavarrozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Footing On Piles: Pile FoundationDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Footing On Piles: Pile FoundationPrince AJNo ratings yet
- 8 PilesDocument19 pages8 Pilesengrusmaahmad219No ratings yet
- GRP 2 - Soil - Foundation PilesDocument74 pagesGRP 2 - Soil - Foundation PilesFELICITY MONTEFALCONo ratings yet
- Week 5c (Deep Foundation) DESIGN OF FLANGED SECTIONDocument33 pagesWeek 5c (Deep Foundation) DESIGN OF FLANGED SECTIONmaisaraaliyyaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Waterproof Systems (BS 8102: 2009) : Structures Against Water From The GroundDocument2 pagesWaterproof Systems (BS 8102: 2009) : Structures Against Water From The Ground04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- DW 2016Document2 pagesDW 201604BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Group 1-7Document30 pagesGroup 1-704BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Idl 56493 1Document142 pagesIdl 56493 104BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Mumbai: Systems of TradeDocument29 pagesMumbai: Systems of Trade04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Mumbai Set CNMurphy LoResDocument15 pagesMumbai Set CNMurphy LoRes04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Walls 561ee04893cb7Document15 pagesDiaphragm Walls 561ee04893cb704BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Sanjana Bhandiwad - 04 - Sem 7 - ABC - Diaphragm WallsDocument18 pagesSanjana Bhandiwad - 04 - Sem 7 - ABC - Diaphragm Walls04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Asian Architecture ARC 2234 Project 1:case Study: NAME: Choo Ai Lin Student Id: 0317253 LECTURER: MR Koh Jing HaoDocument16 pagesAsian Architecture ARC 2234 Project 1:case Study: NAME: Choo Ai Lin Student Id: 0317253 LECTURER: MR Koh Jing Hao04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- 04 - Sanjana Bhandiwad - Concept NoteDocument6 pages04 - Sanjana Bhandiwad - Concept Note04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- PDF HK Diaphragm Wallpdf 1 2Document2 pagesPDF HK Diaphragm Wallpdf 1 204BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- 04 - Sanjana Bhandiwad - Assignment 3 - Methods of Construction of BasementDocument45 pages04 - Sanjana Bhandiwad - Assignment 3 - Methods of Construction of Basement04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Excavation of BasementsDocument32 pagesExcavation of Basements04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Process of Mass Concrete Underpinning: Needle BeamsDocument2 pagesProcess of Mass Concrete Underpinning: Needle Beams04BHANDIWAD SANJANA0% (1)
- Mumbai Set CNMurphy LoResDocument15 pagesMumbai Set CNMurphy LoRes04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Sanjana Bhandiwad 04 Stage 01Document1 pageSanjana Bhandiwad 04 Stage 0104BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Type Information Graphics: Use of Lattice BeamsDocument4 pagesType Information Graphics: Use of Lattice Beams04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Group 1-7Document16 pagesGroup 1-704BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- BLDG TECH Juson Assignment Lecture 4 MASONRYDocument17 pagesBLDG TECH Juson Assignment Lecture 4 MASONRYMa. Janelle GoNo ratings yet
- The Development of Architecture of The Philippines DuringDocument12 pagesThe Development of Architecture of The Philippines DuringmacepeNo ratings yet
- AD Classics - Trellick Tower - Erno Goldfinger - ArchDailyDocument13 pagesAD Classics - Trellick Tower - Erno Goldfinger - ArchDailyarchpavlovicNo ratings yet
- Page 3 BrochureDocument40 pagesPage 3 BrochureHemant UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Echnology Rief: Stone Veneer Walls Laid in MortarDocument4 pagesEchnology Rief: Stone Veneer Walls Laid in Mortarደጀን ገብረስላሴNo ratings yet
- Pricelist 2021: All The Products For Building Industry ProfessionalsDocument28 pagesPricelist 2021: All The Products For Building Industry ProfessionalsSK C&T - KEO ỐP LÁT, CHỐNG THẤM.No ratings yet
- Design Portfolio Swetha SDocument39 pagesDesign Portfolio Swetha SSwetha SureshNo ratings yet
- AC Syllabus 2017Document7 pagesAC Syllabus 2017YamNo ratings yet
- Balaji.E: Curriculum VitaeDocument5 pagesBalaji.E: Curriculum VitaeEngr Balaji100% (1)
- Rimt-College of Architecture: High Rise BuildingDocument43 pagesRimt-College of Architecture: High Rise BuildingKritika RawatNo ratings yet
- Oracle E-Business Suite Single Sign-On Solution: G. The Five-Day, QuickDocument2 pagesOracle E-Business Suite Single Sign-On Solution: G. The Five-Day, QuickAbdallah AttiaNo ratings yet
- 11 Alnatura+Arena-InzellDocument42 pages11 Alnatura+Arena-InzellAida Domingo Losa100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of Network of Interacting Primary and Secondary Beams in Large Span ConstructionDocument9 pagesAnalysis and Design of Network of Interacting Primary and Secondary Beams in Large Span ConstructionselinaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 BiophiliaDocument24 pages5.2 BiophiliaNurFarahinZakariahNo ratings yet
- Region 6 Western Visayas: Ar. Jarina Lydia O. PichayDocument26 pagesRegion 6 Western Visayas: Ar. Jarina Lydia O. PichayChelsea Mae GersaliaNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument3 pages1 PDFFatima Ja'aferNo ratings yet
- New Resume AzharDocument4 pagesNew Resume AzharYassem MalikNo ratings yet
- 00001Document12 pages00001AhmedMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Costing Per Square Meter - Reference - 2023Q1Document3 pagesCosting Per Square Meter - Reference - 2023Q1Cecilia UmagtangNo ratings yet
- Cdera Code of Practice For The Construction of HousesDocument67 pagesCdera Code of Practice For The Construction of HousesAaronJosiahNo ratings yet
- Space Frames: Subject Code: AP-411 Subject Name: Theory of Structures-IvDocument23 pagesSpace Frames: Subject Code: AP-411 Subject Name: Theory of Structures-IvSuman KumariNo ratings yet
- 2001 - Jacques - Aesthetics of The SlumDocument6 pages2001 - Jacques - Aesthetics of The SlumGinebvraNo ratings yet
- Flexible Architecture: Optimization of Technology and CreativityDocument12 pagesFlexible Architecture: Optimization of Technology and CreativityZeba NisarNo ratings yet
- M&E Outstanding WorkDocument10 pagesM&E Outstanding WorkanipchinNo ratings yet
- ECM 366 Assignment 1Document9 pagesECM 366 Assignment 1NORFITRIAH YAHYANo ratings yet
- Soil NailingDocument32 pagesSoil Nailingprajakta chaudhariNo ratings yet
- Ebongs Urban Renewal Sheets and ReportDocument10 pagesEbongs Urban Renewal Sheets and Reportebong abrahamNo ratings yet