Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychiatric Medications
Psychiatric Medications
Uploaded by
pavanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psychiatric Medications
Psychiatric Medications
Uploaded by
pavanCopyright:
Available Formats
0 1 Topics QBank Evidence Videos Groups Products Help ' ( !
/ '
Updated: 1/8/2020 "9
Psychiatric Medications
Damian Apollo
TOPIC QUESTIONS EVIDENCE
Review Topic 3 /3 1 /1
Psychiatric Drug Introduction
Psychiatric medications can be broken down into the following categories:
antidepressants
antipsychotics
bipolar medications
anxiolytics
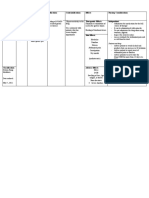
Psychiatric Drug Table
Antidepressants
Name Mechanism Key Indication Key Toxicity
Tricyclics
Blocks reuptake of
Amitryptyline
norepinephrine and serotonin
Depression
Pain syndromes Convulsions
Action on 5-HT, muscarinic,
Coma
Nortriptyline dopaminergic, histaminic
Cardiotoxicity
receptors (among many others)
Anti-cholinergic side effects
Blocks 5-HT, NE, dopamine, Ach
Imipramine Bed-wetting
reuptake (among many others)
Non-Tricyclic SNRIs
Venlafaxine
Depression
Stimulant effects
Serotonin-norepinephrine Anxiety
Sedation
Duloxetine reuptake inhibitor Co-morbid headaches
Increased blood pressure
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
SSRIs
Citalopram
Serotonin syndrome (in combination with
Fluoxetine
Depression MAOi's, SNRI's, TCA's)
Paroxetine
Serotonin reuptake inhibitor Anxiety Sexual dysfunction
Social Anxiety (paroxetine) GI distress
Sertraline SIADH (manage with cyproheptadine)
NDRIs
Lowers seizure threshold
Weak norepinephrine-dopamine Depression Tachycardia
Bupropion
reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) Smoking cessation Headache
NO sexual side effects
MAOIs
Isocarboxazid
Inhibits monoamine oxidase Hypertensive crisis (with tyramine consumption)
Phenelzine Atypical depression
(MAO) increasing catecholamine Serotonin syndrome (with SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs
Social anxiety
Tranylcypromine and dopamine levels as well as many other drugs)
Antipsychotics
Low Potency
Chlorpromazine
Extrapyramidal side effects
Hyperprolactinemia
Psychosis Anti-muscarinic side effects
D2, α1, cholinergic, histaminic
Schizophrenia Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Thioridazine blockade
Mania Tardive dyskinesia
Corneal (chlorpromazine) and retinal
(thioridazine) deposits
High Potency
Droperidol
Extrapyramidal side effects
Hyperprolactinemia
D2 blockade Psychosis Anti-muscarinic side effects
Perphenazine
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Tardive dyskinesia
Atypical SDAs
Clozapine
Agranulocytosis (must monitor WBC levels)
Olanzapine Psychosis
Weight gain
Risperidone Bipolar
Anti-pyramidal symptoms (less than traditional)
Affects serotonin, dopamine, α1, OCD
Anti-cholinergic side effects
and histamine receptors Anxiety
QT prolongation
Quetiapine Depression
Hyperlipidemia (olanzapine)
Mania
Hyperprolactinemia (risperidone)
Bipolar Medications
Teratogenic
Granulocytosis
Aplastic anemia
Bipolar, esp. rapid cycling
SIADH
Carbamazepine Blocks Na+ channels Trigeminal neuralgia
P450 inducer
Anti-epileptic
Steven-Johnson syndrome
Diplopia
Ataxia
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Hypothyroidism
Lithium Unknown Bipolar
Teratogenic
Ebstein anomaly (teratogenic)
Blocks voltage-gated Na+ Hepatotoxic
channels Teratogenic
Bipolar
Inhibits GABA transaminase Tremor
Valproic acid Anti-epileptic
(increases GABA) Weight gain
Absence seizure (2nd line to ethosuximide)
Blocks thalamic T-type Ca2+ GI complications
channels Treat overdose with carnitine
Anxiolytics
Sedation
Benzodiazepines (lorazepam, Increase frequency of GABA Seizures Tolerance
diazepam) channel opening Anxiolytic Respiratory depression
Dependence
Sedative
Respiratory and cardiovascular depression
Barbiturates (phenobarbital, Increase duration of GABA Anxiolytic
Dependence
pentobarbital, thiopental) channel opening Seizures
P450 induction
General anesthesia (thiopental)
Ataxia
Insomnia Headaches
Zolpidem GABA channel agonist
Muscle relaxant Confusion
Dependence
Please rate topic. $#
# $#
$#$#
$ Average 5.0 of 3 Ratings
% QUESTIONS (3) &
QUESTIONS
2 of 3 ' Previous Next ( - .
(M2.PH.16.4688) A 28-year-old female patient with a history of schizophrenia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypothyroidism comes to clinic stating she
would like to be put back on a medication. She recently stopped taking her haloperidol as it made it hard for her to "sit still." She requests to be put on
olanzapine as a friend from a support group said it was helpful. Why should this medication be avoided in this patient? ) Tested Concept
QID: 107491
1 The patient is at a high risk for torsades de pointes
2 There is a high risk for retinopathy
3 The patient has type 2 diabetes
4 The patient may develop galactorrhea
5 Tardive dyskinesia will likely result from the prolonged use of olanzapine
Select Answer to see Preferred Response
* EVIDENCES (1) &
evidenceFootprint +
SHOW EVIDENCE
, TOPIC COMMENTS (9) &
Please login to add comment.
MEDBULLETS Step 2 & 3 !
TOPICS QBANK PRODUCTS ABOUT HELP
ANATOMY CASES PEAK & STUDY PLANS COMPANY CONTACT US
DRUGS TESTIMONIALS PRIVACY POLICY FAQ
VIDEOS
STATS TERMS OF USE PLATFORM TUTORIAL
POSTS VIDEOS
CARDIOVASCULAR Feedback
EVIDENCE IPHONE APP
ENDOCRINE
ANDROID APP
GASTROINTESTINAL
HEME
INFECTIOUS DIS.
NEUROLOGY
NUTRITION
ONCOLOGY
PEDIATRICS
PULMONARY
RENAL
DERMATOLOGY
EAR, NOSE, THROAT
GYNECOLOGY
OBSTETRICS
OPHTHALMOLOGY
ORTHOPEDICS
PSYCHIATRY
RHEUMATOLOGY
Copyright © 2020 Lineage Medical, Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Non Linear PharmacokineticsDocument64 pagesNon Linear PharmacokineticsMoganaa LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Prinsipal Kode Produk Nama ProdukDocument36 pagesPrinsipal Kode Produk Nama ProdukhardimozerNo ratings yet
- Rab Gudang Apotek 2019Document12 pagesRab Gudang Apotek 2019IF RSYMCNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat P3K Daftar Obat P3K (Awal Pengiriman) Harga Obat No Nama Obat NoDocument3 pagesDaftar Obat P3K Daftar Obat P3K (Awal Pengiriman) Harga Obat No Nama Obat NoadminIHC cakramedikaNo ratings yet
- Censo Discapacitados CPT II Ruta 20iiDocument8 pagesCenso Discapacitados CPT II Ruta 20iikarlais salasNo ratings yet
- Subs ActivaDocument164 pagesSubs ActivaMaseaNo ratings yet
- Sakajaja (Sma) PricelistDocument21 pagesSakajaja (Sma) PricelistAnonymous aaAQ6dgNo ratings yet
- SERETIDE DISKUS - GDS35 IPI20 - CompressedDocument2 pagesSERETIDE DISKUS - GDS35 IPI20 - CompressedAvian KrispratamaNo ratings yet
- Infusiones Analgésicas de Lidocaína o Tramadol en Perras Sometidas A Ovariohisterectomía Lateral Bajo Un Protocolo de Anestesia DisociativaDocument14 pagesInfusiones Analgésicas de Lidocaína o Tramadol en Perras Sometidas A Ovariohisterectomía Lateral Bajo Un Protocolo de Anestesia DisociativaDeana Laura SanchezNo ratings yet
- Anti Psychotic DrugsDocument2 pagesAnti Psychotic DrugsArrianne NatividadNo ratings yet
- Moh & SGH SupplyDocument6 pagesMoh & SGH SupplyAnirudhan NairNo ratings yet
- PharmaceuticsDocument2 pagesPharmaceuticsbrian3442No ratings yet
- Dosage AdjustmentDocument10 pagesDosage AdjustmentNido MalghaniNo ratings yet
- Data Obat 19 2 2021Document20 pagesData Obat 19 2 2021k24 mauniNo ratings yet
- Uptd Puskesmas Sindar Raya: Pemerintah Kabupaten Simalungun Dinas KesehatanDocument2 pagesUptd Puskesmas Sindar Raya: Pemerintah Kabupaten Simalungun Dinas KesehatanulfayuliNo ratings yet
- SHKL Pharma Price List - 1st Dec 2023-CashDocument2 pagesSHKL Pharma Price List - 1st Dec 2023-CashojwangamosNo ratings yet
- Barcode Nama Satuan Penggunaan Penggunaan Harga Perbulan Pertiga Bulan Jumlah Total HargaDocument3 pagesBarcode Nama Satuan Penggunaan Penggunaan Harga Perbulan Pertiga Bulan Jumlah Total Hargarsuharapansehat sehatNo ratings yet
- Act 2 NotesDocument3 pagesAct 2 NotesNina CasasNo ratings yet
- GN BN Part IDocument2 pagesGN BN Part ICarla Flor LosiñadaNo ratings yet
- EsomeprazoleDocument2 pagesEsomeprazolenikki shein bullongNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument95 pagesUntitledMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- F1F120072 - Tasya Herzadania Putri - Laprak 5Document26 pagesF1F120072 - Tasya Herzadania Putri - Laprak 5Athaya DwmNo ratings yet
- Dangerous DrugsDocument48 pagesDangerous DrugsNigel HopeNo ratings yet
- Revision - TACN DUOC - Bu I Ôn 1Document4 pagesRevision - TACN DUOC - Bu I Ôn 1Đức BùiNo ratings yet
- Mediwest ProductsDocument34 pagesMediwest Productssj9899100No ratings yet
- Gazette Extraordinary 2022-04!28!40pct Price Hike On 60 Varieties of Medicinal DrugsDocument9 pagesGazette Extraordinary 2022-04!28!40pct Price Hike On 60 Varieties of Medicinal DrugsAdaderana Online100% (1)
- List of Substandard Drugs-2009Document10 pagesList of Substandard Drugs-2009Mohammad Shahbaz AlamNo ratings yet
- CaNaMed 01.01.2024Document273 pagesCaNaMed 01.01.2024roxanamihaelapepiNo ratings yet
- Registered ProductsDocument16 pagesRegistered ProductsDebebe ArgawNo ratings yet
- 113 - Guinea Pig Anesthesia - Jan 2021Document5 pages113 - Guinea Pig Anesthesia - Jan 2021Víctor MezquitaNo ratings yet