Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aarskog Syndrome: Facing V-W) - (4 Hypop
Aarskog Syndrome: Facing V-W) - (4 Hypop
Uploaded by
S. MartinezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aarskog Syndrome: Facing V-W) - (4 Hypop
Aarskog Syndrome: Facing V-W) - (4 Hypop
Uploaded by
S. MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
AARSKOG SYNDROME
TOHRU SHINKAWA, M.D.
YOSHIZUMI YAMAUCHI, M.D.
YUKIO OSADA, M.D.
NOBUYUKI ISHISAWA, M.D.
From the Departments of Urology and Pediatrics,
Miyazaki Medical College, Kiyotake-cho, Miyazaki, Japan
ABSTRACT-A rare case of Aarskog syndrome is presented. The Aarskog syndrome is character-
ized by short stature with typical facial, digital, and genital anomalies.
Aarskog syndrome is characterized by short era1 blood showed a 46, XY pattern. Serum
stature associated with typical facial, digital, growth hormone, serum thyroxine, and urine
and genital anomalies. Since Aarskog’ first 17-ketosteroids determinations were normal, A
described facial-digital-genital syndrome in diagnosis of Aarskog syndrome was established
1970, 25 cases have been reported. We present because of these findings.
another case. Bilateral orchidopexy was done. The size of
the testes was almost normal.
Case Report
A five and one-half-year-old boy was re-
ferred to the hospital because of short stature
and bilateral undescended testes. His parents
were of average build and nonconsanguineous.
An elder sister was normally developed. He was
the product of a normal pregnancy and de-
livery. His birth weight was 3,350 Gm, and
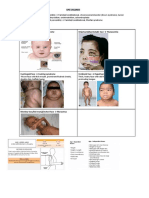
FIGURE 1. (A) Short
height was 49 cm. stature and round face
He was admitted for further evaluation. His with several characteris-
height was 101 cm, 7 cm less than average. tic findings. (B and C,
Round face, hypertelorism, antimongoloid facing v-w). (4 HYPOP-
palpebral slant, ptosis, short stubby nose with lasia and clinodactyly of
anteverted nostrils, and long marked philtrum jijth finger with single
with broad upper lip were observed (Fig. 1A). ventral crease. (C) Scro-
Short fingers, mild syndactyly, hypoplasia, and tum was cleft and scro-
clinodactyly of fifth finger with a single ventral tal skin fold extended
crease were observed (Fig. 1B). The scrotum ventrally around base of
penis.
was cleft, and the scrotal skin fold extended
ventrally around the base of the penis (Fig. 1C).
The testes were undescended and palpated in
the groins. Mental development was normal.
The bone age was retarded (27 months, less
than standard). Karyotype analysis of periph-
624 UROLOGY / DECEMBER1983 / VOLLJMEXXII,NUMBERf?
TABLE I. Characteristic findings * in Aarskog syndrome4
stature Short +
Face: Round +
Hypertelorism +
Antimongoloid slanting of the palpebral fissures +
Ptosis +
Maxillary hypoplasia
Broad nasal bridqe +
Short stubby nose with anteverted nostrils +
Long philtrum +
Linear dimple inferior to lower lip
Dental malocclusion
(Widow's peak) -
Ears: Fleshy ear lobes --__
(Malrotatlon)
(Thickened and downturned superior helices)
Genitals: Scrotum cleft or bifid with scrotal folds encircling +
the penis ventrally
Inquinal hernia
Cryptorchidism +
Hands: Short fingers +
Clinodactyly of fifth finger +
Hypermobility of joints with peculiar positioning
of fingers
Mild syndactyly +
Camptodactyly
Simian creases +
(Short thumbs with limited abduction)
Feet: Broad, flat, turned in
Toes splayed with bulbous tips
Others: Pectus excavatum
Mild mental retardation
-___ (Protruding umbilicus)
Roentqenoqrams: Cervical spine abnormalities
Maxillary hypoplasia
(Hypoplasia of terminal phalanges of fingers) -
(Spina bifida occulta)
(Short nasal spine)
(Fusion of middle and distal phalanges of fifthe toe) -
(Hypoplastic middle phalanges of toes)
/
*Parentheses indicate characteristics have been seen only in one family.
UROLOGY i DECEMBER 1983 i VOLUME XXII, NUMBER 6 625
Comment are observed in facies, hands, and genitals.
Short stature was observed in all cases. Sugar-
Aarskog in 1970’ first described a syndrome
man, Rimoin, and Lachman4 presented a table
in 7 men of a family characterized by short stat-
of the findings in Aarskog syndrome. Our case
ure, peculiar facies, a saddle abnormality of the
satisfied most of the characteristics of the syn-
scrotum, and abnormalities of the hands and
drome (Table I).
feet. Scott2 reported the second family with the
same abnormalities. The facial-digital-genital Kiyotake-cho, Miyazaki 889-16, Japan
(Aarskog) syndrome has been reported in af- (DR. SHINKAWA)
fected males of several families3-‘j In addition to
References
2 cases by Bartsocas and Dimitriou’ and
Melnick and Shildqs 25 cases have been re- 1. Aarskog D: A familial syndrome of short stature associated
with facial dysplasia and genital anomalies, J Pediatr 77: 856
ported. (1970).
X-linked semidominant mode of inheritance 2. Scott CI Jr: Unusual facies, joint hypermobility, genital
anomaly and short stature: a new dysmorphic syndrome, Birth
is suggested by the findings in the pedigrees
Defects 7: 240 (1971).
with partially affected obligate carrier 3. Furukawa CT,‘Hall BD, and Smith DW: The Aarskog syn-
women.1-4 On the other hand, autosomal domi- drome. I Pediatr 81: 1117 (19721.
nant inheritance with partial expression in the 4. Srrgarman GI, Rimoih DL, and Lachman RS: The facial-
digital-genital (Aarskog) syndrome, Am J Dis Child 126: 248
female has not been excluded. (1973).
Chromosomal analyses were performed in 13 5. Funderburk SJ, and Crandall BF: The Aarskog syndrome in
cases.1-3,5 All had normal karyotype. Serum three brothers, Clin Genet 6: 119 (1974).
6. Archibald RM, and German J: The Aarskog-Scott syndrome
growth hormone,1,2,4,8 serum thyroxine,5x8 and in four brothers, Birth Defects 11: 25 (1975).
urine 17-ketosteroids determination* were nor- 7. Bartsocas CS, and Dimitriou JK:,II-Aarskog-Scott syndrome
of unusual facies, joint hypermohility, genital anomaly and short
mal.
stature, ibid. 11: 453 (1975).
It is called the facial-digital-genital syndrome 8. Melnick M, and Shilds ED: Aarskog syndrome: new oral-
because most of the characteristic abnormalities facial findings, Clin Genet 9: 20 (1976).
626 UROLOGY / DECEMBER 1983 / VOLUME XXII, NUMBER 6
You might also like
- Oral Pathology Mnemonics Online Course - PDF versionFrom EverandOral Pathology Mnemonics Online Course - PDF versionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Karen - S Notes-Clinical ExaminationDocument11 pagesKaren - S Notes-Clinical ExaminationGanesh Namasivayam100% (3)
- DR Karen Short NotesDocument412 pagesDR Karen Short NotesNayantara Nair100% (2)
- Cri 188 FinalsDocument12 pagesCri 188 FinalsKaren Angel AbaoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab 2Document4 pagesBiochemistry Lab 2S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- NBDE 2012 All Remembered QsDocument54 pagesNBDE 2012 All Remembered Qschakriy9100% (6)
- CrossCore Rotational Bodyweight Training Mens Fitness ArticleDocument3 pagesCrossCore Rotational Bodyweight Training Mens Fitness Articletrt21No ratings yet
- Peter Ragnar - 3 Non Diet Secrets For Incredible VitalityDocument3 pagesPeter Ragnar - 3 Non Diet Secrets For Incredible VitalityBiljana Percinkova100% (2)
- Global Politics IB GuideDocument67 pagesGlobal Politics IB GuideMikeyJohn100% (1)
- Chinchilla SkullDocument12 pagesChinchilla Skullf.baobao28No ratings yet
- Chromosome Number Final1Document3 pagesChromosome Number Final1Janine NogueraNo ratings yet
- Tetraploidy in A 15-Month-Old GirlDocument5 pagesTetraploidy in A 15-Month-Old GirlGuy HaimNo ratings yet
- Associated DisordersDocument40 pagesAssociated DisordersSonu SonuNo ratings yet
- l3 Orthodontic Case History and Diagnosis - I 17-11-21Document57 pagesl3 Orthodontic Case History and Diagnosis - I 17-11-21Ju JuNo ratings yet
- Catatan Orthopedi AriefDocument8 pagesCatatan Orthopedi Ariefmiwer 765No ratings yet
- Orthodontic DiagnosisDocument19 pagesOrthodontic DiagnosissamNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Examination FiryaLDocument3 pagesThyroid Examination FiryaLFiryal Balushi100% (1)
- Case Seminars WorksheetDocument3 pagesCase Seminars Worksheetsnbmww5p4dNo ratings yet
- Yang2015 Pili TortiDocument3 pagesYang2015 Pili TortiErnawati HidayatNo ratings yet
- EL Husseiny's Essentials of Endocrinology 1247Document152 pagesEL Husseiny's Essentials of Endocrinology 1247حنين عاطفNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetic AbnormalitiesDocument48 pagesCytogenetic AbnormalitiesGlomelyn Rose Ortiz TañedoNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound in Obstet Gyne - 2003 - Delahaye - Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Fetal CraniosynostosisDocument7 pagesUltrasound in Obstet Gyne - 2003 - Delahaye - Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Fetal Craniosynostosisyelly puspitasariNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminationDocument11 pagesClinical ExaminationLaura GranadosNo ratings yet
- LMR Ent - Nose and Paransal SinusesDocument7 pagesLMR Ent - Nose and Paransal SinusesYuku BabyNo ratings yet
- Genetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesDocument1 pageGenetics Dysmorphology in Pediatrics - MedicoNotesJ KPNo ratings yet
- ENT 1.3 Lips and Oral CavityDocument15 pagesENT 1.3 Lips and Oral CavityZazaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination - Karen Notes - SHIRI For BD DoctorsDocument11 pagesClinical Examination - Karen Notes - SHIRI For BD DoctorsHelp LineNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination: The Head and NeckDocument63 pagesPhysical Examination: The Head and Neckapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Goldenhar SyndromeDocument4 pagesGoldenhar Syndrometita luthfiaNo ratings yet
- GPE in ChildrenDocument4 pagesGPE in ChildrenSheera EiyraaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Bone and JointsDocument71 pagesDiseases of Bone and JointsAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Dys Morphis MDocument27 pagesDys Morphis MdrmindhackerNo ratings yet
- Bab II AaDocument7 pagesBab II AaPriskilaNo ratings yet
- Fetal Face and Neck - Student SlidesDocument35 pagesFetal Face and Neck - Student SlidessdafasdNo ratings yet
- 2 Newborn AssesmentDocument23 pages2 Newborn Assesment.No ratings yet
- Final Year Clinicals: Malocclusions and Etiology (Graber)Document31 pagesFinal Year Clinicals: Malocclusions and Etiology (Graber)Sruthy NairNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology FixedDocument3 pagesMedical Terminology FixedBaeman KyottNo ratings yet
- AOT (Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor) : Pyogenic GranulomaDocument54 pagesAOT (Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor) : Pyogenic GranulomaSanNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic AssessmentDocument59 pagesOrthodontic AssessmentSyaifuddin ADamNo ratings yet
- cOMMON gENETIC dISORDERSDocument11 pagescOMMON gENETIC dISORDERSChari RivoNo ratings yet
- Week 1.3Document23 pagesWeek 1.3ginny.mycookiecanNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument18 pagesCase Reportarief wiratamaNo ratings yet
- Syndromes: ContentsDocument5 pagesSyndromes: ContentsRoshni SinghNo ratings yet
- Head Shape Abnormalities and HydrocephalusDocument7 pagesHead Shape Abnormalities and HydrocephalusZweNo ratings yet
- Genereal Examination-Anukul SurgeryDocument4 pagesGenereal Examination-Anukul SurgeryTRASH MAILNo ratings yet
- Speaker: Dr. Shafat A Mir Department of Anaesthesia and Critical Care SKIMS, Srinagar, J&k.indiaDocument74 pagesSpeaker: Dr. Shafat A Mir Department of Anaesthesia and Critical Care SKIMS, Srinagar, J&k.indiatutorial desatuNo ratings yet
- Management of Open Bite: Dr. Madhura Jayant Pednekar Iii MdsDocument75 pagesManagement of Open Bite: Dr. Madhura Jayant Pednekar Iii MdsDrKamran MominNo ratings yet
- CraniosynostosisDocument54 pagesCraniosynostosistameemNo ratings yet
- Skin and Bones 1Document6 pagesSkin and Bones 1Joseph John HiladoNo ratings yet
- Sorge 1996Document4 pagesSorge 1996jahfdfgsdjad asdhsajhajdkNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic FinalDocument858 pagesOrthopedic Finalhashmf180% (10)
- Clerk05 Nervi KranialisDocument14 pagesClerk05 Nervi KranialisIvor Wiguna Hartanto WilopoNo ratings yet
- Mental Dental PathologyDocument19 pagesMental Dental PathologyPooja rajwarNo ratings yet
- BIMC Update PresentationDocument25 pagesBIMC Update PresentationWahyuNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformations of The Larynx and TracheaDocument8 pagesCongenital Malformations of The Larynx and TracheaKaren EidNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck - MusclesDocument3 pagesHead and Neck - MusclesJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Nasal Bone Fractures: Grand Rounds Dr. Ashish GuptaDocument29 pagesNasal Bone Fractures: Grand Rounds Dr. Ashish GuptaCharan KanwalNo ratings yet
- Common SymptomsDocument72 pagesCommon SymptomsBulajyo Pangngay JolinaNo ratings yet
- Prefixes in Medical TerminologyDocument7 pagesPrefixes in Medical Terminologyalerp07100% (1)
- Crs Muthia Khanza (Isi)Document40 pagesCrs Muthia Khanza (Isi)Muthia Khanza AbuBakarNo ratings yet
- Dys MorphologyDocument62 pagesDys Morphologyamal nassarNo ratings yet
- Initial Examination Form: Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Dentistry Dental Teaching CenterDocument2 pagesInitial Examination Form: Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Dentistry Dental Teaching Centersadeen2249No ratings yet
- Initial Examination Form: Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Dentistry Dental Teaching CenterDocument2 pagesInitial Examination Form: Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Dentistry Dental Teaching Centersadeen2249No ratings yet
- Treatmant of Gummy SmileDocument33 pagesTreatmant of Gummy Smileprince wrathNo ratings yet
- Identifying A A RSK Og SyndromeDocument3 pagesIdentifying A A RSK Og SyndromeS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- PlantDerived Edible Nanoparticles and MiRNAs Emerging Frontier For Therapeutics and Targeted DrugDeliveryDocument15 pagesPlantDerived Edible Nanoparticles and MiRNAs Emerging Frontier For Therapeutics and Targeted DrugDeliveryS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Study Design I: Experimental DesignDocument54 pagesStudy Design I: Experimental DesignS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Determining What Analysis To Use?: - For Every Model We Will Cover You Must Ask A Series of QuestionsDocument35 pagesDetermining What Analysis To Use?: - For Every Model We Will Cover You Must Ask A Series of QuestionsS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- CHP 4: Estimating With UncertaintyDocument41 pagesCHP 4: Estimating With UncertaintyS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biometry Lecture 2 Part 2 PostedDocument41 pagesBiometry Lecture 2 Part 2 PostedS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biometry Lecture 1Document59 pagesBiometry Lecture 1S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Statistical AnalysisDocument20 pagesAn Introduction To Statistical AnalysisS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biometry Lecture 3 PostedDocument47 pagesBiometry Lecture 3 PostedS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Biometry Lecture 6 PostedDocument81 pagesBiometry Lecture 6 PostedS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Liposomal Drug DeliveryDocument1 pageLiposomal Drug DeliveryS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Suitability of Liposomes For The Delivery of Hydrophobic Drugs - A Case Study With CurcuminDocument1 pageThe Suitability of Liposomes For The Delivery of Hydrophobic Drugs - A Case Study With CurcuminS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Index: SL.# Description HeadingsDocument2 pagesIndex: SL.# Description HeadingsmadanhseNo ratings yet
- DOH Memo For Local Health Departments 12.3.21Document5 pagesDOH Memo For Local Health Departments 12.3.21News10NBCNo ratings yet
- Foxtail MilletDocument11 pagesFoxtail Milletbhavi kapadiaNo ratings yet
- Medical EthicsDocument25 pagesMedical Ethicsswarajudugade100% (1)
- Retirement Community ResearchDocument5 pagesRetirement Community ResearchMary Jane CabidesNo ratings yet
- Fake News, Phishing, and Fraud: A Call For Research On Digital Media Literacy Education Beyond The ClassroomDocument8 pagesFake News, Phishing, and Fraud: A Call For Research On Digital Media Literacy Education Beyond The ClassroomqwertzNo ratings yet
- NLE DIAGNOSTIC W FREE LECTUREDocument3 pagesNLE DIAGNOSTIC W FREE LECTURETrip Ni TeryoNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Product IdentificationDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Product Identificationمحمد عزتNo ratings yet
- How Do You Feel About Your BodyDocument21 pagesHow Do You Feel About Your BodyFabio VanuzziNo ratings yet
- Coping Skills HandoutsDocument7 pagesCoping Skills HandoutsaharbisonNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Time Weighted Average TWA Noise Level and Noise Dose Levels PDFDocument1 pageCalculating The Time Weighted Average TWA Noise Level and Noise Dose Levels PDFananthu.uNo ratings yet
- Ligamentizacion HT Grafts After ACLDocument10 pagesLigamentizacion HT Grafts After ACLLuisa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Appendix eDocument17 pagesAppendix eTheonee LambiquitNo ratings yet
- Bilingual Reporter, Tanzania JDDocument3 pagesBilingual Reporter, Tanzania JDEng Msofe JamesNo ratings yet
- Common Application Transfer EssayDocument9 pagesCommon Application Transfer Essayafibyrirmfogiz100% (2)
- Massage Professional Ebook, 2nd EditionDocument188 pagesMassage Professional Ebook, 2nd EditionAnh Nguyễn33% (3)
- UNICEF 2016 IECDD Guidance PDFDocument60 pagesUNICEF 2016 IECDD Guidance PDFmcpaulina98No ratings yet
- Changing Faces: A Case-Based Review of Acromegaly: Special Care DentistryDocument5 pagesChanging Faces: A Case-Based Review of Acromegaly: Special Care DentistryZainab HajiNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan, Conclusion, RecommendationDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan, Conclusion, RecommendationMenesio IlaganNo ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument3 pagesObjectiveHazel Mae MaestradoNo ratings yet
- Murray Secretion Scale and Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing FEESDocument7 pagesMurray Secretion Scale and Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing FEESjmunozsilvaNo ratings yet
- Flower RemedyDocument39 pagesFlower RemedyJayant Bodhe75% (4)
- ARS - 1909CT - FAHIM MD AZMAN RAHMAN (TP057341) - Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesARS - 1909CT - FAHIM MD AZMAN RAHMAN (TP057341) - Individual AssignmentFahim AzmanNo ratings yet
- Atls Notes and ScoresDocument2 pagesAtls Notes and ScoresElias SaeedNo ratings yet
- Indo Petroleum Nurse Grade II AdvertisementDocument4 pagesIndo Petroleum Nurse Grade II AdvertisementjaideepsdNo ratings yet
- Attwood MeltdownsDocument50 pagesAttwood MeltdownsGyorgyi Boros100% (1)