Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accessing Instance Variables and Methods:: "Passed Name Is:"
Accessing Instance Variables and Methods:: "Passed Name Is:"
Uploaded by
Rupendra SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accessing Instance Variables and Methods:: "Passed Name Is:"
Accessing Instance Variables and Methods:: "Passed Name Is:"
Uploaded by
Rupendra SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
public Puppy(String name){
// This constructor has one parameter, name.
System.out.println("Passed Name is :" + name );
}
public static void main(String []args){
// Following statement would create an object myPuppy
Puppy myPuppy = new Puppy( "tommy" );
}
}
If we compile and run the above program, then it would produce the following result:
Passed Name is :tommy
Accessing Instance Variables and Methods:
Instance variables and methods are accessed via created objects. To access an instance variable
the fully qualified path should be as follows:
/* First create an object */
ObjectReference = new Constructor();
/* Now call a variable as follows */
ObjectReference.variableName;
/* Now you can call a class method as follows */
ObjectReference.MethodName();
Example:
This example explains how to access instance variables and methods of a class:
public class Puppy{
int puppyAge;
public Puppy(String name){
// This constructor has one parameter, name.
System.out.println("Name chosen is :" + name );
}
public void setAge( int age ){
puppyAge = age;
}
public int getAge( ){
System.out.println("Puppy's age is :" + puppyAge );
return puppyAge;
}
public static void main(String []args){
/* Object creation */
Puppy myPuppy = new Puppy( "tommy" );
/* Call class method to set puppy's age */
myPuppy.setAge( 2 );
/* Call another class method to get puppy's age */
myPuppy.getAge( );
/* You can access instance variable as follows as well */
System.out.println("Variable Value :" + myPuppy.puppyAge );
}
}
If we compile and run the above program, then it would produce the following result:
Name chosen is :tommy
Puppy's age is :2
Variable Value :2
Source file declaration rules:
As the last part of this section let's now look into the source file declaration rules. These rules are
essential when declaring classes, import statements and package statements in a source file.
There can be only one public class per source file.
A source file can have multiple non public classes.
The public class name should be the name of the source file as well which should be
appended by .java at the end. For example: the class name is public class Employee{} then
the source file should be as Employee.java.
If the class is defined inside a package, then the package statement should be the first
statement in the source file.
If import statements are present then they must be written between the package statement
and the class declaration. If there are no package statements then the import statement
should be the first line in the source file.
Import and package statements will imply to all the classes present in the source file. It is not
possible to declare different import and/or package statements to different classes in the
source file.
Classes have several access levels and there are different types of classes; abstract classes, final
classes, etc. we will be explaining about all these in the access modifiers chapter.
Apart from the above mentioned types of classes, Java also has some special classes called Inner
classes and Anonymous classes.
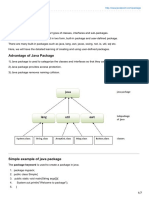
Java Package:
In simple, it is a way of categorizing the classes and interfaces. When developing applications in
Java, hundreds of classes and interfaces will be written, therefore categorizing these classes is a
must as well as makes life much easier.
Import statements:
In Java if a fully qualified name, which includes the package and the class name, is given then the
compiler can easily locate the source code or classes. Import statement is a way of giving the
proper location for the compiler to find that particular class.
For example, the following line would ask compiler to load all the classes available in directory
java_installation/java/io :
import java.io.*;
A Simple Case Study
For our case study, we will be creating two classes. They are Employee and EmployeeTest.
First open notepad and add the following code. Remember this is the Employee class and the class
is a public class. Now, save this source file with the name Employee.java.
The Employee class has four instance variables name, age, designation and salary. The class has
one explicitly defined constructor, which takes a parameter.
import java.io.*;
You might also like
- OEC One Service Manual SM 6888001-1EN 5Document319 pagesOEC One Service Manual SM 6888001-1EN 5victor100% (1)
- Accessing Instance Variables and MethodsDocument3 pagesAccessing Instance Variables and MethodsNazeeh RzeqatNo ratings yet
- Classes and ObjectsDocument10 pagesClasses and ObjectsMargerie FrueldaNo ratings yet
- Lo 1 - 1Document22 pagesLo 1 - 1LJames SacuezaNo ratings yet
- Java-Objects-and-Classe-xian 2Document7 pagesJava-Objects-and-Classe-xian 2Xian Manny MaraonNo ratings yet
- Java Object ClassesDocument6 pagesJava Object Classesraaz_101No ratings yet
- Java Classes and ObjectsDocument7 pagesJava Classes and ObjectsAngeline ChasakaraNo ratings yet
- Objects in Java:: Object - ClassDocument4 pagesObjects in Java:: Object - ClassUdaya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Java Object and ClassesDocument5 pagesJava Object and Classesshu2uNo ratings yet
- CS6501 All Units Notes 2013 RegulationDocument163 pagesCS6501 All Units Notes 2013 Regulationicon4jai_812980786No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PackageDocument10 pagesChapter 4 PackagespNo ratings yet
- Java - Object and ClassesDocument8 pagesJava - Object and ClassesMohammad AyathullaNo ratings yet
- Tutorialspoint Com Java Object ClassesDocument8 pagesTutorialspoint Com Java Object ClassesBima Sakti KrisdiantoNo ratings yet
- OOP Chapter - 2Document24 pagesOOP Chapter - 2eyuel haileNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Encapsulation, Packages and APIDocument7 pagesLecture 7 Encapsulation, Packages and APIRozzellyNo ratings yet
- Final, Package, Class PathDocument11 pagesFinal, Package, Class PathAnirban ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Access Modifiers Lect 4Document9 pagesAccess Modifiers Lect 4Onyango BernardNo ratings yet
- Java - Packages: Creating A PackageDocument4 pagesJava - Packages: Creating A PackageChalew ZeynuNo ratings yet
- Java Unit 3 and 4Document58 pagesJava Unit 3 and 4darknight978745No ratings yet
- Classes in JavaDocument9 pagesClasses in JavaShakuntala vidyalayaNo ratings yet
- Document From Kathawde KomalDocument80 pagesDocument From Kathawde KomalkomalkathawdeNo ratings yet
- Packageof JavaDocument11 pagesPackageof Javakumarishu125No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Inheritance and PolymorphismDocument7 pagesModule 3 - Inheritance and PolymorphismJeff LakiNo ratings yet
- 1 Java SRC File Structure & Import Nov8Document12 pages1 Java SRC File Structure & Import Nov8Sreedhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Java Suggestion Solving 2022Document26 pagesJava Suggestion Solving 2022choddobesh01No ratings yet
- Unit-2 JavaDocument12 pagesUnit-2 Javaamaraiah2012No ratings yet
- Java - PackagesDocument5 pagesJava - PackagesVarun VermaNo ratings yet
- Java Packages PDFDocument5 pagesJava Packages PDFprod chitixNo ratings yet
- Packages in Java and How To Use ThemDocument10 pagesPackages in Java and How To Use ThemDuaa HusseinNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 HTML: Assignment No. 2Document6 pagesTopic 6 HTML: Assignment No. 2Varsha PatilNo ratings yet
- Week011-012-Presentation-Inheritance, Polymorphism and InterfacesDocument44 pagesWeek011-012-Presentation-Inheritance, Polymorphism and InterfacesEmmanuel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6.java (1)Document4 pagesAssignment 6.java (1)veera.deva.0110No ratings yet
- Java PackageDocument68 pagesJava Packagedegadisa104No ratings yet
- Interface Package-1Document24 pagesInterface Package-1rachana saiNo ratings yet
- Basic Java Keywords Explained - Debriefing: PackageDocument4 pagesBasic Java Keywords Explained - Debriefing: PackageJakobb GlootzNo ratings yet
- From ConstructorsDocument28 pagesFrom ConstructorsranjithdesiganNo ratings yet
- 3 AccessAndReuse 1Document36 pages3 AccessAndReuse 1Kami KhanNo ratings yet
- Java Lab Sessions-CSL 201: 1 Intro 2 (3 4)Document20 pagesJava Lab Sessions-CSL 201: 1 Intro 2 (3 4)Cuti MartinaNo ratings yet
- Constructors: Public Class Public PublicDocument2 pagesConstructors: Public Class Public PublicNazeeh RzeqatNo ratings yet
- Java Unit 2Document46 pagesJava Unit 2Shanmukha RaoNo ratings yet
- PackagesDocument6 pagesPackagesHarendra TomarNo ratings yet
- CSC 208 Java ProgrammingDocument15 pagesCSC 208 Java ProgrammingOlamiposi EluwandeNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument20 pagesSolutionSmreeta ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note-6 On JavaDocument71 pagesLecture Note-6 On JavagauravNo ratings yet
- Access Modi FersDocument16 pagesAccess Modi Ferssanket gadakhNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument55 pagesJavapssweatha_561166115No ratings yet
- Packages: Package Com - Javajee.exampleDocument11 pagesPackages: Package Com - Javajee.examplepeter fernandoNo ratings yet
- Declarations and Access ModifiersDocument4 pagesDeclarations and Access ModifiersSam AltafNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument43 pagesUnit Iiiuday franklinNo ratings yet
- Types of Java PackageDocument10 pagesTypes of Java Package.No ratings yet
- Packages N InterfacesDocument31 pagesPackages N InterfacesAnupam SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Java API PackageDocument8 pagesJava API Packagemahima yadavNo ratings yet
- PackagesDocument6 pagesPackagesvoila.albertoNo ratings yet
- Why Use Inheritance in Java: Class: Sub Class/Child Class: Super Class/Parent Class: ReusabilityDocument11 pagesWhy Use Inheritance in Java: Class: Sub Class/Child Class: Super Class/Parent Class: ReusabilityHarshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Skill Programming EXPT 5Document4 pagesSkill Programming EXPT 5mayanksanjay70No ratings yet
- Java PackageDocument7 pagesJava PackageBezimenaNo ratings yet
- What Is Package in JavaDocument6 pagesWhat Is Package in JavaVarmaNo ratings yet
- Java Package Session 10Document6 pagesJava Package Session 10arifmohammad7567No ratings yet
- Encapsulation: Access Private MembersDocument11 pagesEncapsulation: Access Private MembersKimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Advantage of Java PackageDocument9 pagesAdvantage of Java PackageVenu DNo ratings yet
- Java Programming Tutorial With Screen Shots & Many Code ExampleFrom EverandJava Programming Tutorial With Screen Shots & Many Code ExampleNo ratings yet
- Atellica UAS 800 LIS Guide EN Rev G DXDCM 09017fe980617b45 1642093257066Document53 pagesAtellica UAS 800 LIS Guide EN Rev G DXDCM 09017fe980617b45 1642093257066Mukhtar ZakirovNo ratings yet
- Apple Inc Class DiscussionDocument34 pagesApple Inc Class DiscussionmdnhllNo ratings yet
- Stanford ResumeDocument1 pageStanford ResumeUser140035No ratings yet
- Ladbrokes BettingDocument18 pagesLadbrokes BettingLevel BusinessNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Honeywell Video Technology Helps Protect Largest Privately-Funded Construction Project in U.S. HistoryDocument2 pagesCase Study: Honeywell Video Technology Helps Protect Largest Privately-Funded Construction Project in U.S. History0 HourNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social MediaDocument55 pagesImpact of Social Mediashljins smNo ratings yet
- MNFSTDocument39 pagesMNFSTImBotNo ratings yet
- Repair Autocom CDP VciDocument5 pagesRepair Autocom CDP Vcimati881No ratings yet
- Solutions) Mastering Physics HW7Document5 pagesSolutions) Mastering Physics HW7rubik1771No ratings yet
- AVSR Project ReportDocument62 pagesAVSR Project ReportPrajwal Gowda LNo ratings yet
- Free AutoCAD Tutorials - Boolean - Union, Subtract, in AutoCAD 2010 2012 2013Document6 pagesFree AutoCAD Tutorials - Boolean - Union, Subtract, in AutoCAD 2010 2012 2013Vivian KallouNo ratings yet
- Four Layer Diode or SchockleyDocument6 pagesFour Layer Diode or SchockleyJayson Orias100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Doolittle MethodDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Doolittle MethodQuốc Khởi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Centralizing Patient Monitoring System in Real Time: Engr. Junaid Rabbai Assistant ProfessorDocument5 pagesCentralizing Patient Monitoring System in Real Time: Engr. Junaid Rabbai Assistant ProfessorM Kamal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Consulting Brochure enDocument12 pagesConsulting Brochure enbhargavNo ratings yet
- IHP MalaysiaDocument29 pagesIHP MalaysiaaimanabuzarrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 26Document4 pagesLecture 26Rishi SahuNo ratings yet
- EEK ATA Lance: P2/V1/SWG2 TY C++ in 21 Days 31240-9 Marcia 7.9.98 FM LP#2Document15 pagesEEK ATA Lance: P2/V1/SWG2 TY C++ in 21 Days 31240-9 Marcia 7.9.98 FM LP#2Abdulganiyu TeslimNo ratings yet
- f1 BH1747NUC E2Document372 pagesf1 BH1747NUC E2h_878236333No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 94062Document37 pagesChapter 1 94062Yechale TafereNo ratings yet
- Ina 236Document44 pagesIna 236NikitaNo ratings yet
- Delta Ia-Plc All Ul 20230530Document6 pagesDelta Ia-Plc All Ul 20230530gilberto.852021No ratings yet
- What Is Domain Authority?Document2 pagesWhat Is Domain Authority?Ubaid JuttNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Numerical Analysis: Volume I, Finite Difference Method I, Solutions of Equations in R N (RN) IDocument651 pagesHandbook of Numerical Analysis: Volume I, Finite Difference Method I, Solutions of Equations in R N (RN) IRivo Carapucci100% (1)
- LogDocument8 pagesLognikitaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Self Taught Well Summarized Lecture Notes With Relevant Examples For BetterDocument31 pagesCalculus Self Taught Well Summarized Lecture Notes With Relevant Examples For BetterApril IngramNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Hybrid Cloud For Enterprise ArchitectsDocument8 pagesMicrosoft Hybrid Cloud For Enterprise ArchitectssplfriendsNo ratings yet
- CM20200602 cc68c 59114Document22 pagesCM20200602 cc68c 59114olivier.2.gagnonNo ratings yet
- SolidThinking Evolve BrochureDocument6 pagesSolidThinking Evolve BrochureRakesh Patel MageriNo ratings yet