Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cost Behavior
Cost Behavior
Uploaded by
Jhen Nazarro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pages1. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of activity level, variable costs change proportionately with activity level, and mixed costs have both fixed and variable components.
2. Resources can be flexible, committed, or step costs depending on how and when they are acquired and their relationship to excess capacity and cost behavior.
3. Costs can be estimated using methods like time-motion studies, account analysis, or regression analysis of cost data against a driver variable.
Original Description:
stratcost
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of activity level, variable costs change proportionately with activity level, and mixed costs have both fixed and variable components.
2. Resources can be flexible, committed, or step costs depending on how and when they are acquired and their relationship to excess capacity and cost behavior.
3. Costs can be estimated using methods like time-motion studies, account analysis, or regression analysis of cost data against a driver variable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesCost Behavior
Cost Behavior
Uploaded by
Jhen Nazarro1. Fixed costs remain constant regardless of activity level, variable costs change proportionately with activity level, and mixed costs have both fixed and variable components.
2. Resources can be flexible, committed, or step costs depending on how and when they are acquired and their relationship to excess capacity and cost behavior.
3. Costs can be estimated using methods like time-motion studies, account analysis, or regression analysis of cost data against a driver variable.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1.Define and describe fixed, variable, and mixed costs.
o Variable costs change in total as activity usage changes.
o Usually, variable costs increase in direct proportion to increases in
activity output.
o Fixed costs do not change in total as activity output changes.
o Mixed costs have both a variable and a fixed component.
2.Explain the use of resources and activities and their relationship to cost
behavior.
o Flexible resources are acquired as used and needed.
Flexible resources have no excess capacity for these resources.
They are usually considered to be variable costs.
o Committed resources are acquired in advance of usage.
May have excess capacity
Frequently considered fixed
o Step costs are acquired in lumpy amounts.
Narrow steps approximated by a variable cost function
Wide steps approximated as fixed
3.Explain how several methods of cost estimation can be used.
o The industrial engineering method uses physical observation and
analysis to determine what activities in what amounts are needed to
complete a process.
Time and motion studies may be used
Typically expensive and seldom updated
o Account analysis requires the accountant to classify accounts as
either fixed or variable.
Frequently used in practice
Gives good results if accounts are primarily fixed costs or
variable costs
Average account values and average driver values are used to
calculate fixed costs and variable rates
4.Separate mixed costs into their fixed and variable components using the
high-low method, the scatterplot method, and the method of least squares.
o High-low method uses the high and the low data points to form a
straight line.
Slope is variable rate.
Intercept is fixed cost.
Advantages: objective and easy
Disadvantage: nonrepresentative high or low point leads to
misestimated cost function
o Scatterplot method plots data—two points chosen to determine a
line.
Intercept is fixed cost.
Slope is variable rate.
Advantages: identify nonlinearity, outliers, shifts in the cost
relationship
Disadvantage: subjectivity
o OLS (regression) produces a best-fitting line.
5.Evaluate the reliability of the cost formula.
o Coefficient of correlation shows degree to which two variables move
together.
Perfect positive correlation is 1.0.
Perfect negative correlation is −1.0.
o Coefficient of determination shows amount of cost variability
explained by driver.
Often multiplied by 100 and used as percent
o Smaller standard errors of estimate indicate better goodness of fit.
6.Explain how multiple regression can be used to assess cost behavior.
o Has two or more independent variables
o Useful when dependent variable is affected by more than one
independent variable
7.Define the learning curve, and discuss its impact on cost behavior.
o Nonlinear relationship between labor hours and output.
o Doubling of output requires less than a doubling of labor time.
o Cumulative average-time learning curve assumes the cumulative
average time per unit decreases by a constant percentage, or
learning rate, each time the cumulative quantity of units produced
doubles.
o Incremental unit-time learning curve assumes the incremental unit
time decreases by a constant percentage each time the cumulative
quantity of units produced doubles.
8.Discuss the use of managerial judgment in determining cost behavior.
o Used alone or in conjunction with the high-low, scatterplot, or least-
squares methods
o Experienced managers use knowledge of cost and activity-level
relationships to:
Identify outliers
Understand structural shifts
Adjust parameters due to anticipated changing conditions
You might also like
- Solution Manual, Managerial Accounting Hansen Mowen 8th Editions - CH 3Document34 pagesSolution Manual, Managerial Accounting Hansen Mowen 8th Editions - CH 3jasperkennedy084% (25)
- Chapter 11 - AnswerDocument31 pagesChapter 11 - AnsweragnesNo ratings yet
- Stuxnet and Its Hidden Lessons On The Ethics of CyberweaponsDocument9 pagesStuxnet and Its Hidden Lessons On The Ethics of CyberweaponsprofcameloNo ratings yet
- Katherine Byrne, Tuberculosis and The Victorian: Literary ImaginationDocument5 pagesKatherine Byrne, Tuberculosis and The Victorian: Literary ImaginationMaria Eliza GiuboruncaNo ratings yet
- Report On Cost EstimationDocument41 pagesReport On Cost EstimationTuhin SamirNo ratings yet
- D75 14Document8 pagesD75 14JorgeCalvoLara100% (2)
- Black Drama Results: Act 1, Scene 1: Imprisonment of A ShadowDocument15 pagesBlack Drama Results: Act 1, Scene 1: Imprisonment of A Shadowjohn7tago100% (2)
- CHAPTER 3 Activity Cost BehaviorDocument28 pagesCHAPTER 3 Activity Cost BehaviorMudassar Hassan100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Answer Cost AccountingDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Answer Cost AccountingJuline Ashley A CarballoNo ratings yet
- HORN Ch10 SMDocument78 pagesHORN Ch10 SMjoyvai3356No ratings yet
- Cost Behaviour: Discussion QuestionsDocument35 pagesCost Behaviour: Discussion QuestionsParth GandhiNo ratings yet
- Man AccDocument2 pagesMan AccJelay QuilatanNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument21 pagesCh04 Cost Volume Profit Analysiszoe regina castroNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Management Accounting (Volume I) - Solutions ManualDocument19 pagesCost Behavior: Analysis and Use: Management Accounting (Volume I) - Solutions ManualYella Mae Pariña RelosNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument21 pagesCh04 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisYee Sook Ying0% (1)
- Chapter 3 AnswerDocument16 pagesChapter 3 AnswerSia DLSLNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Reviewed - RecordedDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Reviewed - Recordeds11186706No ratings yet
- Solution Manual - Chapter 10Document9 pagesSolution Manual - Chapter 10psrikanthmbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document6 pagesChapter 10Arda Raditya TantraNo ratings yet
- Cost EstimationDocument22 pagesCost EstimationJane DizonNo ratings yet
- TerbaruuuuuuuDocument8 pagesTerbaruuuuuuuNovi RofaNo ratings yet
- Activity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument60 pagesActivity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsGanesh ShankarNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior: Discussion QuestionsDocument44 pagesCost Behavior: Discussion QuestionsFaiz LuthfiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 - AnswerDocument30 pagesChapter 09 - Answerlooter198No ratings yet
- 1 - Cost EstimationDocument22 pages1 - Cost EstimationAbigail PadillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Cost Estimation: Total CostsDocument2 pagesChapter Five: Cost Estimation: Total CostsPattraniteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Answer Cost Accounting PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Answer Cost Accounting PDFCris VillarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CacDocument16 pagesChapter 3 CacDecimNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting - NORAIMAN ROSLIMDocument15 pagesManagerial Accounting - NORAIMAN ROSLIMAiman RoslimNo ratings yet
- Chap 011Document16 pagesChap 011Ahmed A HakimNo ratings yet
- MS 3402 Costs Behavior Determination and PredictionDocument5 pagesMS 3402 Costs Behavior Determination and PredictionMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concept Continuation Lesson Proper: The Analysis of Mixed CostsDocument5 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concept Continuation Lesson Proper: The Analysis of Mixed CostsStephanie AndalNo ratings yet
- Cost Behavior Analysis and UseDocument3 pagesCost Behavior Analysis and Usepablopaul56No ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting by James JiambalvoDocument27 pagesManagerial Accounting by James JiambalvoPooja Grover ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 08 - Forecasting TechniquesDocument20 pagesTutorial 08 - Forecasting TechniquesChanil KarunaratneNo ratings yet
- L8 Cma1Document53 pagesL8 Cma11234778No ratings yet
- Cost Estimation: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument17 pagesCost Estimation: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinAtef RagabNo ratings yet
- Cost EstimationDocument16 pagesCost EstimationNagendran NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing ManuscriptDocument6 pagesVariable Costing ManuscriptDave Alex Reyes MercadoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument54 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementnarunsankarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Cost Drivers & Cost BehaviorsDocument19 pagesChapter 5 - Cost Drivers & Cost BehaviorshthutamuralikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter03 Solutions Hansen Mowen Cost Behavior Sixth Edition PDFDocument18 pagesChapter03 Solutions Hansen Mowen Cost Behavior Sixth Edition PDFRose Ann Moraga FrancoNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Managerial Accounting Decision Making and Motivating PerformanceDocument41 pagesSolutions Manual To Accompany Managerial Accounting Decision Making and Motivating PerformanceJacobTorreswasmxNo ratings yet
- im_ch03Document7 pagesim_ch03Lena RingoNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and Cost Concept Continuation Lesson Proper: The Analysis of Mixed CostsDocument5 pagesManagerial Accounting and Cost Concept Continuation Lesson Proper: The Analysis of Mixed CostsGladymae MaggayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument5 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro Davaoace ender zeroNo ratings yet
- Mowen2e PP Ch03Document47 pagesMowen2e PP Ch03DaveNo ratings yet
- Chap 006Document11 pagesChap 006Judy Anne SalucopNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Fundamental Cornerstones of Managerial Accounting 1st Edition Heitger IRM13Document11 pagesSolution Manual For Fundamental Cornerstones of Managerial Accounting 1st Edition Heitger IRM13Quynh DuongNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cost Behavior (Analysis and Uses)Document17 pagesLecture 3 - Cost Behavior (Analysis and Uses)RODOLFO AUSTRIA JR.No ratings yet
- Steps of Developing A Cost Estimating RelationshipDocument2 pagesSteps of Developing A Cost Estimating RelationshipSenelwa AnayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 How Costs Behave PowerpointDocument45 pagesChapter 10 How Costs Behave PowerpointNCTNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument33 pagesUnit 3 Notessjanani.bme2021No ratings yet
- Horngren - Ca16 - PPT - 10 - Determininng HowCosts BehaveDocument47 pagesHorngren - Ca16 - PPT - 10 - Determininng HowCosts Behavemuhamad fattah alfajriNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Management Accounting: Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas AndalasDocument8 pagesStandard Costing Management Accounting: Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas AndalassintaNo ratings yet
- Akmen Bab 3Document3 pagesAkmen Bab 3Hafizh GalihNo ratings yet
- NOTES CHAPTER V Cost EstimationDocument10 pagesNOTES CHAPTER V Cost EstimationHanna CasasNo ratings yet
- CVPDocument20 pagesCVPThomas K. AddaiNo ratings yet
- PM - Budgeting and ControlDocument24 pagesPM - Budgeting and Controljohn markNo ratings yet
- Finance for Non-Financiers 2: Professional FinancesFrom EverandFinance for Non-Financiers 2: Professional FinancesNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Financial Derivative and Energy Market Valuation: Theory and Implementation in MATLABFrom EverandFinancial Derivative and Energy Market Valuation: Theory and Implementation in MATLABRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (1)
- Umbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesUmbilical Cord Coiling: Case Report and Review of LiteratureHesti hasanNo ratings yet
- Questions Energy Surfaces and Spontaneous ReactionsDocument2 pagesQuestions Energy Surfaces and Spontaneous Reactionshernys NietoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Managing Quality: 07/20/2022 1 Arsi University Om Mba-2020Document33 pagesChapter 7-Managing Quality: 07/20/2022 1 Arsi University Om Mba-2020temesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- Product Demo Feedback FormDocument1 pageProduct Demo Feedback FormVarunSharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit3&4 Network TheoramsDocument73 pagesUnit3&4 Network TheoramsBALAKRISHNA PERALANo ratings yet
- Dap An - DE CUONG - ANH 8Document5 pagesDap An - DE CUONG - ANH 8KienNo ratings yet
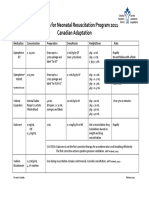
- Medications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationDocument1 pageMedications For Neonatal Resuscitation Program 2011 Canadian AdaptationrubymayNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics PDFDocument2 pagesComputer Graphics PDFAakash KhannaNo ratings yet
- Jeab 1 PsDocument20 pagesJeab 1 PsDharmveer KumarNo ratings yet
- Recalls 10 - Np2Document6 pagesRecalls 10 - Np2Nova Clea BoquilonNo ratings yet
- Sprovieri (Final Assignment)Document9 pagesSprovieri (Final Assignment)Paulo Thiago SprovieriNo ratings yet
- BDD A29045Document9 pagesBDD A29045Laur LaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Kenya Institute of Business and Counselling StudiesDocument16 pagesKenya Institute of Business and Counselling StudiesEdwine Jeremiah ONo ratings yet
- Techniques & Structure PDFDocument6 pagesTechniques & Structure PDFfrank sinatraaNo ratings yet
- PVC Foam Furniture Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPVC Foam Furniture Sheet PDFAbdul Majid100% (1)
- ISBB CompilationDocument6 pagesISBB CompilationElla SalesNo ratings yet
- Section A - QuestionsDocument27 pagesSection A - Questionsnek_akhtar87250% (1)
- Measuring Strain in RocksDocument2 pagesMeasuring Strain in Rocksdarebusi1No ratings yet
- NIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 EmotionsDocument4 pagesNIOS Class 12 Psychology Chapter 10 Emotionsmanahil dollNo ratings yet
- 21 Problems For CB NewDocument31 pages21 Problems For CB NewNguyễn Thảo MyNo ratings yet
- New Record TDocument2 pagesNew Record Tapi-309280225No ratings yet
- Page 5 of 48: Assignment On Garment Manufacturing - Quality Control PDFDocument50 pagesPage 5 of 48: Assignment On Garment Manufacturing - Quality Control PDFShivangi RajouriyaNo ratings yet
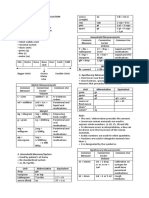
- Metric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseDocument4 pagesMetric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Aegis - Designer and AnalyzerDocument26 pagesAegis - Designer and Analyzeropenid_S1hHcZODNo ratings yet
- Emerging Global Trends in Iot: (Internet of Things)Document28 pagesEmerging Global Trends in Iot: (Internet of Things)EkoPandaraNo ratings yet
- A Meta-Analysis of Motivational Interviewing Twenty-Five Years of Empirical StudiesDocument24 pagesA Meta-Analysis of Motivational Interviewing Twenty-Five Years of Empirical StudiesJavieraRamírezSánchezNo ratings yet