Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fuels and Combustion Problems
Fuels and Combustion Problems
Uploaded by
Deniell Joyce Marquez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
213 views10 pages1. The apparatus used in the analysis of combustible gases is an Orsat's apparatus, which is used for volumetric analysis of the flue gas.
2. Incomplete combustion of carbon in fuels forms carbon monoxide.
3. A gas produced during combustion of fuel oil that cannot be found in flue gases is hydrogen.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The apparatus used in the analysis of combustible gases is an Orsat's apparatus, which is used for volumetric analysis of the flue gas.
2. Incomplete combustion of carbon in fuels forms carbon monoxide.
3. A gas produced during combustion of fuel oil that cannot be found in flue gases is hydrogen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
213 views10 pagesFuels and Combustion Problems
Fuels and Combustion Problems
Uploaded by
Deniell Joyce Marquez1. The apparatus used in the analysis of combustible gases is an Orsat's apparatus, which is used for volumetric analysis of the flue gas.
2. Incomplete combustion of carbon in fuels forms carbon monoxide.
3. A gas produced during combustion of fuel oil that cannot be found in flue gases is hydrogen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 10
CHAPTER 2 FUEL & A.
2 mols carbon dioxide temperature and velocities) to
COMBUSTION B. 1 mol carbon dioxide fuse together to form a
C. 1 mol carbon and 1 mol heavier nucleus the process
1. PAST ME BOARD carbon dioxide is called ___________.
QUESTION D. 1 mol carbon dioxide
Which is not a viscosity A. Fusion
rating? 7. ME BOARD QUESTION B. Fission
What are the immediate C. The photoelectric effect
A. Redwood undesirable product from the D. The Compton effect
B. SSU petroleum based lubricating 13. What is the residue left after
C. Centipoise oil when subjected to high combustion of a fossil fuel?
D. Entropy Degrees API pressure and temperature?
A. Charcoal
2. PAST ME BOARD A. Gums, resins and acids B. Ash
QUESTION B. Sulfer C. Scrapper
Percent excess air is the C. Soots and ashes D. All of the choices
difference between the air D. Carbon residue
actually supplied and the 14. What is formed during
theoretical required divided 8. What kind of bonding do incomplete combustion of
by common gases that exist in carbon in fuels?
free state as diatomic
A. The theoretically air molecules experiences? A. Carbon dioxide
supplied B. Carbon monoxide
B. The actually air supplied A. Ionic bonds C. Nitrogen oxide
C. The deficiency of air B. Covalent bonds D. Oxygenated fuel
supplied C. Metallic bonds
D. The sufficient air D. Nuclear bonds 15. A gas produced by the
supplied
combustion of fuel oil and
9. An Orsat’s apparatus is used cannot be found in the flue
3. ME BOARD QUESTION for gases is:
What is the apparatus used in
the analysis of combustible A. volumetric analysis of the
gases? flue gas A. Oxygen
B. gravimetric analysis of the B. Nitrogen
A. Calorimeter differential flue gas C. Hydrogen
B. Calorimeter gas C. smoke density analysis of D. Carbon dioxide
C. Calorimetry the flue gas
D. Calorimeter D. all of the above 16. Which of the following
chemical reaction in which
4. PAST ME BOARD 10. A theorem that states that the heat is absorbed?
QUESTION total property of a mixture of
Percent excess air is the ideal gases is the sum of the A. Heat reaction
difference between the air properties that the individual B. Endothermic reaction
actually supplied and the gases would have if each C. Exothermic reaction
theoretical air divided by occupied the total mixture D. Combustion reaction
volume alone as the same
A. The sufficient air temperature. 17. A chemical reaction in which
supplied heat is given off.
B. The deficiency air A. Gibbs theorem
supplied B. Dalton’s theorem A. Heat reaction
C. The actually air supplied C. Boltzmannn’s theorem B. Endothermic reaction
D. The theoretically air D. Maxwell’s theorem C. Exothermic reaction
supplied D. Combustion reaction
11. A small enough particles
5. PAST ME BOARD suspended in a fluid will 18. A colorless, odorless mixture
QUESTION exhibit small random of nitrogen and oxygen, with
The viscosity of most movement due to the traces of other gases water
commercially available statistical collision of fluid vapor and same impurities.
petroleum lubricating oil molecules in the particle’s
changes rapidly above surface. This motion is called A. Air
______. B. Helium
A.120°F
C. Water gas
B. 180°F A. Boltzmann motion D. Nitrite
C. 150°F B. Rectilinear motion
D. 130°F C. Kinetic gas motion
6. PAST ME BOARD D. Brownian motion 19. The transfer of air and air
QUESTION characteristics by horizontal
When 1 mol carbon combines 12. When two or more light atoms motion is called __________.
with 1 mol oxygen have sufficient energy
(available only at high A. convection
B. air transfer B. Soot
C. Advection 26. The increase in velocity past C. Residue
D. Adhesion the throat is due to the rapid D. All of the choices
decrease in fire:
20. Properties of non – reaction 33. Rare gases such as helium,
gas mixtures are given by: A. Fluid density argon, krypton, xenon and
B. Fluid specific volume radon that are non - reactive
A. Geometric weighting C. Fluid temperature are called ________.
B. Volumetric weighting D. Fluid pressure
C. Volumetric weighting for A. Non – reactants
molecular weight and B. Stop gases
density, and geometric 27. In an oxidation – reduction
chemical reaction, all of the C. Inert gases
weighting for all other D. Residual gases
properties except entropy following occur except:
D. Arithmetic average
A. the exchange of electrons 34. Kinematics and dynamic
between elements viscosity vary from each other
21. The process of separating B. elements becoming more only by a factor equal to the :
two or more liquids by means positive
of the difference in their C. elements becoming more A. Fluid density
boiling point. negative B. Temperature
D. Nuclear fusion C. Pressure
A. Engler distillation D. Specific gas constant
B. fractional distillation 28. The residual oil left after the
C. Gas scrubbing distillation of gasoline and
D. Fractional crystallization 35. The following properties are
kerosene from crude different for isomers of the
petroleum; yellow to brown same chemical compound
22. The gaseous products of oil, used as a diesel fuel and
combustion of a boiler which except:
for enriching water gas.
contains carbon dioxide,
carbon monoxide. Oxygen, A. Density
A. Diesel oil B. Melting point
nitrogen and water vapor is B. Gasoline oil
called ___________. C. Number of atoms in a
C. LPG mole of each isomers
D. Gas oil D. Specific heat
A. Flue gas
B. Producer gas
C. Product gas 29. A fuel gas is obtained by the 36. Atomic weight of the
D. Universal gas destructive distillation of soft elements in the periodic table
coal is called _______. are not whole numbers
23. A substance whose burning because of:
A. Gas scrub
with oxygen yields heat B. Coal gas
energy as coal, petroleum A. The existence of
C. Alcogas isotopes
and natural gas. D. Water gas B. Imprecise measurements
during the development
A. Air 30. Removing of impurities from a of the periodic table
B. Fluid gas by bubbling it through a C. Round – off error in
C. Fuel liquid purifying agent is called calculating atomic
D. Gas _______. weights
D. The exchange of
24. Stoichiometric ratio is A. Gas Scrubbing reference of the atomic
B. Gas Purifying mass unit from oxygen
A. Chemically correct air - C. Gas Liquefying -16 to carbon -12 in 1961
fuel ratio by volume D. Gas Bubbling 37. The tendency of a pure
B. Chemically correct air – compound to be composed of
fuel ratio by weight the same element combined
31. During the fusion process , in a definite proportion by
C. Theoretical mixture of air mass is lost and converted to
for complete combustion mass.
energy according to:
D. Actual ratio of air to fuel
for maximum efficiency A. The Heisenburg A. Avogadro’s law
uncertainty principle B. Boyle’s law
25. A type of radiation consisting B. The Compton’s law C. The law of definite
of singly charged particles C. Einstein’s law proportions
that generate to intermediate D. The second law of D. Le Chatelier’s principle
distances. thermodynamics
32. A finely divided carbon 38. How do you call the process
A. Nuclear Radiation deposit by the smoke or of removing of impurities from
B. Alpha Radiation flame is called _________. a gas by bubbling it through a
C. Beta Radiation liquid purifying agent?
D. Gamma Radiation A. Fly ash
A. Gas Scrubbing C. Two stroke engine
B. Gas Purifying A. There is an excess of D. Four stroke engine
C. Gas Liquefying one or more reactants
D. Gas Bubbling B. The percentage yield 52. ME BOARD QUESTION
measures the efficiency Which of the following does
39. What is the effect of a of the reaction not belong to the group?
catalyst in a chemical C. Non – Stoichiometric
reaction? reaction are rare in the A. Air injection system
combustion process B. Mechanical injection
A. Absorb the exothermic D. In combustion, air is system
heat of reaction often the excess reactant C. Time injection system
B. Provide the exothermic to assure complete D. Gas admission system
heat of reaction combustion of fuel
C. Lower the activation 53. ME BOARD QUESTION
energy 46. It is the ratio of the volume at Specific heat capacity is an SI
D. Provide the heat of the end of heat addition to the derived unit described as:
sublimation volume at the start of heat
addition. A. J/kg
40. The relationship between the B. W/m*K
concentration of products and A. Compression ratio C. J/m3
reactants in a reversible B. Air- fuel ratio D. J/kg*K
chemical reaction given by C. Volumetric ratio
D. Cut-off ratio 54. ME BOARD QUESTION
A. The ionization constant A device whose primary
B. The equilibrium constant 47. Piston rings are made of: function is to meter the flow of
C. The solubility product refrigerant to the evaporator.
D. Le Chatelier’s principle A. Alloy steel
B. Carbon steel A. Sniffer valve
C. Copper B. Equalizer
41. What fuel gas obtained by the D. Cast iron
destructive distillation of soft C. Thermostatic expansion
coal? valve
48. ME BOARD QUESTION D. Crossover valve
A. Gas scrub Loss power is due to:
B. Coal gas 55. ME BOARD QUESTION
C. Alcogas A. Poor compression The internal combustion
D. Water gas B. Restricted exhaust engines never work in
C. Clogging of air cleaner
D. Low injection pressure A. Rankine cycle
42. The process of splitting the
nucleaus into smaller B. Diesel cycle
49. ME BOARD QUESTION C. Dual combustion cycle
fragments. A branch system of pipes to D. Otto cycle
carry waste emission away
A. Fusion from the piston chambers of
B. Fission an internal combustion 56. The general chemical formula
C. The photoelectric effect engine is called for all hydrocarbons is CnHm.
D. The Compton effect In different combination of
A. Exhaust nozzle interest, as internal
43. The ash that is removed from B. Exhaust deflection pipe combustion engine fuel, n
the combustor after the fuel is C. Exhaust pipe varies from:
burn is the : D. Exhaust manifold
A. 1 to 26
A. Fly ash B. 2 to 54
B. Bottom ash 50. ME BOARD QUESTION C. 2 to 26
C. Scraper ash The type of filter where the D. 1 to 54
D. Top ash filtering element is
replaceable.
57. The general chemical formula
44. A mixture of hydrogen and for all hydrocarbons is CnHm.
carbon monoxide made by A. Paper edge filter
B. Metal edge filter In different combination of
passing steam over how interest, as internal
coke. C. Pressure filter
D. Filter with element combustion engine fuel, m
varies from:
A. Water gas
B. Water vapor 51. ME BOARD QUESTION A. 1 to 26
C. Hydrocarbon When four events takes place B. 2 to 54
D. Air in one revolution of a C. 2 to 26
crankshaft of an engine, the D. 1 to 54
engine is called:
45. All of the following are true of
non-stoichiometric reactions A. Rotary engine
except B. Steam engine
58. The general chemical 65. Hydrocarbons with 5 to 15 B. In the range 60 – 80
formula of a paraffin fuel is carbon atoms are to as : percent
C. Below 60 percent
A. CnH2n A. Light oils D. Between 95% and 100%
B. CnH2n-6 B. Heavy oils
C. CnH2n+2 C. Commercial fuels 72. Volumetric efficiency of a
D. CnH2n-2 D. Lubrication oils well designed engine may be
in the range of:
59. Naphthenes and olefins are 66. In A four stroke engine if a
types of hydro carbons with valve opens 25° before a. 75 to 90 percent
chemical formula of: B.D.C. and close 10° after b. 60 to 75 percent
T.D.C. the valve should be: c. 30 to 50 percent
A. CnH2n d. Below 30 percent
B. CnH2n-6 A. Puppet Valve
C. CnH2n+2 B. Exhaust Valve 73. During idling in a
D. CnH2n-2 C. Inlet Valve compression ignition engine
D. Spring Valve the air fuel ratio may be of the
60. Which of the following types order of :
of hydrocarbons have 67. In a hot wire anemometer the
chemical formula of CnH2n+2? rate of heat loss from sensing A. 30
element is function of: B. 200
C. 150
A. Diolefins A. Mass rate of flow D. 100
B. Aromatics B. Pressure
C. Asphaltics C. Velocity of flow 74. Vapor lock is
D. Paraffins D. All of above
A. Lock of vaporization of
61. Which of the following types 68. Sticking valves fuel to atmospheric
of hydrocarbons have pressure
chemical formula of CnH2n-4? A. Valve tappet clearance B. Excess fuel supply to
incorrect engine because of faster
A. Diolefins B. Valve springs of evaporation
B. Aromatics defective material C. Complete or partial
C. Asphaltics C. Valve guides gummed stoppage of fuel supply
D. Paraffins D. Lubricating oil of poor because of vaporization
quality of fuel in supply steam
62. Which is the chemical formula D. Locking carburetor jets
of an Aromatic type of because of vapor
69. Detonation of pinging noise is pressure
hydrocarbon fuel? due to :
A. CnH2n-6 75. Flash point of liquids is the
B. CnH2n-2 A. Early timing of fuel temperature at which:
C. CnH2n injection
D. CnH2n+2 B. Late timing of fuel A. The fuel emits vapor at a
injection rate which produces an
C. Head of piston inflammable mixture with
63. At atmospheric condition, carbonized
hydrocarbon molecules with a air
D. Valve springs weak or B. The fuel spontaneously
low number of carbon atoms, broken
1 to 4 are ignites
C. The fuel ignites with
A. Liquids 70. The thermal efficiency of a clearly visible flash
B. Atomic dual cycle engine with fixed D. The fuel ignites without
C. Gases compression ratio and fixed spark
D. Light oils quantity of heat and with
increase in pressure ratio, will 76. The mean effective pressure
64. Hydrocarbons with 5 to 15 of a diesel cycle having fixed
A. Increase compression ratio will
carbon atoms are: B. Remain same increase if cut off ratio is
C. Decrease
A. More or less volatile light D. Depends on the other A. Increased
oils factors B. Decreased
B. Referred to as heavy oils C. Independent of
C. Mixtures of many kinds 71. Scavenging efficiency of a compression ratio
of hydrocarbons four stroke diesel engine is: D. Depends on other factor
D. Commercial fuels
A. In the range 80 – 95 77. Hot spots
percent
A. Do not exist in engines
B. are the hottest spots in C. Two isentropic, one D. Front wheel
engines constant volume and one
C. are the spots where constant pressure 90. Odometer is:
heavier function of fuel processes A. An instrument that
are vaporized D. Two constant pressure, indicates the condition of
D. are the defects in S.I. in one constant volume, the battery
engines and one isothermal B. An instrument used for
processes measurement of fuel
78. Flash point for diesel fuel oil consumption
should be: 84. Which is not correct for C. An instrument used for
calculating air standard BHP measurement
A. Maximum 49°C efficiency? D. An instrument used for
B. Maximum 490°C distance measurement
C. Maximum 200°C A. All processes are
D. Maximum 300°C reversible 91. Automobile radiator is filled
B. Specific heat remains with:
79. Morse test is conducted on: unchanged at all
temperatures A. Acidic water
A. Single –cylinder engines C. No account of the B. Alkaline water
B. Multi – cylinder engines mechanism of heat C. Hard water
C. Horizontal engines transfer is considered D. Soft water
D. Vertical engines D. Gases dissociate at
higher temperatures
80. Prony brake is used for 92. The ignition coil acts as:
testing of: 85. The king pin inclination is
generally: A. A capacitor
A. Small engines B. An inductor
B. Large engines A. Less than 0.5° C. An RC circuit
C. Engines having small B. Between 1° and 2° D. A Step up converter
flywheel C. Between 2° and 5°
D. High speed engines D. More than 9° 93. The self starting motor for
automobiles is a:
81. Clog point of an oil refer to:
86. For balancing single cylinder
A. The point of maximum engine a counter weight is A. Universal motor
contamination of oil added to: B. DC Shunt motor
B. The level of impurities A. Piston C. DC series motor
beyond which oil ceases B. Piston pin D. Synchronous motor
to flow C. Cam
C. The temperature at D. Crank 94. Starting motor current may be
which oil solidifies about
D. The temperature at 87. To measure the clearance
which paraffin and waxes between the value and tappet A. 0.15 A
in oil start precipitating of an automobile engine we B. 0.5 A
use a _____. C. 5.1 A
82. Otto cycle consists of D. 25 A
A. Vernier scale
A. Two isentropic and two B. Feeler gauge 95. As a rule before the piston
constant volumes C. Pneumatic gauge are removed, it is essential to
processes D. Slip gauge remove the:
B. Two isentropic and two
constant pressure 88. By supercharging:
processes A. Gudgeon pin
C. Two adiabatic and two B. Circlip
A. Power stroke becomes C. Piston rings
isothermal processes stronger
D. Two isothermal and two D. Crankshaft
B. Loss in exhaust gets
constant volume reduced
processes C. Engine can be made to 96. Common causes for
run smoother excessive oil consumption
83. Diesel cycle consists of: D. Thermal efficiency of the include:
A. Isentropic, isothermal, engine can be improved
constant volume, A. Heavy oil and light
constant pressure 89. Speedometer drive is bearings
process generally taken from: B. High speed and worn
B. Two constant volume, engine
one constant pressure, C. Short trips and cold
and one isothermal A. Dynamo weather
processes B. Flywheel D. Frequent oil changes
C. Fan belt
97. The device that is used for D. None of these D. White exhaust
reducing the exhaust noise is
called _______. 104.Latex is: 110.Oil pan is attached :
A. Exhaust manifold A. A plastic A. To the bottom of the
B. Exhaust pipe B. A cover on writes cylinder block
C. Muffler carrying current to B. In a separate unit away
D. None of the above sparkplugs from the crankcase
C. A variety of lubricant C. At the top of the cylinder
98. The device that is used to D. A milky juice of rubber block
measure the clearance D. At the outside wall of the
between the value and tappet 105.Cross wire grooves on tires crank case
of an internal combustion
engine is measuring by using: 111.Excess oil consumption in
A. Decrease the danger of
skidding engine may be because of:
A. Snap gauge B. Absorb shocks because
B. Slip gauge of road unevenness A. Leakage of oil through oil
C. Feeler gauge C. Provide good traction pan gasket
D. Micrometer D. Provide better load B. Poor quality or improper
carrying capacity viscosity of engine oil
99. Which of the following C. Excessive oil pressure
instrument is used in 106.The diesel fuel pump is D. Any of the above
measuring specific gravity? designed to supply fuel
112.Wheel base of a vehicle is
A. Thermometer A. Just sufficient against the the:
B. Hygrometer demand of the injection
C. Anemometer pump A. Distance between front
D. Hydrometer B. In excess quality than and rear axles
100.Exhaust gas leakage into needed by the injection B. Distance between the
cooling system is most likely pump front tires
to occur because of defective: C. A constant quantity at all C. Extreme length of the
engine speeds vehicle
D. Insufficient quality in D. Width of tires
A. Cylinder head gasket accordance with the
B. Manifold gasket engine speed 113.The percentage of heat
C. Water pump released from fuel – air
D. Any of the above 107.The fuel is injected into the mixture, in an internal
cylinder in Diesel engine combustion engine which is
101.Clutch slippage while clutch is when the piston is: converted into useful work is
engaged is especially A. Exactly at B.D.C. after roughly:
noticeable _________. compression stroke
B. Exactly at T.D.C. before A. 10 percent
A. During idling compression stroke B. 10-20 percent
B. At low speed C. Approaching T.D.C. C. 20-25 percent
C. During acceleration during compression D. 40-45 percent
D. During braking stroke
D. Approaching B.D.C.
during exhaust stroke 114.The efficiency of hydraulic
102.To engage securely and braking system is:
prevent dragging the
clearance between release 108.In the cam, the distance
between the base circle and A. About 90 percent
bearing collar in a clutch is B. 60-80 percent
generally: the nose is known as
________. C. 50-60 percent
D. 40-50 percent
A. 2-3 mm
B. 10-12 mm A. Flank
B. Nose 115.The instrument that is used to
C. 20-22 mm check the state of charge of a
D. 30-32 mm C. Lobe
D. Lift battery is called a ____.
103.Gudgeon pins are made of: A. Hydrometer
109.Dirt or gum in fuel nozzle or
jets can produce: B. Battery charger
A. Same material as that of C. Battery eliminator
piston D. Anemometer
B. Cast iron A. Excessive fuel
C. Hardened and ground consumption
B. Lack of engine power 116.When not in use, self
steel discharge of an automobiles
C. Smoke black exhaust
battery in dry weather is 124.In a vehicle the most D. 9-10 cu.m
generally: probable cause for hard
steering may be: 131.Theoretically air needed for
A. 0.5 to 1% the combustion of one kg of
B. 3 to 5% A. Low tire pressure fuel is:
C. 5 to 7.5% B. Bent wheel spindle
D. Not more than 10% C. Tie rod ends tight A. 100kg
D. Any of the above B. 14.5 kg
117.A laminated glass on C. 16.7 kg
cracking: 125.Poor compression in a two D. 27.4 kg
stroke engine cannot be
A. Burst to sharp edged because of: 132. Which of the following is the
fragments cause of loss power?
B. Burst to granular pieces A. Leaky valves
C. Sandwitched layer taps B. Broken pistons rings A. Poor compression
the fragments C. Leaking cylinder head B. Restricted exhaust
D. Breaks into the farm of gasket C. Clogging of air cleaner
crystals D. Poor fits between D. Low injection pressure
pistons, rings and
118.Wax is applied on car body cylinder
133.A value in the carburetor of
as: an internal combustion
126.The number of exhaust engines which regulates the
A. It is water repellent manifold in a v-8 engine is: proportion of air gasoline
B. It seals off the pores vapor entering the cylinder.
C. The surface shines A. One
D. Any of the above B. Four A. Gate valve
C. There is no exhaust B. Choke calve
119.A spark voltage requires a manifold C. Check valve
voltage of: D. Two D. Globe valve
A. 112 V
B. 124 V 127.The device for smoothing out
C. 220 V 134.What device combines air
the power impulses from the and fuel for burning in
D. 440 V engine is known as: cylinder?
120.The minimum cranking speed A. Clutch
in petrol engine is: A. Intercooler
B. Flywheel B. Regenerator
C. Gear box C. Fuel injection
A. Same as the normal D. Differential D. Carburator
operating speed
B. Half of operating speed 128. The firing order in case of
C. One fourth of operating 135.A passive restraint device
four cylinder in-line engines is consisting of bags in front of
speed generally _________.
D. 60-80 rpm the driver and passenger.
A. 1-2-4-3 A. Air buoy
121.Which oil is more viscous? B. 1-3-4-2 B. Air bag
C. 1-4-3-2 C. Air Balloon
A. SAE 30 D. Either B or C D. Air Duct
B. SAE 50
C. SAE80 129.In case of four cylinder
D. SAE40 136.The heat exchanger used in
opposed cylinder engines, the an Ericsson cycle is:
firing order is: A. Regenerator
122.Engine oil is generally B. Combustion Chamber
changed after: A. 1-4-3-2 C. Intercooler
A. 100km B. 1-3-4-2 D. Recuperator
B. 1500km C. 1-2-3-4 137.In Stirling engine, the heat is
C. 1100km D. 1-2-4-3 added during
D. 2500-6000km
123.The most probable cause for
uneven wear of tire for a truck 130.In a four stroke engine, for A. Isothermal process
is: the combustion of one liter of B. Isometric process
fuel, the volume of air needed C. Isobaric process
would be approximately D. Isentropic process
A. Low tire pressure
B. Excessive camber
C. Tires over loaded A. 1 cu.m 138.In an otto engine, the heat is
D. Any of the above B. 2 cu.m added during
C. 5-7 cu.m
A. Isothermal process D. High melting points B. They have high melting
B. Isometric process points
C. Isobaric process 145.The following are all C. They are nonvolatile and
D. Isentropic process characteristics of nonmetallic have low vapor
except pressures
139.Exhaust stroke of gasoline D. They are good electrical
engine is also known as conductors in the solid
A. Having little or no luster phase
B. Appearing on the right
A. Supercharging end of the periods table
B. Choking C. Having low ductility 152.What kind of bonding do
C. Scavenging D. Being reducing agent common gases that exist in a
D. Knocking free as diatomic molecules
experience?
146.Graduation in the properties
140.The mechanical efficiency of of elements from one
a device is the ratio of the elements to the next are less A. Ionic bonds
pronounced in: B. Covalent bonds
C. Metallic bonds
A. Mechanical energy input D. Nuclear bonds
to the mechanical energy A. The lanthanide series
output of the device B. Periods
B. Ideal energy input to the C. Groups 153.Measure the diffuser’s ability
actual energy input D. Active metals to increase the pressure of
C. Actual energy extracted the fluid is:
to the ideal energy 147.All of the following are
extracted components of a chemical A. Speed recovery factor
D. Actual to the ideal energy elements except: B. Pressure recovery factor
input C. Volume recovery factor
D. Diffuser recovery factor
A. Protons
141.The smallest subdivision of B. Neutrons
an element that can take C. Electrons 154.A decrease in stagnation
place in a chemical reaction D. Ions pressure will decrease the
is a/an mass flux though the:
148.Which of the following is not a
A. Atom prefix used in naming A. Diverging nozzle
B. Molecule isomers? B. Converging nozzle
C. Electron C. Converging-diverging
D. Proton nozzle
A. Para D. None of these
B. Meta
142.The smallest subdivision of a C. Cis
compound that can exist in a D. Bi 155.What is the main power
natural state is a/an generating plant that
produces the most electricity
149.All of the following are types per unit thermal energy in the
A. Atom of chemical bonds except:
B. Molecule fuel input and has the
C. Electron greatest surplus of electricity
D. Proton A. Ionic bonds for most cogeneration
B. Covalent bonds system?
C. Metallic bonds
143.Elements with different D. Nuclear bonds
atomic weights but the same A. Steam engine
atomic number are: B. Steam turbine
150.The equilibrium distance C. Gas turbine
between elements in an ionic D. Diesel engine
A. Isomers bond is function of all the
B. Isotropes following except:
C. Isotopes 156.Air standard efficiency of a
D. Isobars diesel engine depends on
A. Ionic charge
B. Coordination number A. Speed
144.All of the following are C. Atomic weight
characteristics of metal B. Compression ratio
D. Temperature C. Fuel
except:
D. Torque
151.Which of the following
A. High electrical statements is not a
conductivities 157.What is meant by brake
characteristic of ionic horsepower?
B. Tendency to form compounds?
positive ions
C. Tendency to form brittle A. Power developed in the
solids A. They are usually hard, engine cylinder
brittle, crystalline solids
B. Final horsepower D. 0.1% 170.ME BOARD QUESTION
delivered to the Air that controls the rate of
equipment 164.ME BOARD QUESTION combustion in the combustion
C. Actual horsepower The color of lubricating oil chamber is known as:
delivered to the engine
drive shaft A. Does not indicate A. Secondary air
D. Work required to raise a contamination B. Excess air
weight 33,000 lbs at a B. Does not indicate C. Control air
height of one foot in one qualities D. Primary air
minute of time. C. Indicates qualities
D. Indicates viscosity 171.ME BOARD QUESTION
158.ME BOARD QUESTION Percentage of excess air is
Average pressure on a 165.ME BOARD QUESTION the difference between the air
surface when a changing There are two broad types in actually supplied and the
pressure condition exist the classification of lubricating theoretically required divided
oils, these are straight and by:
a. Back pressure
b. Partial pressure A. Active A. Actual air supplied
c. Pressure drop B. Inactive B. Theoretical air supplied
d. Mean effective pressure C. Crooked C. Theoretical less actual
D. Additives supplied
159.ME BOARD QUESTION D. Deficient air supplied
What air pressure is needed 166.ME BOARD QUESTION
for air starting a diesel engine Most commercially available 172.ME BOARD QUESTION
petroleum lubricating oil When fuel oil has a high
A. 350 psi deteriorates starting from viscosity then the fuel oil
B. 250 psi operating temperature of:
C. 450 psi A. Will evaporate easily
D. 150 psi A. 150°F B. Will have a low specific
B. 200°F gravity
160.ME BOARD QUESTION C. 300°F C. Will burn without smoke
Mechanical energy of D. 250°F D. Will flow slowly through
pressure transformed into pipes
energy of heat: 167.ME BOARD QUESTION
An Orsat apparatus is used 173.ME BOARD QUESTION
A. Kinetic energy for: Engines using heavy fuels
B. Enthalpy require heating of the fuel so
C. Heat exchanger A. Volumetric analysis of that the viscosity at the
D. Heat of compression injector is:
the flue gases
B. Gravemetric analysis of
161.ME BOARD QUESTION the flue gases A. Around 200 SSU
Ignition of the air-fuel mixture C. Smoke density analysis B. 100 SSU or less
in the intake of the exhaust of the gases C. 200 SSU + 50
manifold D. All of the above D. 150 SSU or slightly
A. Backlash higher
B. Backfire 168.ME BOARD QUESTION
C. Exhaust pressure The indicator used to 174.ME BOARD QUESTION
D. Back pressure determinate the anti-knock A gas produced by the
characteristics of gasoline. combustion of fuel oil and
162.ME BOARD QUESTION cannot be found in the flue
The total sulfur content in a gases is:
A. Aniline point
diesel fuel must not exceed B. Cetane number
___________. A. Carbon dioxide
C. Octane number
B. Hydrogen
D. Diesel index
C. Oxygen
A. 0.3%
D. Nitrogen
B. 0.5% 169.ME BOARD QUESTION
C. 0.8% Amount of heat liberated by 175.ME BOARD QUESTION
D. 0.11% the complete combustion of a Amount of heat liberated by
unit weight or volume of fuel the complete combustion of a
163.ME BOARD QUESTION is: unit weight or volume of fuel
Total sulfur content in a diesel is:
fuel oil must exceed A. Heating value
B. Latent heat A. Heating value
A. 0.2% C. Sensible heat B. Latent heat
B. 0.5% D. Work of compression C. Sensible heat
C. 0.15%
D. Work of compression D. Turbulent flow C. Brayton cycle
D. Rankine cycle
176.ME BOARD QUESTION 182.ME BOARD QUESTION
The product of complete If the composition of 188.The unit for expressing API
combustion of gaseous hydrocarbon fuel is known, gravity is :
hydrocarbons. the ratio the nitrogen and
oxygen that is supplier in air A. gm/cc
A. Carbon dioxide and is: B. dimensionless numbers
water C. degrees
B. Carbon monoxide A. Equal D. none of the above
C. Carbon monoxide, water B. Constant
and ammonia C. Intensity 189.ASTM coal classification is
D. Water, carbon monoxide D. Fixed based on:
and carbon dioxide
183.ME BOARD QUESTION A. proximate analysis
177.ME BOARD QUESTION The property of liquid in which B. orsat analysis
When the water in the they extend resistance to C. ultimate analysis
products of combustion is in angular or shear deformation D. none of the above
the vapor state, the heating is:
value is:
A. Specific gravity 190.API gravity of water is:
A. Lower heating value B. Specific weight
B. Higher heating value C. Viscosity A. Zero
C. Gross calorific value D. Density B. 10
D. Average heating value C. 1.0
184.ME BOARD QUESTION D. 100
178.ME BOARD QUESTION A property of lubricating oil
At what temperature wherein that measures the thickness 191.Which of the following variety
an oil of any grade becomes of the oil and will help of coal has highest of
cloudy and it freezes, thus its determine how long oil will content?
application is limited. flow at a given temperature is
known as:
A. Cold point A. Lignite
B. Flash point A. Viscosity B. Biturminous coal
C. Pour point B. Flash point C. Grade I steam coal
D. Freezing point C. Cloud point D. Coking coal
D. Cloud point
179.ME BOARD QUESTION 192.Which of the following is a
Dry air can be approximated 185.ME BOARD QUESTION petroleum fuel?
as _____% oxygen and The minimum amount of air
_____% nitrogen by mole required for a complete A. Benzol
numbers. combustion of fuel is called B. Ethyl alcohol
______. C. Methyl alcohol
A. 30% and 70% D. Naphta
B. 70% and 30% A. Dry air 193.Diesel engine fuels are rated
C. 21% and 79% B. Excess air by:
D. 79% and 21% C. Theoretical air
D. Flue gas A. Specific gravity
180.ME BOARD QUESTION B. Calorific value
When H2O in the products of 186.ME BOARD QUESTION C. Cetane number
combustion is in liquid form, The temperature at which D. Octane number
the heating value is know as lubricating will form a cloud.
194.Which of the following needs
A. Higher heating value A. Cloud point to be filtered in a diesel
B. Lower heating value B. Pour point engine?
C. Low and medium heating C. Critical point
value D. Boiling point
D. Average heating value A. Air only
B. Lubricating oil only
187.ME BOARD QUESTION C. Air and diesel oil only
181.ME BOARD QUESTION The ideal cycle based on the
Flow of fluids wherein its D. Air, diesel oil and
concept that the combustion lubricating oil
particles do not have definite process is both diesel and
paths and the paths of the gasoline in the combination of
individual and distinct heat transfer processes that
particles one another is: is constant pressure and
constant volume.
A. Non-uniform flow
B. Unsteady flow A. Ericsson cycle
C. Laminar flow B. Dual cycle
You might also like
- Renaissance Woman: Fat Loss, Muscle Growth & Performance Through Scientific EatingDocument20 pagesRenaissance Woman: Fat Loss, Muscle Growth & Performance Through Scientific EatingBenedict Ray Andhika33% (3)
- CAE 331/513 Building Science: Fall 2016Document46 pagesCAE 331/513 Building Science: Fall 2016RahulNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2 Problem SetDocument3 pagesThermo 2 Problem SetElisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Outline + Essay TemplateDocument7 pagesSynthesis Outline + Essay TemplatefirdausNo ratings yet
- E Voting SystemDocument68 pagesE Voting Systemkeisha baby100% (1)
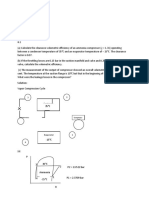
- Meneses, Keziah F.: Cop T T T T T T Where: T T T Cop COP 1.4696 1.47Document19 pagesMeneses, Keziah F.: Cop T T T T T T Where: T T T Cop COP 1.4696 1.47Eriane GarciaNo ratings yet
- BIACS 2 - Seville Biennial: The Unhomely (Review)Document3 pagesBIACS 2 - Seville Biennial: The Unhomely (Review)foggy_notionNo ratings yet
- The Soul of An Octopus - Favorite QuotesDocument7 pagesThe Soul of An Octopus - Favorite QuotesTanya RodmanNo ratings yet
- List of Documents NBA PfilesDocument48 pagesList of Documents NBA PfilesDr. A. Pathanjali Sastri100% (1)
- Wdghwahdg PDFDocument2 pagesWdghwahdg PDFKim Howard CastilloNo ratings yet
- Pipe CNS 02Document29 pagesPipe CNS 02maria katherine pantojaNo ratings yet
- Chimney 1Document22 pagesChimney 1zyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Balingt - Prelim ExamDocument21 pagesBalingt - Prelim ExamRene Niño Macamay BalingitNo ratings yet
- Solid FuelsDocument5 pagesSolid FuelsPritamNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesThermodynamicsmarkalvinbonNo ratings yet
- AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM Prelim ExamDocument1 pageAIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM Prelim ExamJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Paper in IJSER FormatDocument14 pagesRefrigeration Paper in IJSER Formattitto84886No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Problem SetDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer Problem Setkim dianonNo ratings yet
- Pipe Preparatory Problems With Answer Guide in Power Plant and Industrial PlantDocument13 pagesPipe Preparatory Problems With Answer Guide in Power Plant and Industrial PlantRea RebenqueNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument6 pagesThermoE.G Boy GudaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Document3 pagesModule 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel Gamboa100% (1)
- IPE Exit Exam Reviewer (BB)Document41 pagesIPE Exit Exam Reviewer (BB)ChesterJerichoRamosNo ratings yet
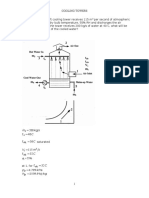
- Cooling TowerDocument6 pagesCooling TowerLucas FurlanNo ratings yet
- Exercises Problem 1 Ref and Air Con MamaclayRADocument3 pagesExercises Problem 1 Ref and Air Con MamaclayRALeyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Apolakai Macdes ProblemDocument18 pagesApolakai Macdes Problempablo valorantNo ratings yet
- CHE 306 - Solved Problems-9Document1 pageCHE 306 - Solved Problems-9Garcia Raph100% (1)
- R&AC Lecture 40Document13 pagesR&AC Lecture 40Mohammed SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Power Plant SW (Gas Turbine-Gas Loop-Cooling Tower)Document2 pagesPower Plant SW (Gas Turbine-Gas Loop-Cooling Tower)Andrew PantaleonNo ratings yet
- PADILLAMD Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 4Document2 pagesPADILLAMD Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 4Leyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Putrika Citta Pramesi 14/369486/TP/11122: 1 2 Container P, Container Freeze Latent P, Fresh P, FrozenDocument2 pagesPutrika Citta Pramesi 14/369486/TP/11122: 1 2 Container P, Container Freeze Latent P, Fresh P, Frozenputrikacitta3924No ratings yet
- Experiment #4 - Testing of A Mini Ice Plant GROUP 14Document12 pagesExperiment #4 - Testing of A Mini Ice Plant GROUP 14Ashley Justine RowanNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Isothermal - This Model Assumes That TheDocument12 pagesCompressors: Isothermal - This Model Assumes That TheRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Chap 08 Soln PDFDocument26 pagesChap 08 Soln PDFsoma sundaramNo ratings yet
- Coaching Problems CFDocument5 pagesCoaching Problems CFDeyn EstoqueNo ratings yet
- Basic Process Control System Module (Revised)Document8 pagesBasic Process Control System Module (Revised)Christy Jane SanchezNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Sciences Reviewer - CompleteDocument87 pagesBasic Engineering Sciences Reviewer - Completeyomz719No ratings yet
- Hematra Cooling TowerDocument4 pagesHematra Cooling Towerjc CincoNo ratings yet
- 7 - FANS (Formulas & Solution To Problems) - by ENGR ROBLESDocument25 pages7 - FANS (Formulas & Solution To Problems) - by ENGR ROBLESandradajc7No ratings yet
- Combustion of CoalDocument12 pagesCombustion of CoalAlteaAl100% (1)
- Educspace - Pumps - Problems SetDocument3 pagesEducspace - Pumps - Problems SetMatthew John SyNo ratings yet
- Exercises Problem 4 Heat TransferDocument3 pagesExercises Problem 4 Heat TransferMeeko TanNo ratings yet
- Mecorrel3 - Quiz3Document3 pagesMecorrel3 - Quiz3John Paul EspañoNo ratings yet
- A Cylindrical Oil Tank 2Document6 pagesA Cylindrical Oil Tank 2Nivek Ko Sa AresNo ratings yet
- 5 - Chimney PDFDocument14 pages5 - Chimney PDFVern JasmineNo ratings yet
- Buok Chapter 7Document5 pagesBuok Chapter 7Edmil Jhon AriquezNo ratings yet
- Exercises Application Word Problems (FOODE)Document4 pagesExercises Application Word Problems (FOODE)azxilNo ratings yet
- MESL - Plane and Solid GeometryDocument8 pagesMESL - Plane and Solid GeometryMark-Lorie Duculan NonesNo ratings yet
- LBYME4A - EE3 - Expt. 1 - Group 2Document15 pagesLBYME4A - EE3 - Expt. 1 - Group 2catalan153709No ratings yet
- 2 Condenser 3: CompressorDocument16 pages2 Condenser 3: CompressorLeslie CatindigNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11-Hvac For Small HouseDocument9 pagesExperiment 11-Hvac For Small Houseengrjayasis20No ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFDocument118 pagesChapter 9-Hydroelectric Plant PDFsindyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration-Systems Part 1Document11 pagesRefrigeration-Systems Part 1Sean GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Hey 22Document6 pagesHey 22AM CruzNo ratings yet
- Ibong Tiririt Pipe 2Document49 pagesIbong Tiririt Pipe 2Mc LesterNo ratings yet
- Handouts PPE Day 5Document5 pagesHandouts PPE Day 5Reinzo GallegoNo ratings yet
- Gas Compressor ProblemsDocument2 pagesGas Compressor Problemskim dianon0% (1)
- MCQ in Machine Design and Shop Practice Part 18 ME Board ExamDocument17 pagesMCQ in Machine Design and Shop Practice Part 18 ME Board Examtagne simo rodrigue100% (1)
- T-MEET324LA Experiment No.9 Cloud and Pour Point Tests Group5 MEE31Document10 pagesT-MEET324LA Experiment No.9 Cloud and Pour Point Tests Group5 MEE31Paul Ryan GeneralNo ratings yet
- Pipe SimulationDocument101 pagesPipe Simulationnathaniel villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument19 pagesFuels and CombustionrickyNo ratings yet
- Rosario Probset General-ChemistryDocument12 pagesRosario Probset General-ChemistryAudreyWalangareDimalibotNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument4 pagesAir Pollutionken russelNo ratings yet
- Module 1.2 PDFDocument9 pagesModule 1.2 PDFJong Shi HaeNo ratings yet
- Cuison Chapter 2Document41 pagesCuison Chapter 2Reinzo Gallego100% (1)
- Review Material Forn ChEDocument10 pagesReview Material Forn ChENobi PanisiganNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Geas: InstructionDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 - Geas: InstructionJhoe TangoNo ratings yet
- Ching, Anthony Jay Graneta, Paulo Lumbo, Marecho Parazo, Jerrald Villar, RavenDocument24 pagesChing, Anthony Jay Graneta, Paulo Lumbo, Marecho Parazo, Jerrald Villar, RavenDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Multipressure SystemsDocument9 pagesMultipressure SystemsDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements: Cams: Group 7 Charlie Dionisio R - Jhun Lemos Jerphoenix Mullaneda Arsilio SilverioDocument21 pagesMachine Elements: Cams: Group 7 Charlie Dionisio R - Jhun Lemos Jerphoenix Mullaneda Arsilio SilverioDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesSolid Mensuration Practice ProblemsDeniell Joyce Marquez100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Refrigerating Machine Reversed Carnot Cycle Simple Vapor Compression CycleDocument14 pagesLecture 1 Refrigerating Machine Reversed Carnot Cycle Simple Vapor Compression CycleDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Actual Vapor Compression CycleDocument7 pagesActual Vapor Compression CycleDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Effects of Operating Conditions in VCCDocument9 pagesLecture 2 Effects of Operating Conditions in VCCDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral Calculus Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculus Solved ProblemsDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Subcooling Superheating and Liquid Suction Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesSubcooling Superheating and Liquid Suction Heat ExchangerDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mathalino: Getac Rugged Mobile ComputingDocument3 pagesMathalino: Getac Rugged Mobile ComputingDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mathalino: Industrial ProgrammingDocument3 pagesMathalino: Industrial ProgrammingDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- 50% Off .Design Domains: MathalinoDocument3 pages50% Off .Design Domains: MathalinoDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mathalino: Ar AutomationDocument4 pagesMathalino: Ar AutomationDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drag and Drop Web Builder: MathalinoDocument3 pagesDrag and Drop Web Builder: MathalinoDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mathalino: Getac Rugged Mobile ComputingDocument3 pagesMathalino: Getac Rugged Mobile ComputingDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mathalino: 017 Computation of Force With Given Component Parallel To A Frame MemberDocument3 pagesMathalino: 017 Computation of Force With Given Component Parallel To A Frame MemberDeniell Joyce Marquez100% (1)
- Earshots Blood, Sweat & Sound: MathalinoDocument3 pagesEarshots Blood, Sweat & Sound: MathalinoDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Rui Ru I R Ui R U I: Thank YOU Than K You THA NK YOU TH AN K YO UDocument1 pageRui Ru I R Ui R U I: Thank YOU Than K You THA NK YOU TH AN K YO UDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Auckland Based Nav Support: MathalinoDocument3 pagesAuckland Based Nav Support: MathalinoDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mathalino: Silo TheatreDocument4 pagesMathalino: Silo TheatreDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Case Study of A Condemned Boiler & Methods To Re-Establish ItDocument43 pagesCase Study of A Condemned Boiler & Methods To Re-Establish Its sivaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 68749835 Electronic Throttle BodyDocument3 pagesData Sheet 68749835 Electronic Throttle BodyDaniel AguirreNo ratings yet
- OSPE DU MedicineDocument101 pagesOSPE DU MedicinesaifNo ratings yet
- LH - Elementary - Student's Book Answer KeyDocument34 pagesLH - Elementary - Student's Book Answer KeyАнастасия ДанилюкNo ratings yet
- Linkages and NetworkDocument28 pagesLinkages and NetworkJoltzen GuarticoNo ratings yet
- T-Systems CPNI Policy Statement - Final 022717 PDFDocument2 pagesT-Systems CPNI Policy Statement - Final 022717 PDFFederal Communications Commission (FCC)No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Patent LawDocument4 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Patent LawSaksham TyagiNo ratings yet
- Frs Whatsapp Chat NotesDocument72 pagesFrs Whatsapp Chat NotesFarai NyaniNo ratings yet
- GIDC Rajju Shroff ROFEL Institute of Management Studies: Subject:-CRVDocument7 pagesGIDC Rajju Shroff ROFEL Institute of Management Studies: Subject:-CRVIranshah MakerNo ratings yet
- Canara BankDocument21 pagesCanara BankRajesh MaityNo ratings yet
- Government of Karnataka: Only For Birth Verification PurposeDocument1 pageGovernment of Karnataka: Only For Birth Verification PurposeAmit VantagodiNo ratings yet
- Ordinary People Summary ChartDocument2 pagesOrdinary People Summary Chartangela_cristiniNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Sensor Networks - Introduction & ArchitecturesDocument32 pagesUnit - 2 Sensor Networks - Introduction & Architecturesmurlak37No ratings yet
- Imesa Minifluor Copertina - en WebDocument52 pagesImesa Minifluor Copertina - en WebAlaa ZoraNo ratings yet
- Deed of DonationDocument2 pagesDeed of DonationMary RockwellNo ratings yet
- Indercos2021 Fulltext Congress BookDocument294 pagesIndercos2021 Fulltext Congress BookDr Sneha's Skin and Allergy Clinic IndiaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Selected Ceramic Companies of BangladeshDocument14 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Selected Ceramic Companies of BangladeshmotaazizNo ratings yet
- Veterinary MicrobiologyDocument206 pagesVeterinary MicrobiologyHomosapienNo ratings yet
- Care of Terminally IllDocument34 pagesCare of Terminally Illbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Ferdinando Carulli - Op 121, 24 Pieces - 4. Anglaise in A MajorDocument2 pagesFerdinando Carulli - Op 121, 24 Pieces - 4. Anglaise in A MajorOniscoidNo ratings yet
- TG0012 enDocument24 pagesTG0012 enDhexter VillaNo ratings yet
- Staying in God's PresenceDocument3 pagesStaying in God's PresenceElmer Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Internet Banking Java Project ReportDocument68 pagesInternet Banking Java Project ReportKUMAR NILESH100% (1)
- Risk Assessment - COVID 19 Restart of Activities Mina Justa-V3Document81 pagesRisk Assessment - COVID 19 Restart of Activities Mina Justa-V3Shmi HectorNo ratings yet