Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Location-Based Services Using Geofencing: Abhishek Singh, Ankit Pal, Divyansh Garg, Dolly Yadav
Location-Based Services Using Geofencing: Abhishek Singh, Ankit Pal, Divyansh Garg, Dolly Yadav
Uploaded by
Rupam PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument11 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringMohd Nik Harith FawwazNo ratings yet
- VT800 User Manual-900DDocument19 pagesVT800 User Manual-900DMigue MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Document6 pagesIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Review of Related Literature ADocument7 pagesChapter 2 Review of Related Literature AMichaelNo ratings yet
- 1 3Document11 pages1 3factorialNo ratings yet
- IJAS - Volume 12 - Issue 2 - Pages 5067-5076Document10 pagesIJAS - Volume 12 - Issue 2 - Pages 5067-5076Shrilaja KNo ratings yet
- Concept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1Document25 pagesConcept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1Bharath HRNo ratings yet
- Sample DocumentationDocument17 pagesSample DocumentationChristian SanohNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Implementation of GPS Based Object Location and Route Tracking On Android DeviceDocument12 pagesResearch Paper Implementation of GPS Based Object Location and Route Tracking On Android DeviceABDULAZEEZNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Positioning System (GPS) ?: SatellitesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Global Positioning System (GPS) ?: Satellitescrunchyrull2No ratings yet
- Concept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1Document6 pagesConcept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1SrikantNo ratings yet
- Searching Nearby Sites Using Google MapsDocument7 pagesSearching Nearby Sites Using Google MapsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- In Campus Location Finder Using Mobile Application Services: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument11 pagesIn Campus Location Finder Using Mobile Application Services: Articles You May Be Interested inmarcoteran007No ratings yet
- E04342730 Project PDFDocument4 pagesE04342730 Project PDFAbhay JangirNo ratings yet
- User Position Detection in An Indoor EnvironmentDocument10 pagesUser Position Detection in An Indoor EnvironmentDediPurniawanNo ratings yet
- Bujang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 991 012137Document10 pagesBujang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 991 012137احمد نديم اسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Hymotrack: A Mobile Ar Navigation System For Complex Indoor EnvironmentsDocument19 pagesHymotrack: A Mobile Ar Navigation System For Complex Indoor EnvironmentshenmusNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Seamless Positioning and Navigation by Using Geo-Referenced Images and Multi-Sensor DataDocument23 pagesSensors: Seamless Positioning and Navigation by Using Geo-Referenced Images and Multi-Sensor DataSC Priyadarshani de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Indoor Positioning and Navigation System For AutonDocument14 pagesIndoor Positioning and Navigation System For AutonMrMsmaxNo ratings yet
- LE THI KHANH LINH 20193549 ICT. Writing Assignment.Document5 pagesLE THI KHANH LINH 20193549 ICT. Writing Assignment.klizNo ratings yet
- Application of GPS-RTK Technology in The Land ChanDocument6 pagesApplication of GPS-RTK Technology in The Land ChanVenkat INo ratings yet
- Waypoint Navigation SystemDocument7 pagesWaypoint Navigation SystemShaukat WazirNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Location Awareness and Sharing System Using GPS and 3G/GPRSDocument16 pagesDesign and Implementation of Location Awareness and Sharing System Using GPS and 3G/GPRScedaserdnaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Uses of GPS?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Uses of GPS?Shiela Mae SalesNo ratings yet
- Journal Paper 1 SazidDocument26 pagesJournal Paper 1 SazidSazid Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- 3749-Article Text-10616-1-10-20170809Document7 pages3749-Article Text-10616-1-10-20170809nisaovo2No ratings yet
- GPS Tracking SystemDocument4 pagesGPS Tracking SystemSreenath SreeNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Tracking System Using GPS and Android OSDocument5 pagesVehicle Tracking System Using GPS and Android OSshobanraj1995No ratings yet
- pp25 Mountain1Document2 pagespp25 Mountain1Ciprian IlieNo ratings yet
- Survey of Indoor Tracking Systems Using Augmented RealityDocument13 pagesSurvey of Indoor Tracking Systems Using Augmented RealityIAES IJAI100% (1)
- 24561-Article Text-37378-1-10-20200616Document8 pages24561-Article Text-37378-1-10-20200616cumacoba267No ratings yet
- Arm Hardware Platform For Vehicular Monitoring and Tracking Using Gps and GSMDocument9 pagesArm Hardware Platform For Vehicular Monitoring and Tracking Using Gps and GSMtango 12No ratings yet
- .Vehicle Tracking With Geo Fencing On Android PlatformDocument4 pages.Vehicle Tracking With Geo Fencing On Android PlatformHakiem HalimNo ratings yet
- 50 DesigningDocument7 pages50 DesigningYoftahiNo ratings yet
- Performance Comparision Between Two Microcontorllers Based GPS ForDocument7 pagesPerformance Comparision Between Two Microcontorllers Based GPS Forاحمد نديم اسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Location Fingerprinting of Mobile Terminals by Using Wi-Fi DeviceDocument4 pagesLocation Fingerprinting of Mobile Terminals by Using Wi-Fi DeviceIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- 18 - V1204050 - Mobile - HDocument6 pages18 - V1204050 - Mobile - HShalini TiwariNo ratings yet
- What Is GPS and How Is It Used in Land Surveying?Document5 pagesWhat Is GPS and How Is It Used in Land Surveying?mdNo ratings yet
- GPS Note Class 11 PhysicsDocument3 pagesGPS Note Class 11 Physicsgautamsushil150No ratings yet
- Exploring The Systems and Tools of Indoor NavigationDocument13 pagesExploring The Systems and Tools of Indoor NavigationAbdurahman AL FurjaniNo ratings yet
- Design of anti-GPS For Reasons of SecurityDocument22 pagesDesign of anti-GPS For Reasons of SecuritySssssjsjsjsjsNo ratings yet
- Mobile Tracking Application: Radhika Kinage, Jyotshna Kumari, Purva Zalke, Meenal KulkarniDocument7 pagesMobile Tracking Application: Radhika Kinage, Jyotshna Kumari, Purva Zalke, Meenal KulkarniArøn ParNo ratings yet
- Geographic Information SystemsDocument22 pagesGeographic Information SystemsAnkit MathurNo ratings yet
- Gps & Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesGps & Its ApplicationsDivya VarshneyNo ratings yet
- GPS Based Location Tracking System Via ADocument7 pagesGPS Based Location Tracking System Via Anikita dubeyNo ratings yet
- GPS Localization Improvement of Smartphones Using Built-In SensorsDocument8 pagesGPS Localization Improvement of Smartphones Using Built-In Sensorszeinab15No ratings yet
- Position Detection and Tracking System (IRACST)Document7 pagesPosition Detection and Tracking System (IRACST)praveenaNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing (RS) and GIS Research Paper R2Document7 pagesRemote Sensing (RS) and GIS Research Paper R2jamesbondmsd07No ratings yet
- Indoor Navigation System For MuseumDocument6 pagesIndoor Navigation System For MuseumIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Location Based Services-388Document4 pagesLocation Based Services-388Friends94 FeniNo ratings yet
- Development of Smart Watch Gps Tracker Application STEM 2018-19Document24 pagesDevelopment of Smart Watch Gps Tracker Application STEM 2018-19Ray MartNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Document4 pagesPerimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Rupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- ETCW08Document4 pagesETCW08Editor IJAERDNo ratings yet
- Indoor Navigation SystemDocument6 pagesIndoor Navigation SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Thesis Gps SystemDocument4 pagesThesis Gps SystemBuyPapersOnlineHighPoint100% (2)
- 5 Equipments Used in The Field of Surveying: Dogma, Jan Katelyne P. 2019-02376 Engr. Irish PolingaDocument7 pages5 Equipments Used in The Field of Surveying: Dogma, Jan Katelyne P. 2019-02376 Engr. Irish PolingaJan Katelyne DogmaNo ratings yet
- Geo-Information: Tracking 3D Moving Objects Based On GPS/IMU Navigation Solution, Laser Scanner Point Cloud and GIS DataDocument16 pagesGeo-Information: Tracking 3D Moving Objects Based On GPS/IMU Navigation Solution, Laser Scanner Point Cloud and GIS DataGopi Krishna ValluriNo ratings yet
- Reference PaperDocument6 pagesReference PaperPratibha VermaNo ratings yet
- 3413 Ijcsea 06Document9 pages3413 Ijcsea 06Rupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Development of Automatic Geofencing and AccidentalDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Automatic Geofencing and AccidentalRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Micro Location For Internet of Things enDocument16 pagesMicro Location For Internet of Things enRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Spatio Temporal Proximity Assitance ProcDocument5 pagesSpatio Temporal Proximity Assitance ProcRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Document4 pagesPerimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Rupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Geofencing and Background Tracking - The Next Features in LBSDocument15 pagesGeofencing and Background Tracking - The Next Features in LBSRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Quanum Manual Multicopter Flying ControllerDocument21 pagesQuanum Manual Multicopter Flying ControllerYimmeeeNo ratings yet
- GPS 15xH/15xL Technical Specifications: 190-00266-03 Revision A December 2009Document40 pagesGPS 15xH/15xL Technical Specifications: 190-00266-03 Revision A December 2009raoultrifan7560No ratings yet
- Modern Survey TechniquesDocument15 pagesModern Survey TechniquesNishant DasNo ratings yet
- Stromberg Carlson GpsDocument103 pagesStromberg Carlson GpsArielNo ratings yet
- Sulky DX20-30 ENDocument24 pagesSulky DX20-30 ENAleksandar DautovicNo ratings yet
- E7 Practice Test U6Document4 pagesE7 Practice Test U6Cao DucLaamNo ratings yet
- Timeprovider 2700: Edge Grandmaster ClockDocument5 pagesTimeprovider 2700: Edge Grandmaster Clockton LustriaNo ratings yet
- Principles of GPSDocument11 pagesPrinciples of GPSWong_Hong_Wei100% (1)
- Strahlenfolter - Chip Implants Already Here - Electronic HarassmentDocument10 pagesStrahlenfolter - Chip Implants Already Here - Electronic Harassmentnwo-mengele-doctorsNo ratings yet
- The Role of Global Positional Systems in Policing and Crime PreventionDocument20 pagesThe Role of Global Positional Systems in Policing and Crime PreventionSaChibvuri JeremiahNo ratings yet
- ABB Obsolescence NoticeDocument8 pagesABB Obsolescence Noticevangeliskyriakos8998No ratings yet
- 2nd Mate Past Question Papers Till November21Document280 pages2nd Mate Past Question Papers Till November21ARYAN DUBEY0% (1)
- Truecam A4 Manual MultilangDocument232 pagesTruecam A4 Manual MultilangCORNELIONo ratings yet
- Pipeline Integrity Management SystemDocument9 pagesPipeline Integrity Management SystemFroylán Ernesto Pompa García100% (1)
- Sim28ml Spec v1507Document1 pageSim28ml Spec v1507MrIhex ShanNo ratings yet
- Gpsmic: Gpsbox: Enabling Location Tracking With EaseDocument10 pagesGpsmic: Gpsbox: Enabling Location Tracking With EasePeter JacobNo ratings yet
- Smart Jacket: Water Safety System Using GPS LocationDocument3 pagesSmart Jacket: Water Safety System Using GPS LocationGRD Journals0% (1)
- Differential GPS (A Method of Processing The GPS Data)Document23 pagesDifferential GPS (A Method of Processing The GPS Data)Saurabh SumanNo ratings yet
- TDS Survey Pro With TSX v4.6.0 User's Manual - ReconDocument367 pagesTDS Survey Pro With TSX v4.6.0 User's Manual - ReconRomeo BlancoNo ratings yet
- Spider 2 User ManualDocument4 pagesSpider 2 User ManualJacob MillerNo ratings yet
- MP 2028 GDocument2 pagesMP 2028 GSrikanth SinghNo ratings yet
- United States District Court: EvidenceDocument39 pagesUnited States District Court: EvidenceJack RyanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Gps Tracking SystemDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Gps Tracking Systemeygyabvkg100% (1)
- How To Interface GPS With 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesHow To Interface GPS With 8051 MicrocontrollerSỹ RonNo ratings yet
- G V 300 Ficha TecnicaDocument2 pagesG V 300 Ficha TecnicaJose Eduardo GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Long Range Locators - Intergallactic PistolsDocument5 pagesLong Range Locators - Intergallactic PistolsSneshko SnegicNo ratings yet
- Seatracer: User ManualDocument26 pagesSeatracer: User ManualSuresh VinzudaNo ratings yet
- Comparing GPS Only With GPS GLONASS Positioning in A Regional Permanent GNSS Network 2007 GPS SolutionsDocument10 pagesComparing GPS Only With GPS GLONASS Positioning in A Regional Permanent GNSS Network 2007 GPS SolutionsMohamed HamedNo ratings yet
- Acr - SLB 2000-100Document2 pagesAcr - SLB 2000-100tassawarNo ratings yet
Location-Based Services Using Geofencing: Abhishek Singh, Ankit Pal, Divyansh Garg, Dolly Yadav
Location-Based Services Using Geofencing: Abhishek Singh, Ankit Pal, Divyansh Garg, Dolly Yadav
Uploaded by
Rupam PrasadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Location-Based Services Using Geofencing: Abhishek Singh, Ankit Pal, Divyansh Garg, Dolly Yadav
Location-Based Services Using Geofencing: Abhishek Singh, Ankit Pal, Divyansh Garg, Dolly Yadav
Uploaded by
Rupam PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
Singh Abhishek et.
al; International Journal of Advance Research and Development
(Volume3, Issue4)
Available online at: www.ijarnd.com
Location-based services using geofencing
Abhishek Singh1, Ankit Pal2, Divyansh Garg3, Dolly Yadav4
1,2,3,4
Student, IMS Engineering College, Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh
ABSTRACT
Geo-fencing (geofencing) is a great feature in a software program that uses Global Positioning System (GPS) or radio frequency
identification (RFID) to define the geographical boundaries feature. Actually geofence is a virtual barrier. Geofencing is an
innovative technology, an online marketplace for proactive contextual services that allows users to easily find interesting services,
can easily subscribe to it and to allow providers offer their services for a variety of applications such as electronic toll collection,
contextual advertising or tourist information systems, even without additional infrastructure. The main objective of this research
was to understand how the use of spatial data can improve advertising performance for customers. Tracking systems and
monitoring, based on global navigation services by satellite, and include geofencing function, could also contribute to the exact
location of an institution or company and increase sales and business perspective efficiently. Instead of large billboards they can
now advertise on smartphones which is economically and accurately tested.
Keywords: Geofencing, GPS, Geo Location, Geofence, Geotification, Geo-Tourist Guide.
1. INTRODUCTION
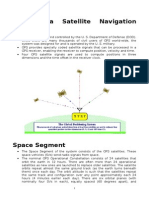
The location-based services (LBS) have recently undergone a massive shift in popularity.While the first generation of LBS has not
attracted much attention in recent years. Knowledge about geographical location of a mobile device. Geo-spatial information is
being used in many fields such as computer software, physical security. In this context, most of the existing technologies focus on
identifying the exact location of the user via Global Positioning System (GPS) in outdoor environments. A different view of the
location aware computing is to focus on the presence of a user in a virtual perimeter of a given geographical landscape. This second
alternative view, which complements the first one is called Geo-fencing and has brought in many benefits. Geo-fence refers to a
virtually fenced geographical area. According to almomani (2011). This concept has been employed to implement various tasks
including equipment theft control, tracking, or automatic house arrest monitoring systems. Social networks have also brought new
ideas and use cases for Location Based Services, including geo-spatial networking. Moreover, various techniques are studied in
order to improve the robustness and security of such a system. The focus of these studies is develop a geofencing system which will
be used in theft controlling management, house arresting, and event management etc using android phone. The objectives include:
a) To develop an automation system that identify theft in a particular geofence region using gps technology.
b) To analyze the importance of geofencing system geofencing combines awareness of the user's current location with awareness
of the user's proximity to locations that may be of interest. To mark a location of interest, you specify its latitude and longitude. To
adjust the proximity for the location, you add a radius. The latitude, longitude, and radius define a geofence, creating a circular area,
or fence, around the location of interest.
You can have multiple active geofences, with a limit of 100 per device user. For each geofence, you can ask Location Services to
send you entrance and exit events, or you can specify a duration within the geofence area to wait, or dwell, before triggering an
event. You can limit the duration of any geofence by specifying an expiration duration in milliseconds. After the geofence expires,
Location Services automatically removes it.
© 2018, www.IJARND.com All Rights Reserved Page | 85
Singh Abhishek et.al; International Journal of Advance Research and Development
Overview of geofencing
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
A geofence is a virtual perimeter for a real-world geographic area. It can be a radius around a location or a pre-defined set of
boundaries. With Plot Researchs you can create Geofences with a radius of between 50 to 50,000 meters. The process of using a
geofence is called geofencing. Geofencing allows you to send notifications to your app users when they are in the vicinity of, for
example, your store. A geofencing is a virtual barrier program that allow an administrator to set up triggers when a device enter (or
exits) the boundaries defined by the administrator so that a text message or email alert can be sent. Geofencing is a technology used
to monitor mobile objects (vehicles, persons, containers…), located by GPS. The geographic coordinates of the tracked object are
automatically and regularly sent to a control center, via mobile phone networks (Almomani, 2011).Referring from the above research
works a new use of geofencing can be in historical and archaeological sites for the purpose of guiding the tourists when the reach
the site.
Geofencing Techniques
Geofencing can be of benefit in numerous domains and has many functions: the monitoring of mobile assets and people within
geographical areas. Various geofencing techniques have been developed to meet different pragmatic needs. The main techniques
are presented below
Geofenced Area
This technique provides automatic monitoring of mobile objects moving around or inside a geofenced area. Alarms are generated
when mobiles respectively enter or exit the boundary. The size of the area can range from a few tens of meters to several kilometers.
The shape of the geofencing can be a simple geometric figure, like square or rectangle, or a more complicated one, like complex
polygon.
Proximity with a point of interest
This technique is intended to detect the proximity of a vehicle in relation to a point of interest (POI). In practice, the geofencing is
a circle, and the POI is located at the center. The radius is parameterized according to the distance that is regarded as "proximity"
to the POI, from a few meters to several tens of kilometers. This method is the simplest way to implement geofencing, Because it
only needs two parameters, coordinates of the center and value of the radius. The algorithm calculates the distance between the
mobile object and the center of the circle. According to whether this distance is lower or higher than the value of the radius, the
mobile object will respectively be considered inside or outside the geofencing.
Route adherence
This technique relates to the monitoring of a mobile object throughout a journey, from the departure point to the final destination.
Geofencing makes it possible to ensure that a vehicle does not deviate from its allocated route.
Review of Related works on Geofencing
© 2018, www.IJARND.com All Rights Reserved Page | 86
Singh Abhishek et.al; International Journal of Advance Research and Development
(Fabric et al, 2012)This research deals with geofencing: an innovative technology, based on telematics and satellite positioning.
Geofencing enables remote monitoring of geographic areas surrounded by a virtual fence (geofence), and automatic detections when
tracked mobile objects enter or exit these areas. The research presents fundamental concepts of geofencing and some applications
based on this technique. Sturdevant Rick W. (2009) affirmed that the Navtar Global positioning System (GPS) is the first satellite
navigation system that enabled users to determine precisely their location in three dimensions and time within billionths of a second
and grew from a concept into a fully operational system in slightly more than two decades. The widely-used GPS system are the
US-based GPS (Global Positioning System) and Russian-based GLOSNASS (Global’naya Navigatsionnaya
Sputnikowaya Sistema, Global Navigation Satellite System) satellite positioning systems. By 1972,the U.S. Air Force(USAF) and
the U.S. Navy had been studying for several years the possibility of improved satellite-based radio navigation. The main reasons
for GPS development were the need to deliver weapons precisely on target and to reverse the proliferation of navigation systems in
the U.S. military. Petri (2015) in his research Locating and Tracking Assets using GPS, states that “Accurate locating or tracking is
required in many fields from navigating for rescuing wounded people in emergency situation to decision-making for striking the
target during the military operations.
Recommendations for using geofencing with the location APIs for Android
We can use the following techniques to optimize power consumption in your apps that use geofencing:
Set the notification responsiveness to a higher value. Doing so improves power consumption by increasing the latency of
geofence alerts. For example, if you set a responsiveness value of five minutes your app only checks for an entrance or exit alert
once every five minutes. Setting lower values does not necessarily mean that users will be notified within that time period (for
example, if you set a value of 5 seconds it may take a bit longer than that to receive the alert).
Use a larger geofence radius for locations where a user spends a significant amount of time, such as home or work. While a
larger radius doesn't directly reduce power consumption, it reduces the
Frequency at which the app checks for entrance or exit, effectively lowering overall power consumption.
3. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
Conclusion
This paper deals with the concept of geofencing. It presents various applications used in the field of surface transport, and the main
control and monitoring techniques based on geofencing.
© 2018, www.IJARND.com All Rights Reserved Page | 87
Singh Abhishek et.al; International Journal of Advance Research and Development
Recommendation
Lastly, future applications based on geofencing should benefit from satellite navigation services, where great improvements are also
expected in location precision, and By providing better accuracy and improved confidence in mobile positioning to integrity
mechanisms, these systems will lead to more efficient geofencing applications.
4. REFERENCES
[1] Anthony.C. Ijeh, David .S. Preston, Chris .O. Imafidon, Titus .B. Watmon, Annette .O. Uwaechie, Aaron Nwadube, Ebrina
Kujabi, Member, IAENG “Geofencing Components and Existing Models”.
[2] Anthony .C. Ijeh, David .S. Preston, Chris .O. Imafidon, Titus .B. Watmon, Annette .O. Uwaechie, Martin Cooke, Peter
Lancaster, Andy Widdess, Mojisola Soremekun, Member, IAENG “Geofencing Security Engineering”.
[3] Anthony .C. Ijeh, David .S. Preston, Chris .O. Imafidon, Titus .B. Watmon, Annette .O. Uwaechie, Samuel Ojeme, Benjamin .R.
Lucas, Member, IAENG “Geofencing Engineering Design and Methodology”.
[4] Aderonke Adegbenjo, Afonne Emmanuel, Department of Computer Science, Babcock University, Ilishan-Remo, Ogun State
“Development of geofencing system for theft control management”.
[5] https://developer.android.com/training/location/geofencing.html.
© 2018, www.IJARND.com All Rights Reserved Page | 88
You might also like
- Universiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringDocument11 pagesUniversiti Malaysia Sarawak: Faculty of EngineeringMohd Nik Harith FawwazNo ratings yet
- VT800 User Manual-900DDocument19 pagesVT800 User Manual-900DMigue MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ijcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)Document6 pagesIjcet: International Journal of Computer Engineering & Technology (Ijcet)IAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Review of Related Literature ADocument7 pagesChapter 2 Review of Related Literature AMichaelNo ratings yet
- 1 3Document11 pages1 3factorialNo ratings yet
- IJAS - Volume 12 - Issue 2 - Pages 5067-5076Document10 pagesIJAS - Volume 12 - Issue 2 - Pages 5067-5076Shrilaja KNo ratings yet
- Concept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1Document25 pagesConcept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1Bharath HRNo ratings yet
- Sample DocumentationDocument17 pagesSample DocumentationChristian SanohNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Implementation of GPS Based Object Location and Route Tracking On Android DeviceDocument12 pagesResearch Paper Implementation of GPS Based Object Location and Route Tracking On Android DeviceABDULAZEEZNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Positioning System (GPS) ?: SatellitesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Global Positioning System (GPS) ?: Satellitescrunchyrull2No ratings yet
- Concept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1Document6 pagesConcept of Geo-Informatics: Chapter - 1SrikantNo ratings yet
- Searching Nearby Sites Using Google MapsDocument7 pagesSearching Nearby Sites Using Google MapsIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- In Campus Location Finder Using Mobile Application Services: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument11 pagesIn Campus Location Finder Using Mobile Application Services: Articles You May Be Interested inmarcoteran007No ratings yet
- E04342730 Project PDFDocument4 pagesE04342730 Project PDFAbhay JangirNo ratings yet
- User Position Detection in An Indoor EnvironmentDocument10 pagesUser Position Detection in An Indoor EnvironmentDediPurniawanNo ratings yet
- Bujang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 991 012137Document10 pagesBujang 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 991 012137احمد نديم اسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Hymotrack: A Mobile Ar Navigation System For Complex Indoor EnvironmentsDocument19 pagesHymotrack: A Mobile Ar Navigation System For Complex Indoor EnvironmentshenmusNo ratings yet
- Sensors: Seamless Positioning and Navigation by Using Geo-Referenced Images and Multi-Sensor DataDocument23 pagesSensors: Seamless Positioning and Navigation by Using Geo-Referenced Images and Multi-Sensor DataSC Priyadarshani de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Indoor Positioning and Navigation System For AutonDocument14 pagesIndoor Positioning and Navigation System For AutonMrMsmaxNo ratings yet
- LE THI KHANH LINH 20193549 ICT. Writing Assignment.Document5 pagesLE THI KHANH LINH 20193549 ICT. Writing Assignment.klizNo ratings yet
- Application of GPS-RTK Technology in The Land ChanDocument6 pagesApplication of GPS-RTK Technology in The Land ChanVenkat INo ratings yet
- Waypoint Navigation SystemDocument7 pagesWaypoint Navigation SystemShaukat WazirNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Location Awareness and Sharing System Using GPS and 3G/GPRSDocument16 pagesDesign and Implementation of Location Awareness and Sharing System Using GPS and 3G/GPRScedaserdnaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Uses of GPS?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Uses of GPS?Shiela Mae SalesNo ratings yet
- Journal Paper 1 SazidDocument26 pagesJournal Paper 1 SazidSazid Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- 3749-Article Text-10616-1-10-20170809Document7 pages3749-Article Text-10616-1-10-20170809nisaovo2No ratings yet
- GPS Tracking SystemDocument4 pagesGPS Tracking SystemSreenath SreeNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Tracking System Using GPS and Android OSDocument5 pagesVehicle Tracking System Using GPS and Android OSshobanraj1995No ratings yet
- pp25 Mountain1Document2 pagespp25 Mountain1Ciprian IlieNo ratings yet
- Survey of Indoor Tracking Systems Using Augmented RealityDocument13 pagesSurvey of Indoor Tracking Systems Using Augmented RealityIAES IJAI100% (1)
- 24561-Article Text-37378-1-10-20200616Document8 pages24561-Article Text-37378-1-10-20200616cumacoba267No ratings yet
- Arm Hardware Platform For Vehicular Monitoring and Tracking Using Gps and GSMDocument9 pagesArm Hardware Platform For Vehicular Monitoring and Tracking Using Gps and GSMtango 12No ratings yet
- .Vehicle Tracking With Geo Fencing On Android PlatformDocument4 pages.Vehicle Tracking With Geo Fencing On Android PlatformHakiem HalimNo ratings yet
- 50 DesigningDocument7 pages50 DesigningYoftahiNo ratings yet
- Performance Comparision Between Two Microcontorllers Based GPS ForDocument7 pagesPerformance Comparision Between Two Microcontorllers Based GPS Forاحمد نديم اسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Location Fingerprinting of Mobile Terminals by Using Wi-Fi DeviceDocument4 pagesLocation Fingerprinting of Mobile Terminals by Using Wi-Fi DeviceIjarcet JournalNo ratings yet
- 18 - V1204050 - Mobile - HDocument6 pages18 - V1204050 - Mobile - HShalini TiwariNo ratings yet
- What Is GPS and How Is It Used in Land Surveying?Document5 pagesWhat Is GPS and How Is It Used in Land Surveying?mdNo ratings yet
- GPS Note Class 11 PhysicsDocument3 pagesGPS Note Class 11 Physicsgautamsushil150No ratings yet
- Exploring The Systems and Tools of Indoor NavigationDocument13 pagesExploring The Systems and Tools of Indoor NavigationAbdurahman AL FurjaniNo ratings yet
- Design of anti-GPS For Reasons of SecurityDocument22 pagesDesign of anti-GPS For Reasons of SecuritySssssjsjsjsjsNo ratings yet
- Mobile Tracking Application: Radhika Kinage, Jyotshna Kumari, Purva Zalke, Meenal KulkarniDocument7 pagesMobile Tracking Application: Radhika Kinage, Jyotshna Kumari, Purva Zalke, Meenal KulkarniArøn ParNo ratings yet
- Geographic Information SystemsDocument22 pagesGeographic Information SystemsAnkit MathurNo ratings yet
- Gps & Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesGps & Its ApplicationsDivya VarshneyNo ratings yet
- GPS Based Location Tracking System Via ADocument7 pagesGPS Based Location Tracking System Via Anikita dubeyNo ratings yet
- GPS Localization Improvement of Smartphones Using Built-In SensorsDocument8 pagesGPS Localization Improvement of Smartphones Using Built-In Sensorszeinab15No ratings yet
- Position Detection and Tracking System (IRACST)Document7 pagesPosition Detection and Tracking System (IRACST)praveenaNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing (RS) and GIS Research Paper R2Document7 pagesRemote Sensing (RS) and GIS Research Paper R2jamesbondmsd07No ratings yet
- Indoor Navigation System For MuseumDocument6 pagesIndoor Navigation System For MuseumIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Location Based Services-388Document4 pagesLocation Based Services-388Friends94 FeniNo ratings yet
- Development of Smart Watch Gps Tracker Application STEM 2018-19Document24 pagesDevelopment of Smart Watch Gps Tracker Application STEM 2018-19Ray MartNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Document4 pagesPerimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Rupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- ETCW08Document4 pagesETCW08Editor IJAERDNo ratings yet
- Indoor Navigation SystemDocument6 pagesIndoor Navigation SystemIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Thesis Gps SystemDocument4 pagesThesis Gps SystemBuyPapersOnlineHighPoint100% (2)
- 5 Equipments Used in The Field of Surveying: Dogma, Jan Katelyne P. 2019-02376 Engr. Irish PolingaDocument7 pages5 Equipments Used in The Field of Surveying: Dogma, Jan Katelyne P. 2019-02376 Engr. Irish PolingaJan Katelyne DogmaNo ratings yet
- Geo-Information: Tracking 3D Moving Objects Based On GPS/IMU Navigation Solution, Laser Scanner Point Cloud and GIS DataDocument16 pagesGeo-Information: Tracking 3D Moving Objects Based On GPS/IMU Navigation Solution, Laser Scanner Point Cloud and GIS DataGopi Krishna ValluriNo ratings yet
- Reference PaperDocument6 pagesReference PaperPratibha VermaNo ratings yet
- 3413 Ijcsea 06Document9 pages3413 Ijcsea 06Rupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Development of Automatic Geofencing and AccidentalDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Automatic Geofencing and AccidentalRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Micro Location For Internet of Things enDocument16 pagesMicro Location For Internet of Things enRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Spatio Temporal Proximity Assitance ProcDocument5 pagesSpatio Temporal Proximity Assitance ProcRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Document4 pagesPerimeter Security Using Geo Fencing Technology IJERTCONV2IS10051Rupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Geofencing and Background Tracking - The Next Features in LBSDocument15 pagesGeofencing and Background Tracking - The Next Features in LBSRupam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Quanum Manual Multicopter Flying ControllerDocument21 pagesQuanum Manual Multicopter Flying ControllerYimmeeeNo ratings yet
- GPS 15xH/15xL Technical Specifications: 190-00266-03 Revision A December 2009Document40 pagesGPS 15xH/15xL Technical Specifications: 190-00266-03 Revision A December 2009raoultrifan7560No ratings yet
- Modern Survey TechniquesDocument15 pagesModern Survey TechniquesNishant DasNo ratings yet
- Stromberg Carlson GpsDocument103 pagesStromberg Carlson GpsArielNo ratings yet
- Sulky DX20-30 ENDocument24 pagesSulky DX20-30 ENAleksandar DautovicNo ratings yet
- E7 Practice Test U6Document4 pagesE7 Practice Test U6Cao DucLaamNo ratings yet
- Timeprovider 2700: Edge Grandmaster ClockDocument5 pagesTimeprovider 2700: Edge Grandmaster Clockton LustriaNo ratings yet
- Principles of GPSDocument11 pagesPrinciples of GPSWong_Hong_Wei100% (1)
- Strahlenfolter - Chip Implants Already Here - Electronic HarassmentDocument10 pagesStrahlenfolter - Chip Implants Already Here - Electronic Harassmentnwo-mengele-doctorsNo ratings yet
- The Role of Global Positional Systems in Policing and Crime PreventionDocument20 pagesThe Role of Global Positional Systems in Policing and Crime PreventionSaChibvuri JeremiahNo ratings yet
- ABB Obsolescence NoticeDocument8 pagesABB Obsolescence Noticevangeliskyriakos8998No ratings yet
- 2nd Mate Past Question Papers Till November21Document280 pages2nd Mate Past Question Papers Till November21ARYAN DUBEY0% (1)
- Truecam A4 Manual MultilangDocument232 pagesTruecam A4 Manual MultilangCORNELIONo ratings yet
- Pipeline Integrity Management SystemDocument9 pagesPipeline Integrity Management SystemFroylán Ernesto Pompa García100% (1)
- Sim28ml Spec v1507Document1 pageSim28ml Spec v1507MrIhex ShanNo ratings yet
- Gpsmic: Gpsbox: Enabling Location Tracking With EaseDocument10 pagesGpsmic: Gpsbox: Enabling Location Tracking With EasePeter JacobNo ratings yet
- Smart Jacket: Water Safety System Using GPS LocationDocument3 pagesSmart Jacket: Water Safety System Using GPS LocationGRD Journals0% (1)
- Differential GPS (A Method of Processing The GPS Data)Document23 pagesDifferential GPS (A Method of Processing The GPS Data)Saurabh SumanNo ratings yet
- TDS Survey Pro With TSX v4.6.0 User's Manual - ReconDocument367 pagesTDS Survey Pro With TSX v4.6.0 User's Manual - ReconRomeo BlancoNo ratings yet
- Spider 2 User ManualDocument4 pagesSpider 2 User ManualJacob MillerNo ratings yet
- MP 2028 GDocument2 pagesMP 2028 GSrikanth SinghNo ratings yet
- United States District Court: EvidenceDocument39 pagesUnited States District Court: EvidenceJack RyanNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Gps Tracking SystemDocument8 pagesLiterature Review Gps Tracking Systemeygyabvkg100% (1)
- How To Interface GPS With 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesHow To Interface GPS With 8051 MicrocontrollerSỹ RonNo ratings yet
- G V 300 Ficha TecnicaDocument2 pagesG V 300 Ficha TecnicaJose Eduardo GalarzaNo ratings yet
- Long Range Locators - Intergallactic PistolsDocument5 pagesLong Range Locators - Intergallactic PistolsSneshko SnegicNo ratings yet
- Seatracer: User ManualDocument26 pagesSeatracer: User ManualSuresh VinzudaNo ratings yet
- Comparing GPS Only With GPS GLONASS Positioning in A Regional Permanent GNSS Network 2007 GPS SolutionsDocument10 pagesComparing GPS Only With GPS GLONASS Positioning in A Regional Permanent GNSS Network 2007 GPS SolutionsMohamed HamedNo ratings yet
- Acr - SLB 2000-100Document2 pagesAcr - SLB 2000-100tassawarNo ratings yet