Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Progress Is Made by Observing Reality Through: Lightweight Framework
Progress Is Made by Observing Reality Through: Lightweight Framework
Uploaded by
ramzi esprimsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Progress Is Made by Observing Reality Through: Lightweight Framework
Progress Is Made by Observing Reality Through: Lightweight Framework
Uploaded by
ramzi esprimsCopyright:
Available Formats
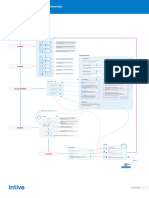
Scrum
A way for people, teams and organizations to deliver value by
working together more efficiently at solving complex problems
Scrum is a lightweight framework using the scientific
method of empiricism to gain knowledge through experience
and observation to make decisions
It uses lean thinking to eliminate waste through
continuous improvement by identifying opportunities to
change work for the better
Scrum consists of Theory | Values | Framework
Theory
Progress is made
by observing reality
through
Presenting
the Facts
Making work visible and
presenting the facts so everyone
Transparency knows what’s going on, they trust
You Can each other, and collaborate to
Change Direction ensure everyone is aware of both
good and bad news
The Scrum Team uses
feedback or results from
inspecting their work to
adapt to change
Adaptation Inspection Checking Your
Work as You Do It
Everyone on the Scrum
Team inspects product,
practices, and continuous
improvement
Values
Direct the Team’s work, actions and behavior
Living these values is what makes Scrum successful! Everyone works
together reinforcing the values and supporting each other
Commitment Focus Openness Respect Courage
Scrum Team Everyone focuses The Scrum Team Team members Scrum Team
members commit to on the work in the and Stakeholders respect each other members have the
achieving their goals sprint and making agree to be open to be capable, courage to do the
and supporting progress towards about all the work independent people right thing and
each other the Team’s goals and challenges treating each other work on tough
with it respectfully problems
Framework
Structure applying the theory and values to the daily
interactions of people
The Framework consists of a Scrum Team of Developers, a Product
Owner, and a Scrum Master who work in time-boxed Sprints.
Scrum Team is accountable for creating a valuable,
useful increment in every sprint
Less than 10 people
Cross-Functional
Self-Managing
Accountable
NO hierarchies or sub-teams
WHOLE team works together
Developers
Commit to delivering a usable increment in each
sprint.This term broadly describes people with specific
skills or knowledge of a specific area
Scrum Master
True leader who is Scrum Product Owner
accountable to the Scrum Team Maximizes the product
Team, Product Owner and value the Team produces
Organization ensuring and collaborates with the
everyone Team to deliver a
understands Scrum valuable, increment in
the Sprint
The Sprint contains four events the Team uses to inspect and adapt
their Scrum Artifacts: Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review and
Sprint Retrospective
Fixed length of 1 month or less
with all 4 events occurring
within the Sprint
Team works toward the Sprint
Goal and quality doesn’t
decrease
Team refines Product Backlog
as needed
Team may need to clarify and renegotiate Scope with PO
No changes are made to endanger the Sprint Goal
Daily Scrum
Daily 15 min meetings for the Scrum
Team to inspect their progress towards
their Sprint Goal and make any
adjustments to their work in a Sprint
Sprint Planning Sprint Review Sprint Retrospective
Scrum Team Scrum Team reviews the Scrum Team reviews the
decides what work outcome from their outcome from their Sprint
they plan to do for Sprint with Stakeholders, with Stakeholders,
a Sprint progress towards their progress towards their
Product Goal, and any Product Goal, and any
adjustments to make adjustments to make
All necessary work to achieve the Product Goal and 4 events occurs in a Sprint. A new Sprint
immediately starts when the previous Sprint Ends. Each new Sprint builds an increment of
product value with each !increment building on the next until the team achieves the Product Goal
Scrum Artifacts consist of three artifacts which are the Product
Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment. Each artifact supports three
corresponding commitments of the: Product Goal, Sprint Goal, and an
Definition of Done
Product Backlog
A prioritized list of items to improve or build a product.
The Scrum Team works together to refine or decompose
the Product Backlog into smaller, work items they
determine ‘Ready’ for Sprint Planning.
Developers who are doing the work will size work items
during Product Backlog Refinement or Sprint Planning.
Products can be a service, physical product or
something more abstract.
Sprint Backlog
Developers plan and manage the work in the Sprint Backlog of what they will
accomplish in the Sprint to achieve their Sprint Goal. The Sprint Backlog contains:
Sprint Goal (Why is this Sprint valuable?)
Product Backlog Items selected for the Sprint
(What can be done in this Sprint?)
Actionable Plan for delivering the Increment
(How the chosen work will get done?)
Increment
The increment is a concrete step towards achieving the
Product Goal with each step building onto he next one
until the goal is reached. An increment must be usable to
provide value.
The Scrum Team can produce multiple increments within a
Sprint or at the end of a Sprint. The Team can deliver theses
increments to stakeholders during or at the end of a
Sprint-delivering value at any time, not only at a Sprint Review.
All products deliver value with a clear boundary, known stakeholders and with a clear
definition of a customer or user
Commitments
Product Goal Sprint Goal Definition of Done
Long-term objective of the Commitment by the Formal description for what
future state of the product. Developers of what they will the outcome of an increment
achieve as the outcome of should be and the quality
It’s a target the Scrum Team
the Sprint. measures for a product.
plans their Product Backlog
items towards defining what The Sprint Goal When a Product Backlog
items will achieve this goal. encourages the Scrum Item meets the Definition of
Team to work together to Done, an increment is
achieve this goal. completed
Tatijana Aleksandrovic https://www.linkedin.com/in/tatijanaaleksandrovic/
You might also like
- PSK I Question AnswerDocument9 pagesPSK I Question Answerjanos BaloghNo ratings yet
- V2000M72 - Maintenance ScheduleDocument29 pagesV2000M72 - Maintenance ScheduleFreddy ChenNo ratings yet
- Additional Cases Ch08Document4 pagesAdditional Cases Ch08amanraajNo ratings yet
- Case-Study Intarlinks-Reboot July2017v3Document10 pagesCase-Study Intarlinks-Reboot July2017v3NameNo ratings yet
- SCRUM Konrad ChabrosDocument36 pagesSCRUM Konrad ChabrosKonrad ChabrosNo ratings yet
- Scrum Training: by Abderrahmen MokraniDocument71 pagesScrum Training: by Abderrahmen MokraniAbderrahmen MokraniNo ratings yet
- Agile Methodology: Iterative Development ModelDocument14 pagesAgile Methodology: Iterative Development Modelapi userNo ratings yet
- Scrum Handbook enDocument12 pagesScrum Handbook enDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Scrum Cheat Sheet 2022Document1 pageScrum Cheat Sheet 2022oumaima idhikaNo ratings yet
- Scrum BookDocument20 pagesScrum BookdharanikumaravelNo ratings yet
- The Scrum Handbook PDFDocument86 pagesThe Scrum Handbook PDFJulio Cruz SuárezNo ratings yet
- What Is ScrumDocument15 pagesWhat Is Scrumaladin007No ratings yet
- 1250 WhitePaper MediumRes PDFDocument8 pages1250 WhitePaper MediumRes PDFSingh Anish K.100% (1)
- Minh ChauDocument12 pagesMinh ChauMinh ChâuNo ratings yet
- Scrum Guide NotesssDocument7 pagesScrum Guide NotesssHelen MylonaNo ratings yet
- Professional Scrum Competency: Understanding and Applying The Scrum FrameworkDocument3 pagesProfessional Scrum Competency: Understanding and Applying The Scrum FrameworkAbbas SafieddineNo ratings yet
- Core Scrum PDFDocument14 pagesCore Scrum PDFtmartel_99No ratings yet
- Executive Scrum@Scale Essence CardsDocument3 pagesExecutive Scrum@Scale Essence CardsChrisNo ratings yet
- Course 5 Agile Project ManagementDocument27 pagesCourse 5 Agile Project ManagementnandchaNo ratings yet
- Security Product Company Nexus Case Study - 0Document3 pagesSecurity Product Company Nexus Case Study - 0swamyNo ratings yet
- Scrum FundamentalsDocument5 pagesScrum FundamentalsMatias SchulzNo ratings yet
- Scrum - A Description From The Scrum Alliance: Agile Atlas CommentariesDocument6 pagesScrum - A Description From The Scrum Alliance: Agile Atlas CommentariesAnonymous p7CY5EWh6No ratings yet
- Moving Your Scrum Downfield: White PaperDocument9 pagesMoving Your Scrum Downfield: White PaperLuis Ernesto Reyes RománNo ratings yet
- SCRUMDocument13 pagesSCRUMTayabaa Shaik100% (2)
- Agile and Scrum Cheat Sheet April 2021Document1 pageAgile and Scrum Cheat Sheet April 2021ReddalNo ratings yet
- ITGov S7 SCRUM-DEVOPS Template 2020IDocument34 pagesITGov S7 SCRUM-DEVOPS Template 2020IJose BryanNo ratings yet
- Scrum Handbook 2010-07-07.finalDocument67 pagesScrum Handbook 2010-07-07.finalclebermdNo ratings yet
- Scrum ProcessDocument36 pagesScrum Processdohuyhoang25062000No ratings yet
- Scrum Framework - Mnemonic 5Document1 pageScrum Framework - Mnemonic 5Lukasz MatgdaNo ratings yet
- ScrumDocument26 pagesScrumfatih kilicNo ratings yet
- Agile ScrumDocument61 pagesAgile ScrumMAFIX BINODNo ratings yet
- SCRUM: Mastering Agile Project Management for Exceptional Results (2023 Guide for Beginners)From EverandSCRUM: Mastering Agile Project Management for Exceptional Results (2023 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- Scrum TheoryDocument3 pagesScrum Theoryarifa_136No ratings yet
- Scrum Master Exam Simulator (Mock Test) - 420 Questions - Volkerdon - The Best Solution To Prepare FDocument1 pageScrum Master Exam Simulator (Mock Test) - 420 Questions - Volkerdon - The Best Solution To Prepare FKonrad ChabrosNo ratings yet
- S OverviewofScrumFrame 1Document7 pagesS OverviewofScrumFrame 1mxiixmNo ratings yet
- Glosario de Términos Scrum (Inglés)Document1 pageGlosario de Términos Scrum (Inglés)yoliNo ratings yet
- 2017-Scrum-Guide-US Summery NoteDocument8 pages2017-Scrum-Guide-US Summery NoteGiang LuongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Agile and ScrumDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Agile and ScrumTushar BajajNo ratings yet
- Manual Tester Workshop: AgileDocument34 pagesManual Tester Workshop: AgileAlexandru Si Larisa Serb-AlexeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ScrumDocument6 pagesIntroduction To ScrumGulush MammadhasanovaNo ratings yet
- February 2010: Scrum: Developed and Sustained by Ken Schwaber and Jeff SutherlandDocument21 pagesFebruary 2010: Scrum: Developed and Sustained by Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherlandscrumdotorg100% (2)
- Quick Scrum PresentationDocument10 pagesQuick Scrum PresentationRugved BhiseNo ratings yet
- Scrum PresentationDocument10 pagesScrum PresentationRugved BhiseNo ratings yet
- Jeff Sutherland's Scrum Handbook: January 2010Document67 pagesJeff Sutherland's Scrum Handbook: January 2010Devesh variaNo ratings yet
- Jeff Sutherland's Scrum Handbook: January 2010Document67 pagesJeff Sutherland's Scrum Handbook: January 2010Devesh variaNo ratings yet
- Agile and Scrum Reference HandoutDocument2 pagesAgile and Scrum Reference HandoutPriscilla Joyce PriscillaNo ratings yet
- LP AgileDocument1 pageLP Agilelileje4639No ratings yet
- Scrum Book of Knowledge - V1.0Document29 pagesScrum Book of Knowledge - V1.0saikrishnatadiboyinaNo ratings yet
- Eb Agile at Scale 101Document11 pagesEb Agile at Scale 101Indymaru EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Jeff Sutherland's Scrum Handbook: January 2010Document67 pagesJeff Sutherland's Scrum Handbook: January 2010Adrian M HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Ict Project Management Using Scrum Day1Document56 pagesIct Project Management Using Scrum Day1Dark LordNo ratings yet
- Scrum Guide - 2011Document17 pagesScrum Guide - 2011Angelo AssisNo ratings yet
- Neli-Carmen Konan: Work History ContactDocument3 pagesNeli-Carmen Konan: Work History ContactharshNo ratings yet
- Agile Methodology: Janessa Marielle CruzDocument34 pagesAgile Methodology: Janessa Marielle CruzJanessa CruzNo ratings yet
- BL 6. Scaled - Professional - ScrumDocument5 pagesBL 6. Scaled - Professional - Scrumdfdg100% (1)
- Lecture 07 SlidesDocument10 pagesLecture 07 Slidesxitibo4337No ratings yet
- Agile L1 FundamentalsDocument48 pagesAgile L1 FundamentalsMeek KeeNo ratings yet
- Scrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressDocument66 pagesScrum Handbook: Scrum Training Institute PressFranky RiveroNo ratings yet
- The Scrum Guide Unfolds: Agile Software Development, #2From EverandThe Scrum Guide Unfolds: Agile Software Development, #2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Scrum: The Agile Framework for Efficient Software Development. Collaborative Teamwork with ScrumFrom EverandScrum: The Agile Framework for Efficient Software Development. Collaborative Teamwork with ScrumNo ratings yet
- From SAFe to Spotify: Comparing Enterprise Agile FrameworksFrom EverandFrom SAFe to Spotify: Comparing Enterprise Agile FrameworksNo ratings yet
- Scrum Agile Software Development Master: Scrum Guide For BeginnersFrom EverandScrum Agile Software Development Master: Scrum Guide For BeginnersNo ratings yet
- What Are Web Services'?: - A Form of Distributed Information System' - "Document62 pagesWhat Are Web Services'?: - A Form of Distributed Information System' - "ramzi esprimsNo ratings yet
- Android Course: By: MR Adnane AymanDocument64 pagesAndroid Course: By: MR Adnane Aymanramzi esprimsNo ratings yet
- Angularjs Form Validation With Ngmessages: Submit Ajax Forms Angular'S Built-In Validation Angular-FormlyDocument6 pagesAngularjs Form Validation With Ngmessages: Submit Ajax Forms Angular'S Built-In Validation Angular-Formlyramzi esprimsNo ratings yet
- Angularjs Form Validation: RequirementsDocument12 pagesAngularjs Form Validation: Requirementsramzi esprimsNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Module 4 Tle Ict CSS 9Document2 pagesSummative Test Module 4 Tle Ict CSS 9Ronaldo Oloroso Abinal Jr.No ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument26 pagesNumerical DifferentiationchibenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: General Principles in Taxation: Aranea, 98 Phil. 148)Document12 pagesChapter 1: General Principles in Taxation: Aranea, 98 Phil. 148)Rover RossNo ratings yet
- Manual Instruction For Shutle Kiln-To NetDocument75 pagesManual Instruction For Shutle Kiln-To NetlonungNo ratings yet
- Ex. 428 JEREMY L. KEATING RICHARD P. GIGLIOTTI and ALEXANDER J. MELEDocument18 pagesEx. 428 JEREMY L. KEATING RICHARD P. GIGLIOTTI and ALEXANDER J. MELEWai DaiNo ratings yet
- Ict 2300Document19 pagesIct 2300Jim Carlo Abegonia Amansec100% (2)
- (Dis) Honesty - The Truth About Lies: A Companion Film Discussion & Activity GuideDocument3 pages(Dis) Honesty - The Truth About Lies: A Companion Film Discussion & Activity GuideKevin MalloryNo ratings yet
- Case Study Grading Rubric Presenter Name: Judges Initials:: Case Presentation/ Uniqueness of CaseDocument1 pageCase Study Grading Rubric Presenter Name: Judges Initials:: Case Presentation/ Uniqueness of CaseKevin DR Sumba100% (2)
- The Four Dimensions of Public Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesThe Four Dimensions of Public Financial ManagementInternational Consortium on Governmental Financial Management100% (2)
- EB 06 LightingDocument45 pagesEB 06 LightingTamNo ratings yet
- Allwinner H3 Datasheet V1.1Document616 pagesAllwinner H3 Datasheet V1.1Daniel Trejo0% (1)
- Quiz 20 Past QuizzesDocument23 pagesQuiz 20 Past QuizzesSarah Joy Corpuz-Cabasag100% (1)
- Phil. Export v. VP EusebioDocument2 pagesPhil. Export v. VP EusebioCZARINA ANN CASTRONo ratings yet
- DAMASK Damage Field: ApplicationsDocument29 pagesDAMASK Damage Field: ApplicationsFalg LeeNo ratings yet
- Cost Hook BKPDocument31 pagesCost Hook BKPDeepanshu AggarwalNo ratings yet
- At-The-Restaurant A2Document4 pagesAt-The-Restaurant A2Mjn AbbasiNo ratings yet
- FTM Business Template - Margin AnalysisDocument9 pagesFTM Business Template - Margin AnalysisSofTools LimitedNo ratings yet
- First Aid Android ApplicationDuc - Chapter 1 4Document26 pagesFirst Aid Android ApplicationDuc - Chapter 1 4paul francoNo ratings yet
- Case Study of The Marubay Rural Renewable Energy TechnologyDocument30 pagesCase Study of The Marubay Rural Renewable Energy TechnologyCollen Sita100% (1)
- Elementary French Companion PDFDocument52 pagesElementary French Companion PDFsoraravenNo ratings yet
- ISO 45001:2018 Migration Self-Assessment Guide: How Ready Are You For ISO 45001?Document16 pagesISO 45001:2018 Migration Self-Assessment Guide: How Ready Are You For ISO 45001?Vikas SinghNo ratings yet
- Afar 2704 Home Office Branch AgencyDocument33 pagesAfar 2704 Home Office Branch Agencylijeh312No ratings yet
- Solar PowerDocument6 pagesSolar PowerkusumchitikaNo ratings yet
- Opc JK Super MTC (4) 25.02.2024Document1 pageOpc JK Super MTC (4) 25.02.2024msconstu2No ratings yet
- Autodesk Inventor - Using The Content Center PT 1Document11 pagesAutodesk Inventor - Using The Content Center PT 1Ndianabasi UdonkangNo ratings yet
- 3kV Cabinet Housed Traction RectifierDocument4 pages3kV Cabinet Housed Traction Rectifierandy_mickNo ratings yet
- Technosales Multimedia Technologies PVT LTD - 36Document1 pageTechnosales Multimedia Technologies PVT LTD - 36Fbsix ApNo ratings yet
- The SEPA Regulation GuidanceDocument23 pagesThe SEPA Regulation GuidanceBaatar SukhbaatarNo ratings yet