Professional Documents
Culture Documents
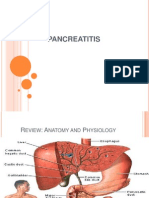
O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart Failure
O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart Failure
Uploaded by
Alec Xavier MirandaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Care Plan 5Document13 pagesCare Plan 5مالك مناصرة100% (2)
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument2 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsJillary LlagunoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocument14 pagesPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Transcribed By: B7: Francisco, Francisco, Fuentes, Gabriel, Galia, Galindon Merry Christmas Happy New Year Mery Christmas Happy New YearDocument8 pagesTranscribed By: B7: Francisco, Francisco, Fuentes, Gabriel, Galia, Galindon Merry Christmas Happy New Year Mery Christmas Happy New Yearcarlo_nonNo ratings yet
- Rug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaDocument40 pagesRug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaNiteesh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicationsDocument14 pagesRespiratory MedicationsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation-2Document40 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation-2Juliza FelicianoNo ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorsDocument2 pagesACE InhibitorsJosephine Irena100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument9 pagesCardiovascular DisordersChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Katzung - AlcoholsDocument5 pagesPharma Katzung - AlcoholsJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- N196 GI Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesN196 GI Exam Study Guideaznknight3230% (1)
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNo ratings yet
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesDocument3 pagesDRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesManuel BetancurNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesElectrolytesChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Pharmacology HandoutDocument84 pagesPharmacology Handoutnanashimii100% (4)
- Pharmacology Questions CardiacDocument5 pagesPharmacology Questions CardiacAmanda SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument69 pagesCardiovascular NotesAnnissaLarnardNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Basic Principles of PharmacologyDocument13 pagesBasic Principles of Pharmacologyemmanuel100% (1)
- Comprehensive Pharmacology Study NotesDocument123 pagesComprehensive Pharmacology Study NotesEdil M Jama100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Endocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersDocument19 pagesEndocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersPhilip SimanganNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument1 pageAbg InterpretationPrincess EspadaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Heart FailureDocument39 pagesDrugs For Heart FailureOngKahYeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Respiratory DrugsDocument44 pagesLecture 10 Respiratory DrugsCristine RamosNo ratings yet
- Renal 1Document37 pagesRenal 1febie pacheco100% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: System DisorderDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: System DisorderDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsSheral Aida100% (2)
- Hepatobiliary Disorders 2Document21 pagesHepatobiliary Disorders 2KatrinaJimenezNo ratings yet
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Genpath 04 - RENAL LABORATORY TESTS - ppt.MEd 2016 (Ninaarajade's Conflicted Copy 2016-10-29) (ASUS's Conflicted Copy 2016-11-14)Document67 pagesGenpath 04 - RENAL LABORATORY TESTS - ppt.MEd 2016 (Ninaarajade's Conflicted Copy 2016-10-29) (ASUS's Conflicted Copy 2016-11-14)RjDNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Document32 pagesAssessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Maricar RosasNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart FailureDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart Failurelynch775100% (2)
- HeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Document101 pagesHeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Putri NurlaeliNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Problem: Nephrotic Syndrome Wilm's Tumor ManagementDocument19 pagesGenitourinary Problem: Nephrotic Syndrome Wilm's Tumor ManagementJayson CruzNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsJessica100% (1)
- Adrenergic Drugs 20.07.018 PDFDocument59 pagesAdrenergic Drugs 20.07.018 PDFHitesh karnNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds To MemorizeDocument4 pagesCardiac Meds To MemorizekellyaeNo ratings yet
- FAELDONEA - B. Concept MapDocument1 pageFAELDONEA - B. Concept MapPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocument3 pagesABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Caring For Clients With Lower Respiratory Disorders PDFDocument35 pagesCaring For Clients With Lower Respiratory Disorders PDFAditya Pratama100% (1)
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (3)
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument172 pagesPharmacology ReviewJan Patrick Arrieta100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingdmsapostolNo ratings yet
- First Part Exam - October 2020Document16 pagesFirst Part Exam - October 2020hassan mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument19 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- CHF Concept MapDocument1 pageCHF Concept MapChristy Wegner Cooper100% (4)
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Hematologic DisordersDocument32 pagesHematologic DisordersQuolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Understanding ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Electrolytessurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Burns Pathophysiology 2Document1 pageBurns Pathophysiology 2Monique Ann DanoyNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pain Perception and ManagementDocument3 pagesPain Perception and ManagementAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- N11 Nursing Foundations IiDocument4 pagesN11 Nursing Foundations IiAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Basic Skills For Clients With Oxygenation ProblemsDocument3 pagesBasic Skills For Clients With Oxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Stress and AdaptationDocument4 pagesStress and AdaptationAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drugs On Reproductive System Physiology: N11 Pharmacology For NursesDocument2 pagesDrugs On Reproductive System Physiology: N11 Pharmacology For NursesAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ProblemsDocument4 pagesOxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- O o o o O: Dyslipidemia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageO o o o O: Dyslipidemia PathophysiologyAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes DrugsDocument3 pagesDiabetes DrugsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual & Psychosocial Issues in CareDocument3 pagesSpiritual & Psychosocial Issues in CareAlec Xavier Miranda100% (1)
- Basic Science Summary For The MRCSDocument111 pagesBasic Science Summary For The MRCSDrKiran Kumar Reddy100% (3)
- Perioperative Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument9 pagesPerioperative Hemodynamic MonitoringjayezmenonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument10 pagesCardiac Tamponadetitusrop10No ratings yet
- UHSDocument13 pagesUHSLatif RanaNo ratings yet
- Ts Us Global Products Accesories Supplies New Docs Accessories Supplies Catalog916cma - PDFDocument308 pagesTs Us Global Products Accesories Supplies New Docs Accessories Supplies Catalog916cma - PDFSRMPR CRMNo ratings yet
- Module One Wellness PlanDocument10 pagesModule One Wellness PlanVICTORIA MORENO DE ALMEIDANo ratings yet
- Nims Tariff ListDocument54 pagesNims Tariff ListsreekanthNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- AtacandDocument4 pagesAtacandljubodragNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputSantana Janai Francisco100% (2)
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005Document56 pagesKey Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005odysseym1No ratings yet
- Sudden Death From Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Case ReportDocument4 pagesSudden Death From Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Case ReportAnonymous JXEtV98KjPNo ratings yet
- Cast Study 1Document4 pagesCast Study 1Thelda Mae Arteche SablanNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Document34 pagesCase Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Angel Hannah100% (1)
- Digoxin (Lanoxin)Document1 pageDigoxin (Lanoxin)ENo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsDocument27 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsSofia Rose Saniel Gonzales100% (1)
- Diagnostic Procedures Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A: Diagnostic Procedure Description Purpose Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Procedures Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A: Diagnostic Procedure Description Purpose Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Simulated Exam RationalesDocument20 pagesSimulated Exam Rationalesrhymes2u100% (3)
- Introduction To Cardiac ElectrophysiologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Cardiac ElectrophysiologyNik-Othman C. Abdullah II100% (1)
- Class AvesDocument4 pagesClass AvesREYGILINE CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- Function Human HeartDocument13 pagesFunction Human Heartshyam_inkNo ratings yet
- (P) Physiology - CimDocument7 pages(P) Physiology - CimfilchibuffNo ratings yet
- MGH 8 - Ihd - NCPDocument12 pagesMGH 8 - Ihd - NCPSesinando Niez Quilao Jr.100% (1)
- Pathfit 2 Module 2Document19 pagesPathfit 2 Module 2[AP-Student] Yesha Mikaela FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Section 5 of The European Resuscitation Council GuidelinesDocument28 pagesSection 5 of The European Resuscitation Council GuidelinesАнђела КостићNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood PressureDocument69 pagesCardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood PressureUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- ECG Case StudiesDocument43 pagesECG Case Studiespaskariatne probo dewiNo ratings yet
- In The Fetal CirculationDocument1 pageIn The Fetal CirculationJesena SalveNo ratings yet
O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart Failure
O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart Failure
Uploaded by
Alec Xavier MirandaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart Failure
O Insert Picture Here From Slide: Heart Failure Heart Failure
Uploaded by
Alec Xavier MirandaCopyright:
Available Formats
N11
PHARMACOLOGY FOR NURSES
~ HEART FAILURE ~
HEART FAILURE
Inadequate oxygen delivery by the heart or circulatory system to meet the demands of the body
o Oxygen delivery = O2 content of the blood x Cardiac Output
Pathophysiology
o Insert picture here from slide
o Heart failure manifestations are primarily because of the compensatory mechanisms
o Problems lie on the compensatory mechanisms of heart failure maladaptive
o Increase of sympathetic discharges activation of alpha and beta receptors increase in blood volume, peripheral resistance
(possible), heart remodeling
o Insert another picture here
Treatment goals
o Eliminate the cause
Surgical or cardiac catheterization
Cardiac transplantation
o Optimize cardiac output
Preload
Contractility
Afterload
o Enhance oxygen delivery
o Align metabolic demands of the body
o Prevent left ventricular remodeling and deterioration of cardiac function
o Enhance effects of natriuretic peptide systems
BNP – promote natriuresis and vasodilation
ANP – promote natriuresis and vasodilation
Regulate detrimental effects of RAAS in HF-REF, inhibit secretion of AVP, nodulate autonomic nervous system
beneficial to the syndrome
BNP analogue Nesiritide failed…..
Cardiac output
o CO = HR X SV
Where SV is determined by preload, contractility, afterload
Decrease preload, increase contractility, decrease afterload (proper optimization)
Treatment goals (physiologic/neurohormonal approach)
o Decrease effects of
RAAS
Angiotensin II
Aldosterone
Adrenergic system
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
AVP/ADH
Pathophysiology
o Myocardial hypertrophy/LV remodeling
Ultimately assoc. with alterations in cellular and subcellular phenotype reducing contractility
Catecholamines
For acute case, Beta agonist are used, but for long term, it is contraindicated as we do not want chronic
sympathetic activation
Aldosterone
Angiotensin II
PHARMACOLOGIC TREATMENTS OF HEART FAILURE
Decrease preload
o Diuretics
Furosemide (K sparing)
Spironolactone (K sparing)
Decrease afterload
o ACE inhibitors (captopril, enalapril)
o Vasodilators
Except CCB contractility will be compromised
Augment contractility if necessary (severe heart failure)
o Beta-agonists
Dobutamine
Dopamine
Epinephrine
o Digoxin/lanoxin
o Decrease catecholamine/sympathetic effects – chronic, stable, heart failure
Beta blockers – carvedilol
Insert slide here
Insert diagram
Mnemonic
o Diuretics
o Inotropes
o Vasodilators
o ACE inhibitors
o Digoxin
o Ivabradine
o Beta blockers
o Aldosterone antagonists (Spironolactone, Eplerenone)
o ARNI (Sacubitril/Valsartan)
Digitalis/Digoxin
Cardiac glycosides
Insert slide here
o Insert diagram here
Insert explanation from Dr. Sison here
o Effects
Increase contractility by increasing the free calcium concentration inside the cell
Benefits r/t enzyme inhibition of noncardiac tissue
Vagal afferent fibers….
Insert slide here
In theory, can reverese heart failure
No net effect on mortality byt reduces hospitalization and death from progressive HF
Increase in sudden death
Mortality rate reduced if Serum level……….
o Other information
75% bioavailability, 20-40% protein bound, 40 hours t1/2 (urinary excretion
Many side effects
Insert slides here
Narrow therapeutic index
o Adverse effects/toxicity
Arrythmia
Bigeminal rhythm
Serious digitalis-induced cardiac arrythmia in hypokalemia
Cholinergic
Vagal and chemoreceptor zone stimulation
Disorientation, hallucination, visual disturbances
Chronic intoxication – calcium overload
Arrythmia more likely in
Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia
o Drug interaction
Insert table here
Beta Agonists
o Beta 1 receptor agonists
Positive chronotropic effect (increase pacemaker activity)
Positive inotropic effect
Insert slides here
Insert table here
o Medications
Dobutamine
Most widely used selective B1 agonist in HF
o 1-2 mins onset of action, half-life of 2 minutes, peak at 10 minutes
o Increase CO, decrease ventricular filling pressure
o Enhance automaticity of sinus node
o B2 receptor mediated ….?
Dopamine
Insert diagram here
Bipyridines
o Inhibit PDE-3 which inactivates cAMP increased cAMP
o Increase myocardial contractility
o Promote vasodilation
o Toxicity: nausea, vomiting, arrythmia, thrombocytopenia, liver enzyme changes
o Medications
Milrinone
Most successful
Oral and parenteral
5-15 minutes onset……
Insert slide here
Amrinone
o Increase contractility, decrease afterload increase CO (please confirm this)
Vasodilators
o Decrease preload, decrease afterload
o Long-acting nitrates
Most helpful in reducing filling pressures and the symptoms of pulmonary congestion
o Hydralazine (arteriolar dilator)
Address fatigue due to low CO
Diuretics
o Decrease preload, decrease afterload
o Not just diuretics but also vasodilators
o Reduce blood volume and direct vascular effects
o Deplete body soduium stores
o In heart failure
Loop diuretics
Insert slide here
o Insert diagram here
o Medications
Loop diuretics
Most potent
Inhibit NaCl reabsorptions in the thick ascending loop of Henle
Commonly used in patients with fluid overload, renal insufficiency, cardiac failure or cirrhosis
Furosemide
o Onset: 2 hours for oral, 20 minutes for IV
o 2-3 hours duration
o Direct vascular effects
o Toxicity
Ototoxicity
Hypokalemia
Dehydration
Allergy (sulfa)
Nephritis (intestinal)
Gout
Aldosterone antagonists
o Block aldosterone-stimulated NA reabsorption….
o Insert slide here
Spironolactone
o Insert slide here
o Adverse effects
Insert slide here
ACE inhibitors
o Decrease afterload, decrease preload
o Insert slide here
o Captopril, mga -pril
o Toxicity
Severe hypotension after initial doses
Insert slide here
Angiotensin-receptor blockers
o Competitive angiotensin II receptor antagonists
o Effect same as ACEIs
Vasodilation and decreased sodium retention
o Do not block bradykinin metabolism
o Same efficacy as ACEIs, more expensive
o Insert more
o Losartan, mga -sartan
Nesiritide
o Acute heart failure
o Synthetic form of BNP
o Increase cGMP in smooth muscles
o Reduce venous and arteriolar tone in experimental drugs
o Insert more
ARNI
o Angiotensin receptor blocker neprilysin inhibitor
o Sacubitril/valsartan (combination drug of what???)
Ivabradine
o If channel inhibitor (sinus node)
o Control spontaneous diastolic depolarization in the sinus node
o Slow down heart rate
o Increase diastolic filling and stroke volume
Beta blockers
o Attenuate adverse effects of high catecholamines including apoptosis
o Upregulation of B receptors
o Decrease heart rate
o Reduce remodeling
o Insert more
o Selectivity
Insert slide here
o Toxicity
Blockade of cardiac, vascular, or bronchial B receptors
Insert more
Binababa Chf Mortality
Insert drugs here
Aldosterone antagonists: spironolactone
o Competitive antagonist of aldosterone
o insert more
o mga -one
SUMMARY OF TREATMENT GOALS (MECHANISTIC)
insert slides here
You might also like
- Care Plan 5Document13 pagesCare Plan 5مالك مناصرة100% (2)
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument2 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsJillary LlagunoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)Document2 pagesPharmacology Notes (Chapter 20 and 21)graycorypNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocument14 pagesPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Transcribed By: B7: Francisco, Francisco, Fuentes, Gabriel, Galia, Galindon Merry Christmas Happy New Year Mery Christmas Happy New YearDocument8 pagesTranscribed By: B7: Francisco, Francisco, Fuentes, Gabriel, Galia, Galindon Merry Christmas Happy New Year Mery Christmas Happy New Yearcarlo_nonNo ratings yet
- Rug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaDocument40 pagesRug Therapy For Heart Failure: Dr. Santhosh RamakrishnaNiteesh Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory MedicationsDocument14 pagesRespiratory MedicationsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation-2Document40 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation-2Juliza FelicianoNo ratings yet
- ACE InhibitorsDocument2 pagesACE InhibitorsJosephine Irena100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument9 pagesCardiovascular DisordersChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Katzung - AlcoholsDocument5 pagesPharma Katzung - AlcoholsJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- N196 GI Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesN196 GI Exam Study Guideaznknight3230% (1)
- Cheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Acidosis and AlkalosisAkasha FrostmourneNo ratings yet
- DRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesDocument3 pagesDRUG SUMMARY TABLE - Anticoagulantes y AntiagregantesManuel BetancurNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal System and Nutrition Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesElectrolytesChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Pharmacology HandoutDocument84 pagesPharmacology Handoutnanashimii100% (4)
- Pharmacology Questions CardiacDocument5 pagesPharmacology Questions CardiacAmanda SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument69 pagesCardiovascular NotesAnnissaLarnardNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument4 pagesElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Basic Principles of PharmacologyDocument13 pagesBasic Principles of Pharmacologyemmanuel100% (1)
- Comprehensive Pharmacology Study NotesDocument123 pagesComprehensive Pharmacology Study NotesEdil M Jama100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocument5 pagesCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Endocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersDocument19 pagesEndocrine: Common Lab Tests For Endocrine and Hormonal DisordersPhilip SimanganNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument1 pageAbg InterpretationPrincess EspadaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Heart FailureDocument39 pagesDrugs For Heart FailureOngKahYeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Respiratory DrugsDocument44 pagesLecture 10 Respiratory DrugsCristine RamosNo ratings yet
- Renal 1Document37 pagesRenal 1febie pacheco100% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: System DisorderDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: System DisorderDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument8 pagesCNS DrugsSheral Aida100% (2)
- Hepatobiliary Disorders 2Document21 pagesHepatobiliary Disorders 2KatrinaJimenezNo ratings yet
- OB Drug ChartsDocument2 pagesOB Drug ChartsNursingSchoolNotesNo ratings yet
- Genpath 04 - RENAL LABORATORY TESTS - ppt.MEd 2016 (Ninaarajade's Conflicted Copy 2016-10-29) (ASUS's Conflicted Copy 2016-11-14)Document67 pagesGenpath 04 - RENAL LABORATORY TESTS - ppt.MEd 2016 (Ninaarajade's Conflicted Copy 2016-10-29) (ASUS's Conflicted Copy 2016-11-14)RjDNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Document32 pagesAssessment of Respiratory Function Chpt.20Maricar RosasNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart FailureDocument31 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology: - Hypertension - Angina Pectoris - Cardiac Arrhythmias - Heart Failurelynch775100% (2)
- HeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Document101 pagesHeartFailure Nursing FIK 2014Putri NurlaeliNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Problem: Nephrotic Syndrome Wilm's Tumor ManagementDocument19 pagesGenitourinary Problem: Nephrotic Syndrome Wilm's Tumor ManagementJayson CruzNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsJessica100% (1)
- Adrenergic Drugs 20.07.018 PDFDocument59 pagesAdrenergic Drugs 20.07.018 PDFHitesh karnNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds To MemorizeDocument4 pagesCardiac Meds To MemorizekellyaeNo ratings yet
- FAELDONEA - B. Concept MapDocument1 pageFAELDONEA - B. Concept MapPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- ABGs Respiratory/MetabolicDocument3 pagesABGs Respiratory/MetabolicJoe B100% (1)
- Caring For Clients With Lower Respiratory Disorders PDFDocument35 pagesCaring For Clients With Lower Respiratory Disorders PDFAditya Pratama100% (1)
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocument3 pagesCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (3)
- Pharmacology ReviewDocument172 pagesPharmacology ReviewJan Patrick Arrieta100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Med Surg Memory Notebook of NursingdmsapostolNo ratings yet
- First Part Exam - October 2020Document16 pagesFirst Part Exam - October 2020hassan mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument19 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- CHF Concept MapDocument1 pageCHF Concept MapChristy Wegner Cooper100% (4)
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 pagesCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Hematologic DisordersDocument32 pagesHematologic DisordersQuolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Understanding ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Electrolytessurviving nursing schoolNo ratings yet
- Burns Pathophysiology 2Document1 pageBurns Pathophysiology 2Monique Ann DanoyNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Pain Perception and ManagementDocument3 pagesPain Perception and ManagementAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- N11 Nursing Foundations IiDocument4 pagesN11 Nursing Foundations IiAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Basic Skills For Clients With Oxygenation ProblemsDocument3 pagesBasic Skills For Clients With Oxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Stress and AdaptationDocument4 pagesStress and AdaptationAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drugs On Reproductive System Physiology: N11 Pharmacology For NursesDocument2 pagesDrugs On Reproductive System Physiology: N11 Pharmacology For NursesAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation ProblemsDocument4 pagesOxygenation ProblemsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- O o o o O: Dyslipidemia PathophysiologyDocument1 pageO o o o O: Dyslipidemia PathophysiologyAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes DrugsDocument3 pagesDiabetes DrugsAlec Xavier MirandaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual & Psychosocial Issues in CareDocument3 pagesSpiritual & Psychosocial Issues in CareAlec Xavier Miranda100% (1)
- Basic Science Summary For The MRCSDocument111 pagesBasic Science Summary For The MRCSDrKiran Kumar Reddy100% (3)
- Perioperative Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument9 pagesPerioperative Hemodynamic MonitoringjayezmenonNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TamponadeDocument10 pagesCardiac Tamponadetitusrop10No ratings yet
- UHSDocument13 pagesUHSLatif RanaNo ratings yet
- Ts Us Global Products Accesories Supplies New Docs Accessories Supplies Catalog916cma - PDFDocument308 pagesTs Us Global Products Accesories Supplies New Docs Accessories Supplies Catalog916cma - PDFSRMPR CRMNo ratings yet
- Module One Wellness PlanDocument10 pagesModule One Wellness PlanVICTORIA MORENO DE ALMEIDANo ratings yet
- Nims Tariff ListDocument54 pagesNims Tariff ListsreekanthNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- AtacandDocument4 pagesAtacandljubodragNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputSantana Janai Francisco100% (2)
- Key Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005Document56 pagesKey Stage 3 Ks3 Science MarkScheme 2005odysseym1No ratings yet
- Sudden Death From Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Case ReportDocument4 pagesSudden Death From Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Case ReportAnonymous JXEtV98KjPNo ratings yet
- Cast Study 1Document4 pagesCast Study 1Thelda Mae Arteche SablanNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Document34 pagesCase Scenario - Week 4 - Group 2Angel Hannah100% (1)
- Digoxin (Lanoxin)Document1 pageDigoxin (Lanoxin)ENo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsDocument27 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems, Working With Other Organ SystemsSofia Rose Saniel Gonzales100% (1)
- Diagnostic Procedures Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A: Diagnostic Procedure Description Purpose Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Procedures Kristian Karl B. Kiw-Is BSN Iv-A: Diagnostic Procedure Description Purpose Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Simulated Exam RationalesDocument20 pagesSimulated Exam Rationalesrhymes2u100% (3)
- Introduction To Cardiac ElectrophysiologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Cardiac ElectrophysiologyNik-Othman C. Abdullah II100% (1)
- Class AvesDocument4 pagesClass AvesREYGILINE CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- Function Human HeartDocument13 pagesFunction Human Heartshyam_inkNo ratings yet
- (P) Physiology - CimDocument7 pages(P) Physiology - CimfilchibuffNo ratings yet
- MGH 8 - Ihd - NCPDocument12 pagesMGH 8 - Ihd - NCPSesinando Niez Quilao Jr.100% (1)
- Pathfit 2 Module 2Document19 pagesPathfit 2 Module 2[AP-Student] Yesha Mikaela FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Section 5 of The European Resuscitation Council GuidelinesDocument28 pagesSection 5 of The European Resuscitation Council GuidelinesАнђела КостићNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood PressureDocument69 pagesCardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood PressureUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- NCP Anaphylactic ShockDocument6 pagesNCP Anaphylactic ShockKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- ECG Case StudiesDocument43 pagesECG Case Studiespaskariatne probo dewiNo ratings yet
- In The Fetal CirculationDocument1 pageIn The Fetal CirculationJesena SalveNo ratings yet