Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Presentation of Pseudo-Foster Kennedy Syndrome in Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
A Presentation of Pseudo-Foster Kennedy Syndrome in Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
Uploaded by
Sri Hudaya WidihasthaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Presentation of Pseudo-Foster Kennedy Syndrome in Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
A Presentation of Pseudo-Foster Kennedy Syndrome in Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
Uploaded by
Sri Hudaya WidihasthaCopyright:
Available Formats
A PRESENTATION OF PSEUDO-FOSTER KENNEDY SYNDROME
IN UNDIAGNOSED DIABETES MELLITUS AND DYSLIPIDEMIA
Sri Hudaya Widihastha 1, Rusti Hanindya Sari 2, Antonia Kartika 2, Dianita Veulina 2
1 Department of Ophthalmology, National Eye Center Cicendo Eye Hospital/Universitas Padjadjaran, Bandung
2
Neuro-ophthalmology Unit, National Eye Center Cicendo Eye Hospital, Bandung
INTRODUCTION DISCUSSION
Pseudo-Foster Kennedy Syndrome is described as unilateral optic disc Pseudo-Foster Kennedy Syndrome typically occur due to bilateral sequential non-arteritic
swelling with contralateral optic atrophy in the absence of an anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION). Identification of risk factors associated with NAION
intracranial mass. We report a case of Pseudo-Foster Kennedy such as DM and dyslipidemia is mandatory. The most important management in NAION is
syndrome in patient with untreated Diabetes Mellitus and dyslipidemia. modification of systemic risk factors.
A 54-year-old male came with a chief complaint of painless blurred vision in CONCLUSION
CASE ILLUSTRATION
the left eye (LE) started one week ago and in the right eye (RE) started two
months ago. He has had history of treated hypertension since 10 years ago. Pseudo-foster Kennedy Syndrome may
Visual acuity of the RE was 2/60 and LE was 0.63. Relative afferent pupillary occur due to uncontrolled systemic
defect was observed on the RE.
disease, such as diabetes mellitus and
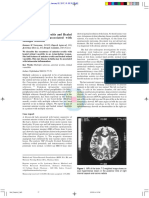
The funduscopy examination revealed optic disc pallor on the RE and optic
dyslipidemia.
disc swelling with peripapillary hemorrhage on the LE. Optical coherence Figure 1. Fundus Photograph of RE showed optic disc pallor and OCT
tomography (OCT) showed retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thinning on the examination on RE showed sectoral RNFL thinning (87 μm)
RE and thickening on the LE.
Laboratory examination showed fasting and two hours post prandial blood
REFERENCES
sugar level of 290 mg/dl and 440 mg/dl, respectively. Total cholesterol were 1. Patil, A., Takkar, A., Goyal, M., Singh, R., Lal, V. Sequential NAION presenting as
pseudo Foster Kennedy syndrome. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2017;
310 mg/dl. 376, 49-51.
2. Cestari, D. M., Gaier, E. D., Bouzika, P., Blachley, T. S., De Lott, L. B., Rizzo, J. F., et al.
Magnetic resonance imaging showed there was no signs of cerebral infarct Demographic, systemic, and ocular factors associated with nonarteritic anterior
ischemic optic neuropathy. 2016; 123 (12), 2446-2455
or space occupying lesion. Patient was diagnosed with Pseudo-Foster 3. Berry, S., Lin, W. V., Sadaka, A., & Lee, A. G. Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic
neuropathy: cause, effect, and management. Eye and Brain. 2017; 9, 23.
Kennedy Syndrome caused by ischemic optic neuropathy.
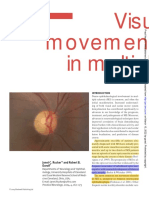
Further management was systemic regulation and neuroprotective agent. Figure 2. Fundus Photograph of LE showed optic disc swelling with
peripapillary hemorrhage and OCT examination on LE showed RNFL Pseudo-foster Kennedy Syndrome, diabetes
thickening (131 μm) KEYWORDS: mellitus, dyslipidemia, non-arteritic anterior
ischemic optic neuropathy
You might also like
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- MICR3001 Past Exam Paper Practices (2018 Discussion)Document25 pagesMICR3001 Past Exam Paper Practices (2018 Discussion)ekampreetNo ratings yet
- Typical, Atypical Optic NeuritisDocument10 pagesTypical, Atypical Optic NeuritisScerbatiuc CristinaNo ratings yet
- Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) : DiseaseDocument9 pagesNon-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) : DiseaseSiti Rokoyah Rezkylia SaktiNo ratings yet
- Posterior ScleritisDocument4 pagesPosterior ScleritisPande GustianaNo ratings yet
- Algoritmo Diagnostico de La Ceguera Monocular en Una Paciente Con NeurosarcoidosisDocument8 pagesAlgoritmo Diagnostico de La Ceguera Monocular en Una Paciente Con NeurosarcoidosisFarid Santiago Abedrabbo LombeydaNo ratings yet
- IndianJOphthalmol51177-524492 143409Document3 pagesIndianJOphthalmol51177-524492 143409novywardanaNo ratings yet
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome After Lumbar PunctureDocument2 pagesPosterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome After Lumbar PunctureMedtext PublicationsNo ratings yet
- 31-Year-Old Man With Balint'S Syndrome and Visual Problems: Clinical History and NeuroimagingDocument4 pages31-Year-Old Man With Balint'S Syndrome and Visual Problems: Clinical History and NeuroimagingwillygopeNo ratings yet
- Internuclear OpthalmoplegiaDocument3 pagesInternuclear OpthalmoplegiaahlibedahNo ratings yet
- Vision Research: Stephanie K. Lynch, Michael D. AbràmoffDocument7 pagesVision Research: Stephanie K. Lynch, Michael D. Abràmoffanka_mihaelaNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Ophthalmology: Introduction: James Goodwin, MD (Attending)Document4 pagesNeuro-Ophthalmology: Introduction: James Goodwin, MD (Attending)Mariano FioreNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis With Ophthalmologic Onset - Case ReportDocument5 pagesMultiple Sclerosis With Ophthalmologic Onset - Case ReportVannyNo ratings yet
- Nefropatías ÓpticasDocument9 pagesNefropatías Ópticasgabyc164No ratings yet
- OpticIschemia BiousseDocument9 pagesOpticIschemia BiousseyetyningsyNo ratings yet
- Foster Kennedy Syndrome: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesFoster Kennedy Syndrome: A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy: Peerooz Saeed, M.D., PH.D., Shahzad Tavakoli Rad, M.D., Peter H. L. T. Bisschop, M.D., PH.DDocument8 pagesDysthyroid Optic Neuropathy: Peerooz Saeed, M.D., PH.D., Shahzad Tavakoli Rad, M.D., Peter H. L. T. Bisschop, M.D., PH.DcatalinaNo ratings yet
- (10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Mechanisms of Visual Loss in PapilledemaDocument8 pages(10920684 - Neurosurgical Focus) Mechanisms of Visual Loss in PapilledemaYusuf BrilliantNo ratings yet
- 93621.2 20170831102324 Covered PDFDocument20 pages93621.2 20170831102324 Covered PDFMary GomezNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Optic Neuritis Associated With Central Nervous System InfectionDocument4 pagesBilateral Optic Neuritis Associated With Central Nervous System InfectionElhoucine MALKINo ratings yet
- Toosy Lancet Neurology 2014Document17 pagesToosy Lancet Neurology 2014Dirga Rasyidin LNo ratings yet
- Approach To Optic Neuropathies: Clinical UpdateDocument12 pagesApproach To Optic Neuropathies: Clinical UpdateHerdy VeristianNo ratings yet
- Uremic Encephalopathy - Feb 2022Document15 pagesUremic Encephalopathy - Feb 2022leozdmNo ratings yet
- Cogan With MEDocument4 pagesCogan With MEDr. Abhishek OnkarNo ratings yet
- Visual Problems Multiple Sclerosis Pract NeurologyDocument12 pagesVisual Problems Multiple Sclerosis Pract NeurologycuentoNo ratings yet
- Macular Edema As Unusual Presentation of Non-Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (Naion)Document9 pagesMacular Edema As Unusual Presentation of Non-Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (Naion)IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Approach To Neurologic DisordersDocument6 pagesApproach To Neurologic DisordersSam VattaraiNo ratings yet
- The Spectrum of Neuromyelitis Optica: ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Spectrum of Neuromyelitis Optica: ReviewRiccardo TroiaNo ratings yet
- Artigo OriginalDocument12 pagesArtigo OriginalAlan LopesNo ratings yet
- A Rare Presentation of Esotropia in High Myopia in A Young AdultDocument3 pagesA Rare Presentation of Esotropia in High Myopia in A Young AdultTinara HusniaNo ratings yet
- 2021 JinDocument9 pages2021 Jingzou2013No ratings yet
- Moon2019 PDFDocument7 pagesMoon2019 PDFGusti Zidni FahmiNo ratings yet
- Isolated Optic Perineuritis As The Presenting Sign of SarcoidosisDocument3 pagesIsolated Optic Perineuritis As The Presenting Sign of Sarcoidosiswawan 88No ratings yet
- WNL 0000000000011792Document12 pagesWNL 0000000000011792jose JimenezNo ratings yet
- Ocular Ischemic Syndrome by Dr. Ruksana PDFDocument18 pagesOcular Ischemic Syndrome by Dr. Ruksana PDFsyntacs skNo ratings yet
- Anatomic and Visual Function Outcomes in Paediatric Idiopathic Intracranial HypertensionDocument6 pagesAnatomic and Visual Function Outcomes in Paediatric Idiopathic Intracranial HypertensionRani PittaNo ratings yet
- SFN Expanding The Genetic Causes of Small Fiber Neuropathy SCN Genes and BeyondDocument13 pagesSFN Expanding The Genetic Causes of Small Fiber Neuropathy SCN Genes and BeyondOTTO VEGA VEGANo ratings yet
- Wong 2020Document5 pagesWong 2020samNo ratings yet
- IJCRR Sep2020 Vol12 Issue17Document13 pagesIJCRR Sep2020 Vol12 Issue17Aravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Foster Kennedy Synd 2Document3 pagesFoster Kennedy Synd 2Anonymous k4F8sAs25No ratings yet
- Visual Anosognosia (Anton-Babinski Syndrome) : Report of Two Cases Associated With Ischemic Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesVisual Anosognosia (Anton-Babinski Syndrome) : Report of Two Cases Associated With Ischemic Cerebrovascular DiseaseHanna EnitaNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Eye Deviation in Acute Stroke: Incidence, Hemispheric Asymmetry, and Lesion PatternDocument7 pagesConjugate Eye Deviation in Acute Stroke: Incidence, Hemispheric Asymmetry, and Lesion PatternAna GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Keratoconus in Cogan ReeseDocument3 pagesKeratoconus in Cogan ReeseDr. Abhishek OnkarNo ratings yet
- The Spectrum of Neuromyelitis Optica: ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Spectrum of Neuromyelitis Optica: ReviewMonica Aleja FernándezNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Vision Loss Associated With Radiofrequency ExposureDocument5 pagesBilateral Vision Loss Associated With Radiofrequency ExposurePisj Belongs To WhatsappNo ratings yet
- The Neuro-Ophthalmology of Multiple Sclerosis: ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Neuro-Ophthalmology of Multiple Sclerosis: ReviewAlicia FilártigaNo ratings yet
- What Are We Seeing?: Is Posterior Cortical Atrophy Just Alzheimer Disease?Document2 pagesWhat Are We Seeing?: Is Posterior Cortical Atrophy Just Alzheimer Disease?Eugenia FiginiNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Disease Prediction From Retinal Colour Fundus Images Using Image ProcessingDocument4 pagesA Survey On Disease Prediction From Retinal Colour Fundus Images Using Image ProcessingijcnesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To Optic Neuropathies: DiagnosisDocument14 pagesClinical Approach To Optic Neuropathies: Diagnosiskmathewjames100% (1)
- Rong Et Al Meta-Analysis of Genetic Association With PACG: Lijia - Chen@cuhk - Edu.hkDocument1 pageRong Et Al Meta-Analysis of Genetic Association With PACG: Lijia - Chen@cuhk - Edu.hkjuan jose mansillaNo ratings yet
- The Hyperacute Vestibular Syndrome Ear or BrainDocument2 pagesThe Hyperacute Vestibular Syndrome Ear or BrainDea CantikNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorders in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Natural History and ManagementDocument15 pagesEye Disorders in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Natural History and ManagementAndreea PleșaNo ratings yet
- Fneur 11 00071Document10 pagesFneur 11 00071Nurvia AndrianiNo ratings yet
- Neurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation.4Document10 pagesNeurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation.4Anakin SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Dementia PSPDocument38 pagesDementia PSPAlexandra CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Optic Neuropathy With Papilledema PDFDocument25 pagesOptic Neuropathy With Papilledema PDFCarolina Jaramillo100% (1)
- Blu Moderno Scientifico PosterDocument5 pagesBlu Moderno Scientifico Posterlely.ca.94No ratings yet
- E53 FullDocument3 pagesE53 FullKhalifa MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer and The EyeDocument9 pagesAlzheimer and The EyeRafiqy Sa'adiy FaizunNo ratings yet
- New Insights Into Schizophrenia: A Look at The Eye and Related StructuresDocument10 pagesNew Insights Into Schizophrenia: A Look at The Eye and Related StructurestratrNo ratings yet
- fneur-13-988825Document8 pagesfneur-13-988825adinda.larastitiNo ratings yet
- Book PentingDocument1 pageBook PentingSri Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
- Revised 22012021-Merge-Script Final-Original ArticleDocument30 pagesRevised 22012021-Merge-Script Final-Original ArticleSri Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
- Translated Copy of Translated Copy of Sumjv1i2p.141-153-2-Converted4Document1 pageTranslated Copy of Translated Copy of Sumjv1i2p.141-153-2-Converted4Sri Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
- Vision 2020 and Global Action Plan (GAP)Document6 pagesVision 2020 and Global Action Plan (GAP)Sri Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
- Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Pusat Mata Nasional Rumah Sakit Mata Cicendo BandungDocument12 pagesFakultas Kedokteran Universitas Padjadjaran Pusat Mata Nasional Rumah Sakit Mata Cicendo BandungSri Hudaya WidihasthaNo ratings yet
- Reading New E2 PDFDocument50 pagesReading New E2 PDFMary Jis100% (1)
- 2012-13 Psychiatry Board ReviewDocument79 pages2012-13 Psychiatry Board Reviewlizzy596100% (1)
- Patofisiologi PsoriasisDocument9 pagesPatofisiologi PsoriasisBilly Y. SinoelinggaNo ratings yet
- General Dentist QCHP 704-1454Document182 pagesGeneral Dentist QCHP 704-1454badarbhai222No ratings yet
- Trali Uptodate PDFDocument36 pagesTrali Uptodate PDFTety M. DorisNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines On: TetanusDocument45 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines On: TetanusHighDee FilmsNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument10 pagesRecurrent Abdominal Pain in ChildrenBariša KiršnerNo ratings yet
- Brain ProtocolsDocument36 pagesBrain Protocolsjeannine100% (3)
- Dubois Et Al. (2000) - The - FAB - A - Frontal - Assessment - Battery - at - BedsideDocument7 pagesDubois Et Al. (2000) - The - FAB - A - Frontal - Assessment - Battery - at - BedsideSusanna BianchiNo ratings yet
- Hydronephrosis Fred LuceDocument69 pagesHydronephrosis Fred LuceKMNo ratings yet
- Ichrak Ghachem, Sabra Riahi, Sana Ben Hmida, Asma Allaya, Samia Younes Department of Neurologie, CHU Taher Sfar MahdiaDocument1 pageIchrak Ghachem, Sabra Riahi, Sana Ben Hmida, Asma Allaya, Samia Younes Department of Neurologie, CHU Taher Sfar Mahdiaإشراق IchrakNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument8 pagesAcute Pancreatitismae bingbingNo ratings yet
- Renal System-Common Symptoms/signs of Renal Disorders and Systemic ExaminationDocument34 pagesRenal System-Common Symptoms/signs of Renal Disorders and Systemic ExaminationNadun MethwadaneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Q and A (Volume 2)Document7 pagesNursing Q and A (Volume 2)Rem Yriz100% (1)
- Classification System For Oral Submucous FibrosisDocument26 pagesClassification System For Oral Submucous FibrosisDR.YASIR SHAFEEQ MohiyuddinNo ratings yet
- Volvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofDocument7 pagesVolvulus: Volvulus Is When A Loop ofranshNo ratings yet
- Atrophic GlossitisDocument7 pagesAtrophic Glossitisbima prabuNo ratings yet
- Patient Education - MICROMEDEXDocument11 pagesPatient Education - MICROMEDEXkyrafangNo ratings yet
- WMS IiiDocument19 pagesWMS IiiAnet Augustine AnetNo ratings yet
- Levodopa Card#4Document2 pagesLevodopa Card#4USMCDOCNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing Assessment 1Document1 page2 Nursing Assessment 1Lorraine GambitoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Postpartum Care ActivityDocument13 pagesDrug Study: Postpartum Care ActivityJohn Paul DimaunahanNo ratings yet
- Symptomatology and Comorbidity of Somatization Disorder Amongst General Outpatients Attending A Family Medicine Clinic in South West NigeriaDocument7 pagesSymptomatology and Comorbidity of Somatization Disorder Amongst General Outpatients Attending A Family Medicine Clinic in South West Nigeriayeremias setyawanNo ratings yet
- A Patient of Poisoning in ICU (Ankit Jain)Document48 pagesA Patient of Poisoning in ICU (Ankit Jain)SharryNo ratings yet
- KKH Baby Bear Book 3rd EditionDocument672 pagesKKH Baby Bear Book 3rd EditionJonathan TayNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care in Aesthetic Medicine Practice: Mohd Shakir Bathusha Plastic SurgeonDocument96 pagesEmergency Care in Aesthetic Medicine Practice: Mohd Shakir Bathusha Plastic SurgeonRangetha ShiniNo ratings yet
- UNIT II MedicalDocument34 pagesUNIT II Medicalangelax1.1No ratings yet
- Saf 2020Document21 pagesSaf 2020yessicaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Hemorrhagic Stroke Care in The Emergency Unit: Natalie Kreitzer and Daniel WooDocument11 pagesOverview of Hemorrhagic Stroke Care in The Emergency Unit: Natalie Kreitzer and Daniel WooIstiqomahsejatiNo ratings yet