Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hyper Local Supply Chain
Hyper Local Supply Chain
Uploaded by
Aishwarya MathurOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hyper Local Supply Chain
Hyper Local Supply Chain
Uploaded by
Aishwarya MathurCopyright:
Available Formats
Hyper Local Supply Chain
HyperLocal supply chain as the name suggests is a supply chain that is used to provide
convenience and efficiency to both supplier and buyer through on demand deliveries in a
short span of time. Such supply chains are located in close proximity of the seller and buyer
and are used to serve a limited geographical area.
It is generally located in areas with high population and high retail density. The products are
services are locally sourced and delivered to the customers in the shortest span of time
possible. This model opens the doors for a number of small-scale businesses.
The USP of Hyper Local supply chains is their speed as they are able to deliver at
unbelievably fast speed and Trust as the consumer is put in a position where they can see
and understand all the steps of the supply chain from purchase to sourcing to delivery.
Consumers know where the product is made and most likely who will be delivering it to
them.
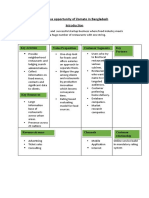
Opportunities: During the pandemic, there was a huge shift in the pattern of how customers
started purchasing. Due to the ongoing restrictions and lockdowns, customers shifted to
online mode of shopping and especially to hyperlocal businesses to get the essential
products and services delivered at the earliest.
This is the right time to get online, especially for offline merchants who might be facing
business ups and downs during this crisis. It’ll be a fully wise decision to starting with an
online business today so that even after the COVID19 crisis, you can get better growth.
Given the very focused geographic spread of a hyperlocal space, the local ventures are
almost guaranteed visibility and customers until they ensure good product and service
quality.
The hyperlocal supply chain is a promising venture for on-demand delivery. This model is
appealing enough for your online business to engage and fulfil faster deliveries.
Challenges:
Increasing competition as a greater number of players are entering the market.
Fleet management can be cumbersome and also the resources spent on the
management can be a lot.
Irregular Operations as the hyperlocal deliveries are extremely scattered and see
seasonal spikes.
Even though hyperlocal model provides the required visibility to stores, sellers have
to shell out additional costs for getting their products listed on these marketplaces.
Fight for exclusivity
Hyperlocal delivery sellers do not have a huge profit margin on their sales.
Therefore, investing in elaborate offline marketing can be a challenge.
Difficult expansion as the scope of hyperlocal model is limited a small geographical
area.
The delivery people are not long-term loyal workers and hence constant hiring and
training process is a huge challenge and adds to the cost.
Examples:
Dunzo:
This amazing Bangalore-based start-up was founded in 2014 by Ankur Agarwal, Dalvir Suri,
Kaber Biswas, and Mukund Jha.
They started taking orders on WhatsApp, but as the business and the customer base
increased, they switched quickly to an omnichannel model, marking presence with the
Android app, iOS app, and website.
Dunzo has diversified its revenue stream into five significant streams.
1. Commission Rate– Dunzo charges a specific commission from the partner store per order;
this commission rate can vary from 15% to 30%.
2. Delivery Charge– Delivery charges range from Rs. 10 to Rs. 60 depending on the distance
and the order value.
3. Surge pricing/ Demand pricing– If the demand in an area increases suddenly, then surge
pricing is applied for that area.
4. Service– Repairs, home service, etc.
5. Miscellaneous Category– This is the #kuchbhi request category launched by Dunzo, thus
the customer for Dunzo can be a 65-year-old man ordering medicines or 12-year-old kid
ordering notebooks.
Dunzo calculates the number of orders per kilometre to decide whether to keep serving a
PIN code as density is an important notion in on-demand delivery. About 500 orders per
kilometre makes economic sense. Anything less would mean delivery persons are covering
longer routes, which makes it uneconomical.
Uber Eats:
Uber Eats is a three-sided hyperlocal marketplace connecting a driver, a restaurant owner
and a customer with Uber Eats platform at the centre.
1. Restaurants pay commission on the orders to Uber Eats.
2. Customers pay the small delivery charges and at times, cancellation fee.
3. Drivers earn through making reliable deliveries on time.
Key Highlights about Uber Eats are:
Fast delivery: Uber Eats promises to deliver within 30 minutes in most of the cities
where they are currently operational. It works on the principle that “We don’t want
your food traveling halfway across town.”
No minimum order concept: The customers can order their favourite snack instead
of a full meal. The standard delivery fee ensures that all orders are fulfilled
irrespective of the order value.
Existing customer base: They already have millions of active Uber users across the
globe who can be potential Uber Eats users.
Better utilization of Uber’s resources: They already have cars/drivers on the road
and an effective system to manage it. The inclusion of Uber Eats will only help to
increase the utilization across Uber’s different verticals. For example, a cabbie who
just finished a trip may handle a food delivery order right afterward.
A top-class algorithm: It has a neatly organized algorithm for order management,
order allocation and order dispatch.
Revenue Streams for Uber Eats:
Standard Delivery Fee OR Convenience Fee: Uber Eats charges a delivery fee
from its customers irrespective of the order value.
Recurring Revenue Share from Restaurant Partners: Uber Eats takes a cut of 15%
to 40% on every order that is fulfilled from the Restaurant partners.
Marketing & Advertising Fee from Restaurant Partners: Uber Eats provides more
access to its restaurant partners and at the same time enables them to reach out
to a larger customer base by providing them marketing through various means
and charging for the same.
Source:
https://www.shiprocket.in/blog/hyperlocal-delivery-challenges/
https://www.livemint.com/news/business-of-life/the-fall-and-rise-of-startups-in-the-
hyperlocal-delivery-space-11605447484485.html
https://www.supplychain247.com/article/3_things_you_should_know_about_hyperlocal_s
upply_chains
https://fourweekmba.com/uber-eats-business-model/
You might also like
- Google Pay Product TeardownDocument10 pagesGoogle Pay Product TeardownhimaniNo ratings yet
- Hyperlocal Grocery Deck 4Document17 pagesHyperlocal Grocery Deck 4sree harshaNo ratings yet
- TVS Logistics-Building A Global Supply Chain - Group 7Document8 pagesTVS Logistics-Building A Global Supply Chain - Group 7Piyush Kumar Pattnayak100% (2)
- Method Statement Trial TrenchDocument6 pagesMethod Statement Trial TrenchSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- Solutions. A1Document11 pagesSolutions. A1Annalyn ArnaldoNo ratings yet
- Big BasketDocument3 pagesBig Basketdineshjain11100% (1)
- Ola Cabs Pre & Post IpoDocument13 pagesOla Cabs Pre & Post IposnehalNo ratings yet
- Meesho PDFDocument2 pagesMeesho PDFPrateek ManochaNo ratings yet
- Pepsi Lipton Number WorkDocument16 pagesPepsi Lipton Number WorkSachin KamraNo ratings yet
- Value Proposition - Marketing Assignment - Parimal Bobade-1Document4 pagesValue Proposition - Marketing Assignment - Parimal Bobade-1Parimal bobadeNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: DunzoDocument5 pagesStrategic Management: DunzoMilind VatsiNo ratings yet
- Assignment SolutionDocument3 pagesAssignment SolutionGeorg PaulNo ratings yet
- Ola Vs Uber Case Presentation - Group 6Document13 pagesOla Vs Uber Case Presentation - Group 6Ashish Sachdeva100% (1)
- Online Shopping DeliveryDocument8 pagesOnline Shopping DeliveryMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- QT SwiggyDocument28 pagesQT SwiggySuman NandanNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - OM Project - SWIGGYDocument19 pagesGroup 4 - OM Project - SWIGGYMudit BansalNo ratings yet
- Myntra FinalDocument10 pagesMyntra FinalThomas TomNo ratings yet
- Pepper TapDocument9 pagesPepper TapDeepak JindalNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Assignment Case Gaga FDocument4 pagesRetail Management Assignment Case Gaga FAsma AliNo ratings yet
- Final FreechargeDocument5 pagesFinal FreechargeTejas JoshiNo ratings yet
- B2B E-Commerce PDFDocument5 pagesB2B E-Commerce PDFNasir MahmudNo ratings yet
- Customer Value Proposition - Big BasketDocument1 pageCustomer Value Proposition - Big BasketKARAN AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Developing A Service Delivery Model To Bridge The Gap Between Services Expected and Provided by ICICI Home Loans.Document43 pagesDeveloping A Service Delivery Model To Bridge The Gap Between Services Expected and Provided by ICICI Home Loans.johnashmitNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Zomato: Submitted By: Kanika Bansal Akansha Gupta Sweena Ritika SinghalDocument37 pagesPresentation On Zomato: Submitted By: Kanika Bansal Akansha Gupta Sweena Ritika SinghalKanika BansalNo ratings yet
- Swiggy Research PaperDocument16 pagesSwiggy Research PaperBunnyNo ratings yet
- Final Manyavar Internal Use PDFDocument24 pagesFinal Manyavar Internal Use PDFAbhishek MhatreNo ratings yet
- OlxDocument5 pagesOlxTarun BangaNo ratings yet
- Seven Eleven Case AnalysisDocument13 pagesSeven Eleven Case AnalysisdodgekpNo ratings yet
- Rapido - Terms and ConditionsDocument9 pagesRapido - Terms and ConditionsPranjal MethiNo ratings yet
- Blu SmartpptDocument12 pagesBlu SmartpptParveNo ratings yet
- HUL's Distribution ChannelDocument8 pagesHUL's Distribution ChannelNirmal Kumar100% (1)
- VijetaDocument2 pagesVijetaPandharinath Rameshrao Chidrawar100% (1)
- Big Basket Have A Very Customized Business ModelDocument6 pagesBig Basket Have A Very Customized Business ModelShilpa SharmaNo ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas: Customer SegmentsDocument7 pagesBusiness Model Canvas: Customer SegmentsPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mahesh & Hiren (Effectiveness of Promotion)Document129 pagesMahesh & Hiren (Effectiveness of Promotion)KrupaliNo ratings yet
- Campus IIM Calcutta Team Members Keerthika, Boominathan, Siddarthan Team Name MaximusDocument4 pagesCampus IIM Calcutta Team Members Keerthika, Boominathan, Siddarthan Team Name MaximusSiddarthanSrtNo ratings yet
- Models of Service MarketingDocument34 pagesModels of Service MarketingPrasang Mangal100% (1)
- Internation Marketing Strategy Report Uber: Word Count - 1634Document7 pagesInternation Marketing Strategy Report Uber: Word Count - 1634DIVYANSHU SHEKHAR100% (1)
- A Case Study On The Marketing Strategy of ZomatoDocument13 pagesA Case Study On The Marketing Strategy of ZomatoSoumyaranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- ZomatoDocument55 pagesZomatoKrupal Lathiya100% (1)
- ZomatoDocument21 pagesZomatoVishwa Patel100% (1)
- Capstone OrginalDocument33 pagesCapstone Orginalshubham palNo ratings yet
- Grofers Case StudyDocument2 pagesGrofers Case StudyUjjwal TamangNo ratings yet
- Business Opportunity of Zomato in BangladeshDocument2 pagesBusiness Opportunity of Zomato in Bangladeshanu sahaNo ratings yet
- SnapdealDocument7 pagesSnapdealMahesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Uninor Marketing StrategiesDocument23 pagesUninor Marketing StrategiesRavi ShahNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Uber and VakrangeeDocument3 pagesQualitative Analysis of Uber and VakrangeeArunabh ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Food App EarningDocument4 pagesFood App EarningSwetha krishnaNo ratings yet
- On Uber EatsDocument6 pagesOn Uber EatsMandita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dabba WalaDocument12 pagesDabba WalaSusmriti ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Marketing of Services PPT ZomatoDocument15 pagesMarketing of Services PPT ZomatoSUMIT MITTALNo ratings yet
- Ebo VS MboDocument4 pagesEbo VS MbotdarukaNo ratings yet
- MTM Cia 3Document24 pagesMTM Cia 3AKHIL THOMAS 1827503No ratings yet
- Dealscope Google Fitbit PDFDocument1 pageDealscope Google Fitbit PDFPrasnth KumarNo ratings yet
- Final Globus - ProjectDocument72 pagesFinal Globus - Projectravi_sms001No ratings yet
- Dmonis PPT Retail Mgmt-2Document23 pagesDmonis PPT Retail Mgmt-2sujit0506No ratings yet
- Online GroceryDocument9 pagesOnline GroceryMayur KashyapNo ratings yet
- Servicescape Report (Uber)Document12 pagesServicescape Report (Uber)pranjal100% (2)
- Field Work Project (Raw) Swiggy/Zomato/Uber EatsDocument11 pagesField Work Project (Raw) Swiggy/Zomato/Uber EatsAmit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument40 pagesQuestionsSandy SantoshNo ratings yet
- Uber Eats: How Does Uber Eats Make Money? Uber Eats Business Model in A NutshellDocument12 pagesUber Eats: How Does Uber Eats Make Money? Uber Eats Business Model in A Nutshellshahnawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Dti 2Document3 pagesDti 2Jasneet BaidNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Investing - A Primer: Private Markets InsightsDocument12 pagesInfrastructure Investing - A Primer: Private Markets InsightsSeye BassirNo ratings yet
- State Bank of India: Batch Number-PAT01IC1921Document23 pagesState Bank of India: Batch Number-PAT01IC1921DIWAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- CFM Unlimited (Final)Document26 pagesCFM Unlimited (Final)Jhazzette MirasNo ratings yet
- BCM Through BRFDocument35 pagesBCM Through BRFkunariefNo ratings yet
- BMW Marketing StrategyDocument21 pagesBMW Marketing StrategyAkshit Bansal75% (12)
- Module 2.1 - Asset ValuationDocument8 pagesModule 2.1 - Asset ValuationGerald RamiloNo ratings yet
- Sharad Finial 6Document67 pagesSharad Finial 6diptanshu gaikwadNo ratings yet
- Case Study TheoryDocument6 pagesCase Study TheoryNORSARINA SIRI BIBFNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapter 6Document38 pagesHRM Chapter 6Nguyễn Quốc Phương UyênNo ratings yet
- Bop Assignment MIPDocument7 pagesBop Assignment MIPMohammad MoosaNo ratings yet
- MasUEbi Part 6 Business PlanDocument89 pagesMasUEbi Part 6 Business PlanYves Armin De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- CM 7 Case 1Document2 pagesCM 7 Case 1Celeste Tumbokon IINo ratings yet
- Final - YouTube Ads - Masterclass Beginners 2020 PDFDocument55 pagesFinal - YouTube Ads - Masterclass Beginners 2020 PDFCleriana CiorneiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory - 2Document11 pagesAuditing Theory - 2Kageyama HinataNo ratings yet
- Resume Sample For MarketingDocument6 pagesResume Sample For Marketingafmrgjwjcowaov100% (1)
- Robinhood Users Get To Own Robinhood - BloombergDocument10 pagesRobinhood Users Get To Own Robinhood - BloombergRafael AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Crushing It With YouTubeDocument30 pagesCrushing It With YouTubeEdwin Cuba Huamani100% (1)
- Ethical BankingDocument3 pagesEthical BankingSadia ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Global Business CIA IIIDocument10 pagesGlobal Business CIA IIISaiyam AhujaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Effect of Supply Chain Strategies and Collaboration On Performance Improvement Using MIMIC ModelDocument10 pagesAnalyzing The Effect of Supply Chain Strategies and Collaboration On Performance Improvement Using MIMIC ModelSiwaporn KunnapapdeelertNo ratings yet
- ONGC MM - Manual+28 - 04 - 2015Document359 pagesONGC MM - Manual+28 - 04 - 2015raviNo ratings yet
- SBD Works (NCB) - November-FinalDocument154 pagesSBD Works (NCB) - November-Finalusman umerNo ratings yet
- The Dry Port Concept Theory and PracticeDocument13 pagesThe Dry Port Concept Theory and PracticeMostafa ShaheenNo ratings yet
- EASMB 54 43-52 LuhJ378Document10 pagesEASMB 54 43-52 LuhJ378Rasi framesNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 DMC AnswersDocument7 pagesQuiz1 DMC AnswersmadenNo ratings yet
- The Dow Theory (Part 1) : Technical AnalysisDocument24 pagesThe Dow Theory (Part 1) : Technical AnalysisHarsh MisraNo ratings yet
- Protection: LateralDocument4 pagesProtection: LateralIvan HandjievNo ratings yet