Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BEE UNIT 2.2 AC Circuit
BEE UNIT 2.2 AC Circuit
Uploaded by
Sai shravya Gorekar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesThe document provides information about AC circuits including:
1) Key topics covered in the Unit-II syllabus such as representation of sinusoidal waveforms, phasor representation, and analysis of single-phase AC circuits with various RLC combinations.
2) Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction which describe how a changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor.
3) Terminology related to alternating quantities such as waveforms, instantaneous values, alternations, cycles, time period, frequency, and angular velocity.
Original Description:
Original Title
BEE UNIT 2.2 AC circuit
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about AC circuits including:
1) Key topics covered in the Unit-II syllabus such as representation of sinusoidal waveforms, phasor representation, and analysis of single-phase AC circuits with various RLC combinations.
2) Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction which describe how a changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor.
3) Terminology related to alternating quantities such as waveforms, instantaneous values, alternations, cycles, time period, frequency, and angular velocity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views6 pagesBEE UNIT 2.2 AC Circuit
BEE UNIT 2.2 AC Circuit
Uploaded by
Sai shravya GorekarThe document provides information about AC circuits including:
1) Key topics covered in the Unit-II syllabus such as representation of sinusoidal waveforms, phasor representation, and analysis of single-phase AC circuits with various RLC combinations.
2) Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction which describe how a changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor.
3) Terminology related to alternating quantities such as waveforms, instantaneous values, alternations, cycles, time period, frequency, and angular velocity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Syllabus
UNIT-II: A.C. Circuits
• Representation of sinusoidal waveforms, peak and rms values, phasor
representation, real power, reactive power, apparent power, power
factor, Analysis of single-phase ac circuits consisting of R, L, C, RL,
RC, RLC combinations (series and parallel), resonance in series
R-L-C circuit. Three-phase balanced circuits, voltage and current
relations in star and delta connections.
AC circuits
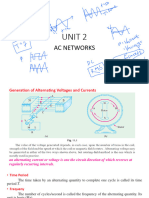
Faraday’s First Law of Electromagnetic Induction :
Whenever a conductor cuts the magnetic lines of force, an emf is
induced in the conductor.
Faraday’s Second Law of Electromagnetic Induction:
The emf induced in the conductor is given by the rate of change
of the flux linkages
AC circuits
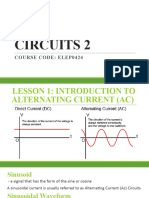
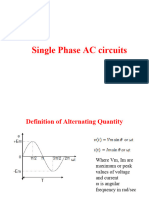
Terminology
• An alternating quantity is one which changes continuously in magnitude and
alternates in direction at regular intervals of time. It rises from zero to maximum
positive value, falls to zero, increases to a maximum in the reverse direction and
falls back to zero again.
• Wave form :- The shape of the curve of the voltage or current when plotted
against time as base is called the wave form
• Instantaneous value :- Value of an alternating quantity at any particular instant
is called the instantaneous value .
• Alternation and cycle :- When a periodic wave goes through one complete set of
positive & negative values, it is said to have completed one cycle. It corresponds
to 3600 or alternation
• Time Period and frequency :- Time taken in seconds by an alternating quantity
to complete one cycle is called time period and is denoted by T.
• Number of cycles completed per second by an alternating quantity is known as
frequency and is denoted by f. Unit is Hertz (Hz) which is equal to cycles /
second.
T = 1/f or f = 1/ T
• Angular velocity :- Each cycle spans 2 π radians in T seconds .
Angular velocity, ω = 2 π / T = 2 π f rad / sec
Numerical problem-1
An alternating current of frequency 50 Hz has a maximum value of 100A. Calculate
(i) its value (1/ 600) sec after the instant the current is zero
(ii) in how many seconds after the zero value , the current attains the value of 86.6A?
Solution
• Maximum value of current , Im = 100A, Frequency , f = 50 Hz
• Instantaneous value of alternating current, starting from the instant the current is zero and
becoming positive is given by i = Im sin ωt
= 100 sin 100 πt (ω = 2 π f = 2 π * 50 = 100 π )
(i) after 1/600 seconds, i = 100 sin 100 π * 1/ 600
= 100 sin π/6 = 50A
(ii) Let the current attain the value of 86.6A after t seconds.
You might also like
- Iec 60831-1Document116 pagesIec 60831-1AngieNo ratings yet
- Ac Fundamentals-NewDocument13 pagesAc Fundamentals-Newlarra100% (2)
- Lecture Notes 1Document7 pagesLecture Notes 1zed cozNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To AC CircuitsDocument21 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To AC CircuitsRoneline LizadaNo ratings yet
- Single Phase, AC Circuits, Basics - RMS and Average QuantitiesDocument42 pagesSingle Phase, AC Circuits, Basics - RMS and Average QuantitiesKavitha NaikNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Module 1Document28 pagesAC Circuits Module 1YoNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Ac CircuitsDocument55 pagesSingle Phase Ac CircuitsgojjimanuNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii: Fundamental of Ac CircuitsDocument24 pagesUnit-Ii: Fundamental of Ac CircuitsAbhay kushwahaNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument21 pagesAC FundamentalsSaikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byDocument23 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byAsh wanth100% (1)
- Lecture 4.5# AcfundamentalsDocument12 pagesLecture 4.5# AcfundamentalsburhanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits and Machines Lecture Notes 2016 NotesDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits and Machines Lecture Notes 2016 NotesSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 9.alternatind Iand VDocument17 pages9.alternatind Iand VKelvin OoNo ratings yet
- ACFDocument29 pagesACFBhairavi MNo ratings yet
- AC CircuitDocument91 pagesAC Circuitcarlverano0428No ratings yet
- BEE Module 5part 3Document67 pagesBEE Module 5part 3BRYAN DEXTER ARCENo ratings yet
- Circuits II 1.01 (Autosaved)Document98 pagesCircuits II 1.01 (Autosaved)Patricia DatinguinooNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering (IT-305) : By: Bhavnesh Kumar R/Faculty Associate School of EngineeringDocument54 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering (IT-305) : By: Bhavnesh Kumar R/Faculty Associate School of EngineeringSaurabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ece131 Unit 2Document189 pagesEce131 Unit 2rahtdf47No ratings yet
- Alternating Voltages and Currents and AC ValuesDocument35 pagesAlternating Voltages and Currents and AC ValuesUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Satu FasaDocument114 pagesSistem Satu FasaRiki SuryaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits LectureDocument21 pagesAC Circuits LectureAko si GianNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii: Fundamental of Ac CircuitsDocument30 pagesUnit-Ii: Fundamental of Ac CircuitsYashNo ratings yet
- ET201 Electrical Circuits PDFDocument241 pagesET201 Electrical Circuits PDFWaLiD FarhaNNo ratings yet
- Analysis of DC & AC Circuits-Steady State DC AnalysisDocument20 pagesAnalysis of DC & AC Circuits-Steady State DC AnalysisSrihari MandavaNo ratings yet
- Electrical AC SirDocument93 pagesElectrical AC SirVedant SheshkerNo ratings yet
- AC NetworksDocument182 pagesAC NetworksNitheesh PotlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - AC Circuits - MG HusseinDocument32 pagesChapter-2 - AC Circuits - MG Husseinضياء بن احمد الكباريNo ratings yet
- Mod2 AC Circuits Provided by MaamDocument72 pagesMod2 AC Circuits Provided by Maamanishdeshmukh369No ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument7 pagesAC FundamentalsJayrMenesNo ratings yet
- آلات طيران المحاضرة السابعةDocument43 pagesآلات طيران المحاضرة السابعةomarjoker808No ratings yet
- Papirntobfgwuifbgbogbg BeeDocument13 pagesPapirntobfgwuifbgbogbg BeeHANZ JERICHO HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- BEE AC Circuit-1Document25 pagesBEE AC Circuit-1Niby J LouisNo ratings yet
- القشرياتDocument19 pagesالقشرياتابراهيم عمارNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of AC Circuits: by byDocument28 pagesFundamental of AC Circuits: by byGURMEHAK MIGLANINo ratings yet
- Theory MidDocument15 pagesTheory MidSantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Part 3 Sinusoidal Current and VoltageDocument46 pagesChapter5 Part 3 Sinusoidal Current and VoltageJOHN BRYNDON LANDICHONo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals Introduction TheoryDocument25 pagesAC Fundamentals Introduction TheoryAlex ZulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- LEC 1 Rev1Document35 pagesLEC 1 Rev1Ovie MacatiagNo ratings yet
- BE - Ac Fundamentals-14052Document28 pagesBE - Ac Fundamentals-14052DeepakDeepNo ratings yet
- Actavis Notes - Session6 - Elex (Compatibility Mode)Document14 pagesActavis Notes - Session6 - Elex (Compatibility Mode)Alfred GaleaNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument16 pagesAC FundamentalsQiyanaNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument16 pagesAC FundamentalsJayson Bryan MutucNo ratings yet
- AC THEORY (Simplified)Document37 pagesAC THEORY (Simplified)Pseudo ?No ratings yet
- Basic AC Theory Handout 01-Mec. EngDocument10 pagesBasic AC Theory Handout 01-Mec. EngParamananda_SurangaNo ratings yet
- New Revised IEEE Unit 2 Alternating Voltage and CurrentDocument81 pagesNew Revised IEEE Unit 2 Alternating Voltage and CurrentNUTS GAMINGNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals & Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Monmoy JahanDocument30 pagesAC Fundamentals & Circuit Theory: Prepared By: Monmoy JahanRehnuma NoorNo ratings yet
- CT1 Unit 2Document29 pagesCT1 Unit 2Ali khan7No ratings yet
- AC Exp 02 StudentDocument6 pagesAC Exp 02 StudentxdbenerobeNo ratings yet
- C1-1 PH ckts-S1Document38 pagesC1-1 PH ckts-S1mhmd.akzrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsDocument40 pagesChapter 10 Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsAeron James V. Basilio100% (1)
- DC and AC FundamentalsDocument32 pagesDC and AC FundamentalsARIVOLI SUNDARAMURTHYNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument55 pagesNotesKhushi TiwariNo ratings yet
- e = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceDocument8 pagese = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceReniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- ACDocument16 pagesACNelson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Amateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam: Study Material 2017Document23 pagesAmateur Wireless Station Operators License Exam: Study Material 2017kundanproNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit 2 Pure ResistiveDocument96 pagesECE131 Unit 2 Pure ResistiveGURMEHAK MIGLANINo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Introduction To Ac CircuitDocument49 pagesModule 2 - Introduction To Ac CircuitScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Cont..Document50 pagesUnit-1 Cont..mitparikh1046No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 1Document25 pagesChem Unit 1Sai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument49 pagesSpectrosSai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 3Document33 pagesChem Unit 3Sai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Transpose of A MatrixDocument1 pageTranspose of A MatrixSai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and Corrosion: Question & Answers:: 1.Q. Derive Nernst Equation and Give ApplicationsDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry and Corrosion: Question & Answers:: 1.Q. Derive Nernst Equation and Give ApplicationsSai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV: Stereochemistry, Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis of Drug MoleculesDocument8 pagesUnit - IV: Stereochemistry, Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis of Drug MoleculesSai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry r18 Unit 4Document5 pagesChemistry r18 Unit 4Sai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- Water & It's Treatment Chemistry Question & Answers:: 1Q. Define Hardness of Water and Give The ClassificationDocument9 pagesWater & It's Treatment Chemistry Question & Answers:: 1Q. Define Hardness of Water and Give The ClassificationSai shravya GorekarNo ratings yet
- EasyLogic DM1000 - DM3000 Series - METSEDM1110Document2 pagesEasyLogic DM1000 - DM3000 Series - METSEDM1110Oussama ChemiNo ratings yet
- Request For Approval Request For ApprovalDocument261 pagesRequest For Approval Request For Approvalatomo333No ratings yet
- LG 32ls3400-Da Chassis lt21c mfl67362816Document45 pagesLG 32ls3400-Da Chassis lt21c mfl67362816Djalma Moreira100% (1)
- 7SR157 - Complete Technical ManualDocument180 pages7SR157 - Complete Technical Manualbureyh98No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 3Document31 pagesChapter 1 3Michael Camit EsoNo ratings yet
- Chassis Ks1a TsDocument106 pagesChassis Ks1a TsAmadou FallNo ratings yet
- X1-Boost: Single Phase Dual MPPT InvertersDocument2 pagesX1-Boost: Single Phase Dual MPPT InvertersMusthaq AhamedNo ratings yet
- EST300 Datasheet EN V01M12Y21Document4 pagesEST300 Datasheet EN V01M12Y21Aziz BasyariNo ratings yet
- Protection Earth Leakage: "Si" and "Sie" Type, A & Ac Class RCCBDocument3 pagesProtection Earth Leakage: "Si" and "Sie" Type, A & Ac Class RCCBa_miticNo ratings yet
- 3M Separable ConnectorDocument29 pages3M Separable ConnectorbuithanhtrungNo ratings yet
- Digital Panel Meters Dm-Series: Model No. DM-80E DM-60E DM-50EDocument4 pagesDigital Panel Meters Dm-Series: Model No. DM-80E DM-60E DM-50EEver LeonNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quarter 4 LASDocument27 pagesScience 9 Quarter 4 LASFerd Reddick LeponNo ratings yet
- Battery, Electrical Machines and Power SupplyDocument14 pagesBattery, Electrical Machines and Power SupplyRed David BallesterosNo ratings yet
- MD 500Document184 pagesMD 500BeeNo ratings yet
- BS 6007 - (0101001)Document26 pagesBS 6007 - (0101001)rommel duranNo ratings yet
- Pvi 7200 Wind Interface 0Document20 pagesPvi 7200 Wind Interface 0KarbonKaleNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Khởi Động Mềm LSDocument32 pagesCatalogue Khởi Động Mềm LShuy taNo ratings yet
- Model Sr560: Low-Noise PreamplifierDocument46 pagesModel Sr560: Low-Noise PreamplifierSohidul MondalNo ratings yet
- 8200-8154 Manual V3 enDocument30 pages8200-8154 Manual V3 enClemente Serrano Jurado100% (1)
- Glgn1610 Iss 1Document51 pagesGlgn1610 Iss 1Manoj Kumar MNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase AC Motor Control With V/HZ Speed Closed Loop Using The DSP56F80XDocument24 pages3-Phase AC Motor Control With V/HZ Speed Closed Loop Using The DSP56F80Xjulio100% (1)
- Brochure of 1500kVA-500kV AC Variable Frequency Resonnat Test SystemDocument12 pagesBrochure of 1500kVA-500kV AC Variable Frequency Resonnat Test SystemKassayeNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics 1Document26 pagesGcse Physics 1h19sy1No ratings yet
- CCPP ID: Not Assigned: Basic InformationDocument2 pagesCCPP ID: Not Assigned: Basic Informationdheeraj patilNo ratings yet
- 078-0132-01D LTM 10a PDFDocument46 pages078-0132-01D LTM 10a PDFMiguel Alves FilhoNo ratings yet
- Safety Relays: Operating Manual-18436-EN-06Document28 pagesSafety Relays: Operating Manual-18436-EN-06Domingos FranciscoNo ratings yet
- LED Waterproof EcoMax 2Document2 pagesLED Waterproof EcoMax 2laboratory yili indonesiaNo ratings yet
- Repair Tips For SONY TVDocument82 pagesRepair Tips For SONY TVomyzar100% (1)
- Ax001 PDFDocument1 pageAx001 PDFAl Fakhamah LiftsNo ratings yet