Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5&6 Module
5&6 Module
Uploaded by
rajee1010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesThe document contains instructions for drawing various sections, developments of surfaces, isometric projections, and perspective views of different geometric solids like cylinders, cones, prisms, and pyramids. The sections include front views, top views, and true shapes of sections. Developments include lateral surfaces of truncated solids. Isometric projections show combinations of solids. Perspective views specify the position and orientation of solids relative to the ground plane, picture plane, and station point.
Original Description:
Original Title
5&6 module
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains instructions for drawing various sections, developments of surfaces, isometric projections, and perspective views of different geometric solids like cylinders, cones, prisms, and pyramids. The sections include front views, top views, and true shapes of sections. Developments include lateral surfaces of truncated solids. Isometric projections show combinations of solids. Perspective views specify the position and orientation of solids relative to the ground plane, picture plane, and station point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pages5&6 Module
5&6 Module
Uploaded by
rajee101The document contains instructions for drawing various sections, developments of surfaces, isometric projections, and perspective views of different geometric solids like cylinders, cones, prisms, and pyramids. The sections include front views, top views, and true shapes of sections. Developments include lateral surfaces of truncated solids. Isometric projections show combinations of solids. Perspective views specify the position and orientation of solids relative to the ground plane, picture plane, and station point.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
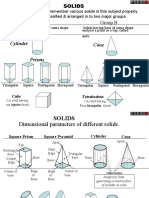
Sections of solids
1. A cylinder of diameter 40 mm and height 60 mm is having its axis
vertical. It is cut by a plane perpendicular to VP and inclined at 30o
to HP. The plane bisects the axis of the cylinder. Draw its front view,
sectional top view, and true shape of section.
2. A cone, base 25 mm diameter and axis 60 mm long, rests with its
base on HP. It is cut by section plane perpendicular to HP, inclined
at 60o to VP and at a distance of 10 mm from its axis. Draw the
sectional front view and the true shape of the section.
3. A regular hexagonal prism of the side of base 30 mm and height 60
mm is resting vertically on its base on HP such that two of the sides
of the base are perpendicular to VP. It is cut by plane inclined at 35o
to HP and perpendicular to VP. The cutting plane bisects the axis of
the pyramid. Draw its front view, sectional top view and true shape
of the section.
4. A pentagonal pyramid, base 30 mm side and axis 65 mm long has
its base horizontal and an edge of the base perpendicular to the
V.P. A horizontal section plane cuts it at a distance of 25 mm above
the base. Draw its front view, true shape of the section and sectional
top view.
Development of surfaces
1. A regular hexagonal prism of the side of base 30 mm and height 60
mm is resting vertically on its base on HP such that two of the sides
of the base are perpendicular to VP. It is cut by plane inclined at 35o
to HP and perpendicular to VP. The cutting plane bisects the axis of
the pyramid. Obtain the development of the lateral surface of the
truncated prism.
2. A lampshade which is formed from a cut cone of base 50 mm
diameter and height 65 mm. The first cutting plane which is
perpendicular to the axis and parallel to the base, cut the cone 10
mm away from the apex. The second cutting plane cuts the cone in
a manner perpendicular to its axis, 25° inclined to its base and
passing through one of the extremities of the base. Draw the
development of the lampshades lateral surface.
3. A vertical chimney of 400 mm diameter joins a roof of an industry,
sloping at 35o with the horizontal. The shortest portion over the roof
is 500 mm. Obtain the shape of the sheet metal from which the
chimney can be fabricated.
4. A pentagonal pyramid of base side 25 mm and altitude 50 mm rests
with a base edge parallel to VP and nearer to it. It is cut by a plane
perpendicular to VP and 35° inclined to HP and bisecting the axis.
Draw the development of the lateral surfaces of the truncated
pyramid.
Isometric Projection
1. A cylinder of diameter 30 mm and axis length 55 mm is mounted
centrally on the top of a square slab of side 60 mm and thickness
20 mm. Draw the isometric projection of the combination of solids.
2. Draw the isometric view of a hopper which is in the form of a frustum
of a cone having a base diameter 350 mm and top base diameter
600 mm. The height of the hopper is 600 mm. Use Scale 1:10.
3. A regular hexagonal prism of the side of base 30 mm and height 60
mm is resting vertically on its base on HP such that two of the sides
of the base are perpendicular to VP. It is cut by plane inclined at 35o
to HP and perpendicular to VP. The cutting plane bisects the axis of
the pyramid. Draw the isometric view of the truncated prism.
4. A sphere of radius 30 mm is kept centrally over a frustum of a square
pyramid of side 80 mm at the bottom, 60 mm at the top and having
a height of 70 mm. Draw the isometric projection of the combination
of solids.
Perspective Projection
1. Draw the perspective view of a square pyramid of base side 30 mm
and height 45 mm, when it rests on the ground plane (GP). A edge
of the base is touching the picture plane (PP). The station point is
situated at a distance of 60 mm in front of the PP, 60 mm above the
GP and lies in the central plane which is 40 mm to the right of the
axis.
2. Draw the perspective view of a square prism of base side 30 mm
and height 60 mm when its rests on the ground plane (GP) in such
a way that the nearest edge of the base is parallel to and 20 mm
behind the picture plane (PP). The station point is situated at a
distance of 40 mm in front of the PP, 75 mm above the GP and lies
in a central plane which is 45 mm to the right of the axis of the prism.
3. Draw the perspective view of a cube of 40 mm side rests on ground
plane (GP) on a face such that a vertical face is parallel to and 10
mm infront of the picture plane (PP). The station point is 40 mm in
front of the PP, 50 mm above the GP and lies in the central plane
which is 65 mm to the right of the axis of the cube.
You might also like
- Adams Solver GuideDocument111 pagesAdams Solver GuideAvk SanjeevanNo ratings yet
- AchamanamDocument16 pagesAchamanamrajee101100% (1)
- mETA v17.0.0 Release Notes PDFDocument21 pagesmETA v17.0.0 Release Notes PDFMihaiGabrielAnghelNo ratings yet
- Question Plate For EgDocument4 pagesQuestion Plate For EgNagaraj Muniyandi0% (1)
- EG Important QuestionDocument1 pageEG Important QuestionsenthurrNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsDhanushree DhanuNo ratings yet
- EGDocument4 pagesEGbalajimeieNo ratings yet
- EG Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesEG Practice QuestionsAjithkumar K.TNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Questions (Iae III)Document5 pagesUnit IV Questions (Iae III)Anonymous 4p20nXgWDZNo ratings yet
- EG Practical QuestionsDocument4 pagesEG Practical QuestionsBruhathi.SNo ratings yet
- Section of SolidsDocument4 pagesSection of Solidsanandandmeena100% (1)
- SBM College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul-5 Engineering Graphics-I Year (2012-13) Sectioning of SolidsDocument4 pagesSBM College of Engineering and Technology, Dindigul-5 Engineering Graphics-I Year (2012-13) Sectioning of SolidsSahaya RajNo ratings yet
- Caed NotesDocument46 pagesCaed Notesrohanshetty5512No ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics II Answer Any Five Questions 5 X 20 100Document1 pageEngineering Graphics II Answer Any Five Questions 5 X 20 100muthuramprodNo ratings yet
- Eg - Unit - 5 Assignment QuestionDocument1 pageEg - Unit - 5 Assignment QuestionsureshNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Isometric ProjectionDocument17 pagesUnit-5 Isometric ProjectionGamesmdNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EGDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank EGMohd AbrarNo ratings yet
- Development of SurfacesDocument2 pagesDevelopment of SurfacesUnamgri ONo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-VDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering I B.Tech-I SEM (20A03101T) Engineering Drawing Unit-Vramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Sample Paper, NIT CalicutDocument3 pagesEngineering Graphics Sample Paper, NIT CalicutMATHEW GEORGENo ratings yet
- Eg 2 TutorialDocument10 pagesEg 2 TutorialGanni GowthamNo ratings yet
- EG Module 3 QuestionsDocument1 pageEG Module 3 QuestionsAjithkumar K.TNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)Document4 pagesQuestion Bank For Test 2 - (Unit 3 and Unit 4)A.R. Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- 22ME160-Engg Graphics Worksheet 6 - 2023-24Document1 page22ME160-Engg Graphics Worksheet 6 - 2023-24ShankarNo ratings yet
- Development of Solid AssignmentDocument1 pageDevelopment of Solid AssignmentDipanshu XiNo ratings yet
- Section of Solids 240416Document11 pagesSection of Solids 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- IsometricDocument2 pagesIsometricanandandmeenaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IV (EG&D)Document1 pageAssignment - IV (EG&D)Sajad HaqueNo ratings yet
- Isometric and Perspective ProjectionsDocument1 pageIsometric and Perspective ProjectionsAdi DwivediNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Section of SolidsDocument14 pagesUnit IV Section of SolidsPrashant UbarhandeNo ratings yet
- Development of Solid SectionsDocument1 pageDevelopment of Solid SectionsSaumya SinhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document1 pageAssignment 8mohimab230105eeNo ratings yet
- Aux Projection 240416Document2 pagesAux Projection 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- Projection of SolidsDocument1 pageProjection of SolidsKHUSHBOO KHUSHBOONo ratings yet
- Qus PaperDocument6 pagesQus PaperBalamurugan KarnanNo ratings yet
- Drawing AssignmentDocument6 pagesDrawing AssignmentJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- EnggqpDocument4 pagesEnggqpRambabuDaraNo ratings yet
- Model Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantDocument1 pageModel Exam Eg 06.07.2022 ImportantculvertsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDocument6 pagesEngineering Graphics - Question Bank Unit - I A) Ellipse, Parabola & HyperbolaDamo Daran GNo ratings yet
- Projection Solids PrismDocument2 pagesProjection Solids PrismKarthick DavoothNo ratings yet
- Solids HWDocument2 pagesSolids HWnavneet patilNo ratings yet
- E.G Q.B. Solutions - Part BDocument28 pagesE.G Q.B. Solutions - Part BTeegavarapu Sriram hrithikNo ratings yet
- EgDocument5 pagesEgSabareesan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- QuestionBank Projection of SolidsDocument4 pagesQuestionBank Projection of SolidsAmritanshu AmritNo ratings yet
- 5 Sections of SolidsDocument1 page5 Sections of SolidsGagan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Development of Surfaces 240416Document7 pagesDevelopment of Surfaces 240416Nagaraj MuniyandiNo ratings yet
- Section of Solid and Development of SurfacesDocument2 pagesSection of Solid and Development of SurfacesPrashantNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Projection of SolidDocument2 pagesUnit 3 - Projection of Solidranjith kumarNo ratings yet
- Eg Unit 4Document6 pagesEg Unit 4rajasekaran23230% (1)
- Geethanjali Institute of Science & Technology: NelloreDocument2 pagesGeethanjali Institute of Science & Technology: Nelloreramu vasaNo ratings yet
- Anna University Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesAnna University Engineering Graphics Question BankflorenceprasadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics AssignmentDocument5 pagesEngineering Graphics AssignmentVegeta899 vegetaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Question BankDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics Question BankSriram JNo ratings yet
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFDocument8 pagesGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LNo ratings yet
- GE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFDocument8 pagesGE6152-Engineering Graphics PDFSivakumar LNo ratings yet
- Important ED-QuetionsDocument8 pagesImportant ED-Quetionssuzanirfan77No ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics QB PDFDocument8 pagesEngineering Graphics QB PDFKarthi SanNo ratings yet
- Sheets 7 To14Document16 pagesSheets 7 To14myselfnoobcoderNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 Section of SolidsDocument1 pageAssignment 6 Section of SolidsBabluNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Unit-IV Question BankDocument5 pagesEngineering Graphics Unit-IV Question BankRaam IsramNo ratings yet
- Eg Unit 5 QPDocument3 pagesEg Unit 5 QPMICHEL RAJ MechNo ratings yet
- GE 2111: Engineering Graphics:: Unit IV - Development of SolidsDocument1 pageGE 2111: Engineering Graphics:: Unit IV - Development of Solidsmuthupecmec4908No ratings yet
- The Quick & Easy Triangle Block Tool: Make 100 Triangle, Diamond & Hexagon Blocks in 4 Sizes with Project Ideas; Packed with Hints, Tips & Tricks; Simple Cutting Charts, Helpful Reference TablesFrom EverandThe Quick & Easy Triangle Block Tool: Make 100 Triangle, Diamond & Hexagon Blocks in 4 Sizes with Project Ideas; Packed with Hints, Tips & Tricks; Simple Cutting Charts, Helpful Reference TablesNo ratings yet
- MEDX 58 Total Productive MaintenanceDocument3 pagesMEDX 58 Total Productive Maintenancerajee101No ratings yet
- Simulation Lab Manual 3107Document30 pagesSimulation Lab Manual 3107rajee101No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Press Tools Dies ProblemsDocument21 pagesUnit 4 Press Tools Dies Problemsrajee101No ratings yet
- Final Yr Project - InstructionsDocument2 pagesFinal Yr Project - Instructionsrajee101No ratings yet
- Time Table - CYBER SECURITYDocument1 pageTime Table - CYBER SECURITYrajee101No ratings yet
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Document8 pagesE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101No ratings yet
- EG ConicsDocument15 pagesEG Conicsrajee101No ratings yet
- Fuzzy QF D Caie PublishedDocument17 pagesFuzzy QF D Caie Publishedrajee101No ratings yet
- Degree Award Ceremony MocDocument1 pageDegree Award Ceremony Mocrajee101No ratings yet
- Kumar2017 Article SuppliersGreenPerformanceEvaluDocument13 pagesKumar2017 Article SuppliersGreenPerformanceEvalurajee101No ratings yet
- Soc 26 6Document6 pagesSoc 26 6rajee101No ratings yet
- Tutorial - Module - 4-Projection of SolidsDocument2 pagesTutorial - Module - 4-Projection of Solidsrajee101No ratings yet
- Sri Stuti EngDocument7 pagesSri Stuti Engrajee101No ratings yet
- MEB3103 Metal Cutting & Machine ToolsDocument47 pagesMEB3103 Metal Cutting & Machine Toolsrajee101No ratings yet
- Swami Desika MangalamDocument59 pagesSwami Desika Mangalamrajee101100% (1)
- Six Sigma DMAIC MethodologyDocument3 pagesSix Sigma DMAIC Methodologyrajee1010% (1)
- CNC LAB Manual PDFDocument33 pagesCNC LAB Manual PDFrajee10133% (3)
- MEBX 14 - Statistics and Quality Control Assignment 3Document2 pagesMEBX 14 - Statistics and Quality Control Assignment 3rajee101No ratings yet
- TPM and OEEDocument46 pagesTPM and OEErajee101100% (1)
- Introduction To 8D The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) Is A Problem SolvingDocument6 pagesIntroduction To 8D The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) Is A Problem Solvingrajee101No ratings yet
- Chips PDFDocument1 pageChips PDFrajee101No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument27 pagesChapter 3 Equilibrium of A ParticledasdaNo ratings yet
- Part H: Groupie+ Module: Groupie+ - User's ManualDocument110 pagesPart H: Groupie+ Module: Groupie+ - User's ManualSâu HeoNo ratings yet
- Projection of SolidsDocument23 pagesProjection of SolidsUsama AnsariNo ratings yet
- Controllogix Controllers, Revision 16: Controllogix Controller Catalog NumbersDocument42 pagesControllogix Controllers, Revision 16: Controllogix Controller Catalog NumbersLeonardusNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their Graphs: 2.5 Graphing Techniques TransformationsDocument10 pagesFunctions and Their Graphs: 2.5 Graphing Techniques Transformationsjose-consueloNo ratings yet
- OVRS-4A Cell InterfaceDocument32 pagesOVRS-4A Cell InterfaceKask84No ratings yet
- Aqwa Theory ManualDocument208 pagesAqwa Theory ManualAnandNo ratings yet
- PH1 ProbSet 0 PDFDocument3 pagesPH1 ProbSet 0 PDFakshat shNo ratings yet
- Hommel-Etamic Measuring Systems: Geometrical Tolerancing in PracticeDocument1 pageHommel-Etamic Measuring Systems: Geometrical Tolerancing in PracticeAlexNo ratings yet
- Cad Lab ManualDocument253 pagesCad Lab ManualVishal parasannavrNo ratings yet
- Aqa Xmca2 W QP Jan10Document8 pagesAqa Xmca2 W QP Jan10Kieran RigbyNo ratings yet
- NZXSTNZXSNZXDLPost Processor Manual PDFDocument191 pagesNZXSTNZXSNZXDLPost Processor Manual PDFMatheus ManciniNo ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument5 pagesGeneral PhysicsCarol BogenggengNo ratings yet
- BIM in Bridge and Infrastructure Design Digital Building ModelsDocument183 pagesBIM in Bridge and Infrastructure Design Digital Building ModelsWirya MuradNo ratings yet
- IFEM Ch02Document11 pagesIFEM Ch02Jadiel OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Pretest College MathDocument18 pagesPretest College MathJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- June 99 Paper 4Document8 pagesJune 99 Paper 4Trishna Patel ŦNo ratings yet
- WS FunctionsDocument8 pagesWS FunctionsasmaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Line Drawing AlgorithmsDocument32 pagesPresentation On Line Drawing AlgorithmsMusariri TalentNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS 2 - MODULE 3 - Lessons 17 19 - As of Nov 5Document57 pagesCALCULUS 2 - MODULE 3 - Lessons 17 19 - As of Nov 5Kim OpenaNo ratings yet
- Milne Radar MethodDocument15 pagesMilne Radar MethodUwe KlaasNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The E Government Quality of Services Case Study X City GovernmentDocument6 pagesEvaluation of The E Government Quality of Services Case Study X City GovernmentEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- 2020 Melaka Physics K2 JawapanDocument16 pages2020 Melaka Physics K2 JawapanLincoln LawNo ratings yet
- HL Paper 1: A Function Is Defined byDocument30 pagesHL Paper 1: A Function Is Defined bySaket GudimellaNo ratings yet
- Double Integrals (Where Limits Are Not Given, But Region of Integration Is Given)Document6 pagesDouble Integrals (Where Limits Are Not Given, But Region of Integration Is Given)rajlagwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 CoordinatesDocument13 pagesChapter 8 CoordinatesWei ZhaoNo ratings yet
- CC100 EngDocument7 pagesCC100 EngMihajlo SvjetlanovićNo ratings yet
- Species Traits in Relation To Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity in Streams: A Test of Habitat Templet TheoryDocument22 pagesSpecies Traits in Relation To Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity in Streams: A Test of Habitat Templet TheoryBenyaAtehortuaNo ratings yet