Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handbook - Weld Defects 08
Handbook - Weld Defects 08
Uploaded by
Danilova SonjaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sample For Solution Manual Thermodynamics in Materials Science by Robert DeHoffDocument6 pagesSample For Solution Manual Thermodynamics in Materials Science by Robert DeHoffMasi0% (1)
- Acid Value SOPDocument3 pagesAcid Value SOPsuresh kumarNo ratings yet
- 15 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Document2 pages15 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Ruby Chong75% (4)
- Hydrogen Embrittlement PDFDocument4 pagesHydrogen Embrittlement PDFVenu Prasad100% (1)
- 7 Forms of Corrosion IDocument39 pages7 Forms of Corrosion IJesus De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Porosity Is Gas Pores Found in The Solidified Weld BeadDocument3 pagesPorosity Is Gas Pores Found in The Solidified Weld BeadMichael ChanNo ratings yet
- Requirme Assignment3Document4 pagesRequirme Assignment3Cyber RoseNo ratings yet
- Weld Defect - WikeepidiaDocument5 pagesWeld Defect - Wikeepidiapuri16No ratings yet
- Corrosion Testing of Metals - Is It Needed?: Presented atDocument21 pagesCorrosion Testing of Metals - Is It Needed?: Presented atandrea assanelliNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Inspector 1667834732Document57 pagesPipeline Inspector 1667834732Dhani de EngineurNo ratings yet
- World Oil CorrosionDocument4 pagesWorld Oil CorrosionmutemuNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Stainless SteelDocument10 pagesCorrosion of Stainless SteelRizky Ilham DescarianNo ratings yet
- HeliCoil Technical Information Corrosion Screw ThreadsDocument6 pagesHeliCoil Technical Information Corrosion Screw ThreadsAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- M 1.2.15 Cast Iron and Cast SteelsDocument20 pagesM 1.2.15 Cast Iron and Cast Steelsdokumen qcNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Corrosion ControlDocument43 pagesCorrosion and Corrosion ControlTEZ ANALYSIS AND STORIESNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal CrackingDocument9 pagesWelding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal Crackinglakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument30 pagesWelding DefectsSane ShajanNo ratings yet
- Proteksi InggrisDocument9 pagesProteksi Inggrisbo_lankNo ratings yet
- Construction MaterialDocument48 pagesConstruction MaterialEnergy HKbuildingNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter5Document10 pages10 Chapter5Dhananjay ShimpiNo ratings yet
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Aluminium. Connection of Aluminium To SteelDocument7 pagesAdvantages & Disadvantages of Aluminium. Connection of Aluminium To SteelDeepti Shrimali0% (1)
- CorrosionDocument16 pagesCorrosionAerocfdfreakNo ratings yet
- Technical Note: Corrosion Protection For Tower StructuresDocument4 pagesTechnical Note: Corrosion Protection For Tower Structuresabdulkawi alasharyNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics - Inspecting Welds in Galvanized Steel 2005-10-023Document3 pagesBack To Basics - Inspecting Welds in Galvanized Steel 2005-10-023Ramakrishnan AmbiSubbiahNo ratings yet
- Stanley Engineering TB68-1 Corrosion MethodsDocument8 pagesStanley Engineering TB68-1 Corrosion MethodskpNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Is The Gradual Destruction of Materials (Usually: MetalsDocument4 pagesCorrosion Is The Gradual Destruction of Materials (Usually: MetalsJonathan KingNo ratings yet
- Aluminium and CorrosionDocument6 pagesAluminium and Corrosionfazyroshan100% (1)
- Corrosion - WikipediaDocument16 pagesCorrosion - WikipediaAVINASHRAJNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Rust, The Most Familiar Example of CorrosionDocument13 pagesCorrosion: Rust, The Most Familiar Example of CorrosionsiswoutNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To CorrosionDocument112 pages1-Introduction To Corrosionazerai2000No ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument10 pagesChemistry AssignmentGurupungav NarayananNo ratings yet
- SMAW ModuleDocument15 pagesSMAW Modulebarry bonzoNo ratings yet
- Welding Defect in GTAWDocument19 pagesWelding Defect in GTAWMuhammad Ghiyats100% (1)
- Stick: Arc WeldingDocument4 pagesStick: Arc WeldingmohitshuklamarsNo ratings yet
- Weldability of Material TWIDocument4 pagesWeldability of Material TWIRaviTeja BhamidiNo ratings yet
- Welding - Defects and RemediesDocument62 pagesWelding - Defects and RemediesAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Corrosion EffectDocument3 pagesCorrosion Effectsamuel sanchezNo ratings yet
- Welding - Defects and RemediesDocument62 pagesWelding - Defects and RemediesAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- FP 247 03 Sand Cast BronzesDocument4 pagesFP 247 03 Sand Cast BronzesnfcastingsNo ratings yet
- Job Knowledge 19Document5 pagesJob Knowledge 19Mehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- SUewBSEA CORROSION11Document4 pagesSUewBSEA CORROSION11mayheartNo ratings yet
- Rusting and CorrosionDocument13 pagesRusting and CorrosionSanyam lambaNo ratings yet
- SMAWDocument7 pagesSMAWMaulikNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld DefectsDocument1 pageHandbook - Weld Defectskaveh-bahiraeeNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument8 pagesShielded Metal Arc WeldingberhaneNo ratings yet
- Galvanic Corrosion WikipediaDocument7 pagesGalvanic Corrosion WikipediaCharles HernandezNo ratings yet
- Weldability of MaterialsDocument5 pagesWeldability of MaterialsclnNo ratings yet
- Weldability of Materials - Aluminium Alloys - Job Knowledge 21Document3 pagesWeldability of Materials - Aluminium Alloys - Job Knowledge 21brijesh kinkhabNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelsDocument16 pagesStainless SteelsGnobelNo ratings yet
- Materials and Processes For Agricultural and Biosystems EngineeringDocument35 pagesMaterials and Processes For Agricultural and Biosystems EngineeringMelanie D. Aquino BaguioNo ratings yet
- Assignment Corrosion RustingDocument5 pagesAssignment Corrosion RustingADEBISI JELEEL ADEKUNLE100% (1)
- Cacat PinholeDocument12 pagesCacat PinholeMaya Ida SilviaNo ratings yet
- 10 Welding Defects & RemediesDocument12 pages10 Welding Defects & RemediesvilukNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Types: Direct Chemical Attack Is Also FundamentallyDocument5 pagesCorrosion Types: Direct Chemical Attack Is Also FundamentallyKemal ToprakNo ratings yet
- Materials and ProcessesDocument21 pagesMaterials and Processessamluvhouse05No ratings yet
- Introduction To /hydrogen Induced Cracking (HIC)Document5 pagesIntroduction To /hydrogen Induced Cracking (HIC)Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in Elec ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCorrosion in Elec Applicationsmohamadsadegh kamaliNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Tool-Steel - A Concise Handbook on Tool-Steel in General - Its Treatment in the Operations of Forging, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering and the Appliances ThereforFrom EverandTool-Steel - A Concise Handbook on Tool-Steel in General - Its Treatment in the Operations of Forging, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering and the Appliances ThereforNo ratings yet
- 25 Best Things To Do in StuttgartDocument42 pages25 Best Things To Do in StuttgartDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 12Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 12Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 11Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 11Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 06Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 06Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 05Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 05Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 1Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 1Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam Welding SafetyDocument1 pageElectron Beam Welding SafetyDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: By:-Abhinav Amol SomwanshiDocument33 pagesAtomic Structure: By:-Abhinav Amol SomwanshimadhurisdnyankunjNo ratings yet
- Heating Effect (Mega)Document8 pagesHeating Effect (Mega)Anant JainNo ratings yet
- Silica Carryover in BoilerDocument3 pagesSilica Carryover in BoilermnasiroleslamiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Activity SheetDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Activity SheetMary Grace LanwangNo ratings yet
- Arlacel 2121 - DC179Document4 pagesArlacel 2121 - DC179simmiNo ratings yet
- BOOST Theory PDFDocument127 pagesBOOST Theory PDFAlmudena9100% (3)
- Synthesis and Characterization of Gan/Pedot-Ppy Nanocomposites and Its Photocatalytic Activity and Electrochemical Detection of MebendazoleDocument11 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Gan/Pedot-Ppy Nanocomposites and Its Photocatalytic Activity and Electrochemical Detection of MebendazoleFRANCIA IVETTE ALVAREZ CALDERONNo ratings yet
- FTIR Spectros PDFDocument3 pagesFTIR Spectros PDFRidaSirtaDewiTRNo ratings yet
- 06 FlamephotometerDocument10 pages06 FlamephotometerHassan GillNo ratings yet
- 11 Glass - Ionomer MaterialsDocument36 pages11 Glass - Ionomer MaterialsPepo BelovedNo ratings yet
- LPP - 1 - StoichiometryDocument4 pagesLPP - 1 - StoichiometryAashiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Refrigeration Cycleskalite123No ratings yet
- Talamban National High School: Subject Teacher: Engr. Zenaida C. Grapa, PH.DDocument2 pagesTalamban National High School: Subject Teacher: Engr. Zenaida C. Grapa, PH.DFlorenz Jay DingdingNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer in Wiped Film Evaporators (CE) PDFDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer in Wiped Film Evaporators (CE) PDFjdgh1986No ratings yet
- Nucleosynthesis WsDocument2 pagesNucleosynthesis Wsbernadeth barajasNo ratings yet
- Course Planner: Subject Wise Syllabus PlanDocument2 pagesCourse Planner: Subject Wise Syllabus PlanRitesh Ranjan100% (1)
- Astm D888-12Document14 pagesAstm D888-12Mardo Mardomardo Mardo Mardomardo50% (2)
- Thermodynamic Properties of Ammonia As An IdealDocument1 pageThermodynamic Properties of Ammonia As An IdealNouha JhiderNo ratings yet
- Energy Studyguide 2015 2016Document4 pagesEnergy Studyguide 2015 2016Jeremy MyersNo ratings yet
- Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiDocument3 pagesBiomentors Classes Online, MumbaiSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Basic Revision NotesDocument55 pagesBasic Revision Noteshabiba ulanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 2022 HigherDocument32 pagesChemistry Paper 1 2022 HigherJohn RodNo ratings yet
- Free Electron TheoryDocument8 pagesFree Electron TheoryNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Class X ChemistryDocument3 pagesClass X ChemistryTejaswi VatsNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationDocument4 pagesDistillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationcsandrasNo ratings yet
- Energies 16 02918Document21 pagesEnergies 16 02918Jesús MateoNo ratings yet
- 5 TTN OeDocument9 pages5 TTN OeHeo Toàn TậpNo ratings yet
Handbook - Weld Defects 08
Handbook - Weld Defects 08
Uploaded by
Danilova SonjaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handbook - Weld Defects 08
Handbook - Weld Defects 08
Uploaded by
Danilova SonjaCopyright:
Available Formats
8/13/13 Handbook - Weld Defects
Variations-
Metal
Transfer
The atmospheric gases that are primarily responsible for porosity in steel are nitrogen and excessive
Equipment
oxygen. However, considerable oxygen can be tolerated without porosity in the absence of nitrogen. Oxygen
in the atmosphere can cause severe problems with aluminum because of its rapid oxide formation. The gas
supply should be inspected at regular intervals to insure freedom from leakage. In addition, excessive
Power
moisture in the atmosphere can cause porosity in steel and particularly aluminum. Care should be exercised
Supply
in humid climates. For example, a continuous coolant flow in water cooled torches can cause condensation
during periods of high humidity and consequent contamination of the shielding gas.
Shielding Excessive oxidation of the work pieces is an obvious source of oxygen as well as entrapped moisture.
Gases
Again, this is particularly true for aluminum where a hydrated oxide may exist. Anodized coatings on
aluminum must be removed prior to welding because they contain water as well as being an insulator.
Wire
Porosity can be caused by inadequate wire deoxidation when welding semi-killed or rimmed steels. The
Electrodes
oxygen in the steel can cause CO porosity if the proper deoxidizing elements are not present.
Foreign matter can be a source of porosity. An example is excessive lubricant on the welding wire. These
Safety hydrocarbons are sources of hydrogen which is particularly harmful for aluminum.
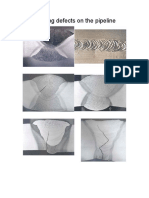
Other causes of porosity may be extremely fast weld solidification rates and erratic arc characteristics.
When solidification rates are extremely rapid, any gas that would normally escape is trapped. Extremely
Welding
Techniques high travel speeds and low welding current levels should be avoided.
Erratic arc characteristics can be caused by poor welding conditions (voltage too low or high, poor metal
transfer) and fluctuation in the wire feed speed. All these occurrences cause severe weld puddle turbulence.
Welding
Conditions This turbulence will tend to break up the shielding gas envelope and cause the molten weld metal to be
contaminated by the atmosphere.
Introduction
Economics
Incomplete
Penetration
Lack of
Weld Fusion
Defects Undercutting
Porosity
Mig Spot
Welding Longitudinal
Cracking
8
Tables
www.esabna.com/EUWeb/MIG_handbook/592mig10_8.htm 1/1
You might also like
- Sample For Solution Manual Thermodynamics in Materials Science by Robert DeHoffDocument6 pagesSample For Solution Manual Thermodynamics in Materials Science by Robert DeHoffMasi0% (1)
- Acid Value SOPDocument3 pagesAcid Value SOPsuresh kumarNo ratings yet
- 15 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Document2 pages15 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Ruby Chong75% (4)
- Hydrogen Embrittlement PDFDocument4 pagesHydrogen Embrittlement PDFVenu Prasad100% (1)
- 7 Forms of Corrosion IDocument39 pages7 Forms of Corrosion IJesus De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Porosity Is Gas Pores Found in The Solidified Weld BeadDocument3 pagesPorosity Is Gas Pores Found in The Solidified Weld BeadMichael ChanNo ratings yet
- Requirme Assignment3Document4 pagesRequirme Assignment3Cyber RoseNo ratings yet
- Weld Defect - WikeepidiaDocument5 pagesWeld Defect - Wikeepidiapuri16No ratings yet
- Corrosion Testing of Metals - Is It Needed?: Presented atDocument21 pagesCorrosion Testing of Metals - Is It Needed?: Presented atandrea assanelliNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Inspector 1667834732Document57 pagesPipeline Inspector 1667834732Dhani de EngineurNo ratings yet
- World Oil CorrosionDocument4 pagesWorld Oil CorrosionmutemuNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Stainless SteelDocument10 pagesCorrosion of Stainless SteelRizky Ilham DescarianNo ratings yet
- HeliCoil Technical Information Corrosion Screw ThreadsDocument6 pagesHeliCoil Technical Information Corrosion Screw ThreadsAce Industrial SuppliesNo ratings yet
- M 1.2.15 Cast Iron and Cast SteelsDocument20 pagesM 1.2.15 Cast Iron and Cast Steelsdokumen qcNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Corrosion ControlDocument43 pagesCorrosion and Corrosion ControlTEZ ANALYSIS AND STORIESNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal CrackingDocument9 pagesWelding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal Crackinglakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument30 pagesWelding DefectsSane ShajanNo ratings yet
- Proteksi InggrisDocument9 pagesProteksi Inggrisbo_lankNo ratings yet
- Construction MaterialDocument48 pagesConstruction MaterialEnergy HKbuildingNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter5Document10 pages10 Chapter5Dhananjay ShimpiNo ratings yet
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Aluminium. Connection of Aluminium To SteelDocument7 pagesAdvantages & Disadvantages of Aluminium. Connection of Aluminium To SteelDeepti Shrimali0% (1)
- CorrosionDocument16 pagesCorrosionAerocfdfreakNo ratings yet
- Technical Note: Corrosion Protection For Tower StructuresDocument4 pagesTechnical Note: Corrosion Protection For Tower Structuresabdulkawi alasharyNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics - Inspecting Welds in Galvanized Steel 2005-10-023Document3 pagesBack To Basics - Inspecting Welds in Galvanized Steel 2005-10-023Ramakrishnan AmbiSubbiahNo ratings yet
- Stanley Engineering TB68-1 Corrosion MethodsDocument8 pagesStanley Engineering TB68-1 Corrosion MethodskpNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Is The Gradual Destruction of Materials (Usually: MetalsDocument4 pagesCorrosion Is The Gradual Destruction of Materials (Usually: MetalsJonathan KingNo ratings yet
- Aluminium and CorrosionDocument6 pagesAluminium and Corrosionfazyroshan100% (1)
- Corrosion - WikipediaDocument16 pagesCorrosion - WikipediaAVINASHRAJNo ratings yet
- Corrosion: Rust, The Most Familiar Example of CorrosionDocument13 pagesCorrosion: Rust, The Most Familiar Example of CorrosionsiswoutNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To CorrosionDocument112 pages1-Introduction To Corrosionazerai2000No ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument10 pagesChemistry AssignmentGurupungav NarayananNo ratings yet
- SMAW ModuleDocument15 pagesSMAW Modulebarry bonzoNo ratings yet
- Welding Defect in GTAWDocument19 pagesWelding Defect in GTAWMuhammad Ghiyats100% (1)
- Stick: Arc WeldingDocument4 pagesStick: Arc WeldingmohitshuklamarsNo ratings yet
- Weldability of Material TWIDocument4 pagesWeldability of Material TWIRaviTeja BhamidiNo ratings yet
- Welding - Defects and RemediesDocument62 pagesWelding - Defects and RemediesAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Corrosion EffectDocument3 pagesCorrosion Effectsamuel sanchezNo ratings yet
- Welding - Defects and RemediesDocument62 pagesWelding - Defects and RemediesAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- FP 247 03 Sand Cast BronzesDocument4 pagesFP 247 03 Sand Cast BronzesnfcastingsNo ratings yet
- Job Knowledge 19Document5 pagesJob Knowledge 19Mehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- SUewBSEA CORROSION11Document4 pagesSUewBSEA CORROSION11mayheartNo ratings yet
- Rusting and CorrosionDocument13 pagesRusting and CorrosionSanyam lambaNo ratings yet
- SMAWDocument7 pagesSMAWMaulikNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld DefectsDocument1 pageHandbook - Weld Defectskaveh-bahiraeeNo ratings yet
- Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument8 pagesShielded Metal Arc WeldingberhaneNo ratings yet
- Galvanic Corrosion WikipediaDocument7 pagesGalvanic Corrosion WikipediaCharles HernandezNo ratings yet
- Weldability of MaterialsDocument5 pagesWeldability of MaterialsclnNo ratings yet
- Weldability of Materials - Aluminium Alloys - Job Knowledge 21Document3 pagesWeldability of Materials - Aluminium Alloys - Job Knowledge 21brijesh kinkhabNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelsDocument16 pagesStainless SteelsGnobelNo ratings yet
- Materials and Processes For Agricultural and Biosystems EngineeringDocument35 pagesMaterials and Processes For Agricultural and Biosystems EngineeringMelanie D. Aquino BaguioNo ratings yet
- Assignment Corrosion RustingDocument5 pagesAssignment Corrosion RustingADEBISI JELEEL ADEKUNLE100% (1)
- Cacat PinholeDocument12 pagesCacat PinholeMaya Ida SilviaNo ratings yet
- 10 Welding Defects & RemediesDocument12 pages10 Welding Defects & RemediesvilukNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Types: Direct Chemical Attack Is Also FundamentallyDocument5 pagesCorrosion Types: Direct Chemical Attack Is Also FundamentallyKemal ToprakNo ratings yet
- Materials and ProcessesDocument21 pagesMaterials and Processessamluvhouse05No ratings yet
- Introduction To /hydrogen Induced Cracking (HIC)Document5 pagesIntroduction To /hydrogen Induced Cracking (HIC)Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in Elec ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCorrosion in Elec Applicationsmohamadsadegh kamaliNo ratings yet
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Tool-Steel - A Concise Handbook on Tool-Steel in General - Its Treatment in the Operations of Forging, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering and the Appliances ThereforFrom EverandTool-Steel - A Concise Handbook on Tool-Steel in General - Its Treatment in the Operations of Forging, Annealing, Hardening, Tempering and the Appliances ThereforNo ratings yet
- 25 Best Things To Do in StuttgartDocument42 pages25 Best Things To Do in StuttgartDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 12Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 12Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 11Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 11Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 06Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 06Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 05Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 05Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 1Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 1Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam Welding SafetyDocument1 pageElectron Beam Welding SafetyDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: By:-Abhinav Amol SomwanshiDocument33 pagesAtomic Structure: By:-Abhinav Amol SomwanshimadhurisdnyankunjNo ratings yet
- Heating Effect (Mega)Document8 pagesHeating Effect (Mega)Anant JainNo ratings yet
- Silica Carryover in BoilerDocument3 pagesSilica Carryover in BoilermnasiroleslamiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Activity SheetDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Activity SheetMary Grace LanwangNo ratings yet
- Arlacel 2121 - DC179Document4 pagesArlacel 2121 - DC179simmiNo ratings yet
- BOOST Theory PDFDocument127 pagesBOOST Theory PDFAlmudena9100% (3)
- Synthesis and Characterization of Gan/Pedot-Ppy Nanocomposites and Its Photocatalytic Activity and Electrochemical Detection of MebendazoleDocument11 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Gan/Pedot-Ppy Nanocomposites and Its Photocatalytic Activity and Electrochemical Detection of MebendazoleFRANCIA IVETTE ALVAREZ CALDERONNo ratings yet
- FTIR Spectros PDFDocument3 pagesFTIR Spectros PDFRidaSirtaDewiTRNo ratings yet
- 06 FlamephotometerDocument10 pages06 FlamephotometerHassan GillNo ratings yet
- 11 Glass - Ionomer MaterialsDocument36 pages11 Glass - Ionomer MaterialsPepo BelovedNo ratings yet
- LPP - 1 - StoichiometryDocument4 pagesLPP - 1 - StoichiometryAashiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Refrigeration CyclesDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Refrigeration Cycleskalite123No ratings yet
- Talamban National High School: Subject Teacher: Engr. Zenaida C. Grapa, PH.DDocument2 pagesTalamban National High School: Subject Teacher: Engr. Zenaida C. Grapa, PH.DFlorenz Jay DingdingNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer in Wiped Film Evaporators (CE) PDFDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer in Wiped Film Evaporators (CE) PDFjdgh1986No ratings yet
- Nucleosynthesis WsDocument2 pagesNucleosynthesis Wsbernadeth barajasNo ratings yet
- Course Planner: Subject Wise Syllabus PlanDocument2 pagesCourse Planner: Subject Wise Syllabus PlanRitesh Ranjan100% (1)
- Astm D888-12Document14 pagesAstm D888-12Mardo Mardomardo Mardo Mardomardo50% (2)
- Thermodynamic Properties of Ammonia As An IdealDocument1 pageThermodynamic Properties of Ammonia As An IdealNouha JhiderNo ratings yet
- Energy Studyguide 2015 2016Document4 pagesEnergy Studyguide 2015 2016Jeremy MyersNo ratings yet
- Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiDocument3 pagesBiomentors Classes Online, MumbaiSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Basic Revision NotesDocument55 pagesBasic Revision Noteshabiba ulanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 2022 HigherDocument32 pagesChemistry Paper 1 2022 HigherJohn RodNo ratings yet
- Free Electron TheoryDocument8 pagesFree Electron TheoryNeelam KapoorNo ratings yet
- Class X ChemistryDocument3 pagesClass X ChemistryTejaswi VatsNo ratings yet
- Distillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationDocument4 pagesDistillation Technology and Modelling Techniques: Part 1: Concepts in DistillationcsandrasNo ratings yet
- Energies 16 02918Document21 pagesEnergies 16 02918Jesús MateoNo ratings yet
- 5 TTN OeDocument9 pages5 TTN OeHeo Toàn TậpNo ratings yet