Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST ND
Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST ND
Uploaded by
MartaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Latin Cheat Sheet CH A by JulieDocument1 pageLatin Cheat Sheet CH A by Julieraifselimi64No ratings yet
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Document3 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Pili Lema BlancoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Grammar 0Document5 pagesReported Speech Grammar 0Katita VieraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting StatementsDocument6 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting Statementsriaadria100% (2)
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechKarola CosmeNo ratings yet
- Grammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFDocument4 pagesGrammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonDocument5 pagesReported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonRishit ChandaNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Short SummaryDocument2 pagesReported Speech Short Summaryfederica fissoreNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechNoa PahlićNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocument10 pagesIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515No ratings yet
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingNo ratings yet
- 1 - Reported Speech - StatementsDocument3 pages1 - Reported Speech - StatementsJohnyNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument4 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsZaniShira100% (1)
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pages01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechZaniShiraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument5 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsSofia AngelovaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechalwiNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechdavidputraaxxNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechYefer romañaNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect Speech Reported SpeechЮля КряталоваNo ratings yet
- Example: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishDocument4 pagesExample: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishRita QuispeNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - SummaryDocument2 pagesReported Speech - SummaryFreddy Murrugarra100% (1)
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 pagesEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect Spech RulesDocument9 pagesDirect & Indirect Spech RulesUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Use Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesUse Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechIeva VaičikauskaitėNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech GRD 7 - Portal 20-21Document5 pagesReported Speech GRD 7 - Portal 20-21khalidtajuddeen2010No ratings yet
- 6 Reported SpeechDocument15 pages6 Reported SpeechAndreea ManoliNo ratings yet
- (GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)Document15 pages(GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)NamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9. Reported SpeechDocument19 pagesLesson 9. Reported SpeechEbru D.No ratings yet
- Reported Speech NotesDocument5 pagesReported Speech NotesChipo MulundikaNo ratings yet
- 4 GR Reported SpeechDocument7 pages4 GR Reported Speechpaula y soniaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: EstudiateDocument5 pagesReported Speech: EstudiateEduar Delgado Santa CruzNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Material Prepared By: Javier Medina, Valeria Martinez, Carlos Monceratt, and Eduardo MoralesDocument9 pagesReported Speech: Material Prepared By: Javier Medina, Valeria Martinez, Carlos Monceratt, and Eduardo MoralesJavier MedinaNo ratings yet
- REPORTED_SPEECH_OVERALLDocument28 pagesREPORTED_SPEECH_OVERALLwivajiNo ratings yet
- USE FormDocument17 pagesUSE FormBernardo RochaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument13 pagesReported Speechjoshe003No ratings yet
- Direct VS Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect VS Indirect SpeechKetua EE 2021 AndrianoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument34 pagesReported SpeechRubicel Cordova0% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument34 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJimin MochiNo ratings yet
- Xenophobia: Reported SpeechDocument21 pagesXenophobia: Reported SpeechJames D Saavedra M100% (1)
- Direct & IndirectDocument10 pagesDirect & Indirectmahbobahaqjo8No ratings yet
- تقرير انكليزي-مريم ياسر شيتDocument8 pagesتقرير انكليزي-مريم ياسر شيتMeMoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech TeoriaDocument4 pagesReported Speech TeoriasilviaNo ratings yet
- Types Conjunctionthings To NoteDocument9 pagesTypes Conjunctionthings To NoteZone ZeeNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reported Speech 1Document10 pagesRules For Reported Speech 1Panna100% (1)
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesRules For Reported SpeechPannaNo ratings yet
- CÂU TRỰC TIẾP GIÁN TIẾP 1Document5 pagesCÂU TRỰC TIẾP GIÁN TIẾP 1duyenloanphungdlp281224No ratings yet
- Direct-Indirect Speech EnglishDocument82 pagesDirect-Indirect Speech EnglishYanuar NugrahaNo ratings yet
- CÂU TƯỜNG THUẬTDocument9 pagesCÂU TƯỜNG THUẬTMy Nguyễn HàNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Ingles IiiDocument31 pagesReported Speech Ingles IiiOscar Andres Rojo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 2º BachilleratoDocument4 pagesReported Speech 2º BachilleratoBlancaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech CompleteDocument6 pagesReported Speech Completegloriasd2005No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGunjan GargNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ChartDocument4 pagesReported Speech ChartAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Sentences, Part-2Document5 pagesTransformation of Sentences, Part-2Shivek agrawalNo ratings yet
- Webster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageFrom EverandWebster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageNo ratings yet
- Question TagsDocument9 pagesQuestion Tagsmira oktavianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 Parsing 1Document108 pagesLecture03 Parsing 1Nada ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Fellas - Google SearchDocument1 pageFellas - Google SearchBuat Hiya hiyaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument25 pagesReported SpeechSarah LewisNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - (Vocab + Grammar)Document5 pagesUnit 6 - (Vocab + Grammar)44 - Vũ Tiến Vinh - 11A1No ratings yet
- Apostila 5 Fase-OficialDocument22 pagesApostila 5 Fase-OficialAyumiMillaNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesPassive Voicesgumo100% (1)
- Intermediate Unit 11aDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit 11agallipateroNo ratings yet
- The Passive Exercises-Mixed Tenses and Two ObjectsDocument3 pagesThe Passive Exercises-Mixed Tenses and Two ObjectsYOUSRA KESSINo ratings yet
- Present Simple-Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Simple-Present ContinuousJennyChartNo ratings yet
- Active Passive - STUDENTDocument8 pagesActive Passive - STUDENTAhmad SufianNo ratings yet
- GerundsDocument3 pagesGerundsIndra HarahapNo ratings yet
- Biblical Hebrew Summary PDFDocument1 pageBiblical Hebrew Summary PDFAres HerzeNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH - STD - 6 Midterm Term 3Document5 pagesENGLISH - STD - 6 Midterm Term 3byakayadaniel834No ratings yet
- THINK L1 Unit 2 Grammar PracticeDocument2 pagesTHINK L1 Unit 2 Grammar PracticeDana KrasnopiorkoNo ratings yet
- 4 Sentence-MeaningDocument11 pages4 Sentence-MeaningCamiRusuNo ratings yet
- D) Style: 4. Basic Components of A Narrative TextDocument14 pagesD) Style: 4. Basic Components of A Narrative TextCeleste De Jong ZumaetaNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument4 pagesPresent SimpleAlam MohammadNo ratings yet
- Degrees Og ComparisonDocument2 pagesDegrees Og ComparisonToma Elena AlinaNo ratings yet
- The Present SubjunctiveDocument3 pagesThe Present SubjunctiveZoe TziavaraNo ratings yet
- 211 Leipzig PDFDocument181 pages211 Leipzig PDFvogliaNo ratings yet
- The Order of Adjectives: Determiner Observation Physical Description Origin Material Qualifier Noun Size Shape Age ColorDocument1 pageThe Order of Adjectives: Determiner Observation Physical Description Origin Material Qualifier Noun Size Shape Age ColorNoor Azni Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Basics of Translation Theory PartDocument117 pagesBasics of Translation Theory PartOlari IuliaNo ratings yet
- Guias Pasivo y ActivoDocument5 pagesGuias Pasivo y ActivoLuigimom Orobio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Phraseological Unit Is A Word Group With A Fixed Lexical Composition and Grammatical StructureDocument10 pagesPhraseological Unit Is A Word Group With A Fixed Lexical Composition and Grammatical StructureДарья ОчманNo ratings yet
- Prueba IV Past PerfectDocument3 pagesPrueba IV Past PerfectFelipe Romero FigueroaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestSasso BluNo ratings yet
- Adunaic - The Vernacular of NumenorDocument21 pagesAdunaic - The Vernacular of Numenordiego_guimarães_64No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in EnglishAdonis CusipagNo ratings yet
Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST ND
Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST ND
Uploaded by
MartaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST ND
Direct Speech Reported Speech: ST ND
Uploaded by
MartaCopyright:
Available Formats
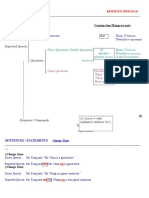
4º ESO Soraya Olmo
REPORTED SPEECH
Different types of sentences
When you use reported speech, you either report:
statements
questions
requests / commands
other types
A. Reporting Statements
When transforming statements, check whether you have to change:
pronouns
tenses
place and time expressions
1- Pronouns
1st and 2nd person change into the person who speaks (I, you →he, she..)
3rd person does not change (he, she, they →he, she, they)
2- Tenses
Direct Speech Reported Speech
Simple Present Simple Past
He said: "I am happy" He said that he was happy
Present Progressive Past Progressive
He said: "I'm looking for my keys" He said that he was looking for his keys
Simple Past Past Perfect Simple
He said: "I visited New York last year" He said that he had visited New York the
previous year.
Present Perfect Past Perfect
He said: " I've lived here for a long time " He said that he had lived there for a long time
Past Perfect Past Perfect
He said: "They had finished the work when He said that they had finished the work when
I arrived" he had arrived"
Past Progressive Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I was playing football when the He said that he had been playing football when
accident occurred" the accident had occurred
Present Perfect Progressive Past Perfect Progressive
He said:"I have been playing football for two He said that he had been playing football for
hours." two hours
4º ESO Soraya Olmo
Past Perfect Progressive Past Perfect Progressive
He said: "I had been reading a newspaper He said that he had been reading a newspaper
when the light went off" when the light had gone off
Future Simple (will+verb) Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I will open the door." He said that he would open the door.
Conditional (would+verb) Conditional (would+verb)
He said: "I would buy Mercedes if He said that he would buy Mercedes if he had
I were rich" been rich"
The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn't, ought to, used to do not normally
change. Example: He said, "She might be right." – He said that she might be right.
Other modal verbs may change:
Modal Direct speech Reported speech
can "I can do it." He said he could do it.
may "May I go out?" He wanted to know if he might go out.
must "She must apply for the job." He said that she must/had to apply for the job.
will "They will call you." He told her that they would call her.
3- Place and time expressions
Direct Speech Reported Speech
Time Expressions
today that day
now then
yesterday the day before
… days ago … days before
last week the week before
next year the following year
tomorrow the next day / the following day
Place
here there
Demonstratives
this that
these those
4º ESO Soraya Olmo
B. Reporting Questions
Types of questions Direct speech Reported speech
With question word (what, "Why" don’t you He asked me why I didn’t
why, where, how...) speak English?” speak English.
“Do you speak He asked me whether / if I
yes or no questions
English?” spoke English.
Same changes as in statements in: pronouns, tenses and place and time expressions.
C. Reporting requests / commands
Direct speech Reported speech
“Nancy,do the exercise.“ He told Nancy to do the exercise.
She said, “don’t be lazy.” He asked her not to be lazy.
Same changes as in statements in: pronouns, tenses and place and time expressions.
D.Reporting suggestions
Direct speech Reported speech
1. Let’s… - “Let’s go to the theatre,” she said. Suggest + gerund
2. Why don’t we…? - “Why don’t we go to the theatre?” - She suggested going to the
she said. theater.
3. Shall we…? - “Shall we go to the theatre?” she said. Suggest+ that + we / they + (not) +
4. Why not…? - “Why not go to the theatre? verb
5. What / How about …? - “What / How about going to -She suggested that we go to the
the theatre? theatre
Same changes as in statements in: pronouns, tenses and place and time expressions.
You might also like
- Latin Cheat Sheet CH A by JulieDocument1 pageLatin Cheat Sheet CH A by Julieraifselimi64No ratings yet
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Document3 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Pili Lema BlancoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Grammar 0Document5 pagesReported Speech Grammar 0Katita VieraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting StatementsDocument6 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) What Is Reported Speech?: A. Reporting Statementsriaadria100% (2)
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechKarola CosmeNo ratings yet
- Grammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFDocument4 pagesGrammar - L2 G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 1 PDFHadjab LyesNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonDocument5 pagesReported Speech Is When You Tell Somebody What You or Another PersonRishit ChandaNo ratings yet
- General RevisionDocument20 pagesGeneral RevisionJESuisAhmedNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Short SummaryDocument2 pagesReported Speech Short Summaryfederica fissoreNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechNoa PahlićNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech Lesson With ExercisesDocument10 pagesIndirect Speech Lesson With Exercisesmohammad515No ratings yet
- Grammar - Notes of Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesGrammar - Notes of Reported SpeechGhost GamingNo ratings yet
- 1 - Reported Speech - StatementsDocument3 pages1 - Reported Speech - StatementsJohnyNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument4 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsZaniShira100% (1)
- 01 Reported Speech 1Document4 pages01 Reported Speech 1katia.khimaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechZaniShiraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsDocument5 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech) : A. Reporting StatementsSofia AngelovaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument17 pagesReported SpeechalwiNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechdavidputraaxxNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechYefer romañaNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesDirect Speech Reported SpeechЮля КряталоваNo ratings yet
- Example: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishDocument4 pagesExample: He Says, "I Write Poems." - He Says That He Writes EnglishRita QuispeNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - SummaryDocument2 pagesReported Speech - SummaryFreddy Murrugarra100% (1)
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 pagesEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNo ratings yet
- Direct & Indirect Spech RulesDocument9 pagesDirect & Indirect Spech RulesUmme AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Use Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesUse Quotation Marks in Direct Speech. Someone Said But Not The Exact Words. We Do Not Use Quotation Marks in Reported SpeechIeva VaičikauskaitėNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech GRD 7 - Portal 20-21Document5 pagesReported Speech GRD 7 - Portal 20-21khalidtajuddeen2010No ratings yet
- 6 Reported SpeechDocument15 pages6 Reported SpeechAndreea ManoliNo ratings yet
- (GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)Document15 pages(GSTT.vn) Chuyên Đề Câu Tường Thuật (Reported Speech)NamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9. Reported SpeechDocument19 pagesLesson 9. Reported SpeechEbru D.No ratings yet
- Reported Speech NotesDocument5 pagesReported Speech NotesChipo MulundikaNo ratings yet
- 4 GR Reported SpeechDocument7 pages4 GR Reported Speechpaula y soniaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: EstudiateDocument5 pagesReported Speech: EstudiateEduar Delgado Santa CruzNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Material Prepared By: Javier Medina, Valeria Martinez, Carlos Monceratt, and Eduardo MoralesDocument9 pagesReported Speech: Material Prepared By: Javier Medina, Valeria Martinez, Carlos Monceratt, and Eduardo MoralesJavier MedinaNo ratings yet
- REPORTED_SPEECH_OVERALLDocument28 pagesREPORTED_SPEECH_OVERALLwivajiNo ratings yet
- USE FormDocument17 pagesUSE FormBernardo RochaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument13 pagesReported Speechjoshe003No ratings yet
- Direct VS Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect VS Indirect SpeechKetua EE 2021 AndrianoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument34 pagesReported SpeechRubicel Cordova0% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument34 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJimin MochiNo ratings yet
- Xenophobia: Reported SpeechDocument21 pagesXenophobia: Reported SpeechJames D Saavedra M100% (1)
- Direct & IndirectDocument10 pagesDirect & Indirectmahbobahaqjo8No ratings yet
- تقرير انكليزي-مريم ياسر شيتDocument8 pagesتقرير انكليزي-مريم ياسر شيتMeMoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech TeoriaDocument4 pagesReported Speech TeoriasilviaNo ratings yet
- Types Conjunctionthings To NoteDocument9 pagesTypes Conjunctionthings To NoteZone ZeeNo ratings yet
- Rules For Reported Speech 1Document10 pagesRules For Reported Speech 1Panna100% (1)
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesRules For Reported SpeechPannaNo ratings yet
- CÂU TRỰC TIẾP GIÁN TIẾP 1Document5 pagesCÂU TRỰC TIẾP GIÁN TIẾP 1duyenloanphungdlp281224No ratings yet
- Direct-Indirect Speech EnglishDocument82 pagesDirect-Indirect Speech EnglishYanuar NugrahaNo ratings yet
- CÂU TƯỜNG THUẬTDocument9 pagesCÂU TƯỜNG THUẬTMy Nguyễn HàNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Ingles IiiDocument31 pagesReported Speech Ingles IiiOscar Andres Rojo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument20 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech 2º BachilleratoDocument4 pagesReported Speech 2º BachilleratoBlancaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech CompleteDocument6 pagesReported Speech Completegloriasd2005No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechGunjan GargNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech ChartDocument4 pagesReported Speech ChartAlex PeraNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Sentences, Part-2Document5 pagesTransformation of Sentences, Part-2Shivek agrawalNo ratings yet
- Webster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageFrom EverandWebster's Word Power Essential Students' Companion: General Knowledge of the English LanguageNo ratings yet
- Question TagsDocument9 pagesQuestion Tagsmira oktavianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 Parsing 1Document108 pagesLecture03 Parsing 1Nada ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Fellas - Google SearchDocument1 pageFellas - Google SearchBuat Hiya hiyaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument25 pagesReported SpeechSarah LewisNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - (Vocab + Grammar)Document5 pagesUnit 6 - (Vocab + Grammar)44 - Vũ Tiến Vinh - 11A1No ratings yet
- Apostila 5 Fase-OficialDocument22 pagesApostila 5 Fase-OficialAyumiMillaNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesPassive Voicesgumo100% (1)
- Intermediate Unit 11aDocument2 pagesIntermediate Unit 11agallipateroNo ratings yet
- The Passive Exercises-Mixed Tenses and Two ObjectsDocument3 pagesThe Passive Exercises-Mixed Tenses and Two ObjectsYOUSRA KESSINo ratings yet
- Present Simple-Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Simple-Present ContinuousJennyChartNo ratings yet
- Active Passive - STUDENTDocument8 pagesActive Passive - STUDENTAhmad SufianNo ratings yet
- GerundsDocument3 pagesGerundsIndra HarahapNo ratings yet
- Biblical Hebrew Summary PDFDocument1 pageBiblical Hebrew Summary PDFAres HerzeNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH - STD - 6 Midterm Term 3Document5 pagesENGLISH - STD - 6 Midterm Term 3byakayadaniel834No ratings yet
- THINK L1 Unit 2 Grammar PracticeDocument2 pagesTHINK L1 Unit 2 Grammar PracticeDana KrasnopiorkoNo ratings yet
- 4 Sentence-MeaningDocument11 pages4 Sentence-MeaningCamiRusuNo ratings yet
- D) Style: 4. Basic Components of A Narrative TextDocument14 pagesD) Style: 4. Basic Components of A Narrative TextCeleste De Jong ZumaetaNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument4 pagesPresent SimpleAlam MohammadNo ratings yet
- Degrees Og ComparisonDocument2 pagesDegrees Og ComparisonToma Elena AlinaNo ratings yet
- The Present SubjunctiveDocument3 pagesThe Present SubjunctiveZoe TziavaraNo ratings yet
- 211 Leipzig PDFDocument181 pages211 Leipzig PDFvogliaNo ratings yet
- The Order of Adjectives: Determiner Observation Physical Description Origin Material Qualifier Noun Size Shape Age ColorDocument1 pageThe Order of Adjectives: Determiner Observation Physical Description Origin Material Qualifier Noun Size Shape Age ColorNoor Azni Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Basics of Translation Theory PartDocument117 pagesBasics of Translation Theory PartOlari IuliaNo ratings yet
- Guias Pasivo y ActivoDocument5 pagesGuias Pasivo y ActivoLuigimom Orobio MartinezNo ratings yet
- Phraseological Unit Is A Word Group With A Fixed Lexical Composition and Grammatical StructureDocument10 pagesPhraseological Unit Is A Word Group With A Fixed Lexical Composition and Grammatical StructureДарья ОчманNo ratings yet
- Prueba IV Past PerfectDocument3 pagesPrueba IV Past PerfectFelipe Romero FigueroaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument3 pagesTestSasso BluNo ratings yet
- Adunaic - The Vernacular of NumenorDocument21 pagesAdunaic - The Vernacular of Numenordiego_guimarães_64No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in EnglishAdonis CusipagNo ratings yet