Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orbital Magnetic Moment
Orbital Magnetic Moment
Uploaded by
arkit challamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orbital Magnetic Moment
Orbital Magnetic Moment
Uploaded by
arkit challamCopyright:
Available Formats
8.
3 Orbital Magnetic Moment of an Atom
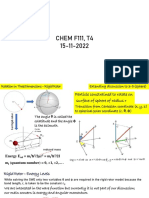
We consider an electron mass m, charge e revolving round the nucleus of an atom i a
circular orbit of radius [Fig. 8.2
r ry-plane with a velocity of magnitude
in the v
The charge - e circulating the loop is equivalent to a circuit,
ev
I=- (8.2)
27TT
where T is the period of revolution.
A current loop is quivalent to a magnetic shell of magnetic
dipole moment f1.
ev 2 = evr
O X
L= Current X area = IA =
2
2TT
f o r circular orbit, area A = Tr°j Z
Fig. 8.2: Electron revolving round a
or, = - mUr = - L. nucleus in an atom
2m 2m
Since, magnetic moment l and angular momentum L are both vectors. The implication
are oppositely directed.
of the negative sign is that 7 and L
The ratio of the orbital magnetic moment to the angular momentum of the electron is
Orbital magnetic moment
Orbital angular momentum 2m (8.3)
agnetic moment of the atom is generally written as
e
IE9L, (8.4)
were gi
wher = 1 and is called the orbital g-factor of the electron.
Again, quantum meçhanically.
Z= VI +1)h,
ere&is the orbital aneular monentum quantum nuinber ot the atom having valuesl =
0, 1,
2
eh
917Vi(l +1)h = 2m Vl+1). (8.4)
where g = 1 and is called the orbital
g-factor.
h
Forl=0, 4 =
0; for =
1, 4u =
V22m for = 3. 41 =
V6m
Z-component of Orbital Magnetic Moment
The 2-component of orbital angular momentum quantum iumber is
Lz = mh,
where m is the orbital magnetic quantum number. For a given value of l , mi = l, (l - 1), ..
0, 1,., (-1+1), -1, i.e., (21 +1) values of m.
The Z-component of orbital magnetic moment
e eh
(4)z= 2m Lz =- 2m (8.5)
For m 1, (u)z = - h .
2m
Bohr magneton: A Bohr magneton is the unit of magnetic moment and has the value.
eh
B 2m
(8.6)
Substituting, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C, m =
=9.1 x 10-3 kg and h = - 1.055 x 10-34 J-s we
we
have
1.6 x 10-19x 1.055 x 10-34
PB= =
9.27 x 104* J/tesla.
2x9.1 x 10-31 (8.7)
The physical significance of the Bohr magneton 2m is that it is the smallest unit
of magnetic monent of the atom and is quantised like magnetic moment of the moment
charge, mass, etc.
Quantisation of Magnetic Moment
The Z-component of orbital magnetic
moment
eh
(Pu)z = 2m = = -HBm,
(8.8)
where i s the smallest unit of magnetic moment known
the Bohr magneton and mi is
as
an
integral number given by mj l, (l -1)...0, 1,..., (-1+1), -t.
=
Thus magnetic moment is always an
integral multiple of the smallest unit Bohr magneto.
This shows the quantisation of magnetic
moment.
Magnetic Dipole in a Magnetic Field
Ifmagnetic dipole of moment ri be placed in a magnetic field B, then
a
experience a potential energy V, the energy of interaction between the classically it will
the magnetic field is given by magnetic moment and
EB- B. (8.9)
If Bis in the 2-direction, then
EB-()z B =#sBm. (8.10)
Since, m is quantised, the potential energy V is also quantised. So, in
the atomic state of a given
a
magnetic field
splits into (2l + 1) different states according to the
magnetic quantum number m.
You might also like
- Miessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM CH 02 CM FinalDocument17 pagesMiessler-Fischer-Tarr5e SM CH 02 CM FinalKatieYoung100% (2)
- Bohr Model of H-AtomDocument18 pagesBohr Model of H-AtomBhargav100% (1)
- UntitledDocument61 pagesUntitledchandrakanth maheshNo ratings yet
- Review of "Chap.1 Origin of Magnetism": June 21,2006Document20 pagesReview of "Chap.1 Origin of Magnetism": June 21,2006Umiatin RamdhaniNo ratings yet
- AP Unit 3Document16 pagesAP Unit 3dhanushdhanu9157No ratings yet
- Belur Zeeman Effect1Document20 pagesBelur Zeeman Effect1nirmalya.sankardasNo ratings yet
- Atom Models: Example 7.10 SolutionDocument12 pagesAtom Models: Example 7.10 SolutionDebanuj BasakNo ratings yet
- Atoms: Chapter - 12Document30 pagesAtoms: Chapter - 12nandani lakhwaniNo ratings yet
- 5-Bohr's Atomic ModelDocument10 pages5-Bohr's Atomic ModelKush GuptaNo ratings yet
- (L2) Atomic PhysicsDocument58 pages(L2) Atomic PhysicsJayesh AhirwarNo ratings yet
- Lecture L16 - Central Force Motion: Orbits: Energy IntegralDocument8 pagesLecture L16 - Central Force Motion: Orbits: Energy IntegralKRITANTNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument12 pagesAtomsmidhunesh41No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Magnetic Fields in MatterDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Magnetic Fields in MatterMadhumika ThammaliNo ratings yet
- 01 03Document32 pages01 03humayunbashaNo ratings yet
- Em Manual 16.01.18Document4 pagesEm Manual 16.01.18shilasharmin1064No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure-49-50Document2 pagesAtomic Structure-49-50amanb03xxNo ratings yet
- Lamb ShiftDocument28 pagesLamb ShiftMohammad zaid ZazNo ratings yet
- Lect-2 Atomic Structure and Quantum TheoryDocument35 pagesLect-2 Atomic Structure and Quantum Theoryroman leeNo ratings yet
- Phy Activity P-IIDocument9 pagesPhy Activity P-IINaveenNo ratings yet
- Wave Model - Hydrogen Case - 2023-2024Document36 pagesWave Model - Hydrogen Case - 2023-2024rahmaderradji23No ratings yet
- PanPearl2009 PaperDocument6 pagesPanPearl2009 PaperLakshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MagnetismDocument29 pagesIntroduction To MagnetismJure MrduljasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties and The Zeeman Effect - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument5 pagesMagnetic Properties and The Zeeman Effect - Chemistry LibreTextsKRISHNA KUMAR GODARANo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure ChemDocument20 pagesAtomic Structure ChemsearchhistorycollectionNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry (DAS 103) Unit - 1 Electron (E)Document9 pagesApplied Chemistry (DAS 103) Unit - 1 Electron (E)HRITIKNo ratings yet
- ERev SolDocument14 pagesERev SolEmuNo ratings yet
- Orbital Magnetic Moment of An AtomDocument10 pagesOrbital Magnetic Moment of An Atomrohitau88No ratings yet
- Atoms PDFDocument24 pagesAtoms PDFAdinarayanaNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics PDFDocument20 pagesModern Physics PDFPrathm MittalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Lectures 2018Document119 pagesAn Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Lectures 2018Nataliya LyutenkoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument14 pagesAtomic StructurechemceptualwithfaizNo ratings yet
- Pan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2006 2006 年泛珠江三角物理競賽 Part-1 卷-1Document7 pagesPan Pearl River Delta Physics Olympiad 2006 2006 年泛珠江三角物理競賽 Part-1 卷-1narutoNo ratings yet
- TheoryPresentationPt1 Web 032017Document172 pagesTheoryPresentationPt1 Web 032017piotrNo ratings yet
- Chap04 PDFDocument32 pagesChap04 PDFSehrelilNo ratings yet
- Numericals Chapter 20Document8 pagesNumericals Chapter 20usamasaeed9112No ratings yet
- 6-Bohr's Model ContinuedDocument16 pages6-Bohr's Model ContinuedKush GuptaNo ratings yet
- MSC NotesDocument9 pagesMSC Notesesa.classesNo ratings yet
- Interference DiffractionDocument44 pagesInterference DiffractionMansi NegiNo ratings yet
- Quantum 2010Document20 pagesQuantum 2010manizamansha212No ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument19 pagesQuantum MechanicsniguisisiNo ratings yet
- States of Spin One-Half: 2.1 The Stern-Gerlach ExperimentDocument19 pagesStates of Spin One-Half: 2.1 The Stern-Gerlach ExperimentSK AnastNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03Document12 pagesLecture 03Mohit RawatNo ratings yet
- Waves in Media: Ashcroft and Mermin, Solid State Physics (Saunders College, 1976, Page 553)Document42 pagesWaves in Media: Ashcroft and Mermin, Solid State Physics (Saunders College, 1976, Page 553)Amina lbrahimNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC MODELS AtomicphysicsDocument24 pagesATOMIC MODELS Atomicphysicsahsanbgayo100% (1)
- Modern Physics (Exam:6)Document7 pagesModern Physics (Exam:6)Arnab BhowmikNo ratings yet
- MPM Part1Document6 pagesMPM Part1Robert PalmerNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Atomic Structure: Overview of Bohr's Atomic ModelDocument38 pagesAtomic Structure: Atomic Structure: Overview of Bohr's Atomic Modelmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem. I Ch. 1Document98 pagesInorganic Chem. I Ch. 1Shifa GhannamNo ratings yet
- Helium AtomDocument8 pagesHelium AtomehmedNo ratings yet
- NOTE: Bohr's ModelDocument43 pagesNOTE: Bohr's ModelmsccenterNo ratings yet
- BITS Pilani Chemistry Hamilton OperatorDocument11 pagesBITS Pilani Chemistry Hamilton OperatorNaresh SehdevNo ratings yet
- Quals 2012 Sec 4Document16 pagesQuals 2012 Sec 4puput123No ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Interaction of Radiation With Matter: MediumDocument17 pagesLecture 5: Interaction of Radiation With Matter: MediumSathish JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- 02ModernPhysics 1 PCDocument59 pages02ModernPhysics 1 PCSuhaib FidaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Hall Effect - BDocument7 pagesQuantum Hall Effect - Bspow123No ratings yet
- 01-The Integer Quantum Hall Effect I PDFDocument7 pages01-The Integer Quantum Hall Effect I PDFBheim LlonaNo ratings yet
- CPS Periodic Properties R B PDFDocument18 pagesCPS Periodic Properties R B PDFPrince SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction Physics Talks - 110617Document17 pagesElectromagnetic Induction Physics Talks - 110617godparticle.chessNo ratings yet
- Intensity PDFDocument21 pagesIntensity PDFKesavan KomandurNo ratings yet
- Cosmology in (2 + 1) -Dimensions, Cyclic Models, and Deformations of M2,1. (AM-121), Volume 121From EverandCosmology in (2 + 1) -Dimensions, Cyclic Models, and Deformations of M2,1. (AM-121), Volume 121No ratings yet
- Chauhan - ScienTraumaDocument28 pagesChauhan - ScienTraumaGodiram Kina LačkićNo ratings yet
- Quantum Field Theory IIDocument27 pagesQuantum Field Theory IIRoberto Flores ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument30 pagesChapter IILenon AndetklNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Chemistry Sk015 SESSION 2020 / 2021Document36 pagesAtomic Structure: Chemistry Sk015 SESSION 2020 / 2021Daniel LimNo ratings yet
- Term SymbolDocument20 pagesTerm SymbolRirin Zarlina100% (1)
- Alexander Burinskii - Two Stringy Systems of The Kerr Spinning ParticleDocument22 pagesAlexander Burinskii - Two Stringy Systems of The Kerr Spinning ParticleSteam29No ratings yet
- Syllabus I Sem To 8th Sem 2018-22 BatchDocument164 pagesSyllabus I Sem To 8th Sem 2018-22 BatchRaviNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term Xii Physics 2021Document12 pages1ST Term Xii Physics 2021RiyazNo ratings yet
- BITSAT2008 BRDocument22 pagesBITSAT2008 BRAkshay ParvatkerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Mechanics - 9781107189638 - Ejercicio 6 - Quizlet PDFDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Mechanics - 9781107189638 - Ejercicio 6 - Quizlet PDFErik BavezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NumericalsDocument2 pagesChemistry NumericalsUsama TahirNo ratings yet
- Clebsch GordanCoeffDocument11 pagesClebsch GordanCoeffkhalid rokonNo ratings yet
- Quantum Formalism: 1.1 Summary of Quantum States and ObservablesDocument48 pagesQuantum Formalism: 1.1 Summary of Quantum States and Observablesprivado088No ratings yet
- Entanglement The Greatest Mystery in Physics by Amir D. Aczel (Abee) PDFDocument303 pagesEntanglement The Greatest Mystery in Physics by Amir D. Aczel (Abee) PDFhadzimusic100% (1)
- Problems303 13 SolDocument1 pageProblems303 13 SolNitish PutrevuNo ratings yet
- The Bohm-Penrose-Hameroff Model For ConsciousnessDocument14 pagesThe Bohm-Penrose-Hameroff Model For ConsciousnesssonnydsNo ratings yet
- Quantum Coherence in Microtubules: A Neural Basis For. Emergent Consciousness?Document28 pagesQuantum Coherence in Microtubules: A Neural Basis For. Emergent Consciousness?anon_496879006No ratings yet
- Theory of Quantum Diffusion of Atoms in Crystals (Journal of Physics C Solid State Physics, Vol. 7, Issue 16) (1974)Document18 pagesTheory of Quantum Diffusion of Atoms in Crystals (Journal of Physics C Solid State Physics, Vol. 7, Issue 16) (1974)Dumitru PascuNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Homework Set 2: Due August 21Document4 pagesSolutions: Homework Set 2: Due August 21Michel Rodrigues Andrade100% (2)
- Bloch TheoremDocument2 pagesBloch TheoremSurajNo ratings yet
- Molecular ShapesDocument76 pagesMolecular ShapesLaica BlazaNo ratings yet
- Quantum CryptographyDocument21 pagesQuantum Cryptographysanjula4vNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends WorksheetDocument5 pagesPeriodic Trends WorksheetChristy HuynhNo ratings yet
- Intro To Phonons-CastepDocument57 pagesIntro To Phonons-CastepgadasNo ratings yet
- Week 3 PDFDocument20 pagesWeek 3 PDFGerson MisaelNo ratings yet
- Consciousness As The Subject and Object of PhysicsDocument15 pagesConsciousness As The Subject and Object of PhysicsMeditatia Transcendentala RomaniaNo ratings yet
- Murray Gell MannDocument5 pagesMurray Gell MannTomás JordánNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Oscillator & Rigid Rotor: Recap: - Separation of Variables For Solving Schrödinger EquationDocument9 pagesHarmonic Oscillator & Rigid Rotor: Recap: - Separation of Variables For Solving Schrödinger EquationDmidNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Spectroscopy Techniques and ApplicationsDocument86 pagesUnit 6 Spectroscopy Techniques and ApplicationsDr. Ruma Arora SoniNo ratings yet