Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gnercury - : of Tadiiß
Gnercury - : of Tadiiß
Uploaded by
Tabib HabibOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gnercury - : of Tadiiß
Gnercury - : of Tadiiß
Uploaded by
Tabib HabibCopyright:
Available Formats
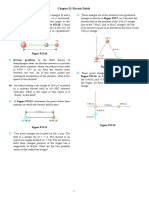
The diagram shows a rigid wire AB pivoted at the point A so that it is free to
move In a vertical ptane. The lower end of the wire dips into mercury. A
uniform magnetic field of 6.0 x 10-3 T acts Into the paper throughout the
diagram.
gnercury•
g When the current is switched on. the wire continuously moves up out of the mercury
and then falls back again. Explain this mölion. [2]
h The force on the wire due to the current may be taken to act at the midpoint of the
wire, When the current is first switched on. the moment of this force about A is
3.5 N m. Calculate:
the force acting on the wire ii) the current in the wire.
I State Faradafs law of etectromagnetjc induction.
Lenz's law expresses an important conservation law. Name this conservation law.
k I) Define magnetic flux for a coil placed at right angles to a magnetic field
Il) Determine for which of the two coils X and Y, each placed at right angles to
Ole magnetic field, is the magnetic flux linkage the greatest. 121
Of tadiiß
3.0em and
turns
TOTAL: t 20 marks
Page 9 ono
(close to
Perm.ttmty of free space
Scanned with CamScanner
Spc•cd a
Ste
u a oenne tne moment ot a force.
b State two conditions that must be met for the equilibrium of an
extended object.
C. Describe what is meant by renewable and [2) non-renewable energy
sources. Name three renewable and three non-renewable energy sources.
d. State three advantages and three
disadvantages of Nuclear power. (1)
The diagram below shows the initial state of two identical balls A and B before
collision and the final state immediately after the collision. The mass of each ball is
1.2 kg.
dtrct'tton
ms'
Before the collision. the velocity of A is 3.0 m s-i and B is stationary. A
makes an oblique collision with B.
After the collision, A moves off at an angle of 30 0 to its original direction and has a
velocity of 2.6 m s-1 . B is deflected at an angle Owith a velocity of 1.5 m s-t.
e Explain why the final momentum of the system in a direction at right angles to
the initial velocity of A is zero. Hence determine the angle O.
f Show that the total momentum of the system is conserved.
g State Newton's second law or motion in words and then write-down the
formulae for the law.
h A missile was launched from an airbase of country X to reach the
enemy base across the border in country Y. The launch velocity was set
at 500 ms-I at a launch angle of 41 degrees to the horizontal. Taking
ms-2 and ignoring air resistance calculate, the following:
Page 7 of
a) Total flight time of the missite before it lands in the enemy territory.
b) Maximum height reached above the horizontal level.
c) The range of the missile reached before hitting the ground.
d) Qualitatively state with reasons about the above three quantities
(i.e.,
Total flight time, Maximum height, and Range) if there were to be air
resistance to the flight path of the missile.
The diagram shows the horizontal forces acting on a 920 kg car.
Scanned with CamScanner
The total forward force actin on the car is 400 N. The dra on the car depends on its
soeed v
a) Total flight time of the missile before It lands in the enemy temtory-
b) Maximum height reached above the horizontal level,
c) The range of the missile reached before hitting the ground-
d) Qualitatively state with reasons about the above three quantities (i.e..
Total flight time, Maximum height, and Range) if there were to be air
resistance to the flight path Of the missile, [41
The diagram shows the horizontal forces acting on a 920 kg Cat,
20 ms '
The total forward force acting on the car is 400 N. The drag on the car depends
on its speed v and is gtven by the expression; drag 0.3v z i at a particular instant
the car is travelling at a speed of 20 m s-1 , Calculate; I) the net force on the car
[21 2) the acceleration of the car, [21
j Explain why you cannot use. v —u + at to determ•ne the velocity of
the car after a time f.
TOTAL: 1 20 marks
QII. a Define gravitational field strength at a point in space. [21 b Show that the
gravitational constant G has the unit N m: kg-2. [21
c The gravitational field strength on the surface of the Moon is I -6 N kg
What is the weight of an astronaut of mass 80 kg standing on the surface of
the Moon? [
2
1
d Explain what is meant by the electric field strength at a
point.
I
l
l
e Explain what is meant by the electric potential at a point.
f Describe some of the similarities and differences between the electrical
force due to a point charge and the gravitational force due to a point mass.
[41
Page 8 of
The diagram shows a rigid wire AB pivoted at the point A so that it is free to move
in a vertical plane. The lower end of the wire dips into mercury. A uniform
magnetic field Of 6.0 10-3 T acts into the paper throughout the diagram-
Scanned with CamScanner
g When the current is switched on. the wire continuously moves up out Of the
mercury and then falls back again. Explain this motion, 121
h The force on the wire due to the current may be taken to act at the midpoint
of the wire. When the current is first switched on. the moment of this force
about A is
In-5 N r-n
Scanned with CamScanner
Q6. i) The diagram shows a simple electrical thermometer
based on a negative temperature coefficient (NTC)
thermistor. At 30 o c the thermistor has a 5.0 v resistance
of 2.4 k!) and this decreases to 430 Q at 100 0 C. The
battery has negligible internal resistance.
Calculate the maximum input voltage into
the datalogger.
to datalogger
131
Explain terms LDR and N TC thermistor with
reference to band theory in semiconductor
materials121 and devices.
TOTAL: 1 5 marks
Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- A-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersDocument46 pagesA-Level Exam (2001) Papers and AnswersAston Hamilton100% (3)
- Iso 10003 - 2018 (Eng)Document44 pagesIso 10003 - 2018 (Eng)mblancol75% (4)
- Mainframe Admin Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesMainframe Admin Course SyllabusENDLURI DEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand General Knowledge (Objective Question)Document8 pagesJharkhand General Knowledge (Objective Question)Gunjan86% (28)
- AITS - 15 (P-I) Question PaperDocument17 pagesAITS - 15 (P-I) Question Paperbhavya.chandak.201076No ratings yet
- Problem SetNo 3 4CC EE4CDocument7 pagesProblem SetNo 3 4CC EE4CrotcdublinNo ratings yet
- Phy 12th GyangangaDocument4 pagesPhy 12th GyangangabhartiyaanujNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS H.Y 12th REVISION SHEETDocument6 pagesPHYSICS H.Y 12th REVISION SHEETGeetanjli GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lightning Phenomena and Protection Systems: Problem 3.1Document9 pagesChapter 3 Lightning Phenomena and Protection Systems: Problem 3.1Nouman ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Board PhysicsDocument9 pagesBoard PhysicsDurgesh Yadav100% (1)
- Jee 31dec2023 QP MorDocument10 pagesJee 31dec2023 QP MorphychemgodNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QuestionsDocument23 pagesPhysics Model QuestionsQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- Chinese Physics Olympiad 2019 Finals Theoretical Exam: Translated By: Wai Ching Choi Edited By: Kushal ThamanDocument11 pagesChinese Physics Olympiad 2019 Finals Theoretical Exam: Translated By: Wai Ching Choi Edited By: Kushal ThamanMinh Công100% (1)
- Physics SQPDocument108 pagesPhysics SQPS. BALA MURALI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Paper - 2Document25 pagesPaper - 2Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Model QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhysics Model QuestionsQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- Final 2018Document3 pagesFinal 2018Ashraf WaleedNo ratings yet
- Paper1 2000Document13 pagesPaper1 2000Lawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics Practice Paper Round 1-2023-24Document4 pages12th Physics Practice Paper Round 1-2023-24adityarajsinh9990No ratings yet
- INPhO 2001Document6 pagesINPhO 2001gudapudi ramaniNo ratings yet
- EEL1176 Tutorial 3 - 2022Document3 pagesEEL1176 Tutorial 3 - 2022j2yshjzzsxNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam IdeaDocument419 pagesPhysics Exam IdeaAditya50% (2)
- You May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorDocument5 pagesYou May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorSpringOrchidNo ratings yet
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsDocument53 pagesSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuNo ratings yet
- Problem Class Questions For PHY008 Atomic and Nuclear PhysicsDocument14 pagesProblem Class Questions For PHY008 Atomic and Nuclear Physicstsania nkdNo ratings yet
- Competishun: PhysicsDocument13 pagesCompetishun: PhysicsDevarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- PHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Document11 pagesPHYF125 Tutorial Questions T2 2122Agag HsgsNo ratings yet
- Physics - XII (Holiday Home Work)Document10 pagesPhysics - XII (Holiday Home Work)VIVAAS .SNo ratings yet
- (101 Marks) : (1 Mark)Document31 pages(101 Marks) : (1 Mark)trishaNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 10Document10 pagesPhysics Set 10bijayakumal819No ratings yet
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics TestDocument2 pagesAnant Achievement Classes Physics TestUTSAV JAINNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and FieldDocument10 pagesElectric Charges and FieldSunit Singh MakhijaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 12th PAPER SEPTEMBER 2023Document6 pagesPHYSICS 12th PAPER SEPTEMBER 2023mehakNo ratings yet
- Fall 2004 Part 1Document5 pagesFall 2004 Part 1eka123No ratings yet
- Without This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFDocument4 pagesWithout This Message by Purchasing Novapdf : Print To PDFAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Model SolutionDocument5 pagesModel SolutionQuantum HeatNo ratings yet
- Additional Problems 2Document3 pagesAdditional Problems 2Joane RozzNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Document6 pagesCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Chandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- IES 2003 EE Conventional Paper01Document5 pagesIES 2003 EE Conventional Paper01Shubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Case Based StudyDocument24 pagesClass 12th Case Based StudyshiviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Ws G12Document2 pagesChapter 1 Ws G12Vinushree SanthoshkumarNo ratings yet
- Physice 2011 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFDocument5 pagesPhysice 2011 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Document419 pagesXam Idea Previous Years Question Papers 2008-2012Mohammed Farhad77% (13)
- RevisionDocument3 pagesRevisionKaifkhanNo ratings yet
- Inc - Cbse Class Xii Term 1 - Examination - Physics Support MaterialDocument6 pagesInc - Cbse Class Xii Term 1 - Examination - Physics Support Materialrajpurohitshubham349No ratings yet
- Set-1 (Phy. - PST)Document4 pagesSet-1 (Phy. - PST)shreyasinghchampNo ratings yet
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFDocument14 pagesSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- D2 - Electromagnetism - Q - SolvedDocument37 pagesD2 - Electromagnetism - Q - SolvedfreanchieNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument92 pagesClass 12 Physicsniyatigupta5623No ratings yet
- Physics 222 - Test 2 - Spring 2010Document2 pagesPhysics 222 - Test 2 - Spring 2010eltytanNo ratings yet
- Compact 1168571Document2 pagesCompact 1168571deepak bamelNo ratings yet
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Apeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsDocument4 pagesApeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsabhilashagoelNo ratings yet
- Phy Set-2 QPDocument5 pagesPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNo ratings yet
- 12TH PHYSICS FTDocument10 pages12TH PHYSICS FTABHISHEK PANDANo ratings yet
- Paper - 5Document16 pagesPaper - 5Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tulay ESDocument1 pageTulay ESmarlon novisioNo ratings yet
- Diff AmpDocument54 pagesDiff AmpUday GulghaneNo ratings yet
- R1600H Sistema ImplementosDocument31 pagesR1600H Sistema ImplementosLuis Angel Pablo Juan de Dios100% (1)
- Job Notification NHM Odisha Recruitment 2015 16 For 19 District Programme Manager Other PostsDocument12 pagesJob Notification NHM Odisha Recruitment 2015 16 For 19 District Programme Manager Other PostsJeshiNo ratings yet
- 1575517183688JlPSe5QaAila2orp PDFDocument15 pages1575517183688JlPSe5QaAila2orp PDFPr Satish BethaNo ratings yet
- SM Assignment 1Document7 pagesSM Assignment 1saseelaNo ratings yet
- Ielts Listening Section 4 40 Practice TestsDocument41 pagesIelts Listening Section 4 40 Practice TestsRajinder Singh Kahlon100% (1)
- Faq Margin IciciDocument39 pagesFaq Margin IciciamitthemalNo ratings yet
- 11.11th IPhO 1979Document11 pages11.11th IPhO 1979fienny37No ratings yet
- Preliminary Investigation On New Century Health Clinic (NCHC)Document16 pagesPreliminary Investigation On New Century Health Clinic (NCHC)Erlind GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- A Court Case On Letters of Credit & UCP600Document2 pagesA Court Case On Letters of Credit & UCP600gmat1287No ratings yet
- Huawei AirEngine 5760-51 Access Point DatasheetDocument16 pagesHuawei AirEngine 5760-51 Access Point DatasheetJsdfrweporiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Handouts ARGDocument26 pagesLesson Handouts ARGsamantha sisonNo ratings yet
- Hdat2en 4 52Document156 pagesHdat2en 4 52blahh12345689No ratings yet
- Experiments in Art and Technology A Brief History and Summary of Major Projects 1966 - 1998Document12 pagesExperiments in Art and Technology A Brief History and Summary of Major Projects 1966 - 1998mate maricNo ratings yet
- 2003 Nissan Maxima NaviDocument167 pages2003 Nissan Maxima NaviMarco OchoaNo ratings yet
- Cisco GGSNDocument386 pagesCisco GGSNtrunto0% (1)
- Nile International Freight ServicesDocument19 pagesNile International Freight ServicessameerhamadNo ratings yet
- Duplichecker-Plagiarism-Bab (2,3)Document2 pagesDuplichecker-Plagiarism-Bab (2,3)Sarah MaharaniNo ratings yet
- GRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALDocument10 pagesGRP 3 Keesha & Marie Faye Abdellah Power Point FINALevangelo22656No ratings yet
- Mapa de Concessões 1 1Document1 pageMapa de Concessões 1 1Venkat PachaNo ratings yet
- Split Up Syllabus Class Xii Physics 22-23Document1 pageSplit Up Syllabus Class Xii Physics 22-23ROHIT SIHRANo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUnefoussiNo ratings yet
- Establishing An FFSDocument2 pagesEstablishing An FFSAndrew George ADEMNo ratings yet
- Ra 8294Document2 pagesRa 8294Rio TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Mass, Volume, and Density: Goals Shape Formula Symbols Table 2.1Document5 pagesMass, Volume, and Density: Goals Shape Formula Symbols Table 2.1SandyNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis of Complex Networks 2011Document501 pagesStructural Analysis of Complex Networks 2011kemalihsan_17959No ratings yet