Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis 29-7 BE
Photosynthesis 29-7 BE
Uploaded by
Claw Gamer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesThis document discusses several photosynthetic pigments:
- Chlorophyll-a is a universal pigment found in all oxygen-liberating photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll-b is an accessory pigment found in euglenoids, green algae, and higher plants.
- The structure of chlorophyll includes a porphyrin head and a phytol tail. The tail remains embedded in the lipid bilayer of the thylakoid membrane.
- Carotenoids are accessory pigments that absorb different wavelengths of light, protecting chlorophyll-a from photo-oxidation and converting lethal oxygen into molecular oxygen. Beta-carotene also acts as a precursor for
Original Description:
Original Title
Photosynthesis 29-7 BE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several photosynthetic pigments:
- Chlorophyll-a is a universal pigment found in all oxygen-liberating photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll-b is an accessory pigment found in euglenoids, green algae, and higher plants.
- The structure of chlorophyll includes a porphyrin head and a phytol tail. The tail remains embedded in the lipid bilayer of the thylakoid membrane.
- Carotenoids are accessory pigments that absorb different wavelengths of light, protecting chlorophyll-a from photo-oxidation and converting lethal oxygen into molecular oxygen. Beta-carotene also acts as a precursor for
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views5 pagesPhotosynthesis 29-7 BE
Photosynthesis 29-7 BE
Uploaded by
Claw GamerThis document discusses several photosynthetic pigments:
- Chlorophyll-a is a universal pigment found in all oxygen-liberating photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll-b is an accessory pigment found in euglenoids, green algae, and higher plants.
- The structure of chlorophyll includes a porphyrin head and a phytol tail. The tail remains embedded in the lipid bilayer of the thylakoid membrane.
- Carotenoids are accessory pigments that absorb different wavelengths of light, protecting chlorophyll-a from photo-oxidation and converting lethal oxygen into molecular oxygen. Beta-carotene also acts as a precursor for
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
i.
Chl-a : Universal Pigment (Found in all O2 liberating photosynthetic
Organisms)
Blue Green Colour in Chromatogram
ii. Chl-b : Accessory photosynthetic pigment found in Euglenoids, Green Algae
and Higher plants.
Yellowish green in chromatogram.
iii. Chl-c
iv. Chl-d
v. Chl-e
Photosynthetic Pigments
Chlorophyll-a C55H72O5N4Mg CH3 Group in IInd pyrrol ring
Chlorophyll-b C55H70O6N4Mg CHO Group in IInd pyrrol ring
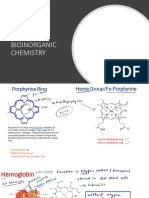
Structure of Chlorophyll :- Chlorophyll (Tadpole like)
Porphyrine Head Phytol Tail (C20H39OH)
• Size = 15 x 15 Å • Size = 20 Å
• It is Hydrophilic in nature • It is Hydrophobic
• It consist of four N-containing • Tail remains
pyrrol ring (together called as embedded in lipid
tetra pyrrol ring). bilayer of thylakoid
• All the N of pyrrol ring membrane.
connected with central
Phytol tail is absent
structure with Mg present in
in Chl-c.
the centre.
Chlorophyll synthesis :
Light
Succinyl CoA + Glycine Protochlorophyll Chlorophyll
2H
• This reaction is catalyzed by Iron (Fe)
Photosynthetic Pigments
Functions of carotenoids
1) They are accessory pigments and make photosynthesis more efficient
by absorbing different wavelengths of light.
2) They protect chl-a from photo oxidation and they also protect
photosynthetic machinery by converting lethal nascent oxygen into
unharmful molecular oxygen, Thus, also called shield pigments.
(3) β-carotene is acts as a precursor of vitamin-A
(4) They help in entomophily and zoochory.
Phycobillins
3. Phycobillins :
• They are hot water soluble pigment
• They lack Mg and phytol tail.
Types of phycobillins:
i. Phycocyanin (Blue)
ii. Phycoerithrin (Red)
iii. Allophycocyanin (Light blue)
• They occur exclusively in BGA and Red algae as an accessory
pigments.
You might also like
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument67 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISLujinelle FusinganNo ratings yet
- SET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsDocument61 pagesSET-NET Pericyclic ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Enthuse Smart Delivered Lecture A71b64b8 87aa 4ed5 PDFDocument67 pagesPhotosynthesis Enthuse Smart Delivered Lecture A71b64b8 87aa 4ed5 PDFAkash GargNo ratings yet
- History: Chlorophyll (Also Chlorophyl) Is Any of Several Related GreenDocument5 pagesHistory: Chlorophyll (Also Chlorophyl) Is Any of Several Related GreenRamesh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Describe Photosynthetic Pigments (Chlorophyll and Carotenoids)Document14 pagesDescribe Photosynthetic Pigments (Chlorophyll and Carotenoids)Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Yilmaz 2016Document5 pagesYilmaz 2016Eduardo TarangoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Chlorophyll and Other PigmentsDocument7 pagesImportance of Chlorophyll and Other PigmentsIan Gabriel MayoNo ratings yet
- 1 Photosynthesis-WPS OfficeDocument4 pages1 Photosynthesis-WPS OfficeCasaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument25 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsRaichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Chlorophyll - WikipediaDocument53 pagesChlorophyll - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument63 pagesPhotosynthesisselesmabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 PPIDocument15 pagesLecture 13 PPIabeehazakeeshNo ratings yet
- 5 FotosintesiDocument29 pages5 FotosintesiSerena DamianNo ratings yet
- Leactre Heme MetabolismDocument68 pagesLeactre Heme MetabolismMedico TeferiNo ratings yet
- BIO 324-Chap7,8Document61 pagesBIO 324-Chap7,8yarabeaini1No ratings yet
- Lecture Photosynthesis CPDocument21 pagesLecture Photosynthesis CPpranav.biophdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyanophyta: Cell Structures ContDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Cyanophyta: Cell Structures ContClaudia Yuli AstutieNo ratings yet
- Kuliah5-6 Fotosintesis.Document16 pagesKuliah5-6 Fotosintesis.17Masna Karina KalsumNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - PhotosynthesisDocument76 pagesUnit 8 - PhotosynthesisIzzy Dynielle SolamilloNo ratings yet
- PHOTOBIOLOGYDocument49 pagesPHOTOBIOLOGYserimawarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesisprabhat ranjan mishraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Spinach Extraction TLCDocument13 pagesExperiment 3 Spinach Extraction TLCshamalenrajan03No ratings yet
- Bio Inorganic Chemistry One Shot Revision by MadCh 230604 100239Document51 pagesBio Inorganic Chemistry One Shot Revision by MadCh 230604 100239sharmaashwani.iitgnNo ratings yet
- Bio1101 Lect6Document15 pagesBio1101 Lect6dorisger07No ratings yet
- Biochem XXDocument20 pagesBiochem XXMazz RudyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsPritamNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Q2 Lesson 9.1 Pigments StudentDocument47 pagesGen Bio 1 Q2 Lesson 9.1 Pigments StudentreyesrichijoyNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Introduction, Structure and Functions) : Smita Rastogi & U. N. DwivediDocument17 pagesBiomolecules (Introduction, Structure and Functions) : Smita Rastogi & U. N. DwivediEmmanuel UgwuNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis CO AssimilationDocument30 pagesPhotosynthesis CO AssimilationUttam GurungNo ratings yet
- 436154638-The-Study-of-Chlorophyll-Content-in-Various-Plants 4.docx - 20231113 - 184531 - 0000Document11 pages436154638-The-Study-of-Chlorophyll-Content-in-Various-Plants 4.docx - 20231113 - 184531 - 0000Saran.kNo ratings yet
- Porphyrin Metbolism 2023Document55 pagesPorphyrin Metbolism 2023kenaabebe87No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Membrane LipidsDocument28 pagesBiosynthesis of Membrane Lipidsangela marie abadillaNo ratings yet
- 231020190lipid Chemistry (Dr.e. Shaat) Lecture 2 Students - 2019Document23 pages231020190lipid Chemistry (Dr.e. Shaat) Lecture 2 Students - 2019slmen1269No ratings yet
- ChlorophyllDocument1 pageChlorophyllVB TwinsNo ratings yet
- Bioinorganic Chemistry: by Shilpendu GhoshDocument60 pagesBioinorganic Chemistry: by Shilpendu GhoshShilpendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- CHLOROPLASTDocument30 pagesCHLOROPLASTJohn Lorenz Mendoza FarnazoNo ratings yet
- Study of Chlorophyll Content in Various PlantsDocument15 pagesStudy of Chlorophyll Content in Various PlantsKunguma Vignesh57% (7)
- Unit-Iv-Lipids and PorphyrinsDocument29 pagesUnit-Iv-Lipids and PorphyrinsNila ArivoliNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Structure & SynthesisDocument24 pagesHemoglobin Structure & SynthesisIMDCBiochemNo ratings yet
- Bio PPT Chloroplast ProjectDocument39 pagesBio PPT Chloroplast ProjectjnaseemNo ratings yet
- Lipida 1Document46 pagesLipida 1zikri manggala putraNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Spectrophotometric Characterization o F Photosynthetic Pigments Rodney F BoyerDocument4 pagesIsolation and Spectrophotometric Characterization o F Photosynthetic Pigments Rodney F BoyerLucy ZuluNo ratings yet
- 091220190vitamins B12, Folic, C (E.sh) Lecture 3 Students 2018Document32 pages091220190vitamins B12, Folic, C (E.sh) Lecture 3 Students 2018slmen1269No ratings yet
- The Study of Chlorophyll Content in Various PlantsDocument16 pagesThe Study of Chlorophyll Content in Various PlantssasidharanNo ratings yet
- Cbse BioDocument20 pagesCbse BioHrituraj banikNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Week 6 Light Dependent and Light Independent ReactionDocument119 pagesGen Bio Week 6 Light Dependent and Light Independent ReactionJustine TalattadNo ratings yet
- Amount of Chlorophyll in Five LeafDocument24 pagesAmount of Chlorophyll in Five LeafRakshitha MgowdaNo ratings yet
- 22 MembranesDocument27 pages22 MembranesSierra OrtizNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12 Bio (2021) STEPDocument26 pagesWorksheet 12 Bio (2021) STEPAbrar AzharNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologyHrituraj banikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 PolymerDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Polymerlevisha suppiahNo ratings yet
- Chlorophylls and Other PigmentsDocument6 pagesChlorophylls and Other PigmentsHope Ladyline EspanolaNo ratings yet
- WK 9 PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesWK 9 PhotosynthesisKuku MandavaNo ratings yet
- Heme BiosyntesisDocument26 pagesHeme BiosyntesisNibras MohNo ratings yet
- Polymer Types and ApplicationDocument23 pagesPolymer Types and Applicationvivekanand879355443612No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationArka MisraNo ratings yet
- The Chlorophyll EncyclopediaDocument28 pagesThe Chlorophyll EncyclopediaPrachurjo DuttaroyNo ratings yet
- Algal Pigments PDFDocument5 pagesAlgal Pigments PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- FY B.Sc. Photosynthetic PigmentsDocument3 pagesFY B.Sc. Photosynthetic PigmentsVijendraNo ratings yet
- Pain-Free Biochemistry: An Essential Guide for the Health SciencesFrom EverandPain-Free Biochemistry: An Essential Guide for the Health SciencesNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. (Part-II) (Chemistry) (For Colleges) - 18.082020Document120 pagesM.Sc. (Part-II) (Chemistry) (For Colleges) - 18.082020KuNdAn DeOrENo ratings yet
- Actinometria QuimicaDocument42 pagesActinometria QuimicasgpizarroNo ratings yet
- Hill Reaction PDFDocument10 pagesHill Reaction PDFKc0911No ratings yet
- Photochemistry and SpectrosDocument41 pagesPhotochemistry and Spectrosyt HehkkeNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: A2 Biology (9700) 2022-2023Document31 pagesPhotosynthesis: A2 Biology (9700) 2022-2023Youssef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Handouts)Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis (Handouts)Jelea MagallanesNo ratings yet
- T.Y. SyllabusDocument24 pagesT.Y. SyllabusNirav SharmaNo ratings yet
- A GENERAL BIOLOGY I 12 Q2M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDocument18 pagesA GENERAL BIOLOGY I 12 Q2M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutmariaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus (2016)Document52 pagesChemistry Syllabus (2016)Vipin singhNo ratings yet
- M2 - General Bio 1 - Q2Document10 pagesM2 - General Bio 1 - Q2Remilyn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Raven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test BankDocument13 pagesRaven Biology of Plants 8th Edition Evert Test Bankwilliamvanrqg100% (33)
- Botany - AssignmentDocument2 pagesBotany - AssignmentLeah Hope CedroNo ratings yet
- Excited States and Photochemistry of Organic Molecules Klessinger M Michl J VCH 1995Document281 pagesExcited States and Photochemistry of Organic Molecules Klessinger M Michl J VCH 1995Semanu TcheyiNo ratings yet
- HoltAPRG 08 C10 FinalDocument10 pagesHoltAPRG 08 C10 Finaledward_wang_1No ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesThe Calvin CycleYanni MerkhanelNo ratings yet
- Amaterasun Products Knowlege For PartnerDocument17 pagesAmaterasun Products Knowlege For PartnerMuhammad GathanNo ratings yet
- ChloroplastDocument12 pagesChloroplastDavidNo ratings yet
- Kumare 1Document12 pagesKumare 1api-3765516No ratings yet
- 2011 - Stephenson Et Al. - Improving Photosynthesis For Algal Biofuels Toward A Green RevolutionDocument9 pages2011 - Stephenson Et Al. - Improving Photosynthesis For Algal Biofuels Toward A Green RevolutionmbrancovNo ratings yet
- C3, C4 and CAM Essay QuestionDocument3 pagesC3, C4 and CAM Essay QuestionDVRao100% (1)
- Chloroplast 1.2Document5 pagesChloroplast 1.2Ishita Kumari100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Document51 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Trisha DeniseNo ratings yet
- 13 - Photosynthesis AQA BookletDocument28 pages13 - Photosynthesis AQA BookletSevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDocument11 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsAyush singh PrinceNo ratings yet
- Q2Week-2 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesQ2Week-2 Photosynthesisjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Photoenolization-Induced Oxirane Ring Opening in 2,5-Dimethylbenzoyl Oxiranes To Form Pharmaceutically Promising Indanone DerivativesDocument10 pagesPhotoenolization-Induced Oxirane Ring Opening in 2,5-Dimethylbenzoyl Oxiranes To Form Pharmaceutically Promising Indanone DerivativesDiogomussumNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment (Module 6)Document2 pagesFormative Assessment (Module 6)Keisha Gabrielle RabanoNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesistravelfunda2000No ratings yet
- Activation Photochemical EnglishDocument1 pageActivation Photochemical EnglishplennyNo ratings yet