Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tachypnea - Use of Accessory Muscles in Breathing - O2: 91% - Nasal Flaring
Tachypnea - Use of Accessory Muscles in Breathing - O2: 91% - Nasal Flaring
Uploaded by
Benjie Dimayacyac0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
beb ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesTachypnea - Use of Accessory Muscles in Breathing - O2: 91% - Nasal Flaring
Tachypnea - Use of Accessory Muscles in Breathing - O2: 91% - Nasal Flaring
Uploaded by
Benjie DimayacyacCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
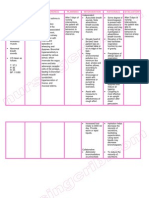
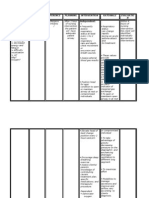
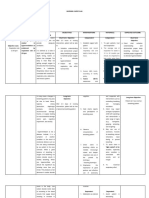
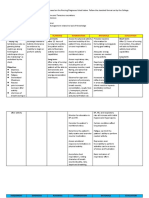
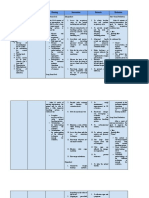
Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: Ineffective After hr of nursing Independent:
Objective: breathing pattern intervention the
• Tachypnea related to broncho patient indicates, • Place patient • A sitting position
constriction as either verbally or with proper body permits maximum
• Use of
evidenced by through behavior, alignment (semi- lung excursion
accessory used of accessory feeling fowler position) for and chest
muscles in muscle, nasal comfortable when maximum expansion.
breathing flaring, tachypnea, breathing. breathing pattern.
O2: 91%
• O2: 91% • Suction
• Nasal flaring secretions, as • This is to clear
• necessary. blockage in
airway.
• Stay with the
patient during • This will reduce
acute episodes of the patient’s
respiratory anxiety, thereby
distress. reducing oxygen
demand.
• Monitored vital • to obtain
Signs baseline data
• Assess for • Respiratory rate
discomfort and rhythm
changes are early
warning signs of
impending
respiratory
difficulties.
Dependent:
• Administered O2 • Oxygen therapy
regulated at 2 lpm is tx that increase
via nasal cannula the amount of
as ordered and oxygen your lungs
administered received and
prescribed deliver to the
respiratory blood.
medication
Collaborative:
• Consult dietitian • COPD may
for dietary cause malnutrition
modifications. which can affect
breathing pattern.
Good nutrition can
strengthen the
functionality of
respiratory
muscles.
• Provide • Beta-adrenergic
respiratory agonist
medications and medications relax
oxygen, per airway smooth
doctor’s orders. muscles and
cause
bronchodilation to
open air
passages.
You might also like
- QualifiedPhysio Acute-Respiratory Interview Preparation Pack PDFDocument36 pagesQualifiedPhysio Acute-Respiratory Interview Preparation Pack PDFdanypunct100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - BronchitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Bronchitisderic94% (36)
- Concept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument1 pageConcept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseWayne Calderon75% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaderic93% (60)
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument14 pagesNeonatal Respiratory Distress SyndromeDrex CuritanaNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Diseases (RISK FOR INJURY) REVISED!Document2 pagesParkinson's Diseases (RISK FOR INJURY) REVISED!Benjie Dimayacyac100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearanceniomi0884% (31)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- NCP 3Document3 pagesNCP 3James Francisco GarcesaNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperthermia IBPDocument4 pagesNCP Hyperthermia IBPJohn Patrick CuencoNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAmple CasaclangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlansJayson Sumampong100% (1)
- NCP For Septicemia - PernitesDocument3 pagesNCP For Septicemia - PernitesFrancis Adrian Lañojan PernitesNo ratings yet
- Sabal, Pearl Angeli - Ineffective Breathing Pattern (NCP)Document3 pagesSabal, Pearl Angeli - Ineffective Breathing Pattern (NCP)Sam EugenioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing DX Inference Planning Intervention Ratoinale Evaluatio N S - IndependentDocument8 pagesAssessment Nursing DX Inference Planning Intervention Ratoinale Evaluatio N S - IndependentJillian MendozaNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCase Study:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument5 pagesNCP FinalYoongiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ige (Cap)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ige (Cap)Algen UbasaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- NCP For Tuberculosis.Document7 pagesNCP For Tuberculosis.Kirstie ClaireNo ratings yet
- Care Plan On Asthma 2-1Document5 pagesCare Plan On Asthma 2-1chaudharitrushar007No ratings yet
- Cap NCPDocument2 pagesCap NCPkyshb100% (2)
- Pulmonary Embol-WPS OfficeDocument49 pagesPulmonary Embol-WPS OfficeBryan BuendiaNo ratings yet
- Copd 2Document3 pagesCopd 2guadalupedeamargaretNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivNo ratings yet
- Copd - NCPDocument6 pagesCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Student Name: Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Past History Diagnosis: Type of DietDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan: Student Name: Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Past History Diagnosis: Type of Dietyeid7878No ratings yet
- NCP Lung CancerDocument2 pagesNCP Lung CancerAnn Pauline GoducoNo ratings yet
- Princess NCP COPDDocument3 pagesPrincess NCP COPDPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Kelompok IDocument14 pagesBronchitis: Kelompok ILinda Permata Sari100% (1)
- NCP PDFDocument8 pagesNCP PDFThee AzirahNo ratings yet
- Patient With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPatient With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Nursing Care PlanDhevy Sa'PhuttRyyNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Collection of Mucus in The Airways (Pneumonia) andDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange Related To Collection of Mucus in The Airways (Pneumonia) andBetina De JesusNo ratings yet
- NICUDocument14 pagesNICUDanica Yen PagalNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationVen Belista86% (14)
- Ramon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingDocument7 pagesRamon Magsaysay Memorial Medical Center Inc.: College of NursingHannah GaerlanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationannice_12No ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Management PlanGem Crystal GuinamosNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation Respiration: Hypoxia Is A Condition in Which The Body or A Region ofDocument3 pagesOxygenation Respiration: Hypoxia Is A Condition in Which The Body or A Region ofMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDocument5 pagesNursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
- Task 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesTask 1. My Plan For You!: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTine SabaulanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesNCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternJose Marlon CandelariaNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document7 pagesNCP 2Kerks Von Gladiel NapaoNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisFrom EverandAsthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisNo ratings yet
- The Essential COPD Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Shed Excess Fats, Build Muscle And Unleash Your Body Potential With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Essential COPD Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Shed Excess Fats, Build Muscle And Unleash Your Body Potential With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseFrom EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Respiratory MedicineFrom EverandEvidence-Based Respiratory MedicinePeter G. GibsonNo ratings yet
- Benefits and Challenges of Online Consultations: Gantt Chart For The StudyDocument2 pagesBenefits and Challenges of Online Consultations: Gantt Chart For The StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Benefits & Challenges of Online Consultation Among Medical Doctors in Dasmariñas, CaviteDocument10 pagesBenefits & Challenges of Online Consultation Among Medical Doctors in Dasmariñas, CaviteBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument22 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- NCP Kuya TedDocument3 pagesNCP Kuya TedBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Or Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOr Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis in ChildrenDocument16 pagesBronchiolitis in ChildrenNym Angga Santosa100% (1)
- Et TubeDocument31 pagesEt Tubeinno so qtNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument4 pagesBronchitisGokul SmartNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Lecture 8 - Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesBiology 2 Lecture 8 - Respiratory Systemryle34No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Plan of Care/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvlatuationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Plan of Care/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvlatuationgoyaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance PDFDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance PDFPratiksha AmbedkarNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPleural Effusion Secondary To Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyIris Caberte100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology by Dennis Munoz2Document1,273 pagesAnatomy and Physiology by Dennis Munoz2Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Review - Spinal Cord Injury - 2Document1 pageReview - Spinal Cord Injury - 2Sarah MendozaNo ratings yet
- Aits Neet Grand Test - 23 Paper Key (04-05-2023)Document10 pagesAits Neet Grand Test - 23 Paper Key (04-05-2023)vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
- Bearcub Ventilator BrochureDocument2 pagesBearcub Ventilator BrochureRICARDO CARRILLONo ratings yet
- Home Based CareDocument34 pagesHome Based CaremewselectionsNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema Vs Pneumonia OrderDocument25 pagesPulmonary Edema Vs Pneumonia OrderRizqon RohmatussadeliNo ratings yet
- Performing Nasopharyngeal/Nasotracheal Suctioning Purposes:: Excellent Very Good Good Fair PoorDocument6 pagesPerforming Nasopharyngeal/Nasotracheal Suctioning Purposes:: Excellent Very Good Good Fair PoorJmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- Open Source Ventilator PakistanDocument104 pagesOpen Source Ventilator Pakistanmushahid980No ratings yet
- First AidDocument48 pagesFirst AidPeter AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation 1 CopdDocument48 pagesCase Presentation 1 CopdPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Bra Kay MEDICAL NURSING 9TH APRIL, 2022 PDFDocument10 pagesBra Kay MEDICAL NURSING 9TH APRIL, 2022 PDFMercy NelsonNo ratings yet
- CL 2 SafehandlingDocument49 pagesCL 2 SafehandlingVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Causes, Workup and Management of Epistaxis: AssignmentDocument4 pagesCauses, Workup and Management of Epistaxis: AssignmentFarhan AfzalNo ratings yet
- NIV Fs 9108147 e 1911 1 PDFDocument4 pagesNIV Fs 9108147 e 1911 1 PDFliuchenshitaoNo ratings yet
- Newborn. Assessment and Care of The Normal NewbornDocument73 pagesNewborn. Assessment and Care of The Normal NewbornKarjana183No ratings yet
- Biology Standard 10 X NEET NTSE KVPY Foundation Explorer Key Explanation Brain Mapping Academy HClass 10 PDFDocument73 pagesBiology Standard 10 X NEET NTSE KVPY Foundation Explorer Key Explanation Brain Mapping Academy HClass 10 PDFKhushi Gupta100% (3)
- Measurements To Guide Your Patient Care: EfficiaDocument12 pagesMeasurements To Guide Your Patient Care: EfficiaXinwen ChenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument15 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMariam Yiani Aspiras RacelesNo ratings yet
- European Consensus On The Management of RDSDocument41 pagesEuropean Consensus On The Management of RDSDeddy Supriyadi100% (1)
- Pengaruh Posisi Condong Kedepan Dan Terapi Pursed Lips Breathing Terhadap Derajat Sesak Napas Penderita Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Kronik (PPOK)Document7 pagesPengaruh Posisi Condong Kedepan Dan Terapi Pursed Lips Breathing Terhadap Derajat Sesak Napas Penderita Penyakit Paru Obstruktif Kronik (PPOK)Leli FebriantiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of LungsDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Lungs31 PASION, ROCHELLE C.No ratings yet