Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 May/June 2019
Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 May/June 2019
Uploaded by
CamilleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 May/June 2019
Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 May/June 2019
Uploaded by
CamilleCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge Assessment International Education
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
GEOGRAPHY 0460/12
Paper 1 May/June 2019
MARK SCHEME
Maximum Mark: 75
Published
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of the
examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not indicate the
details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners’ meeting before marking began, which would have
considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for
Teachers.
Cambridge International will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge International is publishing the mark schemes for the May/June 2019 series for most
Cambridge IGCSE™, Cambridge International A and AS Level and Cambridge Pre-U components, and
some Cambridge O Level components.
This syllabus is regulated for use in England, Wales and Northern Ireland as a Cambridge International Level 1/Level 2 Certificate.
This document consists of 21 printed pages.
© UCLES 2019 [Turn over
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Generic Marking Principles
These general marking principles must be applied by all examiners when marking candidate answers.
They should be applied alongside the specific content of the mark scheme or generic level descriptors
for a question. Each question paper and mark scheme will also comply with these marking principles.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 1:
Marks must be awarded in line with:
• the specific content of the mark scheme or the generic level descriptors for the question
• the specific skills defined in the mark scheme or in the generic level descriptors for the question
• the standard of response required by a candidate as exemplified by the standardisation scripts.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 2:
Marks awarded are always whole marks (not half marks, or other fractions).
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 3:
Marks must be awarded positively:
• marks are awarded for correct/valid answers, as defined in the mark scheme. However, credit
is given for valid answers which go beyond the scope of the syllabus and mark scheme,
referring to your Team Leader as appropriate
• marks are awarded when candidates clearly demonstrate what they know and can do
• marks are not deducted for errors
• marks are not deducted for omissions
• answers should only be judged on the quality of spelling, punctuation and grammar when these
features are specifically assessed by the question as indicated by the mark scheme. The
meaning, however, should be unambiguous.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 4:
Rules must be applied consistently e.g. in situations where candidates have not followed
instructions or in the application of generic level descriptors.
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 5:
Marks should be awarded using the full range of marks defined in the mark scheme for the question
(however; the use of the full mark range may be limited according to the quality of the candidate
responses seen).
GENERIC MARKING PRINCIPLE 6:
Marks awarded are based solely on the requirements as defined in the mark scheme. Marks should
not be awarded with grade thresholds or grade descriptors in mind.
© UCLES 2019 Page 2 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
1(a)(i) 500 000 1
1(a)(ii) Natural population growth: 2
Difference between the number of birth and deaths / BR-DR / BR higher
than DR / more births than deaths;
Net migration:
Difference between immigration and emigration / more moving in than out /
immigration-emigration;
2 @ 1 mark
1(a)(iii) Net migration bigger than natural population growth= 3
1999–2011 inclusive / 2014;
More emigrants than immigrants= 1992;
Largest increase in population= 2011;
3 @ 1 mark
1(a)(iv) Ideas such as: 4
Low BR / fertility rates;
Use of / availability of contraception / family planning is widespread / can
afford contraception;
Availability of abortions;
Educated about family planning / problems of large population growth;
Women are educated / many women have careers / emancipation;
Expense of large families / people want to buy luxury goods;
Benefits are available for elderly / no need for many children to look after the
elderly / old people have pensions / care homes;
Education is compulsory;
Low IMR rates;
Get married later / have children later;
Children not needed as workers / on farms;
Secular society / religious beliefs do not prevent use of contraception;
Etc.
4 @ 1 mark
1(b)(i) Ideas which compare growth such as: 3
More growth in Africa overall;
Population was higher in Europe in 1800 but higher in Africa in 2100;
Growth was more rapid in Europe up to 1950 / or any period before that as
long as not a single year;
Growth has been much more rapid in Africa since 1950 / or any period after
that as long as not a single year;
Europe`s population is predicted / estimated to decrease (from 2015) but
Africa`s predicted to increase;
Statistics with units to MAX. 1 RESERVE – needs to be comparative and
include 2 dates for each of Europe and Africa. Do not need to be supporting
statements made.
3 @ 1 mark
© UCLES 2019 Page 3 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
1(b)(ii) Ideas such as : 5
Lack of housing / overcrowded houses / shanty towns;
Pressure on health care;
Pressure on educational facilities;
Lack of employment;
Lack of food / farmland / starvation / need to import more food;
Pressure on water supplies / lack of water;
Pressure on sanitation / lots of waste / waste disposal problems;
Traffic congestion / jams;
Overuse of agricultural land / desertification / have to farm marginal land;
Deforestation;
Air / water pollution;
Poverty;
Pressure on electricity / power / fuel shortages;
Etc.
Note:
Can develop each line of MS once
5 @ 1 mark or development
© UCLES 2019 Page 4 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
1(c) Levels marking 7
Level 1 (1–3 marks)
Statements including limited detail which describe and/or comment on the
success of a population policy.
e.g. One Child Policy
Level 2 (4–6 marks)
More developed statements which describe and/or comment on the success
of a population policy. Can use 3 × L2 for description or evaluation.
(Note: Max. 5 if no named or inappropriate example)
Level 3 (7 marks)
Uses named example.
Comprehensive and accurate statements which describe and comment
(both at L2) on the success of a population policy including some place
specific reference.
Note: Anti natal policies e.g. China One Child Policy
Ideas will cover the following – so credit only 1 × L2 for each of the ideas
below, although other ideas such as applying to have a child / increasing the
age of marriage can also be credited.
Any country with an anti natal policy follows the marking structure for China.
Whereas pro natal policies e.g. Singapore / France can develop any ideas
to L2, without using the China marking structure.
Incentives – e.g. One Child Policy & Free education (L2)
Penalties – One Child Policy & use of fines (L2)
Exceptions – One Child Policy & not penalized for twins or if first child
disabled (L2)
Enforcement – One Child Policy & Granny Police (L2)
Not: allow second child is the first born is a girl in rural areas – too
generalized
Content Guide:
Policy could be to reduce or increase population growth and could refer to
natural growth or migration.
Answers are likely to refer to:
• Limits on numbers of children
• Methods of enforcement
• Provision of contraception
• Legislation about abortion
• Impact on birth rates
• Female infanticide
© UCLES 2019 Page 5 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
1(c) • Imbalance of sex ratios
• Reduced birth rate
• Less pressure on schools
• Less pressure on food
• Less pressure on medical care
• Etc.
Place specific reference is likely to consist of:
Named parts of the chosen country,
Population data,
Specific aspects of policy etc.
Statistics (can also be credited as PS)
© UCLES 2019 Page 6 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
2(a)(i) A method of arranging settlements based on the size of their population. 1
2(a)(ii) The larger / smaller the population the less / more settlements there will be / 2
inversely proportional;
E.g. more villages than cities (must compare two settlement types)
2 @ 1 mark
2(a)(iii) Examples such as: 3
Department store;
(Specialist shops such as) Jeweller;
Wedding dress shop;
Umbrella shop:
National stadium;
Theatre;
(International) airport;
University;
Parliament;
Embassy
HQ;
Etc.
Note:
Can give 3 different high order shops
3 @ 1 mark
2(a)(iv) Ideas such as: 4
There is a large population / lots of customers / large market / large
demand;
The sphere of influence is a large area / many people travel from a long
distance / large catchment area;
Enough people to meet threshold;
Capital cities are a focus of route networks / good transport links;
Many tourists will visit / use the services;
Wealthy people live there;
Etc.
4 @ 1 mark
2(b)(i) Post office(s); 3
Doctors / surgeries;
Shops;
Schools;
Bank;
Cashpoint / ATM
3 @ 1 mark
© UCLES 2019 Page 7 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
2(b)(ii) Ideas such as: 5
People move away from rural areas / move to city / urbanisation;
Decline of population in some rural areas;
Services are unprofitable / uneconomical / not sustainable
Less demand / customers;
Increased mobility / car ownership;
Many people use services in the urban areas where they work;
Poor communications make supplying resources to these services difficult /
expensive;
Internet / online shopping;
Ageing population / young people leave;
Etc.
5 @ 1 mark or development
© UCLES 2019 Page 8 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
2(c) Levels marking 7
Level 1 (1–3 marks)
Statements including limited detail which describe / state the function and/or
explain why the chosen settlement has that function.
Level 2 (4–6 marks)
Uses named example.
More developed statements which explain why the chosen settlement has
that function
(Note: Max. 5 if no named or inappropriate example)
Level 3 (7 marks)
Uses named example.
Comprehensive and accurate statements with some place specific
reference.
Content Guide:
Answers will depend on the function of the chosen settlement which may
include:
Port,
Capital city,
Industrial town,
Route centre,
Market town,
Administrative centre,
Tourist resort
Service centre / offers services
Note: Do not accept examples of services
Place specific reference is likely to consist of:
Locational details,
Specific details of land uses related to the function,
Named parts of settlement etc.
Statistics (can also be credited as PS)
© UCLES 2019 Page 9 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
3(a)(i) Confluence 1
3(a)(ii) Ideas such as: 2
White / fast flowing water / rapids;
Rocks / boulders / stones (in channel);
Shallow / varying depths;
Uneven long profile / gradient etc.
=0:
Steep gradient
Valley
Large load
Wide / narrow / large / small
Waterfall
Trees
Comparing the two rivers
2 @ 1 mark
3(a)(iii) Ideas such as: 3
Fast flowing;
Has energy;
Materials carried by river;
Corrasion / hydraulic action / abrasion / attrition or description of process
e.g. rocks collide with each other
3 @ 1 mark
3(a)(iv) Ideas such as further downstream it is likely to be: 4
Wider river;
Broader valley
Deeper;
Faster / velocity increase;
Greater volume / discharge;
(Total) load gets larger
Size of load / sediment smaller;
More deposition / deposition instead of erosion
More lateral erosion;
Higher hydraulic radius / wetted perimeter / smoother riverbed;
More meandering / oxbow lake present;
A flood plain may develop;
Valley (sides) will be less steep / flatter;
Gradient of river gets less;
Etc.
4 @ 1 mark
© UCLES 2019 Page 10 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
3(b)(i) Features such as: 3
White water / spray / turbulent / foam;
Vertical / steep (drop / sides) / cliff;
Plunge pool / deep pool;
Overhang / cave / undercut;
Double waterfall / steps / ledge / separates at top;
Widens as gets lower;
3 @ 1 mark
3(b)(ii) Ideas such as: 5
Hard rock overlies softer rock / (passes over) hard then soft / alternating
hard and soft;
Hard rock resists erosion / softer rock is eroded rapidly;
Undercutting / overhang develops;
Overhang collapses;
Retreat of waterfall / process repeats;
Specific named methods of erosion or description of (1 MAX)
No reserve on diagram, but must be labelled to credit relevant ideas. Do not
double credit ideas on diagram.
5 @ 1 mark or development
© UCLES 2019 Page 11 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
3(c) Levels marking 7
Level 1 (1–3 marks)
Statements including limited detail which explain the causes of a flood.
Level 2 (4–6 marks)
Uses named example.
More developed statements which explain the causes of a flood.
(Note: Max. 5 if no named or inappropriate example)
Level 3 (7 marks)
Uses named example.
Comprehensive and accurate statements including some place specific
reference.
Content Guide:
Answers are likely to refer to:
Heavy rainfall,
Rainfall over a long period of time,
Impermeable rocks,
Rocks reach saturation level,
Snow / ice melt,
Deforestation,
Urban development
Storm surges
High spring tides
Cyclones – so coastal flooding idea fine at estuary
Lack of river management
Place specific reference is likely to consist of:
Locational details,
Named places along the river / in the drainage basin,
Statistics (can also be credited as PS) e.g. rainfall amounts
© UCLES 2019 Page 12 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
4(a)(i) Volcanoes are in a roughly circular pattern / around / surrounding the 1
Pacific;
4(a)(ii) Ideas such as: 2
Both are in the Pacific Ocean / on Pacific plate;
Ruapehu is in the Ring of Fire but Mauna Loa is not / Ruapehu is on the
edge and Mauna Loa is in the centre / hot spot;
Ruapehu is further south / Ruapehu is in S.Hemisphere and Mauna Loa in
N. Hemisphere;
Ruapehu is further west / Mauna Loa is further East;
Mauna Loa is nearer equator;
Ruapehu is East of Australia but Mauna Loa is West Of USA;
2 @ 1 mark
4(a)(iii) Ideas such as: 3
Subduction / one plate sinks under the other;
Oceanic plate is heavier / denser;
Destruction of / melting of crust;
Build up of pressure;
Magma released through weakness / crack etc
Note: Divergent plates idea =0 marks for question.
3 @ 1 mark
4(b)(i) Ideas such as: 3
(General) Increase in number of earthquakes over the time period / most
earthquakes in 2015;
Especially since 2013 / 2014;
Little change between 2010–2012 / 13;
More variation / fluctuations in 2015;
3 @ 1 mark
4(b)(ii) Ideas such as: 4
Evacuation procedures;
Buildings which are earthquake / volcano proof – accept details to MAX 2;
National earthquake day;
Education about what to do during earthquake / volcano / safety drills;
Train emergency services;
Survival kit / emergency food supply
Landuse zoning / exclusion zone;
Lava diversion channels;
Spray lava with water;
Shelters from volcanoes;
Wearing masks to protect from dust;
Flexible gas pipes / cut offs;
Etc.
4 @ 1 mark
© UCLES 2019 Page 13 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
4(b)(iii) Ideas such as MEDCs / LEDCs: 5
Invest more / less money in methods of protection / monitoring;
Instigate evacuation procedures more / less effectively;
Educate people so that they can protect themselves from the impacts;
Provide better healthcare / hospitals / doctors / ambulances;
Provide quicker / more efficient rescue services / helicopters
Build stronger / weaker buildings;
Have better / poor road network;
Etc.
Do not need LEDC / MEDC stated or comparative answer
5 @ 1 mark or development
© UCLES 2019 Page 14 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
4(c) Levels marking 7
Level 1 (1–3 marks)
Statements including limited detail which explain why people live close to an
active volcano.
Job = L1 e.g. of job = L2
Level 2 (4–6 marks)
Uses named example.
More developed statements which explain why people live close to an active
volcano.
(Note: Max. 5 if no named or inappropriate example)
Level 3 (7 marks)
Comprehensive and accurate statements which explain why people live
close to an active volcano, including some specific details.
Content Guide:
Answers are likely to refer to:
Fertile soils,
Mining / quarrying
Tourism,
Prepared to take the risks / risks are outweighed by benefits,
Geothermal power
Friends / family
Scientists
Can’t afford to move
Note: Develop each idea for 1 × L2 max.
These ideas simply stated = L1, can develop each idea once for L2.
Jobs or earn money – use as development once ie 1 × L2.
Place specific reference is likely to consist of:
Locational details,
Named areas / features etc.
Statistics
© UCLES 2019 Page 15 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
5(a)(i) Producing output / produce / product / crops / food to use / feed family / self 1
/ tribe
5(a)(ii) Gives water / provides water / won’t dry out / have water constantly / they do 2
not go for long spells without water;
Plants grow (faster / bigger) / keeps them alive / don’t die / more crops;
Note: No reference to water =0. Must have first idea to gain credit for
second mark, as idea of irrigation needs to be understood.
2 @ 1 mark
5(a)(iii) Ideas such as: 3
Using low / intermediate technology / lack technology / machinery ;
Have the skills to be able to use these methods / don’t have skills to use
machinery;
Relatively low cost / people are poor / affordable method;
Do not require sources of fuel (electricity) / they use manpower;
Animal power is used / are available;
Easy to maintain / build;
Made from local materials;
Etc.
3 @ 1 mark
5(a)(iv) Methods such as: 4
Crop rotation / fallowing;
Use of fertilizers / animal manure;
Insecticides / pesticides / herbicides;
Greenhouses / glasshouses / polytunnels;
Mulching;
Use HYVs / GM / disease resistant / or example;
Mechanization / automation;
4 @ 1 mark
© UCLES 2019 Page 16 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
5(b)(i) Ideas such as: 3
Feeding;
Planting;
Sowing
Harvesting;
Shearing;
Spreading fertiliser;
Slaughtering animals;
Irrigating;
Ploughing;
Weeding;
Lambing;
Herding;
Spraying;
Milking;
Etc.
Note: Jobs that the farmer does.
3 @ 1 mark
5(b)(ii) If crops fail the farmers will be able to depend on animals / crops; 5
Animal manure can be used for crops;
Crops / crop waste can be used for animal feed;
Animals used to plough fields;
Farmers can use all types of land / e.g. fertile soils for crops and infertile
soils for grazing;
Work will be spread throughout the year;
Income will come into the farm at various different times;
Can adapt to changes in demand;
Enables crop rotation;
Etc.
If the candidate refers to crops or animals only, do no credit.
5 @ 1 mark or development
© UCLES 2019 Page 17 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
5(c) Levels marking 7
Level 1 (1–3 marks)
Statements including limited detail which explain why there have been food
shortages.
Level 2 (4–6 marks)
Uses named example.
More developed statements which explain why there have been food
shortages.
(Note: Max. 5 if no named or inappropriate example)
Level 3 (7 marks)
Uses named example.
Comprehensive and accurate statements, including some place specific
reference.
Content Guide:
Issues such as:
Drought,
War,
Poverty,
Overuse of the land,
Population increase,
Export of cash crops,
Lack of cultivable land,
Unequal distribution of land,
Flooding,
Poor storage of food,
Poor distribution of food / aid
Desertification
Note: Do not credit the causes of drought or war as L2 statements – they
need to explain how these factors cause food shortages
Place specific reference is likely to consist of:
Locational details / named areas within country chosen
Specific details of issues / dates
Statistics (can also be credited as PS)
© UCLES 2019 Page 18 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
6(a)(i) One 1
6(a)(ii) Renewable: 2
Hydro-electric / HEP;
Geothermal;
Wind.
Non-renewable:
Coal;
Oil / thermal;
2 @ 1 mark
6(a)(iii) Ideas such as: 3
Both have oil fired / thermal power stations;
Both have HEP;
Oil is more important / more thermal stations in Sonara / 4 in Sonora and 2
in Sinaloa;
HEP is more important / more HEP stations in Sinaloa / 5 in Sinaloa and 1 in
Sonora;
Sonora has mainly oil but Sinaloa has mainly HEP;
Sonara has a geothermal power station, Sinaloa does not;
3 types of power in Sonora and 2 in Sinaloa;
Note: Must be comparative
3 @ 1 mark
6(a)(iv) Ideas such as areas which can generate large amounts of HEP: 4
Have lots of rainfall;
Mountainous / have steep slopes;
Experience periods of melting snow / ice
Have many places to build dams / reservoirs;
Have large / fast flowing river(s) / waterfalls;
Have large areas of land which can be flooded / open space / sparsely
populated;
Etc.
4 @ 1 mark
© UCLES 2019 Page 19 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
6(b)(i) Northwest / Chihuahua / Los Ramones (1) reserved 3
No name =0 for answer.
Correct pipeline but wrong description =1.
Chihuahua pipeline:
From El Paso to El Encino;
North to south / to the South;
500 km long;
Inland;
Northwest:
Tuscon to Mazatlan;
NW to SE / to the SE;
1500 km long;
Coastal
Los Ramones:
Agua Dulce to Aguascalientes / Queretaro;
NE to SW / SSW / to the SW / SSW;
1000 km;
Inland;
2 @ 1 for description
3 @ 1 mark
6(b)(ii) Ideas such as: 5
Expensive;
Prices fluctuate;
Impact on balance of trade;
Reliance on a fuel which is non-renewable / will eventually run out / may
have to find alternative fuel;
Specified impact(s) on natural environment e.g. air pollution, global
warming;
Supply may be restricted (if there are political disputes);
Problems of damage to pipeline / explosions / leaks;
Etc.
5 @ 1 mark or development
© UCLES 2019 Page 20 of 21
0460/12 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme May/June 2019
PUBLISHED
6(c) Levels marking 7
Level 1 (1–3 marks)
Statements including limited detail which explain how an economic activity is
causing the natural environment to be at risk.
Level 2 (4–6 marks)
Uses named example.
More developed statements which explain how an economic activity is
causing the natural environment to be at risk.
(Note: Max. 5 if no named or inappropriate example)
Manufacturing / agriculture / tourism acceptable as types of economic
activity, along with other appropriate examples.
Location must generally be smaller than a country, however there may be
exceptions e.g. Sahel.
Level 3 (7 marks)
Uses named example.
Comprehensive and accurate statements, including some place specific
reference.
Content Guide:
Answers could refer to any economic activity at any scale and are likely to
refer to issues such as:
Air pollution,
Water pollution,
Destruction of vegetation,
Impacts on ecosystems / food chains,
Impacts on climate,
Soil erosion
Global issues
Deforestation / industry / burning fossil fuels cannot be accepted as valid
economic activity, therefore max. 5.
Place specific reference is likely to consist of:
Locational details / named areas within country / area chosen
Statistics (can also be credited as PS)
© UCLES 2019 Page 21 of 21
You might also like
- Progress in Mathematics Grade 5Document537 pagesProgress in Mathematics Grade 5shilpa01020385% (41)
- Know Your Cousins by Terrill Bunyan BouldinDocument52 pagesKnow Your Cousins by Terrill Bunyan Bouldinchad_bouldin100% (3)
- IGCSE Geography Paper 1 Mark Scheme March 2020 PDFDocument14 pagesIGCSE Geography Paper 1 Mark Scheme March 2020 PDFG D Amaya RomeroNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument21 pagesGeographySafeguarding1 BurngreaveNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/11 October/November 2019Document18 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/11 October/November 2019Miguel Oubiña SánchezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 March 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 March 2019Apollonas Marios SofroniouNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 October/November 2019Document19 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 October/November 2019Miguel Oubiña SánchezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/11 October/November 2021Document19 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/11 October/November 2021Jasmine UhmNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 October/November 2018Document18 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/12 October/November 2018Catherine RanganayiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/11Document19 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/11tebidnerus05No ratings yet
- Correzioni Paper Scuola 2Document15 pagesCorrezioni Paper Scuola 2Leonardo SilenziNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/13 May/June 2018Document15 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/13 May/June 2018totola5341No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/11 October/November 2018Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/11 October/November 2018Godwin SikanyikaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/12 February/March 2022Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/12 February/March 2022Mimi XoaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/13 May/June 2020Document14 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/13 May/June 2020Miguel Oubiña SánchezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Development Studies 0453/02 October/November 2019Document8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Development Studies 0453/02 October/November 2019heyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/13Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/13jamescNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/13 October/November 2017Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/13 October/November 2017pingpong playerNo ratings yet
- 0455 s18 Ms 23Document20 pages0455 s18 Ms 23Sukrit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 9696/23 May/June 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 9696/23 May/June 2019xerxesNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Pakistan Studies 0448/02 May/June 2017Document19 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Pakistan Studies 0448/02 May/June 2017Mohammed KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/21 May/June 2019Document18 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/21 May/June 2019Shayan KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Pakistan Studies 2059/02 October/November 2017Document19 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Pakistan Studies 2059/02 October/November 2017Alish JNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Agriculture 0600/12 October/November 2019Document27 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Agriculture 0600/12 October/November 2019walaa ahmadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/22 October/November 2019Document10 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/22 October/November 20194nbcdhxzmwNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/12Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Geography 0460/12rdtyghNo ratings yet
- 0457 s19 Ms 13 PDFDocument14 pages0457 s19 Ms 13 PDFLily SternickNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/11 May/June 2018Document14 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/11 May/June 2018Shadman ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 2281/21 May/June 2019Document18 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 2281/21 May/June 2019Nivesh BangarigaduNo ratings yet
- 0460 s19 Ms 22Document8 pages0460 s19 Ms 22Ebid AlfatikhNo ratings yet
- 9696 s21 Ms 23 PDFDocument15 pages9696 s21 Ms 23 PDFLara BrownNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/41 May/June 2019Document14 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/41 May/June 2019srividhyaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Travel & Tourism 0471/21 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Travel & Tourism 0471/21 May/June 2019LayaanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/21 May/June 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/21 May/June 2019SimonaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/22 October/November 2019Document23 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/22 October/November 2019dinaj.baigNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelDocument18 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary LevelAmna Siddiqui100% (1)
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/22 March 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/22 March 2019AhmedNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperDocument15 pagesMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question PaperalvinkoyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/22 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/22 May/June 2019Mariana TrovatelliNo ratings yet
- 0460 Geography: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument14 pages0460 Geography: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersalvinkoyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/43 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/43 May/June 2019srividhyaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Geography 9696/21 October/November 2020Document15 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Geography 9696/21 October/November 2020Spencer HastingsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/12 May/June 2019Document92 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/12 May/June 2019janmarkowski23No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 May/June 2019Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/32 May/June 2019fredmelly663No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/21 October/November 2019Document21 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/21 October/November 2019shrutisonibkn18No ratings yet
- Global Perspectives 0457 - s19 - Ms - 11Document13 pagesGlobal Perspectives 0457 - s19 - Ms - 11Maha Mahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 9696/22 October/November 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 9696/22 October/November 2019Lakshin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/21 May/June 2019Document8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/21 May/June 2019Valeria VallettaNo ratings yet
- 0460 Geography: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument11 pages0460 Geography: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SerieshpaundiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/12 October/November 2019Document92 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/12 October/November 20198dnjb4td6pNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/21 October/November 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/21 October/November 2019sikkenderNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/12 May/June 2019Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 5014/12 May/June 2019janggodanxdNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Geography 9696/22 May/June 2022Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Geography 9696/22 May/June 2022farah qNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 May/June 2019Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 0610/42 May/June 2019Hana GABERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Computer Science 0478/13 October/November 2019Document14 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Computer Science 0478/13 October/November 2019janm23No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/11 May/June 2019Document95 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/11 May/June 2019janmarkowski23No ratings yet
- 0460 - w15 - 1 - 2 - Ms GeoDocument15 pages0460 - w15 - 1 - 2 - Ms GeoSheila Ester NyangeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/21 May/June 2018Document17 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Economics 0455/21 May/June 2018[ C A K E S ]No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/12 March 2019Document15 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Environmental Management 0680/12 March 2019tawiekayyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/21 May/June 2019Document15 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: History 0470/21 May/June 2019janmarkowski23No ratings yet
- 2059 s19 Ms 1Document19 pages2059 s19 Ms 1Asif NazeerNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Mainstream School Funding: School Financial Success Guides, #5From EverandForecasting Mainstream School Funding: School Financial Success Guides, #5No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC P1 MEMO Sept 2023 Afr Eastern CapeDocument17 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC P1 MEMO Sept 2023 Afr Eastern CapeCamilleNo ratings yet
- Dance Studies NSC MEMO Nov 2023 AfrDocument30 pagesDance Studies NSC MEMO Nov 2023 AfrCamilleNo ratings yet
- Visual Arts P1 May June 2022 EngDocument20 pagesVisual Arts P1 May June 2022 EngCamilleNo ratings yet
- Dance Studies NSC QP May June 2023 EngDocument11 pagesDance Studies NSC QP May June 2023 EngCamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics Control Test QP March 2024 Free StateDocument14 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics Control Test QP March 2024 Free StateCamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC P1 QP Sept 2023 Afr GautengDocument19 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC P1 QP Sept 2023 Afr GautengCamilleNo ratings yet
- 8a End of Unit Test StandardDocument8 pages8a End of Unit Test StandardCamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC P2 QP Sept 2023 Eng GautengDocument24 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC P2 QP Sept 2023 Eng GautengCamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC Control Test QP March 2024 LimpopoDocument15 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC Control Test QP March 2024 LimpopoCamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC Common Test MEMO March 2024 KZNDocument10 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC Common Test MEMO March 2024 KZNCamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC P1 QP Nov 2023 EngDocument23 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC P1 QP Nov 2023 EngCamilleNo ratings yet
- English FAL P1 May-June 2021Document14 pagesEnglish FAL P1 May-June 2021CamilleNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Physics NSC P1 QP May June 2024 EngDocument20 pagesPhysical Sciences Physics NSC P1 QP May June 2024 EngCamilleNo ratings yet
- Angles Polygon Answers PDFDocument8 pagesAngles Polygon Answers PDFCamilleNo ratings yet
- Solutions: DifferentiationDocument18 pagesSolutions: DifferentiationCamilleNo ratings yet
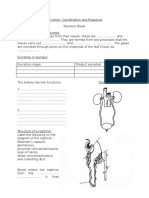
- Excretion and Coordination and Response Revision SheetDocument4 pagesExcretion and Coordination and Response Revision SheetCamilleNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Paper 1 - Mark SchemeDocument2 pagesArithmetic Paper 1 - Mark SchemeCamilleNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Paper 1Document13 pagesArithmetic Paper 1CamilleNo ratings yet
- A Raisin in The Sun Study Guide QuestionsDocument2 pagesA Raisin in The Sun Study Guide QuestionsCamilleNo ratings yet
- 8 Plus Maths Paper 1Document14 pages8 Plus Maths Paper 1CamilleNo ratings yet
- Mean Mode Frequency Table PDFDocument8 pagesMean Mode Frequency Table PDFCamilleNo ratings yet
- Reasoning ProblemsDocument1 pageReasoning ProblemsCamilleNo ratings yet
- Recognise and Use Square Numbers and Cube Numbers and The Notation For Squared and Cubed 1Document2 pagesRecognise and Use Square Numbers and Cube Numbers and The Notation For Squared and Cubed 1CamilleNo ratings yet
- Perrycollins 270 27720scottDocument8 pagesPerrycollins 270 27720scottJay McKearnNo ratings yet
- Anr303Document4 pagesAnr303Chileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- RotavatorDocument6 pagesRotavatorjattboy1100% (1)
- Cost, Production and Price Spread of Cereal Crops in Nepal-A Time Series Analysis 2072Document174 pagesCost, Production and Price Spread of Cereal Crops in Nepal-A Time Series Analysis 2072ABHIMANYU KHADGANo ratings yet
- Low Cost House Construction ManualDocument52 pagesLow Cost House Construction ManualHenry Vds1No ratings yet
- Pastoralists Primarily Depend On Which of The Following Activities For Their LivelihoodDocument4 pagesPastoralists Primarily Depend On Which of The Following Activities For Their LivelihoodAsad IbrarNo ratings yet
- Watson, P. J. - Food Production, Origins ofDocument7 pagesWatson, P. J. - Food Production, Origins ofluis_albornoz4494No ratings yet
- 01.laporan Bulanan Januari 2019Document45 pages01.laporan Bulanan Januari 2019Haidir AnwarNo ratings yet
- Final Da Rice Mechanization ProgramDocument23 pagesFinal Da Rice Mechanization ProgramJohn Paul ArazoNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument795 pagesParts of Speechbon zoNo ratings yet
- Api TLC 2Document3 pagesApi TLC 2aparna tiwariNo ratings yet
- Tabel Cu Muncile AgricoleDocument7 pagesTabel Cu Muncile AgricoleStephanosNo ratings yet
- Broschure - Oekosem KM 1103 Englisch - Low PDFDocument8 pagesBroschure - Oekosem KM 1103 Englisch - Low PDFAnonymous 1XBCMXNo ratings yet
- Luz Farms, Petitioner, vs. The Honorable Secretary of The Department of Agrarian Reform, RespondentDocument27 pagesLuz Farms, Petitioner, vs. The Honorable Secretary of The Department of Agrarian Reform, RespondentQuennie Jane SaplagioNo ratings yet
- 4 SandflyDocument4 pages4 Sandfly173Swapnaneil BujarbaruahNo ratings yet
- Mizoram at A Glance 2018Document64 pagesMizoram at A Glance 2018Johana VangchhiaNo ratings yet
- SchemesTap 1st To 31st January 2024 Lyst2197Document56 pagesSchemesTap 1st To 31st January 2024 Lyst2197adarsh prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On HorticultureDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On HorticultureAbhishek VatsaNo ratings yet
- TLE6 Module6 Caring Orchard TreesDocument30 pagesTLE6 Module6 Caring Orchard TreesLorranne Maice D. MoranoNo ratings yet
- Phillips McDougall Digital Farming & Robotics in Crop Protection 2019 - Sample Report PDFDocument20 pagesPhillips McDougall Digital Farming & Robotics in Crop Protection 2019 - Sample Report PDFsharmendrayadavNo ratings yet
- Hart - The Political Economy of West African AgricultureDocument240 pagesHart - The Political Economy of West African AgricultureviniNo ratings yet
- Mission & Values - Kuala Lumpur Kepong Berhad KLK MalaysiaDocument1 pageMission & Values - Kuala Lumpur Kepong Berhad KLK MalaysiaDima Atsyari NNo ratings yet
- Approved CommoditiesDocument60 pagesApproved Commoditieskbalaji029No ratings yet
- Ex. No. 1 Nursery Tools and ImplementsDocument7 pagesEx. No. 1 Nursery Tools and ImplementsMeiraba Meitei100% (1)
- Chabrier 1 SurvieDocument1 pageChabrier 1 SurvieChristian ChabrierNo ratings yet
- Juke Girl (1942) DraftDocument158 pagesJuke Girl (1942) DraftEx PiredNo ratings yet
- Muhanga District Development Plan 2013-2018-1 01Document116 pagesMuhanga District Development Plan 2013-2018-1 01Joseph Tuseku Officiel100% (1)
- Big History 2 Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesBig History 2 Case AnalysisErrol AlejandroNo ratings yet
- ABE43 ReviewerDocument16 pagesABE43 ReviewerFrancine Ann AgapayNo ratings yet