Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
libbyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 12 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.2 Organelles and Compartmentalization PowerPointDocument59 pages12 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.2 Organelles and Compartmentalization PowerPointmike bevnNo ratings yet
- Biology Staar Eoc ReviewDocument62 pagesBiology Staar Eoc Reviewapi-26963416No ratings yet
- CH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Document3 pagesCH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dani Jo OwensNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology and Genetics Book 3 PDFDocument68 pagesMolecular Biology and Genetics Book 3 PDFPawan Gupta50% (2)
- Chapter 03Document4 pagesChapter 03Teehee JonesNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionmohammedNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Protein SynthesisDocument39 pagesGene Expression - Protein SynthesisTawonga ManjiniNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Transcription of DNA To RNADocument2 pagesTranscription of DNA To RNAReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- Cyto Unit 3Document3 pagesCyto Unit 3Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic ContinuationDocument5 pagesNucleic ContinuationHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: DNA TranscriptionDocument21 pagesCentral Dogma: DNA TranscriptionAmiel MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument24 pagesTranscription and TranslationGenesis FloresNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene Expressionaymnhssn2020No ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and ProteinsDocument47 pagesDNA, RNA and ProteinsShanice RhuleNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- DNA Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesDNA Transcription and TranslationBrian Paguia100% (1)
- M.I.T LessonsDocument12 pagesM.I.T LessonsChassy KammyNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Document48 pagesDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Script Assignment BioDocument2 pagesScript Assignment BioWAN NUR ALEEYA TASNIM BINTI WAN MOHAMED HAZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 BIO 1510Document34 pagesChapter 15 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaDocument51 pagesLecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaBakalJenazahNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN SynthesisDocument37 pagesPROTEIN SynthesisChirag KothariNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerFrancesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids IIDocument7 pagesNucleic Acids IIMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument5 pagesTranscription & TranslationJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Cels 191Document8 pagesCels 191naazhasan2004No ratings yet
- Sci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationDocument7 pagesSci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationMel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0-1Document10 pagesLesson 0-1Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- RNA - Polymerase 1 ClassDocument21 pagesRNA - Polymerase 1 ClassSeemaNo ratings yet
- Biology Gene Expression Article Title: Expression of Biological InformationDocument6 pagesBiology Gene Expression Article Title: Expression of Biological InformationNUR FAQIHAH BINTI FARISH MoeNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation and Transcription PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Translation and Transcription PDFSim QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0Document6 pagesLesson 0Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionDocument46 pages3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Cell Division & Protein SynthesisDocument21 pages4.9 Cell Division & Protein Synthesis2023875802No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis, Brief NoteDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis, Brief NoteosunfisanayomideNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsDocument12 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsAnne RussellNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Bio Keypoints ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Keypoints ReviewerFrancisNo ratings yet
- RNAProtein Synthesis VocabDocument2 pagesRNAProtein Synthesis VocabdherSZN ツNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Dna & RnaDocument58 pagesNucleic Acids Dna & RnaValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetJo JoNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- ASS 7 (bbt193003) MGDocument7 pagesASS 7 (bbt193003) MGAbuzar KhanNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- SCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - Protein SynthesisJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 12Document7 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 12Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis Online 1st ClassDocument43 pagesProtein-Synthesis Online 1st ClassAkasha khanNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument75 pagesTranscriptionspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Biochemistry - PPT 01Document28 pagesBiochemistry - PPT 01Rasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument38 pagesPersonal DevelopmentlibbyNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument30 pagesEnvironmental SciencelibbyNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Investigation of Phenomena: ResearchDocument3 pagesThe Scientific Investigation of Phenomena: ResearchlibbyNo ratings yet
- Communication: Verbal and Non-VerbalDocument4 pagesCommunication: Verbal and Non-VerballibbyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2libbyNo ratings yet
- Control Points in The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesControl Points in The Cell CyclelibbyNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 2a-D Cells and Biological Molecules - Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument73 pagesFlashcards - 2a-D Cells and Biological Molecules - Edexcel Biology IGCSEsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Cytology OrganellesDocument33 pagesCytology OrganellesMitzel SapaloNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, SR Aiims S60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22-01-19 - PDFDocument20 pagesSR Elite, SR Aiims S60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22-01-19 - PDFPankaj JakharNo ratings yet
- 8 - 2 BiologyDocument5 pages8 - 2 Biologyminda.eslteacherNo ratings yet
- Q1. Choose The Correct Answer. 1X50 50Document7 pagesQ1. Choose The Correct Answer. 1X50 50Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Examination in Science 10Document5 pagesThird Periodical Examination in Science 10Mary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-Cuadra0% (1)
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2Document4 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2tifqbfgig100% (2)
- DNA-RNA Worksheet 1Document4 pagesDNA-RNA Worksheet 1inder19125% (4)
- SassafasDocument462 pagesSassafashasla18No ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis HomeworkDocument5 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis HomeworkKarla Long100% (1)
- The Cell As A Candy FactoryDocument4 pagesThe Cell As A Candy FactoryRetnayu CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Nengovhela Study GuideDocument129 pagesNengovhela Study Guidebrighton nyama100% (1)
- Ivy Jean MartinezDocument11 pagesIvy Jean MartinezmarjmarjNo ratings yet
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument33 pagesProtein BiosynthesisLucy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Cell StructureDocument36 pagesCell Theory and Cell StructureRosana Beatrix GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Polikanov 2019-05-14 Curriculum Vitae YuryDocument6 pagesPolikanov 2019-05-14 Curriculum Vitae Yuryapi-460295531No ratings yet
- Time Test 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Name: ID: CohortDocument3 pagesTime Test 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Name: ID: CohortShidevNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Non Coding RNADocument22 pagesNon Coding RNANaomiKerryaThompsonNo ratings yet
- Revision Test End of Semester Exam 2020 - Attempt Review PDFDocument14 pagesRevision Test End of Semester Exam 2020 - Attempt Review PDFaskldhfdasjkNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: TOPIC 3.2.2 Dot 1-6Document23 pagesSyllabus: TOPIC 3.2.2 Dot 1-6BonnyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- Rodak's Hematology 6th Edition Test BankDocument255 pagesRodak's Hematology 6th Edition Test Bankromerolourdes4No ratings yet
- 11a Revision Pack T1Document36 pages11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNo ratings yet
- AS Level Biology Cell Structure, Function and Magnification Name: - 1Document7 pagesAS Level Biology Cell Structure, Function and Magnification Name: - 1Chryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
libbyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
libbyCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA Replication and In lagging strand synthesis,
Protein Synthesis there is a need for a primer
terminus, which is provided
by an RNA molecule.
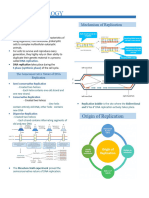
DNA Replication or DNA Synthesis
the process of making an A primase or RNA
identical copy of a DNA polymerase synthesizes RNA.
molecule. The 3’OH of the RNA is where
occurs during the S phase of new DNA nucleotides are
the cell cycle added thus new DNA is built
DNA strands separate and in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
serve as templates for the
production of new DNA Transcription or RNA Synthesis
molecules. DNA ‘s code must be copied and
taken to the cytosol
A summary of DNA Replication DNA is unwound and one strand
is used as template for the
production of an RNA molecule.
An RNA polymerase makes RNA
in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
Promoters - Specific regions in
the DNA that allow the binding of
transcription factors
transcription factors – make
possible the binding of RNA
polymerase.
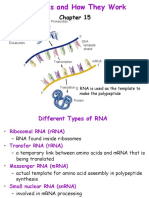
Three major types of RNA are:
Features of Replication: 1. messenger RNA (mRNA)
Semiconservative 2. transfer RNA (tRNA) and
o the resulting DNA 3. ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
consists of one old and
one new strand mRNA Processing
Maintained Base Pairing After the DNA is transcribed into
o Adenine pairs with RNA, editing must be done to the
Thymine, nucleotide chain to make the
o Guanine pairs with RNA functional
Cytosine Introns, non-functional segments
of DNA are snipped out of the
New DNA molecules are
chain
produced in the 5’ to 3’
direction
mRNA Editing
Semidiscontinuous
Exons, segments of DNA that
o The leading strand is
code for proteins, are then
synthesized in a
rejoined by the enzyme ligase
continuous manner (5’
A guanine triphosphate cap is
to 3’) while the lagging
added to the 5” end of the newly
strand is produced
copied mRNA
discontinuously in
short stretches called A poly A tail is added to the 3’
Okazaki fragments. end of the RNA
The newly processed mRNA can
then leave the nucleus
mRNA Transcript
• mRNA leaves the nucleus
through its pores and goes to the
ribosomes
Translation
the process of decoding the
mRNA into a polypeptide chain
Ribosomes read mRNA three
bases or 1 codon at a time and
construct the proteins
Codons and Anticodons
The 3 bases of an anticodon are
complementary to the 3 bases of
a codon
Example: Codon ACU and
Anticodon UGA
Ribosomes
Made of a large and small subunit
Composed of rRNA (40%) and
proteins (60%)
Have two sites for tRNA
attachment --- P and A
Step 1- Initiation
mRNA transcript start codon
AUG attaches to the small
ribosomal subunit
Small subunit attaches to large
ribosomal subunit
Step 2 – Elongation
As ribosome moves, two tRNA
with their amino acids move into
site A and P of the ribosome
Peptide bonds join the amino
acids
End Product –The Protein!
The end products of protein
synthesis is a primary structure
of a protein
A sequence of amino acid bonded
together by peptide bonds
You might also like
- 12 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.2 Organelles and Compartmentalization PowerPointDocument59 pages12 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.2 Organelles and Compartmentalization PowerPointmike bevnNo ratings yet
- Biology Staar Eoc ReviewDocument62 pagesBiology Staar Eoc Reviewapi-26963416No ratings yet
- CH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Document3 pagesCH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dani Jo OwensNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology and Genetics Book 3 PDFDocument68 pagesMolecular Biology and Genetics Book 3 PDFPawan Gupta50% (2)
- Chapter 03Document4 pagesChapter 03Teehee JonesNo ratings yet
- DNADocument64 pagesDNAsapphireriego01No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis: 1) Nucleus: The First Stage of Protein Synthesis Occurs Here. It Is Named TranscriptionmohammedNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Protein SynthesisDocument39 pagesGene Expression - Protein SynthesisTawonga ManjiniNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Transcription of DNA To RNADocument2 pagesTranscription of DNA To RNAReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- Cyto Unit 3Document3 pagesCyto Unit 3Vince CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Nucleic ContinuationDocument5 pagesNucleic ContinuationHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: DNA TranscriptionDocument21 pagesCentral Dogma: DNA TranscriptionAmiel MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument24 pagesTranscription and TranslationGenesis FloresNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene Expressionaymnhssn2020No ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and ProteinsDocument47 pagesDNA, RNA and ProteinsShanice RhuleNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- DNA Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesDNA Transcription and TranslationBrian Paguia100% (1)
- M.I.T LessonsDocument12 pagesM.I.T LessonsChassy KammyNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protsin 2020Document48 pagesDna Rna Protsin 2020RaragloriaaNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument15 pagesTranscriptioncamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- Polypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionDocument3 pagesPolypeptide Synthesis: TranscriptionliklyNo ratings yet
- Script Assignment BioDocument2 pagesScript Assignment BioWAN NUR ALEEYA TASNIM BINTI WAN MOHAMED HAZMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 BIO 1510Document34 pagesChapter 15 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaDocument51 pagesLecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaBakalJenazahNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN SynthesisDocument37 pagesPROTEIN SynthesisChirag KothariNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerFrancesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids IIDocument7 pagesNucleic Acids IIMargaret Nicole AboNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument5 pagesTranscription & TranslationJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Cels 191Document8 pagesCels 191naazhasan2004No ratings yet
- Sci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationDocument7 pagesSci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationMel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0-1Document10 pagesLesson 0-1Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- RNA - Polymerase 1 ClassDocument21 pagesRNA - Polymerase 1 ClassSeemaNo ratings yet
- Biology Gene Expression Article Title: Expression of Biological InformationDocument6 pagesBiology Gene Expression Article Title: Expression of Biological InformationNUR FAQIHAH BINTI FARISH MoeNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation and Transcription PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Translation and Transcription PDFSim QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0Document6 pagesLesson 0Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document27 pagesLecture 5Animikh RayNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionDocument46 pages3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Cell Division & Protein SynthesisDocument21 pages4.9 Cell Division & Protein Synthesis2023875802No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis, Brief NoteDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis, Brief NoteosunfisanayomideNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsDocument12 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsAnne RussellNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Bio Keypoints ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Keypoints ReviewerFrancisNo ratings yet
- RNAProtein Synthesis VocabDocument2 pagesRNAProtein Synthesis VocabdherSZN ツNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Dna & RnaDocument58 pagesNucleic Acids Dna & RnaValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetJo JoNo ratings yet
- Bio AssessmentDocument5 pagesBio Assessmentxx nataliaNo ratings yet
- ASS 7 (bbt193003) MGDocument7 pagesASS 7 (bbt193003) MGAbuzar KhanNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- SCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 (4TH Quarter) - Protein SynthesisJyña Khura TanoNo ratings yet
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 12Document7 pagesBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 12Noor JanahiNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis Online 1st ClassDocument43 pagesProtein-Synthesis Online 1st ClassAkasha khanNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument75 pagesTranscriptionspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Biochemistry - PPT 01Document28 pagesBiochemistry - PPT 01Rasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument38 pagesPersonal DevelopmentlibbyNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument30 pagesEnvironmental SciencelibbyNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Investigation of Phenomena: ResearchDocument3 pagesThe Scientific Investigation of Phenomena: ResearchlibbyNo ratings yet
- Communication: Verbal and Non-VerbalDocument4 pagesCommunication: Verbal and Non-VerballibbyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 2libbyNo ratings yet
- Control Points in The Cell CycleDocument3 pagesControl Points in The Cell CyclelibbyNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 2a-D Cells and Biological Molecules - Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument73 pagesFlashcards - 2a-D Cells and Biological Molecules - Edexcel Biology IGCSEsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Cytology OrganellesDocument33 pagesCytology OrganellesMitzel SapaloNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, SR Aiims S60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22-01-19 - PDFDocument20 pagesSR Elite, SR Aiims S60 & SR Neet MPL Neet Part Test - 4 Paper - 22-01-19 - PDFPankaj JakharNo ratings yet
- 8 - 2 BiologyDocument5 pages8 - 2 Biologyminda.eslteacherNo ratings yet
- Q1. Choose The Correct Answer. 1X50 50Document7 pagesQ1. Choose The Correct Answer. 1X50 50Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Examination in Science 10Document5 pagesThird Periodical Examination in Science 10Mary Grace Jerna Artazo Nozal-Cuadra0% (1)
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2Document4 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis Homework 2tifqbfgig100% (2)
- DNA-RNA Worksheet 1Document4 pagesDNA-RNA Worksheet 1inder19125% (4)
- SassafasDocument462 pagesSassafashasla18No ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna Protein Synthesis HomeworkDocument5 pagesDna Rna Protein Synthesis HomeworkKarla Long100% (1)
- The Cell As A Candy FactoryDocument4 pagesThe Cell As A Candy FactoryRetnayu CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Nengovhela Study GuideDocument129 pagesNengovhela Study Guidebrighton nyama100% (1)
- Ivy Jean MartinezDocument11 pagesIvy Jean MartinezmarjmarjNo ratings yet
- Protein BiosynthesisDocument33 pagesProtein BiosynthesisLucy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Cell StructureDocument36 pagesCell Theory and Cell StructureRosana Beatrix GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Polikanov 2019-05-14 Curriculum Vitae YuryDocument6 pagesPolikanov 2019-05-14 Curriculum Vitae Yuryapi-460295531No ratings yet
- Time Test 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Name: ID: CohortDocument3 pagesTime Test 1 Multiple Choice Questions: Name: ID: CohortShidevNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Non Coding RNADocument22 pagesNon Coding RNANaomiKerryaThompsonNo ratings yet
- Revision Test End of Semester Exam 2020 - Attempt Review PDFDocument14 pagesRevision Test End of Semester Exam 2020 - Attempt Review PDFaskldhfdasjkNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: TOPIC 3.2.2 Dot 1-6Document23 pagesSyllabus: TOPIC 3.2.2 Dot 1-6BonnyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- Rodak's Hematology 6th Edition Test BankDocument255 pagesRodak's Hematology 6th Edition Test Bankromerolourdes4No ratings yet
- 11a Revision Pack T1Document36 pages11a Revision Pack T1Najat BteichNo ratings yet
- AS Level Biology Cell Structure, Function and Magnification Name: - 1Document7 pagesAS Level Biology Cell Structure, Function and Magnification Name: - 1Chryssa EconomouNo ratings yet