Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer: CHAID (Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector) Analysis Is An Algorithm Used For
Answer: CHAID (Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector) Analysis Is An Algorithm Used For
Uploaded by
Prashant kudryaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Hotel Lease AgreementDocument4 pagesHotel Lease AgreementDavid Brito50% (2)
- Interview Questions: Always Find A Link Between The StepsDocument9 pagesInterview Questions: Always Find A Link Between The StepsKarimNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Document7 pagesFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Rafael100% (1)
- SFM Case4 Group7Document5 pagesSFM Case4 Group7AMAAN LULANIA 22100% (1)
- Banking Notes PDFDocument130 pagesBanking Notes PDFfledpengelNo ratings yet
- Developing and Implementing Commercial Loan Pricing ModelsDocument5 pagesDeveloping and Implementing Commercial Loan Pricing Modelsr.jeyashankar95500% (1)
- WACC and Vol: Counterpoint Global InsightsDocument13 pagesWACC and Vol: Counterpoint Global InsightsHoward QinNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Agencies DissertationDocument7 pagesCredit Rating Agencies Dissertationdipsekator1983100% (1)
- Credit Analyst Q&ADocument6 pagesCredit Analyst Q&ASudhir PowerNo ratings yet
- Credit AnalystDocument9 pagesCredit AnalystJimsy Antu100% (1)
- Research Paper On Credit Appraisal ProcessDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Credit Appraisal Processgatewivojez3100% (1)
- Credit Rating GROUP 11Document11 pagesCredit Rating GROUP 11Siddharth Shah0% (1)
- Bank and Insurance Management QuestionsDocument4 pagesBank and Insurance Management QuestionsMarta CrescenziNo ratings yet
- Credit Analyst Questions and Answers 1693198236Document9 pagesCredit Analyst Questions and Answers 1693198236hh2rwfs8f5No ratings yet
- Thesis Credit Rating AgenciesDocument4 pagesThesis Credit Rating AgenciesWhoCanWriteMyPaperForMeUK100% (2)
- Fina4400 Final ExamDocument3 pagesFina4400 Final ExamBouchraya MilitoNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Research PapersDocument4 pagesCredit Risk Research Papersh00yfcc9100% (1)
- Additional InfoDocument25 pagesAdditional InfoSaravananNo ratings yet
- Additional InfoDocument25 pagesAdditional InfoSanthu SaravananNo ratings yet
- Moodys Analytics Riskcalc Transfer Pricing SolutionDocument9 pagesMoodys Analytics Riskcalc Transfer Pricing SolutionManuel CámacNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CS - 08-11-2020Document6 pagesAssignment 1 CS - 08-11-2020Amina NasirNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 TR SirDocument25 pagesUNIT 5 TR SirgauthamNo ratings yet
- Credit GrantingA Comparative Analysis ofDocument18 pagesCredit GrantingA Comparative Analysis ofAhmad SanusiNo ratings yet
- Credit Score Research PapersDocument7 pagesCredit Score Research Papershxmchprhf100% (1)
- Capital Structure Decision ReportDocument14 pagesCapital Structure Decision ReportPratik GanatraNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Agencies Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesCredit Rating Agencies Literature Reviewfat1kifywel3100% (1)
- Week 7: Corporate Credit Risk Models Based On Stock PriceDocument19 pagesWeek 7: Corporate Credit Risk Models Based On Stock PriceNhat Khanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis On Ratio AnalysisDocument5 pagesPHD Thesis On Ratio Analysisaflodnyqkefbbm100% (2)
- Credit Management NotesDocument31 pagesCredit Management NotesAnis Ur Rehman Kakakhel33% (3)
- Research Papers On Credit Risk ManagementDocument7 pagesResearch Papers On Credit Risk Managementgvzexnzh100% (1)
- Accounting Textbook Solutions - 59Document19 pagesAccounting Textbook Solutions - 59acc-expertNo ratings yet
- Credit Analysis NotesDocument5 pagesCredit Analysis NotesNoni100% (1)
- Pricing CTRP RiskDocument36 pagesPricing CTRP RiskJin DongNo ratings yet
- Chapters 10 and 12 Credit Analysis and Distress Prediction3223Document45 pagesChapters 10 and 12 Credit Analysis and Distress Prediction3223alfiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Company ValuationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Company Valuationfys374dr100% (1)
- Amortization:: Amortization Is The Process of Decreasing, or Accounting For, An Amount Over ADocument5 pagesAmortization:: Amortization Is The Process of Decreasing, or Accounting For, An Amount Over ASrikanth GuruNo ratings yet
- Peer To Peer Lending Risk Analysis: Predictions From Lending ClubDocument10 pagesPeer To Peer Lending Risk Analysis: Predictions From Lending Clubortegadelia810No ratings yet
- Muthyam Anusha, (18wj1e0044), Credit Risk ManagementDocument59 pagesMuthyam Anusha, (18wj1e0044), Credit Risk Managementaurorashiva1No ratings yet
- Credit Rating and Credit GapDocument14 pagesCredit Rating and Credit Gaprahul-singh-659250% (2)
- Definition of Credit RiskDocument5 pagesDefinition of Credit RiskraviNo ratings yet
- Credit Management NotesDocument27 pagesCredit Management NotesHannan Ahmad0% (1)
- Northwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementDocument24 pagesNorthwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementChura HariNo ratings yet
- CitigroupDocument15 pagesCitigroupAnurag PatelNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Agencies PHD ThesisDocument7 pagesCredit Rating Agencies PHD Thesiszxtccvgld100% (1)
- Literature Review On Capm ModelDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Capm Modelaflshtabj100% (1)
- Project 3Document11 pagesProject 3Goku NarutoNo ratings yet
- Bankruptcy Risk ThesisDocument4 pagesBankruptcy Risk Thesisjessicasimmssterlingheights100% (2)
- Unit 5 4Document37 pagesUnit 5 4manjarisingh2502No ratings yet
- Credit RatingsDocument71 pagesCredit Ratingsmldc2011No ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics of Mba FinanceDocument8 pagesDissertation Topics of Mba FinanceWriteMyPaperCanada100% (1)
- Credit Rating01Document17 pagesCredit Rating01Ferlyan Huang 正莲No ratings yet
- Objective of Project ReportDocument13 pagesObjective of Project ReportPinakisgNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Credit Appraisal ProcessDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Credit Appraisal Processtqpkpiukg100% (1)
- Counterparty Risk Subject To Additional Termination Event ClausesDocument36 pagesCounterparty Risk Subject To Additional Termination Event ClausesgileperNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis CourseworkDocument8 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Courseworkpqltufajd100% (2)
- Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CA1 - Paper I Core Applications ConceptsDocument23 pagesInstitute of Actuaries of India Subject CA1 - Paper I Core Applications ConceptsYogeshAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Brso97lm PDFDocument14 pagesBrso97lm PDFAyoub BelgachaNo ratings yet
- Debt Ratio - Capitalization RatioDocument2 pagesDebt Ratio - Capitalization Ratiocorporateboy36596No ratings yet
- A Literature Review of Concepts of Credit Ratings and Corporate ValuationDocument26 pagesA Literature Review of Concepts of Credit Ratings and Corporate ValuationHarsh Vyas100% (1)
- SCM CH 6Document5 pagesSCM CH 6Kalayou TekleNo ratings yet
- Bank Audit Guidance Note 2021Document975 pagesBank Audit Guidance Note 2021Arif AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4aMFA3053 SukukDocument45 pages4aMFA3053 Sukukksenju47No ratings yet
- Investment Organizer ToolDocument57 pagesInvestment Organizer ToolBarun SinghNo ratings yet
- R1 GTC 2020Document116 pagesR1 GTC 2020Julia Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Finance and Investment Week 7. Mutual Funds 2022Document65 pagesFinance and Investment Week 7. Mutual Funds 2022Mostafa SakrNo ratings yet
- Commercial Real Estate Purchase Agreement: Buyer's Initials - Seller's InitialsDocument14 pagesCommercial Real Estate Purchase Agreement: Buyer's Initials - Seller's InitialsChibuzor Victor100% (1)
- Jennifer Williamson Recently Quit Her Job As An Investment Banker PDFDocument1 pageJennifer Williamson Recently Quit Her Job As An Investment Banker PDFhassan taimourNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On A Study On SME BankDocument40 pagesInternship Report On A Study On SME BankAbu Hamzah NomaanNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire-I: This Questionnaire Prepared For Clients/ Customers of Wegagen Bank S.C Hawassa BranchDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire-I: This Questionnaire Prepared For Clients/ Customers of Wegagen Bank S.C Hawassa BranchNesru SirajNo ratings yet
- Lease 1Document5 pagesLease 1richard kayNo ratings yet
- Note On Schedule III AmendmentsDocument2 pagesNote On Schedule III AmendmentsJainam ShahNo ratings yet
- Debt Investments TutorialDocument4 pagesDebt Investments TutorialRawan YasserNo ratings yet
- C. Limited PartnerDocument13 pagesC. Limited PartnerKrisha BendijoNo ratings yet
- Financial EngineeringDocument3 pagesFinancial Engineeringluvnica6348No ratings yet
- Analysis Condominium RulesDocument12 pagesAnalysis Condominium RulesMingalar JLSNo ratings yet
- Sales Topic 1Document55 pagesSales Topic 1Choi LyraNo ratings yet
- Sabadell 3Q20 Results PresentationDocument73 pagesSabadell 3Q20 Results PresentationMiguel RamosNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management Live Project Report by Pranay Jindal in Jindal Steel and PowerDocument83 pagesWorking Capital Management Live Project Report by Pranay Jindal in Jindal Steel and Powera0mittal7No ratings yet
- q2 w8 Business and Consumer LoansDocument20 pagesq2 w8 Business and Consumer Loanshikkiro hikkiNo ratings yet
- Convertible Loan Agreement Template: How To Use This TemplateDocument11 pagesConvertible Loan Agreement Template: How To Use This TemplateGaos FakhryNo ratings yet
- Testate Estate of Concordia Lim VS City of ManilaDocument2 pagesTestate Estate of Concordia Lim VS City of ManilaRia GabsNo ratings yet
- NBFC Faqs (Rbi)Document9 pagesNBFC Faqs (Rbi)VipuljainyNo ratings yet
- BH Ffm13 TB Ch02Document14 pagesBH Ffm13 TB Ch02Umer Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- General Power of AttorneyDocument2 pagesGeneral Power of Attorneysaqib nawazNo ratings yet
- Far Drill2Document4 pagesFar Drill2Jung Hwan SoNo ratings yet
- ReSA-WCM-BUDGETING 240531 153818Document23 pagesReSA-WCM-BUDGETING 240531 153818Rayhanah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Benefit-Cost Analysis: Financial and Economic Appraisal Using SpreadsheetsDocument6 pagesBenefit-Cost Analysis: Financial and Economic Appraisal Using SpreadsheetsrodskogjNo ratings yet
- Phan Tich Va Dau Tu Chung KhoanDocument98 pagesPhan Tich Va Dau Tu Chung KhoanThái Minh ChâuNo ratings yet
Answer: CHAID (Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector) Analysis Is An Algorithm Used For
Answer: CHAID (Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector) Analysis Is An Algorithm Used For
Uploaded by
Prashant kudryaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer: CHAID (Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector) Analysis Is An Algorithm Used For
Answer: CHAID (Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector) Analysis Is An Algorithm Used For
Uploaded by
Prashant kudryaCopyright:
Available Formats
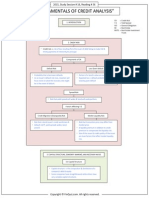
Q1: Examine the decision tree in Exhibit 8 and come up with a strategy which Ajay and his team
should adopt to identify credit worthy customers early in the assessment phase.
Answer: CHAID (Chi-square Automatic Interaction Detector) analysis is an algorithm used for
discovering relationships between a categorical response variable and other categorical predictor
variables. It is useful when looking for patterns in datasets with lots of categorical variables and is a
convenient way of summarising the data as the relationships can be easily visualised. CHAID is often
used in direct marketing to understand how different groups of customers might respond to a
campaign based on their characteristics. So, suppose, for example, that we run a marketing campaign
and are interested in understanding what customer characteristics (e.g., gender, socio-economic
status, geographic location, etc.) are associated with the response rate achieved.
LTV (Loan to Value Ratio) = Total loan requested/Market Value
FOIR (Fixed Obligation to Income Ratio) = (EMI + Ongoing Loan EMI)/Total House hold Income
In exhibit 8 decision tree analysis - Ajay and his team should adopt to identify credit worthy customers
who has LTV & FOIR value lowest among all customers may credit worthy customers early in the
assessment phase. FOIR value lowest in case of Tier 1 cities of India.
Q2) Using the classification table in Exhibit 10, answer the below questions:
a) Given 100 loan applicants who have been approved a loan, how many of them would the model
be able to correctly predict as sanctions?
b) Calculate the proportion of actual rejects which have been incorrectly classified as sanctions
Q3) Apply the CHAID decision tree on the 100 data points provided Exhibit 11 and construct the
classification table. (Assume the cut-off - 0.8). Is it similar to the one provided in Exhibit 10? What
are your conclusions regarding the CHAID decision tree results?
Q4) Examine the decision tree in Exhibit 8 and explain why derived variables such as LTV and FOIR
have better explanatory power than the individual variables used to derive them?
Answer: [Loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is a number lenders use to determine how much risk they're taking
on with a secured loan. It measures the relationship between the loan amount and the market value of
the asset securing the loan, such as a house or car.
If a lender provides a loan worth half the value of the asset, for example, the LTV is 50%. As LTV
increases, the potential loss the lender will face if the borrower fails to repay the loan also rises,
creating more risk.
Loan-to-value ratio can apply to any secured loan but is most commonly used with mortgages. In fact,
several bank mortgage programs specify LTV limits as part of their qualifying criteria.
FOIR (Fixed Obligations to Income Ratio) is a popular parameter which banks use to determine loan
eligibility. FOIR takes into account all the fixed obligations that a borrower is supposed to meet
regularly on a monthly basis. The fixed obligations do not include statutory deductions from the salary
such as Provident Fund, professional tax and deductions for investments such as insurance or a
recurring deposit. Banks have different FOIR for different loans. It can be 50% for a Personal Loan
whereas the requirement can be 35% to 40% for a Home Loan. Usually, the banks fix up the FOIR as
50%.]
CHAID method is more computationally efficient in identifying potential interactions when
compared with adding all possible interactions in either of the stepwise, backward, or forward
feature selection procedures in logistic regression. Also, the customer profile created based
on the CHAID tree could provide a better understanding about the variable interactions.
CHAID decision tree in Exhibit 8 - decision tree based CHAID analysis is applied to identify
potential variable interactions, it has been observed that LTV and FOIR are the interaction
terms identified by CHAID analysis and they are all statistically significant.
You might also like
- Hotel Lease AgreementDocument4 pagesHotel Lease AgreementDavid Brito50% (2)
- Interview Questions: Always Find A Link Between The StepsDocument9 pagesInterview Questions: Always Find A Link Between The StepsKarimNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Document7 pagesFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 16 - Reading 56Rafael100% (1)
- SFM Case4 Group7Document5 pagesSFM Case4 Group7AMAAN LULANIA 22100% (1)
- Banking Notes PDFDocument130 pagesBanking Notes PDFfledpengelNo ratings yet
- Developing and Implementing Commercial Loan Pricing ModelsDocument5 pagesDeveloping and Implementing Commercial Loan Pricing Modelsr.jeyashankar95500% (1)
- WACC and Vol: Counterpoint Global InsightsDocument13 pagesWACC and Vol: Counterpoint Global InsightsHoward QinNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Agencies DissertationDocument7 pagesCredit Rating Agencies Dissertationdipsekator1983100% (1)
- Credit Analyst Q&ADocument6 pagesCredit Analyst Q&ASudhir PowerNo ratings yet
- Credit AnalystDocument9 pagesCredit AnalystJimsy Antu100% (1)
- Research Paper On Credit Appraisal ProcessDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Credit Appraisal Processgatewivojez3100% (1)
- Credit Rating GROUP 11Document11 pagesCredit Rating GROUP 11Siddharth Shah0% (1)
- Bank and Insurance Management QuestionsDocument4 pagesBank and Insurance Management QuestionsMarta CrescenziNo ratings yet
- Credit Analyst Questions and Answers 1693198236Document9 pagesCredit Analyst Questions and Answers 1693198236hh2rwfs8f5No ratings yet
- Thesis Credit Rating AgenciesDocument4 pagesThesis Credit Rating AgenciesWhoCanWriteMyPaperForMeUK100% (2)
- Fina4400 Final ExamDocument3 pagesFina4400 Final ExamBouchraya MilitoNo ratings yet
- Credit Risk Research PapersDocument4 pagesCredit Risk Research Papersh00yfcc9100% (1)
- Additional InfoDocument25 pagesAdditional InfoSaravananNo ratings yet
- Additional InfoDocument25 pagesAdditional InfoSanthu SaravananNo ratings yet
- Moodys Analytics Riskcalc Transfer Pricing SolutionDocument9 pagesMoodys Analytics Riskcalc Transfer Pricing SolutionManuel CámacNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 CS - 08-11-2020Document6 pagesAssignment 1 CS - 08-11-2020Amina NasirNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 TR SirDocument25 pagesUNIT 5 TR SirgauthamNo ratings yet
- Credit GrantingA Comparative Analysis ofDocument18 pagesCredit GrantingA Comparative Analysis ofAhmad SanusiNo ratings yet
- Credit Score Research PapersDocument7 pagesCredit Score Research Papershxmchprhf100% (1)
- Capital Structure Decision ReportDocument14 pagesCapital Structure Decision ReportPratik GanatraNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Agencies Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesCredit Rating Agencies Literature Reviewfat1kifywel3100% (1)
- Week 7: Corporate Credit Risk Models Based On Stock PriceDocument19 pagesWeek 7: Corporate Credit Risk Models Based On Stock PriceNhat Khanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis On Ratio AnalysisDocument5 pagesPHD Thesis On Ratio Analysisaflodnyqkefbbm100% (2)
- Credit Management NotesDocument31 pagesCredit Management NotesAnis Ur Rehman Kakakhel33% (3)
- Research Papers On Credit Risk ManagementDocument7 pagesResearch Papers On Credit Risk Managementgvzexnzh100% (1)
- Accounting Textbook Solutions - 59Document19 pagesAccounting Textbook Solutions - 59acc-expertNo ratings yet
- Credit Analysis NotesDocument5 pagesCredit Analysis NotesNoni100% (1)
- Pricing CTRP RiskDocument36 pagesPricing CTRP RiskJin DongNo ratings yet
- Chapters 10 and 12 Credit Analysis and Distress Prediction3223Document45 pagesChapters 10 and 12 Credit Analysis and Distress Prediction3223alfiNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Company ValuationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Company Valuationfys374dr100% (1)
- Amortization:: Amortization Is The Process of Decreasing, or Accounting For, An Amount Over ADocument5 pagesAmortization:: Amortization Is The Process of Decreasing, or Accounting For, An Amount Over ASrikanth GuruNo ratings yet
- Peer To Peer Lending Risk Analysis: Predictions From Lending ClubDocument10 pagesPeer To Peer Lending Risk Analysis: Predictions From Lending Clubortegadelia810No ratings yet
- Muthyam Anusha, (18wj1e0044), Credit Risk ManagementDocument59 pagesMuthyam Anusha, (18wj1e0044), Credit Risk Managementaurorashiva1No ratings yet
- Credit Rating and Credit GapDocument14 pagesCredit Rating and Credit Gaprahul-singh-659250% (2)
- Definition of Credit RiskDocument5 pagesDefinition of Credit RiskraviNo ratings yet
- Credit Management NotesDocument27 pagesCredit Management NotesHannan Ahmad0% (1)
- Northwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementDocument24 pagesNorthwestern University J.L. Kellogg Graduate School of ManagementChura HariNo ratings yet
- CitigroupDocument15 pagesCitigroupAnurag PatelNo ratings yet
- Credit Rating Agencies PHD ThesisDocument7 pagesCredit Rating Agencies PHD Thesiszxtccvgld100% (1)
- Literature Review On Capm ModelDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Capm Modelaflshtabj100% (1)
- Project 3Document11 pagesProject 3Goku NarutoNo ratings yet
- Bankruptcy Risk ThesisDocument4 pagesBankruptcy Risk Thesisjessicasimmssterlingheights100% (2)
- Unit 5 4Document37 pagesUnit 5 4manjarisingh2502No ratings yet
- Credit RatingsDocument71 pagesCredit Ratingsmldc2011No ratings yet
- Dissertation Topics of Mba FinanceDocument8 pagesDissertation Topics of Mba FinanceWriteMyPaperCanada100% (1)
- Credit Rating01Document17 pagesCredit Rating01Ferlyan Huang 正莲No ratings yet
- Objective of Project ReportDocument13 pagesObjective of Project ReportPinakisgNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Credit Appraisal ProcessDocument7 pagesLiterature Review of Credit Appraisal Processtqpkpiukg100% (1)
- Counterparty Risk Subject To Additional Termination Event ClausesDocument36 pagesCounterparty Risk Subject To Additional Termination Event ClausesgileperNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis CourseworkDocument8 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Courseworkpqltufajd100% (2)
- Institute of Actuaries of India Subject CA1 - Paper I Core Applications ConceptsDocument23 pagesInstitute of Actuaries of India Subject CA1 - Paper I Core Applications ConceptsYogeshAgrawalNo ratings yet
- Brso97lm PDFDocument14 pagesBrso97lm PDFAyoub BelgachaNo ratings yet
- Debt Ratio - Capitalization RatioDocument2 pagesDebt Ratio - Capitalization Ratiocorporateboy36596No ratings yet
- A Literature Review of Concepts of Credit Ratings and Corporate ValuationDocument26 pagesA Literature Review of Concepts of Credit Ratings and Corporate ValuationHarsh Vyas100% (1)
- SCM CH 6Document5 pagesSCM CH 6Kalayou TekleNo ratings yet
- Bank Audit Guidance Note 2021Document975 pagesBank Audit Guidance Note 2021Arif AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4aMFA3053 SukukDocument45 pages4aMFA3053 Sukukksenju47No ratings yet
- Investment Organizer ToolDocument57 pagesInvestment Organizer ToolBarun SinghNo ratings yet
- R1 GTC 2020Document116 pagesR1 GTC 2020Julia Jimenez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Finance and Investment Week 7. Mutual Funds 2022Document65 pagesFinance and Investment Week 7. Mutual Funds 2022Mostafa SakrNo ratings yet
- Commercial Real Estate Purchase Agreement: Buyer's Initials - Seller's InitialsDocument14 pagesCommercial Real Estate Purchase Agreement: Buyer's Initials - Seller's InitialsChibuzor Victor100% (1)
- Jennifer Williamson Recently Quit Her Job As An Investment Banker PDFDocument1 pageJennifer Williamson Recently Quit Her Job As An Investment Banker PDFhassan taimourNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On A Study On SME BankDocument40 pagesInternship Report On A Study On SME BankAbu Hamzah NomaanNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire-I: This Questionnaire Prepared For Clients/ Customers of Wegagen Bank S.C Hawassa BranchDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire-I: This Questionnaire Prepared For Clients/ Customers of Wegagen Bank S.C Hawassa BranchNesru SirajNo ratings yet
- Lease 1Document5 pagesLease 1richard kayNo ratings yet
- Note On Schedule III AmendmentsDocument2 pagesNote On Schedule III AmendmentsJainam ShahNo ratings yet
- Debt Investments TutorialDocument4 pagesDebt Investments TutorialRawan YasserNo ratings yet
- C. Limited PartnerDocument13 pagesC. Limited PartnerKrisha BendijoNo ratings yet
- Financial EngineeringDocument3 pagesFinancial Engineeringluvnica6348No ratings yet
- Analysis Condominium RulesDocument12 pagesAnalysis Condominium RulesMingalar JLSNo ratings yet
- Sales Topic 1Document55 pagesSales Topic 1Choi LyraNo ratings yet
- Sabadell 3Q20 Results PresentationDocument73 pagesSabadell 3Q20 Results PresentationMiguel RamosNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management Live Project Report by Pranay Jindal in Jindal Steel and PowerDocument83 pagesWorking Capital Management Live Project Report by Pranay Jindal in Jindal Steel and Powera0mittal7No ratings yet
- q2 w8 Business and Consumer LoansDocument20 pagesq2 w8 Business and Consumer Loanshikkiro hikkiNo ratings yet
- Convertible Loan Agreement Template: How To Use This TemplateDocument11 pagesConvertible Loan Agreement Template: How To Use This TemplateGaos FakhryNo ratings yet
- Testate Estate of Concordia Lim VS City of ManilaDocument2 pagesTestate Estate of Concordia Lim VS City of ManilaRia GabsNo ratings yet
- NBFC Faqs (Rbi)Document9 pagesNBFC Faqs (Rbi)VipuljainyNo ratings yet
- BH Ffm13 TB Ch02Document14 pagesBH Ffm13 TB Ch02Umer Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- General Power of AttorneyDocument2 pagesGeneral Power of Attorneysaqib nawazNo ratings yet
- Far Drill2Document4 pagesFar Drill2Jung Hwan SoNo ratings yet
- ReSA-WCM-BUDGETING 240531 153818Document23 pagesReSA-WCM-BUDGETING 240531 153818Rayhanah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Benefit-Cost Analysis: Financial and Economic Appraisal Using SpreadsheetsDocument6 pagesBenefit-Cost Analysis: Financial and Economic Appraisal Using SpreadsheetsrodskogjNo ratings yet
- Phan Tich Va Dau Tu Chung KhoanDocument98 pagesPhan Tich Va Dau Tu Chung KhoanThái Minh ChâuNo ratings yet