Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bisc207 Reviewer 6
Bisc207 Reviewer 6
Uploaded by
Anabelle McKenlyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bisc207 Reviewer 6
Bisc207 Reviewer 6
Uploaded by
Anabelle McKenlyCopyright:
Available Formats
BISC207 REVIEWER 6
1. Regeneration (3rd step of calvin cycle)
The 5-carbon molecule needed for carboxylation is regenerated. Regeneration accounts for 12 of
the 15 steps in the Calvin cycle. A tremendous amount of reshuffling is required to produce
three 5-carbon RuBP molcules from the five remaining 3-carbon triose phosphate molecules.
ATP is required for this step
2. What happens during the calvin cycle?
CO2 is reduced and converted into organic substances (NADPH provides electrons and hydrogen,
ATP provides additional energy)
3. carbon fixation
involves capturing CO2 molecules with the key enzyme rubisco
4. what molecule is oxidized in the photosynthetic reaction?
H2O
5. CO2
What is the initial carbon input in the calvin cycle?
6. Where does the calvin cycle occur?
The stroma
m
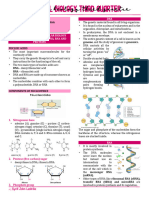
7. DNA
er as
2 strands that run antiparallel
co
8. backbone of DNA eH w
composed of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules, bases project into the center of the
o.
double helix
rs e
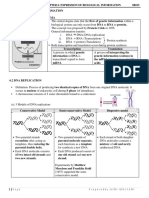
9. What happens during DNA replication?
ou urc
the two strand of parental DNA separate, each parent strand serves as the template for the
synthesis of a daughter strand
o
10. semiconservative model of DNA replication
aC s
suggests that after DNA replication, the new DNA duplex consists of one old strand and one new
vi re
strand
11. conservative model of DNA replication
y
suggests that after DNA replication, the new DNA duplex consists of two newly-synthesized
daughter strands, leaving the parental duplex intact
ed d
12. replicaiton
ar stu
the process where DNA makes a copy of itself
13. Where does DNA synthesis begin?
sites that act as replication origins
is
14. What shape is DNA in most bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts?
Th
circular
15. How many origins are in circular chromosomes?
one
sh
16. origin of replication
each point where DNA replication is initiated
17. helicase (key player in DNA replication)
unwinds the double-stranded DNA
18. single strand binding proteins (key player in DNA replication)
temporarily bind to each side and keep them separated
19. DNA polymerase (key player in DNA replication)
"walks" down the DNA strands and adds complementary nucleotides to each strand; highly
conserved among species
20. subunit of DNA polymerase (key player in DNA replication)
proofreads the new DNA
This study source was downloaded by 100000823724189 from CourseHero.com on 08-04-2021 15:54:51 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/101082516/BISC207-REVIEWER-6docx/
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- Long Range Gene Regulation in Hormone-Dependent CancerDocument16 pagesLong Range Gene Regulation in Hormone-Dependent CancerMaricruz GarcíaNo ratings yet
- CH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Document3 pagesCH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dani Jo OwensNo ratings yet
- Chap11 LearnObjDocument4 pagesChap11 LearnObjamariliyahNo ratings yet
- Protein Expression HandbookDocument118 pagesProtein Expression HandbookLuis Arístides Torres SánchezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 BBT312 DNA Replication Part IDocument24 pagesLecture 7 BBT312 DNA Replication Part IBol BirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationDocument4 pagesLesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationTherese TimbalNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesDNA Replicationlubuto TuntepeNo ratings yet
- 3.dna ReplicationDocument7 pages3.dna ReplicationCharm BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument3 pagesReplicationHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document6 pagesLecture 2tiaria.wilson24No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument6 pagesIlovepdf Mergedmngnmg8No ratings yet
- Central Dogma of LifeDocument17 pagesCentral Dogma of LifeSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Erick Flesch - DNA-Replication-Overview-and-ReviewDocument2 pagesKami Export - Erick Flesch - DNA-Replication-Overview-and-ReviewFuckyouNo ratings yet
- (H2) CI2.2 - DNA ReplicationDocument12 pages(H2) CI2.2 - DNA ReplicationTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Yacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211Document5 pagesYacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211joeyacomine100% (1)
- 6.2. DNA Replication PDFDocument75 pages6.2. DNA Replication PDFShania TehNo ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- S Phase and DNA ReplicationDocument15 pagesS Phase and DNA Replicationdiego angelesNo ratings yet
- 4 DnaDocument6 pages4 Dnadr_47839666No ratings yet
- D1.1 (Dna Structure & Replication)Document11 pagesD1.1 (Dna Structure & Replication)D-WizardNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of DNA Replication (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument1 pageMolecular Mechanism of DNA Replication (Article) - Khan AcademyShreyansh PareekNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of LifeDocument17 pagesCentral Dogma of Lifemozhi74826207100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Is Semi-ConservativeDocument19 pagesDNA Replication Is Semi-ConservativeEuphoriaNo ratings yet
- Initiation of DNA Replication: RepliconDocument20 pagesInitiation of DNA Replication: RepliconAbdullah satti7eNo ratings yet
- Presentationprint TempDocument27 pagesPresentationprint TempGandepelli SwetchaNo ratings yet
- MQ C6 (Questions)Document8 pagesMQ C6 (Questions)Carin TanNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument15 pagesCertificateAbhishek AryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.2 - DNA ReplicationDocument100 pagesChapter 6.2 - DNA Replicationnie20060301No ratings yet
- Composed of A BaseDocument23 pagesComposed of A Basetanvi bhallaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 EM PDFDocument24 pagesLecture 2 EM PDFhuang SteffiNo ratings yet
- Replication of DNADocument10 pagesReplication of DNA3lyooNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesBiochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Solutions Manualandrewjohnsonkmrawgsiod100% (31)
- Biochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument40 pagesBiochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (14)
- DNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?Document33 pagesDNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?AkshiNo ratings yet
- Dnareplication 151218084840Document145 pagesDnareplication 151218084840RIYA MUNJALNo ratings yet
- 2.7 7.1DNAReplicationDocument33 pages2.7 7.1DNAReplicationKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- 2.7 NewDocument64 pages2.7 NewReeya WhabiNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Expectedoutside. CBG. 03Document10 pagesExpectedoutside. CBG. 03FaieryNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription, and TranslationDocument46 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translationpapa3rikusNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - DNA Replication During The S PhaseDocument23 pages5.2 - DNA Replication During The S PhaseAna JuatasNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular BiologyJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesBiochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (16)
- Biochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankDocument17 pagesBiochemistry 8th Edition Campbell Test BankchristinecohenceyamrgpkjNo ratings yet
- 1.5 - DNA Replication - Introduction To Prokaryotic ReplicationDocument7 pages1.5 - DNA Replication - Introduction To Prokaryotic ReplicationKhyati GuptaNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFazalea freyaNo ratings yet
- 6 BIO462 Chapter 6Document21 pages6 BIO462 Chapter 6Syafiqah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Biochemistry - December 1990 - TH MMES - Eukaryotic DNA Replication PDFDocument14 pagesEuropean Journal of Biochemistry - December 1990 - TH MMES - Eukaryotic DNA Replication PDFFarhadullah KhanNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisFrezelVillaBasiloniaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Unit IV and VDocument60 pagesMolecular Biology Unit IV and VchitraNo ratings yet
- 2.7-7.1 Replication-MKDocument19 pages2.7-7.1 Replication-MKadham fadelNo ratings yet
- 1901BS085 - Molecular Biology, PDFDocument7 pages1901BS085 - Molecular Biology, PDFThe FourNo ratings yet
- L2 & 3 The NucleusDocument54 pagesL2 & 3 The NucleusAmarachi MaduabuchiNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication NotesDocument3 pagesDna Replication NotesYash VardhanNo ratings yet
- Replikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)Document62 pagesReplikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)adinda tyasprabandariNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- ٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Document19 pages٣٢٥ Molecular Biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument7 pagesDNA Replication and RepairJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Quiz-2Document1 pageChapter 1 Quiz-2Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Quiz-5Document2 pagesChapter 4 Quiz-5Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Quiz-2Document1 pageChapter 4 Quiz-2Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Quiz-3Document2 pagesChapter 1 Quiz-3Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Quiz-4Document2 pagesChapter 1 Quiz-4Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Leadership 101Document1 pageLeadership 101Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Quiz-5Document1 pageChapter 1 Quiz-5Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Bisc207 Reviewer 7Document2 pagesBisc207 Reviewer 7Anabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Chem Exam 2aDocument1 pageChem Exam 2aAnabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Obligations (VSA-IRS) : Diligence of A Good Father of A FamilyDocument43 pagesPart 1: Obligations (VSA-IRS) : Diligence of A Good Father of A FamilyAnabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- CONTRACTS Definition Stages1 With AnswersDocument13 pagesCONTRACTS Definition Stages1 With AnswersAnabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument19 pagesContractsAnabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- BLT REV Midterm Exam PDFDocument14 pagesBLT REV Midterm Exam PDFAnabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Module 1.3 - Peformance Incentives and DisincentivesDocument10 pagesModule 1.3 - Peformance Incentives and DisincentivesAnabelle McKenlyNo ratings yet
- Genetic TechnologyDocument36 pagesGenetic TechnologyAnggraeni Kusuma Wardani100% (1)
- Gene Expression in ProkaryotesDocument43 pagesGene Expression in ProkaryotesravibiriNo ratings yet
- Pan-Cancer Landscape of Aberrant DNA Methylation Across Human TumorsDocument24 pagesPan-Cancer Landscape of Aberrant DNA Methylation Across Human Tumors戴义宾No ratings yet
- RNAi NotesDocument6 pagesRNAi Notesaman jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Essay For Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesEssay For Protein Synthesisbsr3rf42100% (1)
- Bioc Module 2 Lab ReportDocument11 pagesBioc Module 2 Lab ReportMimi BoisterNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular BiologyAlbert Tesoro Silang Jr.No ratings yet
- DNA Polymerase in SOS ResponseDocument2 pagesDNA Polymerase in SOS ResponsemuhsinNo ratings yet
- Gene MutationDocument20 pagesGene Mutationdheeresh aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Chromosomes and Cell DivisionDocument31 pagesGenetics: Chromosomes and Cell DivisionPaqui Miranda GualdaNo ratings yet
- Prado - Detailed Lesson Plan in Educ 10DDocument14 pagesPrado - Detailed Lesson Plan in Educ 10DJohn Bernard RiliNo ratings yet
- WS1 - 11 Grade - The Genetic Code and DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesWS1 - 11 Grade - The Genetic Code and DNA ReplicationMerey ZiyabekNo ratings yet
- Advance Bacterial GeneticsDocument5 pagesAdvance Bacterial GeneticsEvi RoviatiNo ratings yet
- MeiosisPuzzle FinalDocument5 pagesMeiosisPuzzle Finalgopan629No ratings yet
- Module 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentFelix BrockmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document18 pagesLecture 7Gülüzar ÖzbolatNo ratings yet
- CRISPR Cas9 GENE EDITING RESEARCH TECHNOLOGIES CLINICAL APLICATION AND ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONDocument14 pagesCRISPR Cas9 GENE EDITING RESEARCH TECHNOLOGIES CLINICAL APLICATION AND ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONBadtz MaruNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Lecture By: Lanny HartantiDocument17 pagesMolecular Biology Lecture By: Lanny HartantiDEVI SETYA ARIANINo ratings yet
- s21097 PDFDocument12 pagess21097 PDFOsvaldo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Bio Assignment 1Document6 pagesBio Assignment 1hooriya bilalNo ratings yet
- BIOTECH Q3.Week 3-4 - Science 8Document15 pagesBIOTECH Q3.Week 3-4 - Science 8Clark BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lac OperonDocument17 pagesLac OperonSugiyati NingrumNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiotechnologyDocument40 pagesMolecular BiotechnologyBhaskar GangulyNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Sentiment Analyze Craft and Structure Page 344. Read Pages 338-340 HW: Read Pages 341-342Document12 pagesDeclaration of Sentiment Analyze Craft and Structure Page 344. Read Pages 338-340 HW: Read Pages 341-342يزن جانسيزNo ratings yet
- 2022 H2 Prelim P2 - AnsDocument31 pages2022 H2 Prelim P2 - Ansclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Polypeptides and Defined SequenceDocument7 pagesProteins: Polypeptides and Defined SequenceAurora ThetNo ratings yet
- MCAT Study ScheduleDocument21 pagesMCAT Study ScheduleSahara Prepetit100% (1)
- Gene LibrariesDocument14 pagesGene Librariessharmamaddy32No ratings yet