Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quantitative Measures of HDFC Bank & Definition: ND TH
Quantitative Measures of HDFC Bank & Definition: ND TH
Uploaded by
Karina Manaf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesThis document defines several quantitative measures used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and HDFC Bank to regulate liquidity and monetary policy. It describes the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) as the amount of deposits commercial banks must keep in reserves with the RBI. The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) requires banks to invest a percentage of assets in approved government securities. The repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends funds to banks, while the reverse repo rate is the rate at which it borrows from banks. The Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate allows banks to borrow overnight from RBI in emergencies. The bank rate influences commercial bank lending rates. It provides
Original Description:
Original Title
8th sem Banking Law
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines several quantitative measures used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and HDFC Bank to regulate liquidity and monetary policy. It describes the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) as the amount of deposits commercial banks must keep in reserves with the RBI. The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) requires banks to invest a percentage of assets in approved government securities. The repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends funds to banks, while the reverse repo rate is the rate at which it borrows from banks. The Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate allows banks to borrow overnight from RBI in emergencies. The bank rate influences commercial bank lending rates. It provides
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesQuantitative Measures of HDFC Bank & Definition: ND TH
Quantitative Measures of HDFC Bank & Definition: ND TH
Uploaded by
Karina ManafThis document defines several quantitative measures used by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and HDFC Bank to regulate liquidity and monetary policy. It describes the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) as the amount of deposits commercial banks must keep in reserves with the RBI. The Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) requires banks to invest a percentage of assets in approved government securities. The repo rate is the interest rate at which RBI lends funds to banks, while the reverse repo rate is the rate at which it borrows from banks. The Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate allows banks to borrow overnight from RBI in emergencies. The bank rate influences commercial bank lending rates. It provides
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
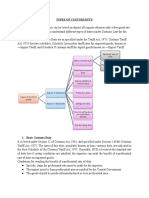
QUANTITATIVE MEASURES OF HDFC BANK & DEFINITION
(CRR, SLR, REPO RATE, REVERSE REPO RATE, MSF RATE, BANK RATE)
Cash Reserve Ratio(CRR)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) requires banks to keep a portion of their deposits in cash so
that it can be supplied to customers in an emergency. The Cash Reserve Ratio is the amount of
cash that must be held in reserves in relation to a bank's overall deposits. The cash reserve is
either held in the bank's vault or sent to the Reserve Bank of India. Under the CRR requirements,
banks do not receive any interest on money held by the RBI.
Unlike the Statutory Liquidity Ratio, or SLR, which can be maintained in gold or currency, the
Cash Reserve Ratio, or CRR, must only be maintained in cash.
In India, the Cash Reserve Ratio is determined by the Monetary Policy Committee of the
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in its periodic Monetary and Credit Policy. Every six weeks, the
Reserve Bank of India conducts a monetary policy review, which includes a review of the CRR.
The CRR is one of the RBI's key weapons for maintaining a targeted level of inflation,
controlling the money supply, and ensuring liquidity in the economy. The lower the CRR, the
more liquidity there is in the banking system, which leads to increased investment and lending,
and vice versa. Higher CRR may have a negative effect on the economy because it reduces the
supply of loanable funds, which delays investment.
CRR rate in India is- 3.5% as of today but will increase to 4% by may 22nd
CRR rate of HDFC bank is- 3.0% till March 26th 2021
Statutory Liquidity Ratio(SLR)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) uses the statutory liquidity ratio as a monetary policy
instrument to determine the liquidity available to banks. SLR mandates that banks invest a
certain percentage of their assets in various federal and state government securities.
As per RBI, liquid assets may be maintained in cash, or in gold valued at a price not exceeding
the current market price, or Unencumbered investment in approved securities.
The term "approved securities" refers to securities issued by the central government or any state
government, as well as other securities that the RBI can specify from time to time. The SLR
status of securities issued by the Government of India and state governments is determined by
the RBI.
Current SLR rate in India is- 18%
SLR rate of HDFC bank is- 3.0%
Repo Rate
In the event of a liquidity crunch, the Reserve Bank of India loans money to commercial banks at
the repo pace. Monetary authorities use the repo rate to monitor inflation.
The term "repurchase option" or "repurchase agreement" is used in banking to describe the repo
rate. When there is a cash shortage, commercial banks borrow money from the central bank,
which is then repaid at the applicable repo rate. These short-term loans are provided by the
central bank in exchange for securities such as Treasury bills or government bonds. The central
bank uses this monetary policy to regulate inflation or raise bank liquidity. When the government
has to regulate prices and limit borrowing, it raises the repo rate. When there is a need to inject
more capital into the economy to promote economic development, on the other hand, the repo
rate is reduced. An rise in the repo rate means commercial banks must pay more interest on
money lent to them, and thus a shift in the repo rate affects public borrowings like home loans
and EMIs. Various financial and investment instruments are indirectly based on the repo rate,
from interest paid by commercial banks on loans to returns on deposits.
Current Repo rate in India is- 4%
Repo rate of bank is- 4.40%
Reverse Repo Rate
This is the pace at which a country's central bank compensates its commercial banks for storing
excess funds in the central bank. The RBI also uses a monetary policy known as the reverse repo
rate to monitor the flow of money in the economy. When a country's central bank needs
liquidity, it borrows it from commercial banks and pays interest at the reverse repo rate. The
reverse repo rate issued by RBI is usually lower than the repo rate at any given time. While the
repo rate is used to monitor cash flow in the market, the reverse repo rate is used to regulate
liquidity in the economy. When the economy is experiencing inflation, the RBI raises the reverse
repo rate to allow commercial banks to deposit money with the central bank and earn interest. As
a result, surplus funds are absorbed from the economy, reducing the amount of capital available
for public borrowing.
Current Reverse Repo Rate is- 3.35%
Reverse Repo Rate of bank is- 4.0%
Marginal Standing Facility Rate (MSF Rate)
The Reserve Bank of India's Marginal Standing Facility allows banks to borrow funds from the
RBI in emergency situations when their liquidity is fully depleted. This short-term borrowing
scheme allows scheduled banks to obtain funds from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) overnight
in the event of a severe cash shortage by presenting authorised government securities. Banks
often experience liquidity shortages as a result of a financial gap created by a mismatch in
deposit and loan portfolios. Such shortfalls do not last long, and banks may reach the RBI for
one-day cash within the limits of the Statutory Liquidity Ratio to deal with such emergencies
(SLR).
Current MSF Rate in India is- 4. 25%
MSF Rate of HDFC Bank is- 4.65%
Bank Rate
The bank rate is the interest rate at which the central bank lends money to commercial banks.
Commercial banks' lending rates are influenced by bank rates. Higher bank rates would result in
higher bank lending rates. The central bank will raise the bank rate in order to reduce liquidity,
and vice versa.
Current Bank Rate in India is- 4.25%
Bank Rate of HDFC Bank is- 4.65%
You might also like
- Project On Indian Banking Sector ReformsDocument30 pagesProject On Indian Banking Sector Reformshaneen75% (44)
- Regional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementFrom EverandRegional Rural Banks of India: Evolution, Performance and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) - Repo Rate & Reverse Repo Rate (UPSC Notes)Document2 pagesCash Reserve Ratio (CRR) - Repo Rate & Reverse Repo Rate (UPSC Notes)Deepanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- Four Weapons of The RBI-1Document14 pagesFour Weapons of The RBI-1yashjadhav08No ratings yet
- Mehul Banking Article 1-1Document13 pagesMehul Banking Article 1-1Mehul ShahNo ratings yet
- Rbi NotesDocument5 pagesRbi NotesprincebanswarNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy, Objective, InstrumentsDocument6 pagesMonetary Policy, Objective, InstrumentsChiragDahiyaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAaa NbbNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument35 pagesStructure and Functions of Reserve Bank of IndiashivaNo ratings yet
- Bank RateDocument4 pagesBank RateAnonymous Ne9hTRNo ratings yet
- Cash Reserve Ratio Is A Specified Minimum Fraction of The TotalDocument5 pagesCash Reserve Ratio Is A Specified Minimum Fraction of The Totalalen paulNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Rbi KBDocument5 pagesMonetary Policy Rbi KBMuzamil KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Statutory Liquidity RatioDocument2 pagesStatutory Liquidity RatioGomathiRachakondaNo ratings yet
- All Banking Related Questions PDF - Exampundit - SatishDocument49 pagesAll Banking Related Questions PDF - Exampundit - SatishRaj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Repo Rate - Meaning, Reverse Repo Rate & Current Repo RateDocument10 pagesRepo Rate - Meaning, Reverse Repo Rate & Current Repo Ratevikas royNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Report: On "Repo Rate and Impact On GDP"Document10 pagesFinancial Management Report: On "Repo Rate and Impact On GDP"Anjali BhatiaNo ratings yet
- CRR of Bank Alflah: What Is Bank Rate?Document3 pagesCRR of Bank Alflah: What Is Bank Rate?Mirza HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Basic TermsDocument4 pagesBasic TermsmohitgaandhiNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy of India - WikipediaDocument4 pagesMonetary Policy of India - Wikipediaambikesh008No ratings yet
- Eco 8Document4 pagesEco 8jiyonpandey675No ratings yet
- What Is Monetary PolicyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Monetary PolicyBhagat DeepakNo ratings yet
- Current RateDocument2 pagesCurrent RatesumitbabaNo ratings yet
- RBI Policy Weak Policy Given The Economy & Frozen Credit MarketsDocument10 pagesRBI Policy Weak Policy Given The Economy & Frozen Credit MarketsKeigan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument30 pagesEconomics NotesMohandas PeriyasamyNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy 09 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Sankalp HinglishDocument4 pagesIndian Economy 09 - Daily Class Notes - UPSC Sankalp HinglishjakatiupdateclassesNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument30 pagesEconomics NotesVishal AnandNo ratings yet
- Cash Reserve RatioDocument2 pagesCash Reserve RatioKrishna Mund ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy of IndiaDocument5 pagesMonetary Policy of IndiaSudesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Main Functions Financial SupervisionDocument9 pagesMain Functions Financial SupervisionAjay MykalNo ratings yet
- CRR & SLR and Computation - PPTX BVB 204Document20 pagesCRR & SLR and Computation - PPTX BVB 204679shrishti SinghNo ratings yet
- Repo RateDocument5 pagesRepo RateSweta SinghNo ratings yet
- FIM-Module II-Banking InstitutionsDocument11 pagesFIM-Module II-Banking InstitutionsAmarendra PattnaikNo ratings yet
- About Reserve Bank of India (RBI)Document3 pagesAbout Reserve Bank of India (RBI)Newton KumamNo ratings yet
- Use Unclaimed DepositsDocument5 pagesUse Unclaimed DepositsalkjghNo ratings yet
- 2.FIM-Module II-Banking InstitutionsDocument11 pages2.FIM-Module II-Banking InstitutionsAmarendra PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Current SLR in India - 18.00%: How Does Statutory Liquidity Ratio WorkDocument20 pagesCurrent SLR in India - 18.00%: How Does Statutory Liquidity Ratio WorkhahNo ratings yet
- RBI and Functions YKKDocument30 pagesRBI and Functions YKKMALKANI DISHA DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Statutory Liquidity RatioDocument2 pagesStatutory Liquidity RatioRamNo ratings yet
- Role of CRR and SLRDocument9 pagesRole of CRR and SLRVineeta Malan50% (2)
- Monetary Policy ToolsDocument2 pagesMonetary Policy ToolsSudhir ShanklaNo ratings yet
- Cash Reserve RatioDocument6 pagesCash Reserve RatioAmitesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Hat Is SLRDocument5 pagesHat Is SLRIndu GuptaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Repo Rate?Document14 pagesWhat Is A Repo Rate?Sumit SumanNo ratings yet
- Latest RBI Bank Rates in Indian Banking - AUGUST 2018: SLR Rate, CRRDocument2 pagesLatest RBI Bank Rates in Indian Banking - AUGUST 2018: SLR Rate, CRRNiyati SoodNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Is of Two KindsDocument16 pagesMonetary Policy Is of Two KindsSainath SindheNo ratings yet
- What Is Bank Rate?Document2 pagesWhat Is Bank Rate?Narender HoodaNo ratings yet
- Banking InterviewDocument30 pagesBanking InterviewJaya JamdhadeNo ratings yet
- Mem (Monetary Policy)Document9 pagesMem (Monetary Policy)Himanshu RatnaniNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument5 pagesMonetary PolicySahaya Arul.M.No ratings yet
- RBI Functions: 1. Monopoly of Note IssueDocument5 pagesRBI Functions: 1. Monopoly of Note Issueshivam shandilyaNo ratings yet
- RRB Po Clerk Capsule 2015Document59 pagesRRB Po Clerk Capsule 2015Abhishek GeraNo ratings yet
- RRB Po GK Power CapsuleDocument59 pagesRRB Po GK Power CapsuleDetective ArunNo ratings yet
- What Is SLR, CRR, Bank Rate, Repo and Reverse Repos and Difference Between CRR and SLR?Document2 pagesWhat Is SLR, CRR, Bank Rate, Repo and Reverse Repos and Difference Between CRR and SLR?ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Bank RateDocument4 pagesWhat Is Bank RateKamal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ruhi Agrawal Assignment (Banking)Document32 pagesRuhi Agrawal Assignment (Banking)Shraddha GawadeNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ii: ON How Do Rbi Manages Currency Note IN INDIADocument3 pagesAssignment-Ii: ON How Do Rbi Manages Currency Note IN INDIAJasmin AtwalNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics: Monetary & Fiscal Policy InstrumentsDocument27 pagesMacro Economics: Monetary & Fiscal Policy InstrumentsACRNo ratings yet
- Repo RateDocument3 pagesRepo RaterajzzeshNo ratings yet
- Bank RatesDocument3 pagesBank RatesJamessapna BondNo ratings yet
- Product and Process PatentDocument2 pagesProduct and Process PatentKarina ManafNo ratings yet
- Types of Custom DutyDocument3 pagesTypes of Custom DutyKarina ManafNo ratings yet
- Manish Kumar Vs Union of India.rDocument3 pagesManish Kumar Vs Union of India.rKarina ManafNo ratings yet
- Trademarks Act, 1999: Different Forms of Trade Mark Objective History and EvolutionDocument25 pagesTrademarks Act, 1999: Different Forms of Trade Mark Objective History and EvolutionKarina ManafNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector Reforms in IndiaDocument43 pagesBanking Sector Reforms in IndiaChandini KambapuNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument32 pagesMonetary PolicyAbhi JainNo ratings yet
- Monetary Policy Monetary Policy: Jyoti Ranjan Sahu Devi Priyadarshni Mohapatra Neha MohantyDocument19 pagesMonetary Policy Monetary Policy: Jyoti Ranjan Sahu Devi Priyadarshni Mohapatra Neha Mohantysarmistha sahooNo ratings yet
- Credit CTRL RBIDocument14 pagesCredit CTRL RBISatyajeet MohaNo ratings yet
- Banking NotesDocument30 pagesBanking NotesAditi RahurikarNo ratings yet
- Auction of State Government Securities 10,930 Cr. (Face Value)Document2 pagesAuction of State Government Securities 10,930 Cr. (Face Value)A-Series OfficialNo ratings yet
- Financial Sector Reforms in India Since 1991Document17 pagesFinancial Sector Reforms in India Since 1991Palash BairagiNo ratings yet
- Central BankDocument17 pagesCentral BankGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions For Clerical To Officer Cadre Promotion TestDocument335 pagesObjective Questions For Clerical To Officer Cadre Promotion TestDeepu Nani83% (6)
- Credit Creation by RbiDocument24 pagesCredit Creation by RbiABIGAIL SHIJU 20213116No ratings yet
- Money and Banking: Chapter - 8Document36 pagesMoney and Banking: Chapter - 8Nihar NanyamNo ratings yet
- Money and Banking 2Document2 pagesMoney and Banking 2Gautami PatilNo ratings yet
- Mfs Question BankDocument2 pagesMfs Question Bankpateljitendra2136No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document32 pagesUnit 2humaidjahangirNo ratings yet
- Rbi Monetary PolicyDocument5 pagesRbi Monetary PolicyRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- PPB - Complete PDFDocument185 pagesPPB - Complete PDFishantkathuriaNo ratings yet
- Banking Awareness Capsule Sbi Po Bob PoDocument48 pagesBanking Awareness Capsule Sbi Po Bob PoLokesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Dey's Sample PDF - Economics-XII Exam Handbook 2021-22 - Term-IDocument82 pagesDey's Sample PDF - Economics-XII Exam Handbook 2021-22 - Term-Iicarus falls67% (3)
- Central BankingDocument28 pagesCentral Bankingneha16septNo ratings yet
- Bharat Petroleum Corporation LTDDocument15 pagesBharat Petroleum Corporation LTDsagunkumarNo ratings yet
- Questions (FMIS)Document22 pagesQuestions (FMIS)Onkar Ashok Kelji0% (1)
- Banking Short NotesDocument15 pagesBanking Short NotesTanjin keyaNo ratings yet
- Yesfin PDFDocument226 pagesYesfin PDFAnupriya NagpalNo ratings yet
- The Tools of Monetary PolicyDocument53 pagesThe Tools of Monetary Policyrichard kapimpaNo ratings yet
- THE Banking Regulatio N ACT, 1949Document16 pagesTHE Banking Regulatio N ACT, 1949Ashokkumar MadhaiyanNo ratings yet
- University of Mumbai BLCK BookDocument50 pagesUniversity of Mumbai BLCK BookPranay SawantNo ratings yet
- SBT AR Eng 2011Document92 pagesSBT AR Eng 2011gmp_07No ratings yet
- Jan 192014 Dos 01 eDocument11 pagesJan 192014 Dos 01 erakhalbanglaNo ratings yet
- Clerk Competition BoosterDocument70 pagesClerk Competition Boosterdheeru0071No ratings yet