Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Water and Its Treatment-7,8
Water and Its Treatment-7,8
Uploaded by
Tushar SharmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Water and Its Treatment-7,8
Water and Its Treatment-7,8
Uploaded by
Tushar SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit-1b Water and its treatment
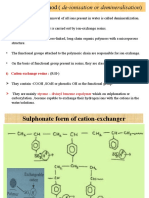
Ion –exchange method
Ion exchange is a process by which ions held on a porous, essentially insoluble solid
(resin) are exchanged for ions in solution that is brought in contact with it.
Ion exchange resins are insoluble, cross linked, high molecular weight organic polymers
having a porous structure. The functional groups attached to the chains are responsible
for the ion exchange properties.
Process:
The hard water is passed through a cation exchange column. All cations like Ca2+, Mg2+
etc are removed by the resin and equivalent amount of H + ions are released from the
column to the water.
2RCOO-H+ + Ca2+ (RCOO-)2 Ca2+ + 2H+
After passing through the cation exchange column, the hard water is passed through
anion exchange column, when all the anions like SO42-, Cl- etc present in hard water are
removed and taken up by the resin. An equivalent amount of OH- is released from this
column to the water.
[R-N+(CH3)]OH- + Cl- [R-N+(CH3)]Cl- + OH-
The H+ and OH- ions released from the cation exchange resin and the anion exchange
resin respectively combine to give water molecule.
H+ + OH- H2O
Such water produced is free from any ions; hence is known as demineralised water. Since
it is free from any ions, acidity or alkalinity, it is pure like distilled water.
Demineralization of water by ion exchange process
Compiled by Dr ARUNIMA NAYAK & Dr BRIJ BHUSHAN Page 1
Unit-1b Water and its treatment
Regeneration
During process, both cation and anion exchange the resins get exhausted i.e capacity to
exchange H+ and OH- ions is lost.
The cationic resins can be generated by passing solution of dil. HCI or H2SO4 through
first the 1st column.
The regeneration reactions are:
Washing the column with deionized water releases the Ca 2+, Mg 2+ ions or Cl-, SO42-
ions into the sink.
Similarly the anion exchange resins can be regenerated by passing solution of dil. NaOH
through the second column and regeneration is represented as:
The column is washed with deionized water and ions like Na+, Cl-, SO42- are released
into the sink.
Advantages and disadvantages of ion exchange process are:
Advantages Disadvantages
The ion exchange process can be used to Very costly process as equipment and
soften highly acidic or alkaline waters chemicals are costly
The process produces water of very low Presence of turbidity reduces the
hardness (<2ppm). Very good for use in efficiency of the process
high pressure boilers
For water to be used for domestic purpose, water softening by ion exchange process will
include only cation exchange resin. This is because, only cations responsible for hardness
like Ca2+, Mg 2+ etc need to be removed. Regeneration is carried out by using inexpensive
brine or NaCl solution.
Compiled by Dr ARUNIMA NAYAK & Dr BRIJ BHUSHAN Page 2
Unit-1b Water and its treatment
Reverse Osmosis (RO):
Reverse Osmosis is a process where water is demineralized using a semi permeable
membrane at high pressure. Reverse osmosis is osmosis in reverse.
A semi permeable membrane is a selective membrane which does not permit the passage
of dissolved solute particles.
Osmosis is the phenomenon by which water or any solvent starts to flow from a region of
low concentration to high concentration when the two solutions are separated by a semi
permeable membrane. The flow continues till the concentration is equal on both sides of
the membrane. This is most commonly observed in plants. If you don't water your plants
they wilt. A plant cell is a semi permeable (water flows through the membrane but salts
don't) membrane with the living stuff on the inside in a salt solution. Water is drawn into
the cell from the outside because pure water will move across a semi permeable
membrane to dilute the higher concentration of salt on the inside. This is how water is
drawn in from the ground when you water your plants. If you salt your plants (over
fertilize or spill some salt on the grass), the plant will wilt because the salt concentration
on the outside of the cell is higher than the inside and water then moves across the
membrane from the inside to the outside.
To reverse this process, you must overcome the osmotic pressure equilibrium across the
membrane because the flow is naturally from dilute to concentrate. We want more pure
water so we must increase the salt content in the cell (concentrate side of the membrane).
To do this we increase the pressure on the salty side of the membrane and force the water
across. The amount of pressure is determined by the salt concentration. As we force water
out, the salt concentration increases requiring even greater pressure to get more pure
water.
Diagrammatic representation of Reverse Osmosis
Advantage:
1. It is simple and reliable process of water softening.
2. It is not expensive.
3. It is energy efficient
4. It operates at low temperature.
5. The life of semi permeable membrane is 2 years and can be replaced within
minutes.
Compiled by Dr ARUNIMA NAYAK & Dr BRIJ BHUSHAN Page 3
Unit-1b Water and its treatment
What is calgon conditioning of a boiler feed water?
Ans: It is addition of calgon i.e.: sodium hexa metaphosphate in boiler water to
prevent the formation of scale and sludge. Calgon removes scale forming Ca2+, Mg2+.
Compiled by Dr ARUNIMA NAYAK & Dr BRIJ BHUSHAN Page 4
You might also like
- Ion Exchange Exp.2Document6 pagesIon Exchange Exp.2Arbab 02No ratings yet
- Minbooklist 136254Document156 pagesMinbooklist 136254МаратNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Line Impedances and Mutual Coupling of Parallel LinesDocument8 pagesMeasurement of Line Impedances and Mutual Coupling of Parallel LinesKhandai SeenananNo ratings yet
- Sequence of Operation of FahuDocument1 pageSequence of Operation of FahuahmedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project: Water Treatment Using Ion Exchange ResinsDocument5 pagesChemistry Project: Water Treatment Using Ion Exchange ResinsAman KapoorNo ratings yet
- 1844 159 578 Water-4Document24 pages1844 159 578 Water-4Mercy SajiNo ratings yet
- Demineralized Process Water..Document52 pagesDemineralized Process Water..teweleNo ratings yet
- Distilled, Deionised and Demineralised Water and Measuring of The PurityDocument5 pagesDistilled, Deionised and Demineralised Water and Measuring of The PurityVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Water TechnologyDocument22 pagesUnit-I Water TechnologyManivannanVenkatesan100% (1)
- Distilled, Deionized and Demineralized Water and Measuring of The PurityDocument5 pagesDistilled, Deionized and Demineralized Water and Measuring of The PurityAli Emraan TariqNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument25 pagesDM PlantAbdul BokhariNo ratings yet
- 1843 159 578 Water-3Document12 pages1843 159 578 Water-3Mercy SajiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part 3 PPT (1) ChemDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Part 3 PPT (1) Chemneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Materials - QuestionsDocument11 pagesChemistry Materials - QuestionsSanthosh kannaNo ratings yet
- Water Refilling StationDocument8 pagesWater Refilling StationE Li ZerNo ratings yet
- Ppu QBDocument26 pagesPpu QBAnonymous JDXbBDBNo ratings yet
- Chemistry important QuestionsDocument27 pagesChemistry important Questions22211a0525No ratings yet
- Water (Part 2)Document42 pagesWater (Part 2)tusharparmar300No ratings yet
- Deionized - Demineralized Water - LenntechDocument1 pageDeionized - Demineralized Water - LenntecheltonNo ratings yet
- Water SofteningDocument20 pagesWater SofteningHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Water Traetment Lecture 4 NewDocument28 pagesWater Traetment Lecture 4 NewMuzamil RaoNo ratings yet
- DUREZA 1sssssDocument14 pagesDUREZA 1sssssCarolina HerreraNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Method (De-Ionisation or Demineralisation) : I) Cation Exchange ResinsDocument10 pagesIon Exchange Method (De-Ionisation or Demineralisation) : I) Cation Exchange ResinsRaunit VermaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 30 Boil WaterDocument4 pagesLecture 30 Boil WaterMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- PDF Analysis of Hard WaterDocument15 pagesPDF Analysis of Hard Waterpiyushvasve17No ratings yet
- Advanced Wastewater TreatmentDocument16 pagesAdvanced Wastewater TreatmentvikkykambleNo ratings yet
- Water DemineralizationDocument3 pagesWater DemineralizationHazel Marie ArceñoNo ratings yet
- NSE403 L5-8 Dimenerizer22FDocument55 pagesNSE403 L5-8 Dimenerizer22Fabdul hakimNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry WaterDocument41 pagesCAPE Chemistry WaterTeri LambNo ratings yet
- Desalination of Brakish Water5Document3 pagesDesalination of Brakish Water5Tejas YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Ion Exchange, Reverse Osmosis, Calgon, EDTA methodDocument23 pagesUnit 4 Ion Exchange, Reverse Osmosis, Calgon, EDTA methoddrskhasan1No ratings yet
- Demineralized Water Treatment SystemDocument44 pagesDemineralized Water Treatment Systemshaiera100% (1)
- CY6251 Engineering Chemistry II Lecture NotesDocument55 pagesCY6251 Engineering Chemistry II Lecture NotesAravind Phoenix100% (1)
- E1 Water ConditioningDocument15 pagesE1 Water ConditioningChryzl Dumalay SuobironNo ratings yet
- DI in A NutShellDocument5 pagesDI in A NutShellvalentineloboNo ratings yet
- Alphabetical List of Water Treatment UnitsDocument4 pagesAlphabetical List of Water Treatment UnitsReena NasriNo ratings yet
- CY6251 Engineering Chemistry II Lecture Notes PDFDocument55 pagesCY6251 Engineering Chemistry II Lecture Notes PDFSiva Guru100% (1)
- ION-EXCHANGE: Ion-Exchange Resins Are Solid Materials WhichDocument4 pagesION-EXCHANGE: Ion-Exchange Resins Are Solid Materials WhichSha wonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Water Tech-2-External Treatment)Document21 pagesChemistry (Water Tech-2-External Treatment)Anjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Introduction-: Hard WaterDocument6 pagesIntroduction-: Hard WaterUtkarsha KudaveNo ratings yet
- Basics of DeionizationDocument4 pagesBasics of DeionizationChang Chee HongNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange PDFDocument26 pagesIon Exchange PDFTruth SeekerNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange ResinsDocument7 pagesIon Exchange ResinsVirgilMaroNo ratings yet
- Cascade Aerator: How It WorksDocument29 pagesCascade Aerator: How It WorksMahaveer ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chemistry SASTRA University Water TreatmentDocument6 pagesUnit 1 Chemistry SASTRA University Water Treatmentstar100% (1)
- Principles of Ion ExchangeDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Ion ExchangeYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Demineralisation of Water: Rahul Agarwal Varun Aggarwal Pinaki GhoshDocument16 pagesDemineralisation of Water: Rahul Agarwal Varun Aggarwal Pinaki GhoshVarun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Unit II. Part - C. Water Resources ManagementDocument6 pagesUnit II. Part - C. Water Resources ManagementAmruthRaj 'Ambu'No ratings yet
- Demineralization of Water by Ion ExchangeDocument2 pagesDemineralization of Water by Ion ExchangeDeenaNo ratings yet
- Raw Water QualityDocument9 pagesRaw Water QualityzeonNo ratings yet
- Ion ExchangeDocument4 pagesIon ExchangeslchemNo ratings yet
- Types of Hardness of WaterDocument12 pagesTypes of Hardness of WaterAhmad AmrNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment by Ion Exchange ProcessDocument20 pagesWater Treatment by Ion Exchange ProcessRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Nitte International School Chem ProjectDocument25 pagesNitte International School Chem ProjectShashwath GuptaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 PDFPeulh DialloNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Hard WaterDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Hard WaterKannan Mon67% (9)
- MPHARM IP 1Y 2S 203T Pharm - ProductionTechDocument7 pagesMPHARM IP 1Y 2S 203T Pharm - ProductionTechratankale0401No ratings yet
- Demineralization of Water: Dilip Kumar NTPC LTDDocument46 pagesDemineralization of Water: Dilip Kumar NTPC LTDDinesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Pam and TMDDocument13 pagesPam and TMDPoojit PopliNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Hard Water IntroductionDocument21 pagesAnalysis of Hard Water IntroductionShambhavi SonakiyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Water Filtration: Activated Charcoal Is Charcoal That Has BeenDocument7 pagesTypes of Water Filtration: Activated Charcoal Is Charcoal That Has BeenMaricris FajilanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Numerical Practice On Superposition, Norton and Thevenin TheoremsDocument15 pagesLecture 13 - Numerical Practice On Superposition, Norton and Thevenin TheoremsTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Thevenins Theorem and Nortons TheoremDocument15 pagesLecture 12 - Thevenins Theorem and Nortons TheoremTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Analysis of Voltage, Current Sources and Resistances in Series and ParallelDocument11 pagesLecture 4 - Analysis of Voltage, Current Sources and Resistances in Series and ParallelTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 (B) - Superposition TheoremDocument11 pagesLecture 11 (B) - Superposition TheoremTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Star - Delta Transformation and NumericalDocument16 pagesLecture 10 - Star - Delta Transformation and NumericalTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 0 - Introduction To The CourseDocument4 pagesLecture 0 - Introduction To The CourseTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Water Chemistry 1Document2 pagesWater Chemistry 1Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment-5,6Document3 pagesWater and Its Treatment-5,6Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Water and Its Treatment 3,4Document4 pagesWater and Its Treatment 3,4Tushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Punjab PoliceDocument20 pagesPunjab Policevinod512793No ratings yet
- Portfolio AnswersDocument4 pagesPortfolio Answersa73609No ratings yet
- Definition and Objective of AuditDocument7 pagesDefinition and Objective of AuditZednem JhenggNo ratings yet
- Samsung RF27T5501Document164 pagesSamsung RF27T5501Brian MasseyNo ratings yet
- Water Insulation - ENDocument9 pagesWater Insulation - ENNoorul Mufas MnNo ratings yet
- A Profect Report On Star Claytech Pvt. LTDDocument44 pagesA Profect Report On Star Claytech Pvt. LTDraj danichaNo ratings yet
- Visual IdentityDocument38 pagesVisual IdentityyannaNo ratings yet
- Math ResearchDocument4 pagesMath ResearchRaja AliNo ratings yet
- CO2 Supply Agreement - A-ZDocument13 pagesCO2 Supply Agreement - A-ZEslam A. FahmyNo ratings yet
- Session Wise Details:: BA7034-Industrial Relations & Labour WelfareDocument5 pagesSession Wise Details:: BA7034-Industrial Relations & Labour Welfareravideva84No ratings yet
- Pdms List Error CaptureDocument4 pagesPdms List Error Capturehnguyen_698971No ratings yet
- Dynamic Simulation of A Crude Oil DistillationDocument14 pagesDynamic Simulation of A Crude Oil DistillationAL-JABERI SADEQ AMEEN ABDO / UPMNo ratings yet
- Amendment of Information, Formal Vs SubstantialDocument2 pagesAmendment of Information, Formal Vs SubstantialNikkoCataquiz100% (3)
- CH - 04 7-7-11Document47 pagesCH - 04 7-7-11Myla GellicaNo ratings yet
- Analysing Mouse and Pen Flick GesturesDocument6 pagesAnalysing Mouse and Pen Flick GesturesHarini RaoNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Suspension Modeling NotesDocument25 pagesVehicle Suspension Modeling Notesahmetlutfu100% (2)
- Solar Charge Controller User Manual: I Functional CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesSolar Charge Controller User Manual: I Functional CharacteristicsAmer WarrakNo ratings yet
- Hypogear 85W-140 - BP Aust Pty LTDDocument4 pagesHypogear 85W-140 - BP Aust Pty LTDBiju_PottayilNo ratings yet
- (INTRA) - DEC2020-Presntation-MUHAMMAD AMIRUL AKASHAH BIN MOHD FAHMIDocument18 pages(INTRA) - DEC2020-Presntation-MUHAMMAD AMIRUL AKASHAH BIN MOHD FAHMIasfafasfNo ratings yet
- Product Classification: SL110 Series Modular Jack, RJ45, Category 6, T568A/T568B, Unshielded, Without Dust Cover, BlackDocument2 pagesProduct Classification: SL110 Series Modular Jack, RJ45, Category 6, T568A/T568B, Unshielded, Without Dust Cover, BlackDWVIZCARRANo ratings yet
- BFM Group 1 AssignmentDocument30 pagesBFM Group 1 AssignmentnurinNo ratings yet
- Succeeding at WorkDocument11 pagesSucceeding at WorkLai RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Paper Tugas Kelompok ELT Curriculum Developing A Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesPaper Tugas Kelompok ELT Curriculum Developing A Course SyllabusAdies NuariNo ratings yet
- AralPan9 q2 Mod10 Ang-Pamilihan-V5Document29 pagesAralPan9 q2 Mod10 Ang-Pamilihan-V5Wizly Von Ledesma TanduyanNo ratings yet
- Chase: Eventhough This Case Shows How Campany Hires and Layoffs Strategy Would Work Best Due To Unstable Demand ForcestDocument3 pagesChase: Eventhough This Case Shows How Campany Hires and Layoffs Strategy Would Work Best Due To Unstable Demand ForcestCristhian ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Braille Actuator Report MAJORDocument32 pagesBraille Actuator Report MAJORSwapnil BeheraNo ratings yet
- PointersDocument147 pagesPointersSoumya VijoyNo ratings yet