Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development of A Novel 3-Stage BAF System For Enhancing Nitrification Performance at Short Hydraulic Retention Time
Development of A Novel 3-Stage BAF System For Enhancing Nitrification Performance at Short Hydraulic Retention Time
Uploaded by
Nguyen AnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Development of A Novel 3-Stage BAF System For Enhancing Nitrification Performance at Short Hydraulic Retention Time
Development of A Novel 3-Stage BAF System For Enhancing Nitrification Performance at Short Hydraulic Retention Time
Uploaded by
Nguyen AnCopyright:
Available Formats
Development of a Novel 3-Stage BAF System for
Enhancing Nitrification Performance at Short Hydraulic
Retention Time
H. D. Ryu*,J. S. Kim**, G. W. Shin** and S. I. Lee**
* Ministry of Environment, Geum River Basin Environmental Office, 409 Daehak-ro, Yusung-gu, Daejeon 305-706,
Republic of Korea
** Department of Environmental Engineering, Chungbuk National University, 410 Gaesin,
Cheongju, Chugnbuk, Korea
(E-mail: nanumenv@hanmail.net ; j1405j@hanmai.net ; shingw@chungbuk.ac.kr ; gatorlee@chungbuk.ac.kr)
Introduction
The biological aerated filter (BAF) system was developed in Europe and the widely applied all over the world as a novel wastewater treatment system.
It adopts a granular media as the support for microbial biofilms that provide the depth filtration action
BAF also offers a small footprint alternative to conventional oxic processes. In addition, the BAF can achieve the higher nitrification performance
compared to the suspended growth process (SGP), due to the fact that the system is the attachment growth process (AGP).
Although the BAF system has many advantages as mentioned above, the system is required to be effectively operated in shorter hydraulic retention
time (HRT) compared to the present HRT condition because the more stringent effluent criteria for T-N is expected in handling the increased amount of
wastewater.
Nevertheless, it has been reported from the previous studies that the nitrification performance of the BAF system was deteriorated at short HRT.
This work was therefore aimed to propose a new novel 3-stage BAF system which can perform almost perfect nitrification in the short HRT less than 1 h
by incorporating an intermittent aerated BAF reactor into the modified Ludzack-Ettinger (MLE)-type BAF system.
Material and methods Results and Discussion
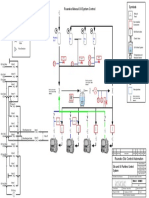
Two lab-scale BAF systems were prepared for this study (Fig. 1). One Fig. 2 clearly showed that the although the NH4-N removal efficiency of
was the MLE-type BAF system used as a “reference” reactor (Fig. 1a) and two systems was almost same at the HRT of 3 and 2 h, that of 3-stage BAF
the other was the proposed 3-stage BAF system (Fig. 1b) designed for system proposed in this work was 8 % higher than that of control BAF
enhancing nitrification performance. system at the HRT of 1 h.
(a) MLE-type BAF (b) Proposed BAF
Backwash water
Control
3-stage BAF
120
100
NH4-N removal (%)
80
Anoxic/ Oxic
60
Anoxic Oxic
40
20
Internal circulation water
0
Run 1 Run 2 Run 3
Fig. 1. Operational concepts of the reference (a) and proposed BAF Operating condition
system (b) in this work. Functions of each column were indicated in
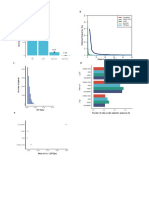
Fig. 2. Comparison of effect of HRT on NH4-N removal between two
parenthesis.
systems.
Table 1. Operating parameters of conventional MLE-type BAF and According to Fig. 3, the intermittently aerated reactor decreased SCOD
3-stage BAF process. concentration in the range of 3-8 mg/L and it finally enhanced the NH4-N
removal of the 3-stage BAF system by facilitating the growth of nitrifiers at
Process MLE-type BAF 3-stage BAF the HRT of 1 h even if the difference of SCOD concentration did not affect
Intermittent the NH4-N removal between two systems at the HRT of 3 and 2 h.
Rector Anoxic Oxic Anoxic Oxic
oxic
Rector Control
Volume (L)
12 12 12 12 12 3-stage BAF
Media 70
packing (%)
50 50 50 25 50
Run 3
Loaded SCOD to oxic reactor (mg/L)
Run 2
60
Media Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene
50
HRT (hr) 3, 2, 1 3, 2, 1
40
Mode
Inermittent Oxic = 1 hr (AIR on & off)
change 30
The municipal wastewater was collected from a wastewater treatment 20
plant, which is located in Cheongju, Korea. The raw influent was
characterized in Table 2. 10 Run 1
Table 2. Characterization of raw municipal wastewater. 0
Parameter Average value 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Operation day
Total chemical oxygen demand (TCOD) (mg/L) 157
Soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) (mg/L) 51 Fig. 3. Loaded concentration of SCOD to oxic reactor.
Suspended solid (SS) (mg/L) 90
Total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) (mg/L) 26 It is therefore believed that the proposed 3-stage BAF system could be
effectively applicable under the condition where the BAF system should be
NH4-N (mg/L) 15 operated in treating a large amount of wastewater (in very short HRT).
PO4-P 1.2
pH 7.2
You might also like
- Pool Care Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePool Care Cheat SheetKeithon PattersonNo ratings yet
- EDUC5711 Week 8 Discussion Assignment Unit 8Document3 pagesEDUC5711 Week 8 Discussion Assignment Unit 8Meleisa WrayNo ratings yet
- CE 085 Wastewater Treatment III MBRDocument28 pagesCE 085 Wastewater Treatment III MBRNguyen An100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Centrifugal Pumps PDFDocument7 pagesFundamentals of Centrifugal Pumps PDFÁlvaro Martínez FernándezNo ratings yet
- Labitec - Aptt - (English) Labitec - Aptt - (Italiano)Document2 pagesLabitec - Aptt - (English) Labitec - Aptt - (Italiano)Ruxandra BANUNo ratings yet
- EGSB ReactorDocument48 pagesEGSB ReactorNanofold100% (1)
- Characterization of Pa6.6 and Pet Fabrics and Films Coated With Thin Films of Tio2 by Reactive SputerringDocument1 pageCharacterization of Pa6.6 and Pet Fabrics and Films Coated With Thin Films of Tio2 by Reactive SputerringSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Distillation Column Control Design Using Steady StateDocument18 pagesDistillation Column Control Design Using Steady Stateb95504048No ratings yet
- Ds RatioMatic RM0500 USADocument4 pagesDs RatioMatic RM0500 USAFrancisco RománNo ratings yet
- Practical HPLC Simulator v1Document742 pagesPractical HPLC Simulator v1LUIS CLAUDIO CAIZA PAUCARNo ratings yet
- Poster 1Document1 pagePoster 1docteur besghaierNo ratings yet
- BHSE CatalogDocument2 pagesBHSE CatalogRojo BlancoNo ratings yet
- Debra Hall Guided Wave ISA Singapore LPG Measurements GWIDocument33 pagesDebra Hall Guided Wave ISA Singapore LPG Measurements GWIPhilNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 5260965Document2 pagesGrundfosliterature 5260965s12originalNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Radio Network Functionality: Idle Mode BehaviorDocument33 pagesWcdma Radio Network Functionality: Idle Mode Behaviormody1850No ratings yet
- IFAC Control Applications in Marine Systems, Fukuoka, Japan 1998Document6 pagesIFAC Control Applications in Marine Systems, Fukuoka, Japan 1998Mohamad Irfan HariyadiNo ratings yet
- S07nmdl1ds ENDocument5 pagesS07nmdl1ds ENYongfeng QianNo ratings yet
- What Is RULER: Oil Analysis For Predictive MaintenanceDocument2 pagesWhat Is RULER: Oil Analysis For Predictive Maintenancemohamed abdelmoniemNo ratings yet
- ABB PQ FilterDocument14 pagesABB PQ FilterTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Innovation of LNGCDocument63 pagesInnovation of LNGCpadangiringNo ratings yet
- Open Babylog Gbr61733xxt04Document1 pageOpen Babylog Gbr61733xxt04MarceloNo ratings yet
- 1 - Hydrocarbon Fluids PEPDDocument217 pages1 - Hydrocarbon Fluids PEPDgilberto monteiroNo ratings yet
- The Only Simulator That... : Modeling Power and PrecisionDocument2 pagesThe Only Simulator That... : Modeling Power and PrecisionJulio TovarNo ratings yet
- Waveshaper 1000b 4000b DsDocument4 pagesWaveshaper 1000b 4000b DsDiego Pérez GalachoNo ratings yet
- Ultimate 3000 Standard HPLC Systems: Giving You MoreDocument12 pagesUltimate 3000 Standard HPLC Systems: Giving You MorehamoumNo ratings yet
- Removal of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Pahs) From Offshore Produced Water Using Advanced Oxidation Processes (Aops)Document2 pagesRemoval of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Pahs) From Offshore Produced Water Using Advanced Oxidation Processes (Aops)Kelly RamosNo ratings yet
- Yl 9100 PlusDocument16 pagesYl 9100 PlusAmica LeeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Hemodynamic Monitoring With Swan GanzDocument1 pageAdvanced Hemodynamic Monitoring With Swan GanzDr.Biswajit jenaNo ratings yet
- Water 639,0 MM (D1) : Termo Paipa Cooling Water Pumps SJM CWP Bsm650-1SDocument1 pageWater 639,0 MM (D1) : Termo Paipa Cooling Water Pumps SJM CWP Bsm650-1SAlexander PinedaNo ratings yet
- Braid PosterDocument1 pageBraid Postercamcason1017No ratings yet
- Metallic Design Level 1 Ball Valve: Air-Powered Double-Diaphragm PumpDocument6 pagesMetallic Design Level 1 Ball Valve: Air-Powered Double-Diaphragm PumpCarlos Alberto OspinaNo ratings yet
- Poster Ex2Document1 pagePoster Ex2jim0410168No ratings yet
- Novelties in Leaching, Solvent Extraction and ElectrowinningDocument37 pagesNovelties in Leaching, Solvent Extraction and ElectrowinningcarlosNo ratings yet
- HHB Stal EngDocument2 pagesHHB Stal EngrafaelNo ratings yet
- MQB100F 7,5/4AW 240 Technical Specification: Data SheetDocument4 pagesMQB100F 7,5/4AW 240 Technical Specification: Data SheetGiangNo ratings yet
- Effective Removal of Mab Aggregrate Using Ca Pure-HADocument2 pagesEffective Removal of Mab Aggregrate Using Ca Pure-HASabir FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Best Rheological Model Drilling FluidsDocument1 pageBest Rheological Model Drilling FluidsVassilios Kelessidis100% (2)
- 2009STMAnnualMeeting Ming-Chuan-HsuDocument1 page2009STMAnnualMeeting Ming-Chuan-HsuMing-Chuan HsuNo ratings yet
- Typical Performance Curve SRU3/038/ (Sru3Wls) With Hyclean SealDocument6 pagesTypical Performance Curve SRU3/038/ (Sru3Wls) With Hyclean SealSonia Marcela AriasNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column Minimizing Energy Requirements With APCDocument12 pagesDistillation Column Minimizing Energy Requirements With APCMadhukar ScribdNo ratings yet
- Active Vs Passive ControlDocument11 pagesActive Vs Passive ControlMelany Fuentes GilerNo ratings yet
- BSP - BG29 Compliant PICV Valve Pack - Installation Instructions MAY 22Document2 pagesBSP - BG29 Compliant PICV Valve Pack - Installation Instructions MAY 22j.iqubalNo ratings yet
- Posterprogb PenmanDocument1 pagePosterprogb Penmanapi-450544194No ratings yet
- AKTA PURIFIER Manual PDFDocument43 pagesAKTA PURIFIER Manual PDFBrano IvanNo ratings yet
- YL9100plus HPLC Total Brochure ENG Original Plus Ver 2.2 SDocument16 pagesYL9100plus HPLC Total Brochure ENG Original Plus Ver 2.2 SAmica LeeNo ratings yet
- Eclipse Winnox Burners: Model WX0100Document4 pagesEclipse Winnox Burners: Model WX0100yulianoNo ratings yet
- S1F Non-Metallic Pump: Technical Data SheetDocument3 pagesS1F Non-Metallic Pump: Technical Data SheetspattacutNo ratings yet
- Regulators Edge 3 Series Regulators: Slam™Document1 pageRegulators Edge 3 Series Regulators: Slam™Dries VandezandeNo ratings yet
- Power Requirement (Agitator and High-Torque Stirrer)Document8 pagesPower Requirement (Agitator and High-Torque Stirrer)DozdiNo ratings yet
- Roanoke Silo System NewDocument1 pageRoanoke Silo System NewDavid Adrián EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Valve Configuration (Annex I) : Receipts Silo 1 Silo 4 Silo 3 Silo 2Document11 pagesValve Configuration (Annex I) : Receipts Silo 1 Silo 4 Silo 3 Silo 2David Adrián EsparzaNo ratings yet
- 2020 322 Moesm4 EsmDocument2 pages2020 322 Moesm4 EsmkjhgfghjkNo ratings yet
- DBB8666 Fuel Filter Data SheetDocument2 pagesDBB8666 Fuel Filter Data SheetJamyansuren TseveendorjNo ratings yet
- Binks AX260L Air Motor BreakdownDocument11 pagesBinks AX260L Air Motor BreakdownAryo KamandanuNo ratings yet
- Marine Reports: Yongkil Glen CHO, Ümüt YIGITDocument17 pagesMarine Reports: Yongkil Glen CHO, Ümüt YIGITNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- GTCNCHUYENKHOA0001Document2 pagesGTCNCHUYENKHOA0001Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- K-Water Institute, K-Waterter, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon 305-730, South Korea Korea Institute of Energy Research, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon, 305-343, South KoreaDocument1 pageK-Water Institute, K-Waterter, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon 305-730, South Korea Korea Institute of Energy Research, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon, 305-343, South KoreaNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Iwa 9219Document1 pageIwa 9219Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- EZLAND's Health & Safety Executive (HSE) Regulations For The Construction SiteDocument26 pagesEZLAND's Health & Safety Executive (HSE) Regulations For The Construction SiteNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Iwa 8932Document1 pageIwa 8932Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- H. Lee, G. H. Yun, T. U. Yoo, S. Kim, J. K. Hwang, W. Lee and Z. YunDocument1 pageH. Lee, G. H. Yun, T. U. Yoo, S. Kim, J. K. Hwang, W. Lee and Z. YunNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- WABAG Operations: Plant Management For The Private and Public SectorDocument14 pagesWABAG Operations: Plant Management For The Private and Public SectorNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Iwa 8418Document1 pageIwa 8418Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- A Bio-Eco Combined Process For Decentralized Wastewater TreatmentDocument1 pageA Bio-Eco Combined Process For Decentralized Wastewater TreatmentNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Micropollutant 2016 ENGDocument12 pagesMicropollutant 2016 ENGNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- J. Cumin, Y. Hong, M. Dagnew, R. Bayly, W. ParkerDocument1 pageJ. Cumin, Y. Hong, M. Dagnew, R. Bayly, W. ParkerNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Filtration2014 EN WebDocument6 pagesFiltration2014 EN WebNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Iwa 8628Document1 pageIwa 8628Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- SludgeDigestion 2016 EN WEBDocument12 pagesSludgeDigestion 2016 EN WEBNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Marapur MBR Technology: Maximum PerformancesDocument12 pagesMarapur MBR Technology: Maximum PerformancesNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- World's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherDocument31 pagesWorld's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Wabag Bioden: Nitrate Removal Biological Denitrifi Cation of Ground WaterDocument6 pagesWabag Bioden: Nitrate Removal Biological Denitrifi Cation of Ground WaterNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- ASABE Paper 141901300Document9 pagesASABE Paper 141901300Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Ed 162869Document495 pagesEd 162869Nguyen AnNo ratings yet
- 8DG61258GAAATCZZA - V1 - 1830 Photonic Service Switch (PSS) Release 7.0 User Provisioning Guide PDFDocument1,946 pages8DG61258GAAATCZZA - V1 - 1830 Photonic Service Switch (PSS) Release 7.0 User Provisioning Guide PDFNishant DosiNo ratings yet
- IMChap 011Document24 pagesIMChap 011Aaron Hamilton100% (2)
- AZ-120 Lab01a-Azure VM Linux ClusteringDocument20 pagesAZ-120 Lab01a-Azure VM Linux ClusteringErosNo ratings yet
- Onkar Rohit ResearchDocument7 pagesOnkar Rohit ResearchBhumika IngleNo ratings yet
- Project Management and Its Effects of Quality Control in ConstructionDocument5 pagesProject Management and Its Effects of Quality Control in Constructionbotch100% (3)
- Activity 1 For Lesson 5Document2 pagesActivity 1 For Lesson 5GUEVARRA EUNICE B.No ratings yet
- Public and Private LawDocument2 pagesPublic and Private LawNinutsa TeliaNo ratings yet
- PGL FIN 2006 01 Subrecipient Financial ProceduresDocument45 pagesPGL FIN 2006 01 Subrecipient Financial ProceduresAilec FinancesNo ratings yet
- A-T - Touhou Hisoutensoku - Readme IMPORTANTDocument2 pagesA-T - Touhou Hisoutensoku - Readme IMPORTANTAlisa Megat AliNo ratings yet
- LM Comandi Marzo 2022Document11 pagesLM Comandi Marzo 2022grazianonetNo ratings yet
- PT-059 TG-6 Uwc 2019-05Document1 pagePT-059 TG-6 Uwc 2019-05Sylvie CatalanNo ratings yet
- BSP Circular 942 PHDocument11 pagesBSP Circular 942 PHJoyce100% (1)
- AlgorithmsDocument23 pagesAlgorithmsVine VapourNo ratings yet
- Skull and Bones ChartDocument72 pagesSkull and Bones ChartWilliam Litynski100% (3)
- General Assembly Scholarship 2012-2013 ApplicationDocument7 pagesGeneral Assembly Scholarship 2012-2013 ApplicationjoesosnowskiNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Social Media Influencer On Brand Image, Self-Concept, and Purchase IntentionDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Social Media Influencer On Brand Image, Self-Concept, and Purchase IntentionLiza NoraNo ratings yet
- Future of EA - 269850Document14 pagesFuture of EA - 269850Renato Cardoso BottoNo ratings yet
- Finals ChapterDocument85 pagesFinals ChapterSyraChiaraDumaguingNo ratings yet
- Smart Money? The Forecasting Ability of CFTC Large Traders: by Dwight R. Sanders, Scott H. Irwin, and Robert MerrinDocument21 pagesSmart Money? The Forecasting Ability of CFTC Large Traders: by Dwight R. Sanders, Scott H. Irwin, and Robert MerrinPerfect SebokeNo ratings yet
- CFA Equity Research Challenge 2011 - Team 9Document15 pagesCFA Equity Research Challenge 2011 - Team 9Rohit KadamNo ratings yet
- Eu Law ExamDocument14 pagesEu Law ExamOla PietruszewskaNo ratings yet
- Merged E-Portfolio HRM 2021-1-286-2Document16 pagesMerged E-Portfolio HRM 2021-1-286-2DrKomal KhalidNo ratings yet
- BillPayment FormDocument2 pagesBillPayment FormThúy An Nguyễn100% (1)
- Download: Setting Goals and ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDownload: Setting Goals and ObjectivesJacques VisserNo ratings yet
- III Year-V Semester: B.Tech. Computer Science and Engineering 5CS4-02: Compiler Design UNIT-1Document11 pagesIII Year-V Semester: B.Tech. Computer Science and Engineering 5CS4-02: Compiler Design UNIT-1shelo berman100% (1)
- Synopsis On NCC Management SystemDocument6 pagesSynopsis On NCC Management Systemarun kaushikNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court: CIR v. Marubeni Corp. G.R. No. 137377Document12 pagesSupreme Court: CIR v. Marubeni Corp. G.R. No. 137377Jopan SJNo ratings yet
- ProductUploadTutorial RenderosityDocument4 pagesProductUploadTutorial RenderositySilvia SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Ulip & Mutual FundDocument55 pagesProject Report On Ulip & Mutual FundGovind BhakuniNo ratings yet