Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infographic Influence OTC Herbal
Infographic Influence OTC Herbal
Uploaded by
Zahra'a Al-AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (47)
- Board Questions in PharmacologyDocument12 pagesBoard Questions in PharmacologyJo Anne100% (6)
- Dilution Reconstitution Injection GuideDocument2 pagesDilution Reconstitution Injection GuideBorislavaSavova100% (1)
- Cannabis: Where Are We and Where Are We Going?Document19 pagesCannabis: Where Are We and Where Are We Going?kath Mil100% (1)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug StudyElleNo ratings yet
- Responsive Documents - CREW: FDA: Regarding FOIA Logs: 6/19/2012 - CREWLog ResponseDocument1,132 pagesResponsive Documents - CREW: FDA: Regarding FOIA Logs: 6/19/2012 - CREWLog ResponseCREWNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drug - PresentationDocument14 pagesAntiemetic Drug - PresentationYue Chen100% (1)
- HYPERTENSIONSSSSDocument1 pageHYPERTENSIONSSSSJulianne Jeamer FabroaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Beta Blocker ACE Inhibitor Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Calcium Channel Blocker Alpha Blocker SympatholyticDocument2 pagesDiuretics Beta Blocker ACE Inhibitor Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Calcium Channel Blocker Alpha Blocker SympatholyticimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drug NameDocument3 pagesHypertension Drug NameWahaj MujahidNo ratings yet
- Question 3 Antifungal DrugDocument4 pagesQuestion 3 Antifungal Drughelianthusannus1997No ratings yet
- Group of Medicines That Affect The Contraction of The Heart MuscleDocument14 pagesGroup of Medicines That Affect The Contraction of The Heart MuscleRuby Ann DimayugaNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument18 pagesRenallittle wordsNo ratings yet
- Dietary SuppDocument4 pagesDietary SuppAl Glen EgarleNo ratings yet
- PHARMACILOGY SUMMryDocument16 pagesPHARMACILOGY SUMMryKathy Real VillsNo ratings yet
- Inap Cardio Icgb PDFDocument5 pagesInap Cardio Icgb PDFFrances Sofia DuranNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Mind MapDocument1 pageHypertension Mind MapBrett DaleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyLizeth Querubin93% (15)
- Question 1 Antifungal DrugDocument4 pagesQuestion 1 Antifungal Drughelianthusannus1997No ratings yet
- Drug Study-DobutamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study-DobutamineCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Patho CirrhosisDocument1 pagePatho CirrhosisPearl Angeli SabalNo ratings yet
- @ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartDocument8 pages@ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartSutanyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)Document7 pagesNCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)MARIA KAWILANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs: Hypertension Dual-Action Alpha and Beta Receptor BlockersDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Drugs: Hypertension Dual-Action Alpha and Beta Receptor BlockersBUAHIN JANNANo ratings yet
- Michael Brian Umali 3A:G6 Classification & BDocument3 pagesMichael Brian Umali 3A:G6 Classification & Bexcel21121No ratings yet
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoNo ratings yet
- DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADocument36 pagesDRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADeling ManuabaNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Assess AnginaDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Assess Anginadeo_gratias14No ratings yet
- For Printing Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pageFor Printing Pathophysiology DMkat garciaNo ratings yet
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 pagesFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- MODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsDocument2 pagesMODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Dopa MineDocument1 pageDopa MineJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Research AssignmentDocument10 pagesPharmacology Research Assignmentapi-596613382No ratings yet
- Drug IndexDocument362 pagesDrug IndexsrhmdNo ratings yet
- Herbal NclexDocument2 pagesHerbal Nclexdarryl delgado100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Cardiovascular Systemcleahis cruzNo ratings yet
- Medications Doc XDocument4 pagesMedications Doc Xezinne obinna-umaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Lipitor: Generic Trade Class Use Side Effect Recommend Toxicity AtorvastatinDocument4 pagesLipitor: Generic Trade Class Use Side Effect Recommend Toxicity AtorvastatinAnita EricNo ratings yet
- Sweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyDocument9 pagesSweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyRon OpulenciaNo ratings yet
- Syahril - SGD 09 Hipertensi - 2108260021 - 10 Maret 2023Document1 pageSyahril - SGD 09 Hipertensi - 2108260021 - 10 Maret 2023bruhwahatNo ratings yet
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diuretic TableDocument4 pagesDiuretic TableRy HopeNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYJessica FabroaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants, ACE InhibitorsDocument2 pagesAnticoagulants, ACE InhibitorsGwyneth CartallaNo ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- DobutamineDocument2 pagesDobutamineJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Injection: 10 MG/ML Oral Solution: 10 Tablets: 20 MG, 40Document4 pagesInjection: 10 MG/ML Oral Solution: 10 Tablets: 20 MG, 40Maria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy NotesDocument70 pagesPharmacy NoteswybzrsvmwkNo ratings yet
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 pagePathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- NovaDocument1 pageNovaNovalia KungKung SinagaNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- KapsulDocument29 pagesKapsulMakinun AminNo ratings yet
- Obiectivele Tratamentului Antidiabetic La Pacientii CudztipisidztipiiDocument11 pagesObiectivele Tratamentului Antidiabetic La Pacientii CudztipisidztipiiDigei BobitzNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics: Guided By: Dhaivat C. ParikhDocument46 pagesNonlinear Pharmacokinetics: Guided By: Dhaivat C. ParikhTushar Bambharoliya100% (5)
- 1 Lec 1-Parasympathetic AgentsDocument33 pages1 Lec 1-Parasympathetic Agentsabdelrahmanmosleh75No ratings yet
- Handy Chart PsychosisDocument3 pagesHandy Chart Psychosismerryavie45No ratings yet
- Lect2 Anes Drugs PDFDocument109 pagesLect2 Anes Drugs PDFJidapa SEELADEENo ratings yet
- Drug Study AdalatDocument4 pagesDrug Study AdalatLea CelestialNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument4 pagesGeneric NamethomjoanneNo ratings yet
- Drug Aproval Process in IndiaDocument3 pagesDrug Aproval Process in IndiaSamit BisenNo ratings yet
- The Percentage of Medication Errors Globally, and in Saudi ArabiaDocument7 pagesThe Percentage of Medication Errors Globally, and in Saudi ArabiaLeen alghamdNo ratings yet
- Ajovy - Fremanezumab - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument6 pagesAjovy - Fremanezumab - Drug Information - UpToDateDiana PhamNo ratings yet
- QMH Drug FormularyDocument60 pagesQMH Drug FormularyproudofskyNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CoughDocument18 pagesDrugs For CoughAbraham BanjoNo ratings yet
- Teknik Anestesi UmumDocument128 pagesTeknik Anestesi UmumRiezka HanafiahNo ratings yet
- Fate of The Drug: Joanne Katherine T. Manlusoc, MSCDocument29 pagesFate of The Drug: Joanne Katherine T. Manlusoc, MSCChinenye AkwueNo ratings yet
- Covid Vac CertificateDocument1 pageCovid Vac CertificateSid KNo ratings yet
- BC Prescription Regulation TableDocument2 pagesBC Prescription Regulation TableJuliaNo ratings yet
- Steroids 1Document9 pagesSteroids 1nafkjfnakfaNo ratings yet
- Contrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall ChartDocument1 pageContrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall Chartapi-358179847No ratings yet
- Lap S5tock 29 Februari 2020Document47 pagesLap S5tock 29 Februari 2020Ridho SaputraNo ratings yet
- Substance AbuseDocument16 pagesSubstance AbuseAkansha JohnNo ratings yet
- PT Sejahtera Surya Intramedika: Daftar HargaDocument51 pagesPT Sejahtera Surya Intramedika: Daftar HargaMahiru UllamasyitohNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios 13 OctDocument41 pagesLista de Precios 13 OctAlvaro LEnin Rossy LopezNo ratings yet
- Valdoxan: Product InformationDocument15 pagesValdoxan: Product InformationGastón PacciaroniNo ratings yet
- No Pabrik / Principle CTH Obat (10 Item) : Daftar Nama - Nama PBF Dan Produk ObatDocument8 pagesNo Pabrik / Principle CTH Obat (10 Item) : Daftar Nama - Nama PBF Dan Produk ObatAPOTEK KF 62 GAJAH MADA JEMBERNo ratings yet
Infographic Influence OTC Herbal
Infographic Influence OTC Herbal
Uploaded by
Zahra'a Al-AhmedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infographic Influence OTC Herbal
Infographic Influence OTC Herbal
Uploaded by
Zahra'a Al-AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
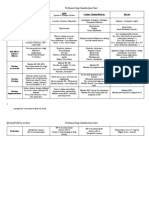
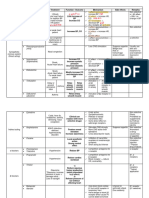
Clinically Significant Drug-Drug Interactions
With OTC and Herbal Products
PROBLEM
Patients are increasingly using over-the-counter (OTC) supplements and herbal
products for both preventative and therapeutic purposes.
Many OTC products can have serious consequences to the cardiovascular (CV) system
via drug-drug interactions.
SOLUTION
Avoid combining potentially interacting OTC supplements or herbal products with CV
medications as outlined in Table 1.
TABLE 1: Products That Interact with CV Medications1-6
Monitoring
Supplement or
CV Medication Interaction Parameter/
Herbal Product
Recommendation
Angiotensin- Increases effects of ACEIs, Blood pressure
Night-blooming cereus
Converting leading to hypotension
Enzyme
Inhibitors Decreases effectiveness
Green tea, Yohimbine of ACEIs, leading to Blood pressure
(ACEIs)
hypertension
Decreases effects of
Alpha-Blockers Butcher’s Broom, Blood pressure
alpha-blockers, leading to
Yohimbine
hypertension
Danshen, Garlic, Ginkgo Electrocardiogram;
Increases bleeding risk
biloba, Saw palmetto avoid if possible
Antiplatelets Increases activity of
Signs and symptoms of
St. John’s wort clopidogrel, leading to
bleeding
increased bleed risk
Fumitory, Lily of the Increases effects of beta-
Blood pressure and
valley, Night-blooming blockers, leading to
heart rate
cereus hypotension and bradycardia
Beta-Blockers
Decreases effects of
Green tea, Ma-huang Blood pressure and
beta-blockers, leading to
(ephedra), Yohimbine heart rate
hypertension and tachycardia
Fumitory, Grapefruit
Increases effects of CCBs,
juice, Hawthorn, Khella, Blood pressure and
leading to vasodilation,
Lily of the valley, Night- heart rate
hypotension, and bradycardia
Calcium Channel blooming cereus
Blockers (CCBs)
Decreases the effects
Blood pressure and
St. John’s wort of CCBs, leading to
heart rate
hypertension and tachycardia
Digoxin serum
Causes hypokalemia,
concentration,
Aloe vera, Licorice increasing risk of digoxin
serum potassium,
toxicity
electrocardiogram
Danshen, Fumitory,
Digoxin serum
Hawthorn, Lily of the Potentiates action of digoxin,
concentration,
Digoxin valley, Night-blooming increasing risk for toxicity
electrocardiogram
cereus, Strophanthus
Digoxin serum
Decreases digoxin
St. John’s wort concentration,
concentration
electrocardiogram
Chan Su, Danshen, Digoxin serum
Interacts with digoxin assay
Ginseng, Uzara root concentration
Potentiates action of nitrates,
Nitrates Hawthorn leading to vasodilation and Blood pressure
hypotension
Monoamine Capsicum, Ma-huang
Oxidase (ephedra), St. John’s Increases blood pressure Blood pressure
Inhibitors wort
Liver fu Serum
Increases effects of
Spironolactone Licorice potassium nction test;
spironolactone
avoid use if possible
Alfalfa, Bilberry,
Danshen, Dong quai,
International normalized
Fenugreek, Garlic,
Increases bleeding risk ratio, signs and
Ginger, Ginkgo biloba,
symptoms of bleeding
Warfarin Grapefruit juice, Khella,
Saw palmetto
International normalized
Ginseng, Green tea, Soy
Decreases effects of warfarin ratio due to need for
milk, St. John’s wort
potential dose increase
Monitoring
Supplement or
CV Medication Interaction Parameter/
Herbal Product
Recommendation
Electrocardiogram
Avoid use in patients
Echinacea, St. John’s
Increases QT interval with a prolonged QTc
wort
and/or congenital QT
Amiodarone syndrome
Decreases effects of
Grapefruit juice, St. Electrocardiogram
amiodarone, leading to
John’s wort Avoid if possible
potential arrhythmias
Electrocardiogram
Echinacea, Ma-huang Avoid use in patients
(ephedra), St. John’s Increases QT interval with a prolonged QTc
Class I wort and/or congenital QT
syndrome
Antiarrhythmic
Drugs
Lily of the valley Increases effects of quinidine Avoid
Decreases effectiveness, Electrocardiogram
St. John’s wort
leading to arrhythmias Avoid use if possible
Increases effects of statins
Grapefruit juice Symptoms of myalgias
and risk of myalgias
Statins
Increases risk of hepatotoxic Liver function test
Echinacea
effects Avoid use if possible
PREVENT POTENTIAL ERRORS
Educate patients and providers about the potential adverse effects of OTC products
and drug-drug interactions with CV medications.
Closely monitor patients with CV disease for harmful effects or toxicities from OTC
products.
Perform accurate patient medication histories to ensure all OTC products are known;
encourage patients to report all OTC and herbal products.
Create OTC/herbal products drug-drug interactions alert database in the electronic
medical record.
To download the infographic and see citations visit
ACC.org/Infographics
©2021 American College of Cardiology W21014
You might also like
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (47)
- Board Questions in PharmacologyDocument12 pagesBoard Questions in PharmacologyJo Anne100% (6)
- Dilution Reconstitution Injection GuideDocument2 pagesDilution Reconstitution Injection GuideBorislavaSavova100% (1)
- Cannabis: Where Are We and Where Are We Going?Document19 pagesCannabis: Where Are We and Where Are We Going?kath Mil100% (1)
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Drug StudyElleNo ratings yet
- Responsive Documents - CREW: FDA: Regarding FOIA Logs: 6/19/2012 - CREWLog ResponseDocument1,132 pagesResponsive Documents - CREW: FDA: Regarding FOIA Logs: 6/19/2012 - CREWLog ResponseCREWNo ratings yet
- Antiemetic Drug - PresentationDocument14 pagesAntiemetic Drug - PresentationYue Chen100% (1)
- HYPERTENSIONSSSSDocument1 pageHYPERTENSIONSSSSJulianne Jeamer FabroaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Beta Blocker ACE Inhibitor Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Calcium Channel Blocker Alpha Blocker SympatholyticDocument2 pagesDiuretics Beta Blocker ACE Inhibitor Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Calcium Channel Blocker Alpha Blocker SympatholyticimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drug NameDocument3 pagesHypertension Drug NameWahaj MujahidNo ratings yet
- Question 3 Antifungal DrugDocument4 pagesQuestion 3 Antifungal Drughelianthusannus1997No ratings yet
- Group of Medicines That Affect The Contraction of The Heart MuscleDocument14 pagesGroup of Medicines That Affect The Contraction of The Heart MuscleRuby Ann DimayugaNo ratings yet
- RenalDocument18 pagesRenallittle wordsNo ratings yet
- Dietary SuppDocument4 pagesDietary SuppAl Glen EgarleNo ratings yet
- PHARMACILOGY SUMMryDocument16 pagesPHARMACILOGY SUMMryKathy Real VillsNo ratings yet
- Inap Cardio Icgb PDFDocument5 pagesInap Cardio Icgb PDFFrances Sofia DuranNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Mind MapDocument1 pageHypertension Mind MapBrett DaleNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyLizeth Querubin93% (15)
- Question 1 Antifungal DrugDocument4 pagesQuestion 1 Antifungal Drughelianthusannus1997No ratings yet
- Drug Study-DobutamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study-DobutamineCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Patho CirrhosisDocument1 pagePatho CirrhosisPearl Angeli SabalNo ratings yet
- @ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartDocument8 pages@ Shopwithkey On Etsy Perfusion Drug Classification ChartSutanyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)Document7 pagesNCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)MARIA KAWILANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs: Hypertension Dual-Action Alpha and Beta Receptor BlockersDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Drugs: Hypertension Dual-Action Alpha and Beta Receptor BlockersBUAHIN JANNANo ratings yet
- Michael Brian Umali 3A:G6 Classification & BDocument3 pagesMichael Brian Umali 3A:G6 Classification & Bexcel21121No ratings yet
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoNo ratings yet
- DRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADocument36 pagesDRUGS USED IN HEART FAILURE 2016 ADeling ManuabaNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Assess AnginaDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Assess Anginadeo_gratias14No ratings yet
- For Printing Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pageFor Printing Pathophysiology DMkat garciaNo ratings yet
- Final patho-HCVDDocument2 pagesFinal patho-HCVDAlvin RamirezNo ratings yet
- MODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsDocument2 pagesMODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Dopa MineDocument1 pageDopa MineJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Research AssignmentDocument10 pagesPharmacology Research Assignmentapi-596613382No ratings yet
- Drug IndexDocument362 pagesDrug IndexsrhmdNo ratings yet
- Herbal NclexDocument2 pagesHerbal Nclexdarryl delgado100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Cardiovascular Systemcleahis cruzNo ratings yet
- Medications Doc XDocument4 pagesMedications Doc Xezinne obinna-umaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Emergency DrugsDocument6 pagesDrug Study Emergency DrugsJhessa Curie PitaganNo ratings yet
- Lipitor: Generic Trade Class Use Side Effect Recommend Toxicity AtorvastatinDocument4 pagesLipitor: Generic Trade Class Use Side Effect Recommend Toxicity AtorvastatinAnita EricNo ratings yet
- Sweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyDocument9 pagesSweet Glomerulus: A Case of Diabetic NephropathyRon OpulenciaNo ratings yet
- Syahril - SGD 09 Hipertensi - 2108260021 - 10 Maret 2023Document1 pageSyahril - SGD 09 Hipertensi - 2108260021 - 10 Maret 2023bruhwahatNo ratings yet
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diuretic TableDocument4 pagesDiuretic TableRy HopeNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGYJessica FabroaNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulants, ACE InhibitorsDocument2 pagesAnticoagulants, ACE InhibitorsGwyneth CartallaNo ratings yet
- 2 5377779365079685362Document23 pages2 5377779365079685362ahmaNo ratings yet
- DobutamineDocument2 pagesDobutamineJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Injection: 10 MG/ML Oral Solution: 10 Tablets: 20 MG, 40Document4 pagesInjection: 10 MG/ML Oral Solution: 10 Tablets: 20 MG, 40Maria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy NotesDocument70 pagesPharmacy NoteswybzrsvmwkNo ratings yet
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 pagePathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- NovaDocument1 pageNovaNovalia KungKung SinagaNo ratings yet
- AntihypertensionDocument17 pagesAntihypertension백지원 (소네트리)No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Vasopressors, Inotropes and Anti-Hypertensives Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- KapsulDocument29 pagesKapsulMakinun AminNo ratings yet
- Obiectivele Tratamentului Antidiabetic La Pacientii CudztipisidztipiiDocument11 pagesObiectivele Tratamentului Antidiabetic La Pacientii CudztipisidztipiiDigei BobitzNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics: Guided By: Dhaivat C. ParikhDocument46 pagesNonlinear Pharmacokinetics: Guided By: Dhaivat C. ParikhTushar Bambharoliya100% (5)
- 1 Lec 1-Parasympathetic AgentsDocument33 pages1 Lec 1-Parasympathetic Agentsabdelrahmanmosleh75No ratings yet
- Handy Chart PsychosisDocument3 pagesHandy Chart Psychosismerryavie45No ratings yet
- Lect2 Anes Drugs PDFDocument109 pagesLect2 Anes Drugs PDFJidapa SEELADEENo ratings yet
- Drug Study AdalatDocument4 pagesDrug Study AdalatLea CelestialNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument4 pagesGeneric NamethomjoanneNo ratings yet
- Drug Aproval Process in IndiaDocument3 pagesDrug Aproval Process in IndiaSamit BisenNo ratings yet
- The Percentage of Medication Errors Globally, and in Saudi ArabiaDocument7 pagesThe Percentage of Medication Errors Globally, and in Saudi ArabiaLeen alghamdNo ratings yet
- Ajovy - Fremanezumab - Drug Information - UpToDateDocument6 pagesAjovy - Fremanezumab - Drug Information - UpToDateDiana PhamNo ratings yet
- QMH Drug FormularyDocument60 pagesQMH Drug FormularyproudofskyNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CoughDocument18 pagesDrugs For CoughAbraham BanjoNo ratings yet
- Teknik Anestesi UmumDocument128 pagesTeknik Anestesi UmumRiezka HanafiahNo ratings yet
- Fate of The Drug: Joanne Katherine T. Manlusoc, MSCDocument29 pagesFate of The Drug: Joanne Katherine T. Manlusoc, MSCChinenye AkwueNo ratings yet
- Covid Vac CertificateDocument1 pageCovid Vac CertificateSid KNo ratings yet
- BC Prescription Regulation TableDocument2 pagesBC Prescription Regulation TableJuliaNo ratings yet
- Steroids 1Document9 pagesSteroids 1nafkjfnakfaNo ratings yet
- Contrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall ChartDocument1 pageContrast Poc Tool Anaphylaxis Wall Chartapi-358179847No ratings yet
- Lap S5tock 29 Februari 2020Document47 pagesLap S5tock 29 Februari 2020Ridho SaputraNo ratings yet
- Substance AbuseDocument16 pagesSubstance AbuseAkansha JohnNo ratings yet
- PT Sejahtera Surya Intramedika: Daftar HargaDocument51 pagesPT Sejahtera Surya Intramedika: Daftar HargaMahiru UllamasyitohNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios 13 OctDocument41 pagesLista de Precios 13 OctAlvaro LEnin Rossy LopezNo ratings yet
- Valdoxan: Product InformationDocument15 pagesValdoxan: Product InformationGastón PacciaroniNo ratings yet
- No Pabrik / Principle CTH Obat (10 Item) : Daftar Nama - Nama PBF Dan Produk ObatDocument8 pagesNo Pabrik / Principle CTH Obat (10 Item) : Daftar Nama - Nama PBF Dan Produk ObatAPOTEK KF 62 GAJAH MADA JEMBERNo ratings yet